Here is the list of all inter-relational charts for easy reference:
Master Interrelational Chart
Go to top| Energetic System | Physical System | Polarity and Planetary | Ayurveda | Homeopathic | Acupuncture | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chakra | Kosha/Sharira | Element | Cavity/Moving El | Finger (per Vamachara) | Body Organ | Charge | Ruler | Zodiac | Body Part | Fn Phalanx | Subdosha | Governs | Cereal | Metals | For Planet | For Zodiac | For Meridian | Points for Subdosha | Points for Charge Well/Spring/Sea Vata/Pitta/Kapha |
|
Crown Sahasrara Nadi: Sushhumna Marma: Adhipati Points: GV-20, GV-20 |
-- | -- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | |||||||
|
Third Eye Ajna Nadi: Shankhini, Payasvini, Gandhari, Pusha, Ida, Pingala, Marma: Sthapani Points: GV-16, M-HN-3 |
-- |
Head (Fire) |
Thumb |
--- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | ||||||
|
Throat Vishuddhi Nadi: Sarasvati Marma: Nila, Manya, Amsa Points: GV-14, CV-23 |
Kosha: Bliss Sharira: Causal |
Ether / Wood |
Neck (Ether) |
Btw Thumb & Index |
Gall Bladder
|
--- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
Prana, Sadhaka, Tarpaka |
Reception of all, Intellect & Memory, Intelligence |
--- | --- | --- | --- | --- | PC-8, PC-7, CV-17, PC-3 |
LV-1, GB-44 LV-2, GB-43 LV-8, GB-34 |
|
Heart Anahata Nadi: Varuna Marma: Hridaya, Amsaphalaka Points: GV-10, CV-17 |
Kosha: Wisdom
Sharira: Astral |
Air / Metal Sanguine Blood |
Chest (Air) |
Index Finger - Jupiter
|
Lungs
|
Neutral | Venus | Libra | Kidneys | Top | Udana |
Speech & Intellect Self-expression |
Oats | Copper | Cuprum Metallicum | Natrum Phosphoricum | PC-6 | LU-11, LI-1 | |
| Positive | Mercury | Gemini | Shoulders | Middle | Alochaka | Vision | Millet | Mercury | Mercurius Vivus | Kali Muriaticum | LV-3 | LU-10, LI-2 | |||||||
| Negative | Saturn | Aquarius | Ankles | Bottom | Bodhaka | Taste | Corn | Lead | Plumbum Metallicum | Natrum Muriaticum | LU-5 | LU-5, LI-11 | |||||||
|
Solar Plexus Manipura Nadi: Vishvodhara Marma: Brihati, Nabhi Points: GV-6, CV-8 |
Kosha: Mental
Sharira: Astral |
Fire Choleric Yellow Bile |
Abdominal (Earth) |
Middle Finger - Saturn
|
Heart
|
Neutral | Mars | Aries | Head | Top | Samana | Digestion | Barley | Iron | Ferrum Metallicum | Kali Phosphorica | SI-5 | HE-9, PC-9, SI-1, TH-1 | |
| Positive | Sun | Leo | Solar Plexus | Middle | Pachaka | Digestion | Wheat | Gold | Aurum Metallicum | Magnesia Phosphorica | SI-5, CV-8 | HE-8, PC-8, SI-2, TH-2 | |||||||
| Negative | Jupiter | Sagittarius | Thighs | Bottom | Kledaka | Moistening of food in stomach | Rye | Tin | Stannum Metallicum | Silicea | ST-36, CV-12 | HE-3, PC-3, SI-8, TH-10 | |||||||
|
Sacral Swadhisthana Nadi: Kuhu Marma: Kukundara, Vitapa Points: GV-3, CV-6 |
Kosha: Energy
Sharira: Physical Astral |
Water Phlegmatic Phlegm |
Pelvic (Water) |
Ring Finger - Sun
|
Kidney
|
Neutral | Moon | Cancer | Chest/Breast | Top | Vyana |
Autonomic nervous system Circulation of all subtances |
Rice | Silver | Argentum Metallicum | Calcarea Fluorica | CV-17 | KD-1, BL-67 | |
| Positive | Mars | Scorpio | Generative | Middle | Bhrajaka | Normal pigmentation of skin | Barley | Iron | Ferrum Metallicum | Calcarea Sulphuricum | LU-7 | KD-2, BL-66 | |||||||
| Negative | Jupiter | Pisces | Feet | Bottom | Shleshaka | Lubrication of joints | Rye | Tin | Stannum Metallicum | Ferrum Phosphoricum | TH-2, KD-10 | KD-10, BL-40 | |||||||
|
Root Muladhara Nadi: Alambusha Marma: Guda Points: GV-1, CV-1 |
Kosha: Food
Sharira: Physical |
Earth Melancholic Black Bile |
Pelvic (Water) |
Little Finger - Mercury
|
Spleen
|
Neutral | Saturn | Capricorn | Knees | Top | Apana | Elimination of all substances | Corn | Lead | Plumbum Metallicum | Calcarea Phosphorica | BL-35, SP-6, CV-2 | SP-1, ST-45 | |
| Positive | Venus | Taurus | Neck | Middle | Ranjaka | Blood | Oats | Copper | Cuprum Metallicum | Natrum Sulphuricum | LV-2 | SP-2, ST-44 | |||||||
| Negative | Mercury | Virgo | Bowels | Bottom | Avalambaka | Energy in Limbs | Millet | Mercury | Mercurius Vivus | Kali Sulphuricum | LU-5, ST-36 | SP-9, ST-36 | |||||||
Cautions in Therapies because of Planetary Relationships
Go to top| Main Planet | Enemy Planets | Friendly Planets | Neutral Planets | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Cereal | Metal | Crystal | Homeopathy | Foods/Smells | Name | Cereal | Metal | Crystal | Homeopathy | Foods/Smells | Name | Cereal | Metal | Crystal | Homeopathy | Foods/Smells | Name | Herb | Metal | Crystal | Homeopathy | Foods/Smells |
| Saturn | Corn | Lead | Black Tourmaline, Coal, Onyx, Salt |
Plumbum Metallicum | Ajwain, Cypress, Horsetail, Tamarind |
Sun, Moon, Mars |
Wheat, Rice, Barley |
Gold, Silver, Iron |
Bloodstone, Citrine, Diamond, Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Quartz, Ruby, Sapphire, Sunstone, White Stones, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum, Argentum Metallicum, Ferrum Metallicum |
Basil, Black Pepper, Camphor, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Frankincense, Garlic, Lotus, Marigold, Mustard, Onion, Saffron, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Mercury, Venus |
Millet, Oats |
Mercury, Copper |
Agate, Azurite, Chrysocolla, Emerald, Mica, Opal, Rose Quartz, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus, Cuprum Metallicum |
Caraway, Cardamom, Daisy, Fennel, Lavender, Licorice, Mint |
Jupiter | Rye | Tin | Amethyst, Lapis Lazuli, Sugilite |
Stannum Metallicum | Agrimony, Dandelion, Sage |
| Jupiter | Rye | Tin | Amethyst, Lapis Lazuli, Sugilite |
Stannum Metallicum | Agrimony, Dandelion, Sage |
Mercury, Venus |
Millet, Oats |
Mercury, Copper |
Agate, Azurite, Chrysocolla, Emerald, Mica, Opal, Rose Quartz, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus, Cuprum Metallicum |
Caraway, Cardamom, Daisy, Fennel, Lavender, Licorice, Mint |
Moon, Mars, Sun |
Rice, Barley, Wheat |
Silver, Iron, Gold |
Bloodstone, Citrine, Diamond, Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Quartz, Ruby, Sapphire, Sunstone, White Stones, Yellow Sulfur |
Argentum Metallicum, Ferrum Metallicum, Aurum Metallicum |
Basil, Black Pepper, Camphor, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Frankincense, Garlic, Lotus, Marigold, Mustard, Onion, Saffron, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Saturn | Corn | Lead | Black Tourmaline, Coal, Onyx, Salt |
Plumbum Metallicum | Ajwain, Cypress, Horsetail, Tamarind |
| Mars | Barley | Iron | Bloodstone, Ruby |
Ferrum Metallicum | Basil, Black Pepper, Garlic, Mustard, Onion |
Mercury | Millet | Mercury | Agate, Mica, Opal, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus | Caraway, Fennel, Lavender, Licorice |
Sun, Moon, Jupiter |
Wheat, Rice, Rye |
Gold, Silver, Tin |
Amethyst, Citrine, Diamond, Lapis Lazuli, Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Quartz, Sapphire, Sugilite, Sunstone, White Stones, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum, Argentum Metallicum, Stannum Metallicum |
Agrimony, Camphor, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Dandelion, Frankincense, Lotus, Marigold, Saffron, Sage, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Venus, Saturn |
Oats, Corn |
Copper, Lead |
Azurite, Black Tourmaline, Chrysocolla, Coal, Emerald, Onyx, Rose Quartz, Salt |
Cuprum Metallicum, Plumbum Metallicum |
Ajwain, Cardamom, Cypress, Daisy, Horsetail, Mint, Tamarind |
| Sun | Wheat | Gold | Citrine, Diamond, Quartz, Sunstone, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum | Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Frankincense, Marigold, Saffron |
Saturn, Venus |
Corn, Oats |
Lead, Copper |
Azurite, Black Tourmaline, Chrysocolla, Coal, Emerald, Onyx, Rose Quartz, Salt |
Plumbum Metallicum, Cuprum Metallicum |
Ajwain, Cardamom, Cypress, Daisy, Horsetail, Mint, Tamarind |
Moon, Mars, Jupiter |
Rice, Barley, Rye |
Silver, Iron, Tin |
Amethyst, Bloodstone, Lapis Lazuli, Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Ruby, Sapphire, Sugilite, White Stones |
Argentum Metallicum, Ferrum Metallicum, Stannum Metallicum |
Agrimony, Basil, Black Pepper, Camphor, Dandelion, Garlic, Lotus, Mustard, Onion, Sage, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Mercury | Millet | Mercury | Agate, Mica, Opal, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus | Caraway, Fennel, Lavender, Licorice |
| Mercury | Millet | Mercury | Agate, Mica, Opal, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus | Caraway, Fennel, Lavender, Licorice |
Moon | Rice | Silver | Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Sapphire, White Stones |
Argentum Metallicum | Camphor, Lotus, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Sun, Venus |
Wheat, Oats |
Gold, Copper |
Azurite, Chrysocolla, Citrine, Diamond, Emerald, Quartz, Rose Quartz, Sunstone, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum, Cuprum Metallicum |
Cardamom, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Daisy, Frankincense, Marigold, Mint, Saffron |
Mars, Jupiter, Saturn |
Barley, Rye, Corn |
Iron, Tin, Lead |
Amethyst, Black Tourmaline, Bloodstone, Coal, Lapis Lazuli, Onyx, Ruby, Salt, Sugilite |
Ferrum Metallicum, Stannum Metallicum, Plumbum Metallicum |
Agrimony, Ajwain, Basil, Black Pepper, Cypress, Dandelion, Garlic, Horsetail, Mustard, Onion, Sage, Tamarind |
| Venus | Oats | Copper | Azurite, Chrysocolla, Emerald, Rose Quartz |
Cuprum Metallicum | Cardamom, Daisy, Mint |
Sun, Moon |
Wheat, Rice |
Gold, Silver |
Citrine, Diamond, Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Quartz, Sapphire, Sunstone, White Stones, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum, Argentum Metallicum |
Camphor, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Frankincense, Lotus, Marigold, Saffron, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
Mercury, Saturn |
Millet, Corn |
Mercury, Lead |
Agate, Black Tourmaline, Coal, Mica, Onyx, Opal, Salt, Yellow and Green stones |
Mercurius Vivus, Plumbum Metallicum |
Ajwain, Caraway, Cypress, Fennel, Horsetail, Lavender, Licorice, Tamarind |
Mars, Jupiter |
Barley, Rye |
Iron, Tin |
Amethyst, Bloodstone, Lapis Lazuli, Ruby, Sugilite |
Ferrum Metallicum, Stannum Metallicum |
Agrimony, Basil, Black Pepper, Dandelion, Garlic, Mustard, Onion, Sage |
| Moon | Rice | Silver | Moonstone, Pearl, Quartz, Sapphire, White Stones |
Argentum Metallicum | Camphor, Lotus, Sandalwood, Water Lily |
None | None | None | None | None | None | Sun, Mercury |
Wheat, Millet |
Gold, Mercury |
Agate, Citrine, Diamond, Mica, Opal, Quartz, Sunstone, Yellow and Green stones, Yellow Sulfur |
Aurum Metallicum, Mercurius Vivus |
Caraway, Chamomile, Cinnamon, Clove, Fennel, Frankincense, Lavender, Licorice, Marigold, Saffron |
Venus, Mars, Saturn, Jupiter |
Oats, Barley, Corn, Rye |
Copper, Iron, Lead, Tin |
Amethyst, Azurite, Black Tourmaline, Bloodstone, Chrysocolla, Coal, Emerald, Lapis Lazuli, Onyx, Rose Quartz, Ruby, Salt, Sugilite |
Cuprum Metallicum, Ferrum Metallicum, Plumbum Metallicum, Stannum Metallicum |
Agrimony, Ajwain, Basil, Black Pepper, Cardamom, Cypress, Daisy, Dandelion, Garlic, Horsetail, Mint, Mustard, Onion, Sage, Tamarind |
Elements
Go to top| Element | Role and Senses | Body Organs | Planet & Zodiac | Dosha, Subdosha, and Dhatu | Taste and Potency | Other Element Roles | Actions of Substance | Foods |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Ether / Wood Temperament: Humor: Direction: West Color: Black Mantra: KHAM |
Role: Space/Emotion Sense: Sound Platonic: Dodecahedron |
System: Skin Physical Organ: Gall Bladder, Liver Knowledge Organ: Ears Action Organ: Vocal cords Finger: Btw Thumb & Index |
Planet: Zodiac: |
Dosha: Vaata Subdosha: Prana, Sadhaka, Tarpaka Dhatu: Reproductive |
Potency: Taste: Bitter |
Ether governed Emotion: Grief Air governed Movement: Lengthening Fire governed Function: Sleep Water governed Liquid: Saliva Earth governed Solid: Hair |
They promote softness, porosity and lightness. | N.A |
|
Air / Metal Temperament: Sanguine Humor: Blood Direction: East Color: Blue Mantra: YAM |
Role: Movement Sense: Touch Platonic: Octahedron |
System: Muscles/Tendons Physical Organ: Lungs, Large Intestine Knowledge Organ: Skin Action Organ: Hands Finger: Index Finger |
Planet: Jupiter, Mercury Zodiac: Aquarius, Gemini, Libra |
Dosha: Vaata Subdosha: Udana, Alochaka, Bodhaka Dhatu: Bone |
Potency: Taste: Pungent, Bitter, Astringent |
Ether governed Emotion: Desire Air governed Movement: Speed Fire governed Function: Thirst Water governed Liquid: Sweat Earth governed Solid: Skin |
They promote roughness, aversion, movement, non-sliminess and lightness. | Fruits, Nuts, Seeds |
|
Fire Temperament: Choleric Humor: Yellow Bile Direction: South Color: Red Mantra: RAM |
Role: Energy/Function Sense: Sight Platonic: Tetrahedron |
System: Circulation Physical Organ: Heart, Small Intestine, Triple Warmer, Pericardium Knowledge Organ: Eyes Action Organ: Feet Finger: Middle Finger |
Planet: Mars, Sun Zodiac: Sagittarius, Aries, Leo |
Dosha: Pitta Subdosha: Samana, Pachaka, Kledaka Dhatu: Plasma, Blood Serum, Lymph, Red blood cells |
Potency: Hot Potency Taste: Sour, Salty, Pungent |
Ether governed Emotion: Anger Air governed Movement: Shaking Fire governed Function: Hunger Water governed Liquid: Urine Earth governed Solid: Blood Vessels |
They promote combustion, metabolism, lustre, radiance, and color. | Grains, Legumes, Sesame seed, Sunflower seed |
|
Water Temperament: Phlegmatic Humor: Phlegm Direction: North Color: White Mantra: VAM |
Role: Force of Attraction Sense: Taste Platonic: Icosahedron |
System: Bones Physical Organ: Kidney, Bladder Knowledge Organ: Tongue Action Organ: Genital Finger: Ring Finger |
Planet: Venus, Moon Zodiac: Pisces, Scorpio, Cancer |
Dosha: Pitta, Kapha Subdosha: Vyana, Bhrajaka, Shleshaka Dhatu: Bone marrow, Nervous tissue |
Potency: Cold Potency Taste: Sweet, Salty |
Ether governed Emotion: Attachment Air governed Movement: Movement Fire governed Function: Lustre Water governed Liquid: Semen/Ovum Earth governed Solid: Flesh/Fat |
They promote stickiness, wet, compactness, moistness, and happiness. | Green vegetables, Cucumber, Melons, Squash, Marrow |
|
Earth Temperament: Melancholic Humor: Black Bile Direction: Center Color: Yellow Mantra: LAM |
Role: Solidity Sense: Smell Platonic: Cube |
System: Connective Physical Organ: Spleen, Stomach Knowledge Organ: Nose Action Organ: Anus Finger: Little Finger |
Planet: Saturn Zodiac: Capricorn, Virgo, Taurus |
Dosha: Kapha Subdosha: Apana, Ranjaka, Avalambaka Dhatu: Muscle, Adipose |
Potency: Cold Potency Taste: Sweet, Sour, Astringent |
Ether governed Emotion: Fear Air governed Movement: Contraction Fire governed Function: Lazziness Water governed Liquid: Blood Earth governed Solid: Bones |
They promote plumpness and stability. | Root vegetables, Tubers, Herb roots, Taro, Beets, Potato, Carrot, Onion, Garlic, Turnip |
Palmistry
Go to top| Mount Name | Finger Name | Chakra | Planet | Phalanx/Zodiac | Mount Location | LifeProcess | Movement in Body | Finger Responsibility | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mount of Moon |
NA | NA | Moon | NA | Located below the Mount of Outer Mars, on the base of the palm, little finger side | Reproducing | Movement of reproduction | NA | |||||||||
| Mount of Outer Mars |
NA | NA | Mars | NA | Palm side, between the Mounts of Mercury and Moon | Nourishing | Movement of speaking | NA | |||||||||
| Plains of Mars |
NA | NA | Mars | NA | Located in the center of the palm between the Mounts of Inner Mars and Outer Mars | Nourishing | Movement of speaking | NA | |||||||||
| Mount of Venus |
Thumb | Third Eye | Venus |
|
Located at the base of the thumb, below the Mount of Inner Mars and surrounded by the life line | Growing | Movement of the glands | Neuter | |||||||||
| Mount of Inner Mars |
Btw Thumb & Index | Throat | Mars | Palm side, between the Mounts of Jupiter and Venus | Nourishing | Movement of speaking | Neuter | ||||||||||
| Mount of Jupiter |
Index Finger | Heart | Jupiter |
|
Located at the base of the Index and above the Mount of Inner Mars | Warming | Movement of thinking | Circulation, Respiration, Heart, Lungs | |||||||||
| Mount of Saturn |
Middle Finger | Solar Plexus | Saturn |
|
Located at the base of the middle finger | Breathing | Movement into upright posture | Digestion, Assimilation, Stomach, Intestines, Colon | |||||||||
| Mount of Sun |
Ring Finger | Sacral | Sun |
|
Located at the base of the ring finger | Circulation | Movement of the blood | Creative energy, Vital force, Genito-urinary | |||||||||
| Mount of Mercury |
Little Finger | Root | Mercury |
|
Located at the base of the little finger above the Mount of Outer Mars | Maintaining | Movement of the breath | Eliminative, Rectum, Bladder |
Pulse
Go to top
|
|
Platonic Solids
Go to top| Platonic | Element | Faces | Vertices | Edges | Quality | Purpose | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dodecahedron | Ether | 12 | 20 | 30 | Awareness Plantary | Connecting with our own DNA and activation of the same. | 3 pentagons meet at 324 degree. |
| Octahedron | Air | 8 | 6 | 12 | Wisdom | Disclosure life purpose or mission. | 4 triangles meet at 240 degree. |
| Tetrahedron | Fire | 4 | 4 | 6 | Love | Being connected to top. | 3 triangles meet at 180 degree. |
| Icosahedron | Water | 20 | 12 | 30 | Awareness Cosmic | Expansion of cosmic consciousness. | 5 triangles meet at 300 degree. |
| Cube | Earth | 6 | 8 | 12 | Will | Energy balance, Healing. | 3 squares meet at 270 degree. |
Colors
Go to top| ColorName | Element | Description | Dinshah Frequency | Dinshah Slide Number | Opposite Color Name |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red | Fire | Not available | 397.3 | 818, 828 | Blue |
| Orange | Not available | 430.8 | 809, 828 | Indigo | |
| Yellow | Earth | Not available | 464.4 | 809 | Violet |
| Green | Not available | 531.5 | 871 | ||
| Blue | Air | Not available | 598.6 | 859, 866 | Red |
| Purple | Not available | 565.0 (Reverse Polarity) | 832, 866 | Scarlet | |
| Black | Ether | Not available | |||
| Silver | Not available | ||||
| White | Water | Not available | |||
| Lemon | Not available | 497.9 | 809, 871 | Turquoise | |
| Turquoise | Not available | 565.0 | 861, 871 | Lemon | |
| Indigo | Not available | 632.1 | 828, 859, 866 | Orange | |
| Violet | Not available | 665.7 | 832, 859, 866 | Yellow | |
| Magenta | Not available | 531.5 (Reverse Polarity) | 818, 828, 866 | ||
| Scarlet | Not available | 497.9 (Reverse Polarity) | 810, 818, 861 | Purple | |
| Red Orange | Not available | 809, 818 | |||
| Orange Yellow | Not available | 809, 826 | |||
| Turquoise Blue | Not available | 859, 877 | |||
| Lemon Green | Not available | 810, 871 | |||
| Green Turquoise | Not available | 871, 877 | |||
| Dark Grey | Not available |
Planets
Go to top| Planet | Position | Deities | Associations | Relationship to other planets | Life Process | Spiritual Exercise | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Saturn Shani Number: 3 (Triangle) Element: Earth Zodiac: Capricorn, Aquarius Cycle: 30 years Age: 56 to 63 years |
Life Process #: 1 From Earth: 7 Evolution: 1 Inner/Outer: Outer |
Graha: Shanaischara Adhi: Prajapati Pratyadi: Yama |
Metal: Lead Day: Saturday Crystal: Onyx, Black Tourmaline, Coal, Salt Cereal: Corn Tree: Conifer, Beech Foods/Smells: Ajwain Cypress Horsetail Tamarind |
Friends: Mercury, Venus Enemies: Sun, Moon, Mars Neutrals: Jupiter |
Influence: Time, harvest, death, peace, endings, completion, tenacity, land or soil Movement: Movement into upright posture Body Organ: Spleen Life Process: Breathing Life Counter: Consumption Description: Breathing is related to Saturn. Taking-in. Steiner emphasizes that this is an occult term, which signifies "intake" from the outside world; the beginning of digestion. It encompasses taking in something as spiritual as thought, light, or oxygen through the lungs; or as physical as taking in food. <br />All these must be transformed as they are accepted by the body. If too much enters that cannot be processed, it will cause damage or illness. A first step is to control quantity and what comes in. If you take-in too much untransformed warmth, you will get burnt, as in radiation illness. Uncontrolled intake of substances that overwhelm you can lead to addiction or, physically as in smoking, can lead to cancer. Lastly, if the body constantly fights overabundance, it gets used up; the typical process of aging. |
Right Option Saturn's strength is being able to discern the essentials and his weaker trait is that he is so convinced of his own opinion that he doesn't really listen. In the exercise 'the right opinion' one must quell one's own opinion to let the other (person or situation) enter one's being. That means that Saturn must let go of his rigidity, because even though he can easily find the essence he must learn to see that he does not always have all the facts. He must also learn not to be afraid to find that there are more facts than he can handle at that time and that by keeping inner calm and silence the essence will finally come to him. The fear arises out of self-interest and is not in service of mankind. |
|
|
Jupiter Guru Number: 4 (Square) Element: Air Zodiac: Sagittarius, Pisces Cycle: 12 years Age: 49 to 56 years |
Life Process #: 2 From Earth: 6 Evolution: 6 Inner/Outer: Outer |
Graha: Brihaspati Adhi: Indra Pratyadi: Brahma |
Metal: Tin Day: Thursday Crystal: Lapis Lazuli, Sugilite, Amethyst Cereal: Rye Tree: Maple Foods/Smells: Agrimony Dandelion Sage |
Friends: Moon, Mars, Sun Enemies: Mercury, Venus Neutrals: Saturn |
Influence: Rulership, occupations, sky, wealth, oaths, treaties, matrimony Movement: Movement of thinking Body Organ: Liver Life Process: Warming Life Counter: Combustion Description: Taking-in. This directs our attention to whatever increases body temperature. One such process is the influence of the thyroid gland. We all know that people who suffer from an under-secretion of the thyroid feel cold and are slow. Thinking is connected to the planet Jupiter. <br /> Substances taken in by breathing need to be absorbed more deeply. This happens when food is taken across the gut wall and into the inner organism, or when substances cross through the membranes into the cells. All of these passings, or ferryings, across walls require warmth, and create warmth. One of these ferrying processes is the ionic pump (such as the sodium potassium pump). Surprisingly 60% of the body's metabolic energy is generated just to keep these pumps going. Sodium and potassium are substances that make electricity flow. They also make our nervous system function, which ultimately allows us to think. Thinking is connected to the planet Jupiter. |
Right Habit The weak side of Jupiter is using his power as might through manipulation. His strong side is that he can oversee a huge amount of connections and can contain much at the same time. Jupiter must try to use his power for the good of mankind and not for personal purposes. He has the possibility to contain much so let him set high ideals. In doing this he must also remember to understand his fellow man and that 'little' problems are just as important as 'big' ones. |
|
|
Mars Mangala Number: 5 (Pentagram) Element: Fire Zodiac: Scorpio, Aries Cycle: 2 years Age: 42 to 49 years |
Life Process #: 3 From Earth: 5 Evolution: 4 Inner/Outer: Outer |
Graha: Mangal Adhi: Prithvi Pratyadi: Ksetrapal |
Metal: Iron Day: Tuesday Crystal: Ruby, Bloodstone Cereal: Barley Tree: Oak Foods/Smells: Basil Black Pepper Garlic Mustard Onion |
Friends: Sun, Moon, Jupiter Enemies: Mercury Neutrals: Venus, Saturn |
Influence: Defense, boldness, war, loyalty, verillity, growth Movement: Movement of speaking Body Organ: Gall Bladder Life Process: Nourishing Life Counter: Conservation Description: It is also connected with Mars. Mars is an aggressive Planet, related to destruction. Nutrition has this same quality.Substances brought in with breathing, then warming, now must be broken down within the body. Nutrition has to do with breaking down of proteins, and building up new ones. Actually, the whole world of biochemical changes belongs to this life process. <br /> If a substance cannot be transformed, illnesses of deposit ensue, such as fat cholesterol, xanthomas, deposits of water (edema), uric acid crystals, (gout), sugar deposits (diabetes) etc. These illnesses are a weakened Mars. |
Right Deed The weak side of Mars is using uncontrolled action to solve problems. Immediate action without thinking the consequences through. The strong side is the fact that he can act; he is not afraid of acting. Mars must learn to think first, to control his actions (this also applies to words). He can start by asking himself if his intended action would disturb his fellow man. This does mean that he has to build in this moment of reflection. He must try to enlarge his vision so that he can oversee the consequences of his deeds. Only with vision and love can he come to the right deed which is always good for all of mankind. |
|
|
Sun Surya Number: 6 (Hexagram) Element: Fire Zodiac: Leo Cycle: N.A Age: 21 to 42 years |
Life Process #: 4 From Earth: 4 Evolution: 2 Inner/Outer: N.A |
Graha: Surya Adhi: Agni Pratyadi: Shiva |
Metal: Gold Day: Sunday Crystal: Sunstone, Quartz, Citrine, Diamond, Yellow Sulfur Cereal: Wheat Tree: Ash Foods/Smells: Chamomile Cinnamon Clove Frankincense Marigold Saffron |
Friends: Moon, Mars, Jupiter Enemies: Saturn, Venus Neutrals: Mercury |
Influence: Illumination, vitality, health, creativity, beauty Movement: Movement of the blood Body Organ: Heart Life Process: Circulation Life Counter: Description: It relates to the beat of the heart and the rhythm of the lungs. The transformed substances must now be transported to the organs that use them. This is done through the cardiovascular system, governed by the Sun and the Ego. Everything to do with flow is a manifestation of circulation, for example the white protein in the blood called albumen. It even looks like the sun, or like an egg, intense at the core, with a white mantle around it. Any disturbance, where circulation suddenly gets out of rhythm, belongs to this pathology. If substances accumulate instead of going where they belong, you have illness. Albuminous processes circulating in the wrong place can cause diarrhea or various forms of allergies (sudden nasal discharges). |
Right Judgment The Sun is the symbol for the harmony between all the planetary qualities. The right judgement is done by detaching oneself from sympathy and antipathy within the situation. |
|
|
Mercury Budha Number: 8 (Octagram) Element: Air Zodiac: Gemini, Virgo Cycle: 100 days Age: 7 to 14 years |
Life Process #: 5 From Earth: 2 Evolution: 5 Inner/Outer: Inner |
Graha: Budha Adhi: Vishnu Pratyadi: Narayana |
Metal: Mercury Day: Wednesday Crystal: Yellow and Green stones, Agate, Opal, Mica Cereal: Millet Tree: Elm Foods/Smells: Caraway Fennel Lavender Licorice |
Friends: Sun, Venus Enemies: Moon Neutrals: Mars, Jupiter, Saturn |
Influence: Wisdom, communication, barter, business, travel Movement: Movement of the breath Body Organ: Lungs Life Process: Maintaining Life Counter: Sclerosis Description: It relates to tissue and cell connections. It is the sum total of making substance into the body's own cells, each one round like little mercury droplets. This process belongs to Mercury. Mercury also controls the intercellular messenger activity between each cell. All repair, scarring and healing belong to Mercury. Too little produces weakness or hypermobility of tendons; too much can cause uterine fibroids or cysts. In congestive heart failure the heart muscle is not maintained enough. |
Right Point of View The weak side of Mercury is that he does not hold direction; he jabs without follow-up. The strong side is his quick grasp of new ideas; he is not afraid of new concepts. If Mercury can learn to hold on to the line of spiritual evolution and the cosmic rhythms, if he can learn to use this as a key for his innovations and his shaking loose of stagnant properties, then he can reach the right point of view and become a healing factor for mankind. |
|
|
Venus Shukra Number: 7 (Heptagram) Element: Water Zodiac: Taurus, Libra Cycle: 256 days Age: 14 to 21 years |
Life Process #: 6 From Earth: 3 Evolution: 7 Inner/Outer: Inner |
Graha: Shukra Adhi: Sachi Pratyadi: Indra |
Metal: Copper Day: Friday Crystal: Azurite, Emerald, Rose Quartz, Chrysocolla Cereal: Oats Tree: Birch Foods/Smells: Cardamom Daisy Mint |
Friends: Mercury, Saturn Enemies: Sun, Moon Neutrals: Mars, Jupiter |
Influence: Fertility, beauty, love, passion, friendship, harmony, nature, family life, relationships Movement: Movement of the glands Body Organ: Kidney Life Process: Growing Life Counter: Maturation Description: Throwing-out. It belongs to the same process that forms tissue or actual organs like liver, lung, kidney, etc. It takes a new impulse, that comes from Venus, to individualize tissues and transform them into organs. When growth comes to an end, and the body as a whole presents itself to our eyes, we have a truly harmonious 'whole' in front of us. Where do we see the Venus forces? They become obvious in the 'beauty' that the human form, in its entirety, has. All maturing has as its crowning point the formation of beauty. |
Right Memory The weak side of Venus is losing herself in her own feelings. The strong side is empathy in feeling. If Venus can create some distance between her feeling and her higher Self she can learn to use her feeling as an organ of perception. Then she can learn from experiences of others and from her own in relation with spiritual growth. In this way she can obtain the right memory, which means seeing things the way they are and not just remembering her own feelings in the situation, but learning from it and making the right connections. By using this right memory she can help her fellow men find their way in the stream of spiritual evolution. |
|
|
Moon Chandra Number: 9 (Enneagram) Element: Water Zodiac: Cancer Cycle: 28 days Age: Birth to 7 years |
Life Process #: 7 From Earth: 1 Evolution: 3 Inner/Outer: Inner |
Graha: Chandra Adhi: Apas Pratyadi: Gauri |
Metal: Silver Day: Monday Crystal: White Stones, Moonstone, Quartz, Sapphire, Pearl Cereal: Rice Tree: Cherry Foods/Smells: Camphor Lotus Sandalwood Water Lily |
Friends: Sun, Mercury Enemies: Neutrals: Venus, Mars, Saturn, Jupiter |
Influence: Enchantment, dreams, midwifery, ancestors, money Movement: Movement of reproduction Body Organ: Brain Life Process: Reproducing Life Counter: Procreation Description: Throwing-out. It is the total opposite of the Saturn forces. It is governed by the Moon. Reproductive forces result in the formation of an embryo that grows and is ultimately a totality; a new world, excreted to the outside at birth. Saturn forces bring the outer world in, the Moon forces take the inner world out. Pathology in the reproductive realm includes genetic diseases. |
Right Word The Moon mirrors and her weak side is that she does this unconsciously, without direction, goal. This quality of being able to mirror can be transformed to conscious mirroring by practising using the right word. The more she watches what she says, in the end she will be able to speak the right word at the right moment to her fellow man. Her own quality of being able to mirror will then be directed toward the spiritual progress of mankind and will be the mirror of deliverance. |
|
|
Common exercise which needs to be performed for all planets in addition to their respective exercise.: The Right Contemplation This exercise is to be done every evening before going to sleep. Before your inner view you unroll the day backwards from the end to the beginning as if it were a film about somebody else, objectively. In the right contemplation exercise you judge with the higher Self. The Self looks at what you did, thought and felt; looks to see if you tried hard enough in practicing the exercises mentioned above; looks to see if you have been continuously aware of your place in the evolutionary stream; looks at your mistakes and imperfections; looks also how your immediate surroundings are coming along and where you can help. The Self also resolves to do better and searches ways which are within your possibilities but always working towards the high ideal. Note: In occult, Mercury is near to earth and not Venus; whereas in modern Astrology it is the opposite. In order words, Modern Astrology is wrong referring (intentionally done) the Mercury as Venus and Venus as Mercury. Otherwise, all the properties of both planets are correct in this database and just the PositionFromEarth is changed. |
|||||||
Zodiac Signs
Go to top| Zodiac | Astrology | Planet | Element | Triguna | Polarity | Charge | HomeopathicMedicine | Crystal | Astral Color | Dates | StartDegree | EndDegree | Alchemical Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Libra Tula Scales |
Quality: Cardinal House: 7th (Marriage and Partnership) |
Venus | Air | Sattva | Transverse | Neutral | Natrum Phosphoricum | Diamond, Opal | Black, Crimson, Light blue | September 22 - October 21 | 180 | 210 | Sublimation, which means immersing one's self, or bringing a separation. |
|
Gemini Mithuna Twins |
Quality: Mutable House: 3rd (Communications) |
Mercury | Air | Rajas | Spiral | Positive | Kali Muriaticum | Beryl, Aquamarine, Dark blue stones | Red, White, Blue | May 20 - June 18 | 60 | 90 | Fixation, a process of stabilization to create perfection. |
|
Aquarius Kumbha Waterman |
Quality: Fixed House: 11th (Hopes and Wishes/Friends) |
Saturn | Air | Tamas | Long Line | Negative | Natrum Muriaticum | Sapphire, Opal, Turquoise | Blue, Opal, Nile green | January 20 - February 18 | 300 | 330 | Multiplication, brings on a separation process to bring more possibilities. |
|
Aries Mesha Ram |
Quality: Cardinal House: 1st (Self) |
Mars | Fire | Sattva | Transverse | Neutral | Kali Phosphorica | Amethyst, Diamond | White, Rose-pink | March 21 - April 19 | 0 | 30 | Calcination, a process of burning away impurities to a very refined state. |
|
Leo Simha Lion |
Quality: Fixed House: 5th (Creativity) |
Sun | Fire | Rajas | Spiral | Positive | Magnesia Phosphorica | Ruby, Diamond | Red, Green | July 24 - Aug 22 | 120 | 150 | Digestion, thus separating good from bad substances. |
|
Sagittarius Dhanush Archer |
Quality: Mutable House: 9th (Mental Exploration) |
Jupiter | Fire | Tamas | Long Line | Negative | Silicea | Carbuncle, Diamond, Turquoise | Gold, Red, Green | November 21 - December 20 | 240 | 270 | Incineration, which burns away the dregs of one's impurities. |
|
Cancer Karkata Crab |
Quality: Cardinal House: 4th (Home) |
Moon | Water | Sattva | Transverse | Neutral | Calcarea Fluorica | Black onyx, Emerald | Green, Russet brown | June 19 - July 23 | 90 | 120 | Dissolution, which involves putting one substance into another to create better health. |
|
Scorpio Vrischika Scorpion |
Quality: Fixed House: 8th (Death and Regeneration) |
Mars | Water | Rajas | Spiral | Positive | Calcarea Sulphuricum | Topaz, Malachite | Golden brown, Black | October 22 - November 20 | 210 | 240 | Separation, which takes things apart to purify them. |
|
Pisces Mina Fishes |
Quality: Mutable House: 12th (Self-Undoing) |
Jupiter | Water | Tamas | Long Line | Negative | Ferrum Phosphoricum | Chrysolite, Pink-shell, Moonstone | White, Pink, Emerald-green, Black | February 19 - March 20 | 330 | 360 | Projection, showing our vulnerability and possible cleaning. |
|
Capricorn Makara Mountain Goat |
Quality: Cardinal House: 10th (Career) |
Saturn | Earth | Sattva | Transverse | Neutral | Calcarea Phosphorica | White onyx, Moonstone | Garnet, Brown, Silver-gray, Black | December 21 - January 19 | 270 | 300 | Fermentation, creates a separation by creating a more pure product and toxin release. |
|
Taurus Vrishaba Bull |
Quality: Fixed House: 2nd (Possessions) |
Venus | Earth | Rajas | Spiral | Positive | Natrum Sulphuricum | Moss agate, Emerald | Red, Lemon yellow | April 20 - May 19 | 30 | 60 | Congelation, whereby cold changes the structure for purification. |
|
Virgo Kanya Virgin |
Quality: Mutable House: 6th (Service and Health) |
Mercury | Earth | Tamas | Long Line | Negative | Kali Sulphuricum | Virgo, Pink jasper, Hyacinth | Gold, Black | August 23 - September 21 | 150 | 180 | Distillation, or creating heat to separate and purify. |
Polarity Principles
Go to top| Name | Nervous System | Dosha | Zodiac | PolarityChange | TypeOfForce | Deity | TypeOfTree | CurrentName | CurrentDirection | StateOfMind | Description | CurrentDescription |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sattva | Parasympathetic | Vaata | Capricorn, Aries, Libra, Cancer |
Neutral | Creative | Brahma | Tree of Life | Transverse | East-West | Super-consciousness mind. | Sattvic principle is one of neutrality. It is the principle of essence and stillness. It is a presentation of the unconditioned neutral state found in all existence. It is, as the Chinese say, the stillness within motion which is at the centre of the any event. It is the Neutral ground from which energy moves. | It emanates from the positive and negative poles (top and bottom) of the neutral sushumna current of the core energy system. It then spirals transversely around the body. Its function is one of intercommunication and binding. It is a neutral feedback pattern and helps to relate the periphery of the energy system to the core. |
| Rajas | Sympathetic | Pitta | Scorpio, Leo, Gemini, Taurus |
Positive | Protective | Vishnu | Tree of Nourishment | Spiral | Foward-Backward | Activity of conscious mind. | Rajasic principle is the positive yang phase of energy movement. It is the driving aspect of energy suggesting action and propulsion whose quality is the expansive, centrifugal phase of energy. It is the drive behind an event or experience. Rajas is the male aspect of our energy system, of assertion, warmth and the sun. | It emanates from the Fire Centre (umbilicus) to encompass the whole of the energy system and it functions to provide the quality of energy for movement, warmth and healing. It governs the distribution of internal vital energy throughout the body. |
| Tamas | Central Or Cerebrospinal | Kapha | Aquarius, Sagittarius, Pisces, Virgo |
Negative | Destructive | Shiv | Tree of Knowledge of Good and Evil | Long Line | North-South | Crystallization effect of Sub-conscious mind or earthbound mind, going into sense life entirely and bound thereby. | Tamasic principle is the negative yin phase of energy movement. It is the quality of the contractive, centripetal phase of energy. It is the phase of completion and of receptivity. It is the female aspect of our energy system, of receptivity and of crystallisation into forms. | It is formed by currents which pulsate individually from each chakra. They emanate from each centre in specific patterns or current lines. Each current is of the quality of energy most like that of its centre. So the current which arises from the Water Centre is thus called the Water current line. They emanate from each chakra, expand outward in a vertical fashion and then return to the centre in a contractive phase. Their function is to regulate and monitor the physiology of the body. |
Vital Essences
Go to top| Name | Dosha | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Prana/Qi Neutral |
Vaata | It is the Original Force of Life. It is the subtle energy of the Air principle (Vaata) masterful force behind all the functions of the body and the mind. It is responsible for the corodination of breathing, the senses and the mind. At a depper level it governs the development of elevated states of conscience. |
| Tejas/Shen Positive |
Pitta | It is the Inner Radiance. It is the subtle energy of the Fire principle (Pitta) through which we take in impressions and feelings. At a deep level it regulations the expansion of the elevated perceptual capacities. |
| Ojas/Jing Negative |
Kapha | It is the Original Vigor. It is the subtle energy of Water principle (Kapha). At a deep level it supports and nourishes all the elevated states of the conscience. Ojas is the essence of the 7 dhatus/tissues. |
Nervous System
Go to top| Name | Triguna | Vital Essence | Dosha | Subdosha | Description | Reflex Relationships | How To Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasympathetic | Sattva | Prana/Qi | Vaata | Prana, Udana, Samana, Vyana, Apana | Parasympathetic nervous system tie the periphery to the central core and manifest as a netural pattern of balance and interrelationship. This system balances the action of the sympathetic nervous system. It brings blood to the core and away from the periphery. It encourages digestion and brings blood to these inner organs. It slows down respiratory and cardiac rhythms and is in ascendance in meditative states. | Pending | Perineal Techniques |
| Sympathetic | Rajas | Tejas/Shen | Pitta | Sadhaka, Alochaka, Pachaka, Ranjaka, Bhrajaka | Sympathetic nervous system is the system which stimulates the body and prepares it for action. It is the 'flight or fright' system. It brings blood to the periphery for muscular action. It causes vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the core of the body and its digestive organs and vasodilation in the periphery which brings blood to the muscles for activity. It is the system of action and doing. It speeds up metabolism, heart and respiratory rates. i.e blood goes from inner most to outer most. | Pending | Coccygeal Techniques |
| Central Or Cerebrospinal | Tamas | Ojas/Jing | Kapha | Tarpaka, Avalambaka, Kledaka, Bodhaka, Shleshaka | Central Nervous system Or Cerebrospinal system is the body's master computer and system of voluntary action. It is the system that the conscious mind functions through and this function is to bring patterns of though and emotion into form and action. | Pending | Cranial & Cranial Pelvic Therapy |
Body Organs
Go to top| Name | Element | Meridian | ReflectedIn | OpensInto | SolidOrHollow | YangOrYin | Controls | Stores | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain | Brain | ||||||||
| Gall Bladder | Ether | Gallbladder Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Judgement, Decision making, Skeletal System | Bile | The gallbladder, a sack-like structure, stores bile (greenish fluid) which is produced by the liver and used in the digestive process. The Gallbladder channel is connected with the Liver channel and is also responsible for the unobstruction of Prana as well as the health of the tendons. The gallbladder, due to its connection with the liver, is directly connected to the Ether element and to Pitta. | ||
| Liver | Ether | Liver Meridian | Nails | Eyes | Solid | Yin | Planning & Strategy | Hun/Ethereal Soul/Blood | The liver is positioned in the right hypochondria (under the breathing diaphragm). It controls the unobstruction of Prana and blood, and is responsible for the health of the tendons due to their connection with Pitta. The liver also receives food nutrients from the stomach and intestines via the portal veins. It produces and stores various vitamins, sugars and minerals. It also digests the Five Elements (e.g. from a vegetable) and turns them into the form which can be used by the body. This is achieved by the Bhuta-Agnis, the five liver fires which digest the elements. The liver is a Pitta organ, since the word pitta itself is translated as bile, a product which is produced by the liver. Liver system with its gall excretion drives the whole into our very EGO. It ensures smooth flow of Qi. Tears are the fluid of Liver. |
| Lungs | Air | Lung Meridian | Throat | Nose | Solid | Yin | Administration, Nervous System | Po/Animal Soul | The lung controls the flow of water and Prana through the body. This occurs because it is only by Prana flowing correctly through the channels that water (body fluids) can similarly flow. It is responsible for the health of the skin and hair, since being a Vata organ it relates to the Air element. There are two lungs in the bodj, one on the right side and one on the left side of the body. Oxygen which carries Prana is taken into the blood and then diffused into the blood stream to be carried elsewhere. Waste carbon dioxide is excreted from the body via the lungs and expiration. Lungs rule exterior (sking, sweat glands, body hair) of the body. If Lung Qi is weak, there may be too much/little sweat and the resistance of Protective Qi will be poor. Lungs move and adjust Water channel. It moves water in 2 directions: (1) To kidney (if the vapor becomes fluid during the use), (2) Circulate and scatter water vapor throughout body, particularly through skin/pores. |
| Large Intestine | Air | Large Intestine Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Waste Conduction, Waste Conveyance, Circulation System | The large intestine consists of four sections, the cecum, ascending, transverse and descending colons and is approximately five feet in length. The large intestine absorbs moisture from the digested food, and is also extremely important in the absorption of Prana from food into the body. It manufactures some vitamins in the intestinal flora, forms feces and expels them by the use of peristalsis (waves). The large intestine is related to Vata and Air, and consequently to the lungs and also has an effect on the skin and hair. The Large Intestine channel is located along the arm in a relative position to the Lung channel. It continues to move turbid parts of food and fluids downwards, while at the same time absorbing water from the waste material. At end of process feces is formed. |
|||
| Heart | Fire | Heart Meridian | Face | Tongue | Solid | Yin | Blood, Blood Vessels | Shen/Seat of Consciousness | The heart controls the flow of blood through the body and is the site of Prana, which often controls mental activity according to Charaka. The heart is responsible for the health of the blood vessels. Physiologically, the heart is an involuntary muscle which acts as a pump, contracting and expanding to force blood to all parts of the body. The heart consists of four separate chambers, the upper two are called the Atria (left and right) while the lower two are called the Ventricles. These compartments are separated by muscular partitions called septa (singular: septum). There are also four valves which regulate the flow of blood, two semilunar valves, one tricuspid and one bicuspid or mitral valves. The heart is related to Kapha because it is essentially made of muscle (Earth), but also it is energetically connected to Pitta and the Fire element as well, through its connection with blood. The heart has a pranic channel (nadi) which commences in the heart. It is then logically called the Heart channel. Heart is that organ, which together with the lung is driving the outer substances into our own ETHERIC organization. Also Sweat originates in the heart. While it remains within the body, it is blood. When it is excreted through the skin, it becomes sweat. Therefore, when there is excessive perspiration, there will not be much blood left in the body. Or when someone loses a great amount of the blood, it will be difficult for him to perspire. |
| Small Intestine | Fire | Small Intestine Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Separate pure from turbid, Digestion System | The small intestine is positioned in the abdominal area and absorbs 90% of all nutrients. It is approximately twenty feet in length. Since the small intestine is a Fire organ and is related to the heart with which it is internally connectedJ it is also involved in the health of the blood vessels. The small intestine is also the site of Agni, the digestive fire. When Agni becomes low (which can occur due to antibiotics, stress etc.) the digestive process will falter, causing malabsorption of nutrients and the consequential effect of Ama, or toxin build-up in the body. Also, due to low Agni (fire) in the small intestine., various germs and molds etc. (e.g. candida) can be allowed a safe passage to the large intestine where they lodge and begin to cause dysfunctions. The Small Intestine channel is located in the arm in a relative position to the Heart channel, with which it is related. Clear is sent to Spleen, and turbid is sent to Large Intestine. It manages Receiving, Containing, and Transforming. |
|||
| Triple Warmer | Fire | Triple Warmer Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Lymphatic System | The tridosha is not a physiological organ per se., but in Ayurveda it is considered as such. Tridosha is a generalization of the three areas of the trunk which relate to the three humors (doshas). These are Vata, Pitta and Kapha. As the trunk can be considered a hollow pipe, then the Tridosha is a hollow organ. Tridoshas literally means "three-humors". The flow of fluids through these three areas of the trunk can be affected by an imbalance in one or more of the three humors, so that the mutual balance of all is reflected in the Tridosha and its pranic channel. The Tridosha (3D) and the pericardium are therefore related and their pranic channels interconnect. It is a pathway that makes organs a complete system. Upper burner is everything above the diaphragm: head, chest, heart, and lungs. Middle burner diaphragm to waist (above naval): spleen and stomach. Lower burner is area below naval including kidney, liver, uterus, intestines, bladder. |
|||
| Pericardium | Fire | Pericardium Meridian | Solid | Yin | Although not strictly an organ per se, the pericardium is nevertheless recognized as one in Ayurveda. It is a sac which surrounds (protective screen) the heart and usually swells with fluid during a disease (pericarditis). It is connected to the diaphragm, the heart blood vessels and the thoracic wall. This organ has an effect on the Kapha flow. Its pranic energy channel is located along the arms. | ||||
| Kidney | Water | Kidney Meridian | Head hair | Ears | Solid | Yin | Water, Reproduction, Growth | Zhi/Essence/Jing/Root of Life/Will | The two kidneys are positioned directly behind the eighth to tenth ribs. It controls water metabolism and is responsible for the bones, marrow and affects the reproductive organs since these are positioned in the Vata area of the trunk. It also separates waste products and water from the blood to excrete as urine. Through its drying action on fluids in the body (just like a flood-gate), the kidneys relate to Vata. When it removes water, it relates to Vata, but while it retains water in the body, it deals with Kapha. The kidney has a pranic channel which connects with the legs. Kidney drives our own Etheric energy (which was converted from outside by Heart and Lungs) into our ASTRAL organization. The kidneys communicate with our outside world. Kidney is the source of reproduction, development and muturation. All circulation of water in body depends on the vaporizing power of kidneys. The spleen also vaporizes pure fluids as it raises the pure essences of food and fluids but its vaporization power is dependent on the Kidney fire. |
| Bladder | Water | Bladder Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Storage of fluids/humors, Reproduction | The urinary bladder is a membranous sack which stores urine after it is produced and excreted by the kidneys. It connects with the kidneys via two pipes called ureters. The bladder and the kidneys both affect the health of the bones, marrow and the reproductive system related to Vata. It receives fluids from the lungs and small intestine, temporarily holds the fluids, transforms them into urine, aided by kidney qì/yáng, and excretes the urine. |
|||
| Spleen | Earth | Spleen Meridian | Lips | Mouth | Solid | Yin | Transformation, Transportation, Blood | Yi/Thought | The spleen controls digestion and the transportation of blood. It is responsible for the muscles. The spleen, positioned in the upper left side of the abdominal cavity, functions also to remove and destroy disease-producing organisms from the blood stream. It stores blood in order to release it when required, as when excessive bleeding occurs. Due to its connection with the blood, the spleen is related to Pitta. However, it is also related to Kapha because of its connection with the earth element and its attribute of growth. In fact, the difference between muscle and fat (both contain earth and water) is that the spleen heavily deals with blood, and through its heat (fire) it turns earth and water (as though by baking) into muscle. It is the heat that makes the difference between muscle and fat. Fat is analogous to gelatin powder (earth) and water, it results in a cold, unstable (floppy) concoction. Muscle, on the other hand, is like making a mixture of cake powder (earth) and water and placing it in the oven (heat) to bake. The result is like a solid structure much more stable than the gelatin (jelly) product. The spleen has a pranic channel which connects with the legs. Spleen governs blood and holds blood in proper places (just like banks of river). Spleen is the Charge of production of Qi and blood. |
| Stomach | Earth | Stomach Meridian | Hollow | Yang | Receiving & Fermenting | The stomach is positioned in the upper part of the abdominal cavity. It is connected with the esophagus at the top end and at the small intestine by the pyloric sphincter or valve. Its main function is to receive and macerate food with the aid of the gastric juices. This mixture is eventually thinned down into chyme which exits the stomach and enters the duodenum (small intestine). Some experts believe that it is a subtle form of chyme which is produced in the stomach and attacks the lung when Kapha is aggravated. The stomach works in conjunction with the spleen which carries on the functions of digestion and absorption. As with the spleen, with which it is internally related, the stomach also affects the muscles. Growth in the body is under the control of Kapha, the anabolic humor. The stomach is a very important part of this humor. The Stomach channel is positioned along the legs in a direct relationship with the spleen. It is responsible for receiving and ripening ingested food and fluids. 'Pure' part is sent to spleen and 'turbid' part is sent to Small Intestine. |
Doshas
Go to top| Dosha | Subdoshas | Responsibility | LocationsInBody | ModernChemistry | Description | Symptoms In Body When Normal | Symptoms In Body When Increased | Symptoms In Body When Decreased | Disorders | Treatment Plan |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Vaata Element: Ether, Air Essence: Prana/Qi Triguna: Sattva Nervous: Parasympathetic Force: Creative Life Activity: Catabolism/Reducing Accumulation: Summer Defective: Rainy Pacification: Autumn |
Prana, Udana, Samana, Vyana, Apana |
Movement Communication Transport |
Colon (Main) Urinary tract Waist Legs Feet Bones Ear and organ of touch (skin) |
Master control system DNA Nervous system Homeostasis Sodium/Potassium balance Mitosis Meiosis Chemical transfer of messsages in brain Excess of enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO) |
Vaata is that primal constituents of the living body, whose structure is Ether-Air (or vital life force and healing power of Vaata i.e Prana), and whose function is Raajasic, it being concerned with the production of those physical and mental proceses which are predominantly raajasic (activating or dynamic) in nature; hence, the presence of vaata is to be inferred in such mental phenomena as exhibition of enthusiasm, concentration, etc., as also in such physical phenomena as respiration, circulation, voluntary action of every kind, excertion and so on. It will be seen that many of these physical phenomena are included among those which modern physiologists would assign primarily to the activities of the Nervous system (both cerebropsinal and autonomic). Besides being located in each and every cell, each dosha has a primary location known as its “seat”. If a dosha is starting to go out of balance, the first symptom will often occur at its seat. |
Enthusiasm, inspiration, expiration, movements, normal processing of dhatus, and normal elimination if excreta. Holds up the systems and organs, initiates upward and downward movements, leads and controls the mind, employs all sense organs in their activity, carries all sense objects, causes structural formation of all bodily dhatus, promotes union in the body, prompts speech, originates touch and sound, is the root of auditory and tactile sense organs, is source of exhiliration and courage, stimulated agni, absorbs dosas, throws out excreta, makes the gross and subtle channels, shapes the foetus and maintains life-span. | Produces emaciation, black dis-coloration, desire for hot things, distention of the abdomen, constipation, loss of strength, sleep and of sensory functions, irrelevant speech, giddiness and timidity (peevishness). Separation, dislocation, division, attachment, tearing malaise, exhilaration, thirst, tremors, circumvention, looseness, piercing pain, pain , movement, tastelessness, numbness, contraction, stiffness, limping. Agitates mind, affects all the sense organs, destroys, deforms or detains the embryo for long, produces fear, grief, confusion, anxiety and excessive delirium and (at the end) stops the vital breath. | Debility of body, the person speaks very little and does very little physical activity, loss of sensation (awareness) and of consciousness and occurrance of all the symptoms of increased kapha. | Cracking in soles, pain in foot, foot drop, numbness in feet, pain in ankles, stiffness in ankles, cramps in calf, sciatica, tearing pain in knees, stiffness in thighs, loss of movement in thighs, lameness, prolapse of rectum, pain in anus, twitching in scrotum, stiffness in penis, pain in groins, pain in pelvis, pain in defecation, upward movement of V (‘udavarta’), limping, hunch back, dwarfism, stiffness in sacral region, stiffness in back, compression in sides, twisting pain in abdomen, cardiac dysfunction, tachycardia, shivering in chest, constriction in chest, chest pain, wasting of arms, stiffness of neck, stiffness of sternomastoid, hoarseness of voice, pain in jaw, cracking of lips, pain in eyes/cleft palate, pain in teeth, loose teeth, dumbness [inability to speak], stammering, astringent taste in mouth, dryness of mouth, loss of taste sensation, loss of smell sensation, ear-ache, “dizziness, in ears” [??], hardness in hearing, deafness, stiffness in eyelids, contraction in eyelids, loss of vision, pain in eyes, squint, twisting of eyebrows, pain in the temporal region, pain in forehead, headache, cracking of scalp, facial paralysis, monoplegia, hemiplegia, polyplegia, convulsions, tetanic convulsions, feeling of darkness before the eyes, giddiness, tremors, yawning, hiccup, malaise, excessive delirium, roughness, coarseness, blackish and reddish luster, insomnia, and instability of mind. | It is pacified by drugs having opposite quality to it’s own qualities. Sweet, sour, salted, unctuous, and hot therapeutic measures, and also application of non-unctuous and unctuous enema, snuffing, diet, massage, anointing, bath, etc. in appropriate dose and time. Non-unctuous and unctuous enema are the most important. They overcome all vata symptoms like cutting down a tree at the roots surely kills all trunk, branches and leaves. Oil is also a prime remedy for Vaata. |
|
Pitta Element: Fire, Water Essence: Tejas/Shen Triguna: Rajas Nervous: Sympathetic Force: Protective Life Activity: Metabolism/Maintenance Accumulation: Rainy Defective: Autumn Pacification: Early Rainy |
Sadhaka, Alochaka, Pachaka, Ranjaka, Bhrajaka |
Metabolism Chemical reactions Digestion Transformation |
Solar Plexus (main) Sweat Chyle Lymph Blood Plasma Stomach Small Intestine Eye Organ of touch (skin) |
Krebs cycle ATP and other high-energy molecules Enzyme synthesis Amonia acid Entropy production Amino acid Enzymes Hormones Mitochondria Bile Hydrochloric acid Endocrine system Oestron-Progesterone level Low thyroid level Thyroxine (if low then Pitta low) |
Pitta is that primal constituent of the living body, whose structure is Fire-Water (or inner light and healing power of Pitta i.e Tejas), and whose function is Saatwic, it being concerned with the production of those physical and mental processes which are predominantly saatwic (balancing or transformative) in nature; hence, the presence of Pitta is to be inferred in such mental phenomena like intellection and clear concentration, as also in such physical phenomena as digestion, assimilation, heat production and so on. It will be seen that many of these physical phenomena are among those which modern physiologists would include under the activities of Thermogenetic and Nutritional systems (including thermogenesis and the activities of glandular or secretory structures), especially of the endocrine glands whose internal secretions or hormones are now known to be of such vital importance in digestion, assimilation, tissue-building and metabolism generally. Besides being located in each and every cell, each dosha has a primary location known as its “seat”. If a dosha is starting to go out of balance, the first symptom will often occur at its seat. |
Vision, digestion, maintenance of body temperature, heat, hunger, thirst, softness in body, appetite, complexion, lustre, cheerfulness and intellect, courage, prowess, exhilaration, clarity. | Burning, heat, inflammation, perspiration, moisture, sloughing, itching, discharge, redness, along with the appearance of respective smell, color and taste, yellow coloration of the feces, urine, eyes, and skin, excess of hunger and thirst, feeling of burning sensation and very little sleep. | Produces weakness of digestive activity, coldness and loss of lustre (complexion). | Heating, scorching, burning, intense burning, fuming, hyperacidity, burning in the stomach and esophagus, internal burning, burning in scapular region, pyrexia, over-perspiration, foul smell in body, tearing of body parts, excessive moisture in blood (possibly uraemic conditions), moistening of muscles, burning in skin, tearing of skin, thickening of skin [[scleroderma]], urticarial patches, pustules, internal hemorrhage, haemmorhagic patches, greenishness, yellowness, bluishness, herpes, jaundice, bitterness in mouth, bloody smell from mouth, foetid smell form mouth, excessive thirst, loss of contentment, stomatitis, inflammation in throat, inflammation in eyes, inflammation in anus, inflammation in penis, discharge of pure blood, fainting, green or yellow color in eyes, urine and feces. | Pitta is pacified immediately by substances opposite to it’s own qualities. Sweet, bitter, astringent and cold measures and application of unction, purgation, pasting, bath, massage, etc. which alleviate pitta. Purgation is the best, because it removes the source of Pitta quite effectively. An analogy: In a wood stove, when we remove the fire from it’s firechamber, the stove surely becomes cold. Ghee is also a top remedy for Pitta. |
|
Kapha Element: Water, Earth Essence: Ojas/Jing Triguna: Tamas Nervous: Central Or Cerebrospinal Force: Destructive Life Activity: Anabolism/Building Accumulation: Early Winter Defective: Spring Pacification: Summer |
Tarpaka, Avalambaka, Kledaka, Bodhaka, Shleshaka |
Structure Cohesion Lubrication |
Chest (main) Head Neck Joints Stomach Small Intestine Fat Plasma Pancreas Nose Tongue |
Lipids Polysaccharides Fatty acid Phospholiquid Interstitial fluid Intercullar fluid Cytoplasm Synovial fluid Cerebral fluid Myelin sheath |
Kapha is that primal constituent of the living body, whose structure is Water-Earth (or ultimate energy reserve of body that manifests from Kapha i.e Ojas), and whose function is Taamasic, it being concerned with the production of those physical and mental processes which are predominantly taamasic (conserving or stabilizing) in nature; hence the presence of kapha is to be inferred in such mental phenomena as the exhibition of courage, forbearance, etc., as also in such physical phenomena as the promotion of bodily strength and build, integration of the structural elements of the body into stable structures, the maintenance of smooth working joints, and so on. It will be seen that many of these physical phenomena are among those which modern physiologists would include under the activities of the Skeletal and Anabolic systems. Besides being located in each and every cell, each dosha has a primary location known as its “seat”. If a dosha is starting to go out of balance, the first symptom will often occur at its seat. |
Lubrication, binding, firmness, heaviness, potency, strength, forbearance, restraint, and absence of greed. Firmness, development, enthusiasm, potency, knowledge, understanding. | Whiteness (e.g white coloration of feces), coldness, itching, immobility, heaviness, unctuousness, numbness, moistening, mucous covering, binding sweetness, chronicity [slow pace/ non-resolving of conditions]. Kapha produces weakness and depletion disorders. It also produces these symptoms: laxity, emaciation, idleness, impotency, ignorance, confusion and other conditions. Debility of digestive activity, excess salivation, lassitude, feeling of heaviness, white coloration (of feces etc.), coldness, looseness of the body parts, dyspnoea, cough and excess of sleep. | Causes dizziness, emptiness of the organs of kapha, tremors of the heart (palpitation) and looseness of the joints. | Saturation, drowsiness, excessive sleep, cold sensation, heaviness in body, lassitude, sweetness in mouth, salivation, mucous expectoration, excess dirt, excess mucous, indigestion, “plastering” of heart*, plastering of throat, accumulation in vessels*, goitre, over-plump-ness, urticarial eruptions, urticarial patches, white lustre, whiteness in urine, eyes and feces. | Substances having the opposite qualities to Kapha reduce it. Pungent, bitter, astringent, sharp, hot and rough measures. Also fomentation, emesis, snuffing, exercise, etc. Emesis is the best. It works surely, just as rice plants will surely dry out and die when the rice field’s earth water dam is opened up. Honey is a top remedy for Kapha. |
SubDoshas
Go to top| SubDosha | Direction | Situated In | Energy Prevades In | Functions | Governs | Description | Disorders |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Prana Lead Breath Dosha: Vaata Element: Ether |
Upward, Inward | Head | Heart | Breathing & Swallowing of food | Reception of all | Prana is present in the head and moves downward and inward. It is connected with higher cerebral function. Prana vayu is located in the cranial cavity and it moves in the head. It also moves down to the throat, heart, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm. Because of this movement, prana is responsible for inhalation.Prana creates a union of outer cosmic prana and inner prana. Prana moves the mind and prana becomes mind. If one controls prana, one can control the mind. Prana is movement of mind, thoughts, feelings, emotions, sensation, and perception. When prana is motionless, it becomes blissful awareness. So, awareness becomes perception, perception becomes sensation, and sensation becomes feelings. Then thoughts arise and feelings become emotions. This is the natural order. Motionless prana is Pure Awareness. The moment prana moves in a particular direction, awareness becomes attention and attention becomes perception. Through perception, prana creates sensation through which one senses the object of perception. Then sensation becomes feelings and feelings create emotion. Therefore, emotion is the reaction to the flow of prana and all emotions come from memory. | Disorders above the belly button. Palpitation, dyspnea, undue awareness of respiration, or breathlessness, anxiety, nervousness, fear and anger, inability to focus mind, stroke, paralysis, grand mal epilepsy, sleep apnea, tremors of Parkinson's disease, bronchitis, asthma, pneumonia, hiccoughs, constant burping. |
|
Udana Upward Breath Dosha: Vaata Element: Air |
Upward | Throat | Circulation flow around head & neck | Moves upward | Speech & Intellect, Self-expression |
The next important vayu is udana, which is upward moving energy. Udana vayu is located in the diaphragm and moves upward through the lungs, bronchi, trachea, and throat. Udana also goes up into the brain and stimulates memory. Udana is the nerve impulse that takes place at the solar plexus and tracheal plexus. It governs the movement of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, and helps the process of exhalation. Udana is responsible for speech and expression. A person cannot speak without exhalation. Prana vayu is the energy that brings oxygen into the lungs and udana vayu is responsible for exhalation of carbon dioxide. Udana vayu helps oxygenation. When oxygenation is good, the person appears fresh and vital. When a child crawls on the floor and tries to raise its head, that is udana vayu. If udana is weak, the child cannot lift its head or support its neck. | Difficulty of speech, such as stuttering or muttering, lack of memory, lack of creativity, and no sense of goal or direction, depression and discoloration of the skin, hoarseness of voice, asthma, pneumonia, emphysema - as well as blushing and flushing. |
|
Samana Equalizing Breath Dosha: Vaata Element: Fire |
Periphery to Center of Body | Abdomen | Abdomen | Isolation, Separation, Splitting |
Digestion | Samana vayu is present in the small intestine and navel. It moves the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. This vayu provides the stimulus for the secretion of digestive juices. Therefore, samana vayu is closely connected with agni (digestive fire). There are agnis in the liver and samana vayu provides the energy to secrete the liver enzymes. The bile that is secreted from the liver, along with the liver enzymes, are accumulated in the gallbladder by samana vayu. It constricts the gallbladder and pushes the bile from the gallbladder through the bile duct into the duodenum. All of these movements are governed by samana vayu. This vayu plays an important role in creating hunger. When one feels hungry, samana is awake. Samana sends a message to prana asking for food. When one eats, samana vayu stimulates the secretion of hydrochloric acid and opens the pyloric valve for movement of foodstuff into the duodenum. Samana vayu brings the foodstuff into the cecum, which is called the second stomach. The entire movement around the belly button is samana vayu and this movement is linear and outward. | Disorders at the belly button. Loss of appetite, indigestion, increased or decreased peristalsis, bloating, lack of absorption and assimilation, poor digestion, malabsorption syndrome. |
|
Vyana Pervading Breath Dosha: Vaata Element: Water |
Circular, Center to Periphery of Body | Heart and Lungs | Whole body | Pulsation, Throbbing |
Autonomic nervous system, Circulation of all subtances |
The main function of vyana vayu is to maintain cardiac activity, circulation, nutrition and oxygenation of cell tissues and organ systems. Vyana vayu is present in the heart and maintains the circulation of arterial blood, venous blood, and lymphatic circulation. Vyana moves throughout the body. Vyana is a strong vayu and all reflex actions, including the corneal reflex, are governed by its energy. It is responsible for the movement of the joints and skeletal muscles through the reflex arc. The reflex arc goes only to the spinal cord and not to the brain, and the spinal cord answers these reflexes. | Poor circulation and sudden lack of oxygenation, when coronary arteries are clogged a person may get ischemic heart disease, Edema, or stagnation of blood in the lower extremities, Horripilation, Shivering. |
|
Apana Downward Breath Dosha: Vaata Element: Earth |
Downward, Outward | Pelvic | Lower Abdomen | Holding | Elimination of all substances | Apana vayu is present in the pelvic cavity, in the cecum, ascending colon, transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, rectum, and urinary tract. Apana vayu is also present in the vagina and cervix of a woman and testicles, prostate, and urethra of a man. It moves downward and outward. It regulates the function of the kidneys. The urine is filtered in the kidneys and drop-by-drop is brought down into the bladder. It also stimulates menstruation, defecation, and flatulence. Apana is motor function working with different segments of the lumbosacral spine. From the lumbosacral spine the message is carried to the bladder to evacuate urine; to the rectum to evacuate feces; to the womb to produce menstruation or delivery of a child. Apana pushes the child from the womb. It nourishes the bones through the colon mucous membrane and the absorption of minerals It regulates the movement of the sciatic nerve and the lower part of the body. It is also responsible for movement of sperm in the man and the desire to make love. In the woman, apana stimulates ovulation, regulates menstruation, and during pregnancy apana nourishes the fetus and moves it during delivery. During intercourse, apana of the man and woman merge together and bring the meeting of the sperm and ovum. Apana is responsible for conception. If apana is weak, conception is not possible. If apana vayu is weak, a woman accumulates fat in the thighs. | Disorders below the belly button are associated with this vayu. Constipation, Diarrhea, Retention of urine, no menstruation or heavy manstruation. Pain during menstruation, pain during sex, lower backache, paint during ovulation, sexual impariment, premature ejaculation or premature orgasm, osteoporosis. |
|
Sadhaka Helper Dosha: Pitta Element: Ether |
N.A | Brain (gray matter) | Heart | Conscious thinking and emotions, Comprehension |
Intellect & Memory | Sadhaka pitta is present in the gray matter of the brain as certain neurotransmitters, and in the heart as part of the cardiac plexus or the heart chakra. It is responsible for knowledge, understanding, comprehension, and appreciation. It transforms sensations into feelings and emotions. It also creates the feeling of “I am" that is ego. In Vedic philosophy the ego is not a bad thing. A person must have self-confidence, self-esteem, and that self-esteem is called ego. ahamkara. Self-esteem is essential for survival and growth. The pitta present in the nervous system that is responsible for all neuro-chemical changes is sadhaka pitta. The gray matter of the brain regulates the temperature of neurons and that is also sadhaka pitta. It is sadhaka pitta that helps to transform molecules of food, water, and air into a biological cellular component called cytoplasm. The content of cytoplasm is further transformed into awareness by subtle cellular metabolic activity because of sadhaka pitta. All biochemical neurotransmitters, which are necessary to maintain higher cerebral activity, fall under sadhaka pitta. The unprocessed cytoplasmic content becomes emotion. Every thought, feeling, and emotion should be processed into intelligence. That which is not processed is crystallized and stored in the connective tissue. Sadhaka pitta also transforms physical sound into nerve impulse, which is carried to the center of hearing where every sound, as a nerve impulse, is transformed, cooked, digested, and translated into meaning. Meaning is feeling. The word “love” creates certain feelings in one's heart. Love cannot be described but pure essence of love can be felt. If you say that anything that cannot be described does not exist, that means you have lost feeling. Feeling is called ESP—extrasensory perception. Sadhaka pitta, which is present in the brain cells as a specialized neuro-chemical substance, creates ESP, the important sixth sense. Prana is a flow of awareness and this flow of intelligence is neuro-electricity that is moving through the nerves and delivering a message. Though messenger molecules are RNA molecules, prana brings the message from DNA to RNA. So there is a functional relationship between DNA molecules, which create new cells, and RNA molecules, which are the messengers. Prana brings the message. Past memory and experience is stored in the RNA/DNA molecules. In the process of recognition, sadhaka pitta penetrates the memory and chooses a particular file from the vast hologram of RNA/DNA molecules. This is a function of buddhi, the intellect. 'Reality' is a product of mind. Reality in this room is different to reality in another room. 'Truth' that is confined by time and space becomes reality. 'Actuality' is a product of the senses. The pencil in someone’s hand is actual to that person at that time. Therefore, it is also reality to them. When you look at them holding the pencil, it is your reality, but only when you touch it does it become actual to you. So what is the relationship between Truth, reality, and actuality? Reality has to pass through actuality, or actuality must come in close contact with reality, in order to realize Truth. So Truth is unconditional, universal absolute. The moment a person experiences that, it becomes personal reality. As long as a person is in the dream, dream is reality. When he comes out of the dream, reality changes, because reality is bound by time and space. Truth is not. In that sense, awareness is Truth, consciousness is reality, and perception is actuality. So perception has to pass through consciousness in order to reach awareness, which means actuality has to go through reality in order to reach the Truth. This transformation is governed by sadhaka pitta. It is sadhaka pitta that bridges this function of looking and listening with total existence. Then existence becomes actual. When we internalize actuality, or reality, it becomes Truth. Truth has a relationship with reality and actuality, but actuality and reality may not have a relationship to the Truth, because the bridge between actuality and reality of Truth is sadhaka pitta. Therefore, we can only have a clear relationship with Truth if sadhaka pitta is healthy. Sadhaka pitta is necessary for the transformation of an object into pure experience. When experience is recorded in the brain cells, it becomes memory and memory is knowledge. | No information available. |
|
Alochaka Seer Dosha: Pitta Element: Air |
N.A | Eyes | Eyes | Maintains iris color, Visual perception |
Vision | Alochaka pitta is present in the eye and governs the luster, color, and translucence of the eye. It is present in the cornea to maintain transference and translucence. It is present in the iris to maintain color and in the lens to maintain transference. It is also present in the vitreous humor and in the cone and rod cells. Alochaka pitta is necessary for optical perception. It maintains the temperature of the eyeball, the color of the iris, color vision, and vision of light. When you look at an object, that image is formed on the retina and absorbed by the sharp quality of alochaka pitta into the optic nerve. Then prana vayu carries that image to the mind for interpretation. Alochaka pitta maintains visual perception and three-dimensional vision. If you have only one eye, what you see is a flat picture. Binocular vision, with two eyes, is three-dimensional. One of the important functions of alochaka pitta, along with prana, is accommodation (ability to focus), which means the constriction or dilation of the pupil, so that appropriate light is allowed to enter and fall on the retina for clear perception of an object. Alochaka pitta is responsible for generating the visual impulse, which prana then carries to the mind, to buddhi, where interpretation of the impulse is accomplished by sadhaka pitta. So, alochaka pitta meets sadhaka pitta in buddhi, where interpretation of visual perception takes place. This meeting point is in the occipital cortex, the posterior (back) portion of the head. If there is trauma at this meeting point, a person may become blind. Alochaka pitta is also associated with emotions. Different emotions bring a different chemistry to the tears. Tears of joy and love are sweet, scanty, and cool, and come from the lateral (outer) side of the eye. Tears of anger come from the center of the eye and are sour to the taste, and hot. Tears of frustration, grief, sadness, and fear come from the medial (inner) side and are bitter and astringent to the taste. Eyes have the capacity to see the truth. When you look without judgment, without interference of thought and mind, the eyes become the windows of God and you can perceive the Truth. If your thought and mind interfere, then you perceive reality, because reality is a product of your mind. We need sensitive alochaka pitta that can perceive the truth of reality, the truth of actuality. When you perceive the Truth, there is love, clarity, compassion, and pure awareness. | Glaucoma, changes in the eyes leading to shortsightedness or farsightedness. If alochaka pitta is increased, it may create conjunctivitis, styes, iritis, burning sensation in the eye, and photophobia. |
|
Pachaka Cooker Dosha: Pitta Element: Fire |
N.A | Small Intestine, Stomach |
Small Intestine, Stomach |
Digestion, Absorption & Assimilation of food |
Digestion | The pitta present in the stomach and small intestine is called pachaka pitta. The intestinal digestive juice that is secreted from the villi of the small intestine is also pachaka pitta. The pachaka pitta in the stomach is a part of jathara agni. Jathara means stomach. This agni is the central fire, gastric fire, and this digestive fire in the stomach is the main agni in the body. When the gastric fire in the stomach is high and there is more secretion of hydrochloric acid and digestive enzymes, the stomach becomes grouchy and creates the sensation of hunger. The pachaka pitta in the stomach and the pachaka pitta in the small intestine work together. Jathara agni is composed of pachaka pitta, prana vayu, samana vayu, and kledaka kapha. This pitta governs the digestion in the stomach within the first two hours after the ingestion of food. Then the pyloric valve opens and the food passes into the duodenum, the upper part of the small intestine. | Hyperacidity, hypoglycemia, and craving for sugar, gastritis, peptic ulcer, indigestion, anorexia, and dyspepsia. |
|
Ranjaka Colorer Dosha: Pitta Element: Earth |
N.A | Liver, Spleen, Intrinsic Factor in Stomach |
Liver, Spleen, Intrinsic Factor in Stomach |
Produces bile, Liver enzymes, Gives color to blood, Blood formation |
Blood | Ranjaka pitta in the liver gives color to all tissues. Skin color, hair color and the color of eyes are related to ranjaka pitta. Ranjaka pitta is responsible for erythrogenesis, the creation of red blood cells in the bone marrow, which are mixed with rasa dhatu, the plasma. Thus, ranjaka pitta is responsible for giving color to the blood. Ranjaka pitta in the stomach is intrinsic factor, which is responsible for the production of blood in the bone marrow. Ranjaka pitta in the spleen kills bacteria and parasites as well as produces some white blood cells (rasa dhatu), so its job is more protective. There is a functional integrity between the liver, stomach, spleen, and bone marrow. If the function of the liver is affected, the bone marrow will also be affected. If the function of the stomach is affected, it will affect the liver. In a way, the spleen and liver also have functional integrity. The job of the spleen is to filter the blood and to send unwanted, heavy, old red blood cells to the liver; the liver destroys them and separates the hemoglobin from the blood. Then the liver utilizes the hemoglobin that is liberated for the production of bile salts, pigment, and enzymes. Therefore, when the spleen is enlarged the liver may also be enlarged, and vice versa. There is a fine line between ranjaka agni, bhuta agni (element fires), and rakta agni. Ranjaka agni incorporates bhuta agni. It gives color to rasa dhatu and transforms rasa into immature (asthayi) rakta dhatu. Bhuta agni is the specialized function of ranjaka agni in the liver that converts food and other substances into their elemental components. Rakta agni does further transformation of asthayi rakta into mature (sthayi) rakta dhatu, essential to the maturation of red blood cells. There are 5 bhuta agnis: Nabhasa agni (Ether fire), Vayavya agni (Air fire), Tejo agni (Fire), Apo agni (Water fire), Parthiva agni (Earth fire). There is a relationship between ranjaka pitta and alochaka pitta, the pitta associated with the eyes. If the sclera is yellow, it is due to a disorder of ranjaka pitta and alochaka pitta. The eyes and liver are connected, and toxicity in the liver may create visual disturbance. Photophobia is sensitivity to light due to toxicity in the liver. The same thing happens if a person drinks too much alcohol. When the liver metabolizes alcohol, excess pitta is produced. Visual perception on a subtle level is also affected, because a ranjaka pitta disorder may even affect the sadhaka pitta of the brain. | Hepatitis, anemia, chronic fatigue syndrome, mononucleosis. When kapha disturbs ranjaka pitta, the person may develop gallstones. If kapha is long-standing and lingers in the liver, the person may develop high cholesterol, fatty degeneration of the liver, or steatorrhea (fatty diarrhea). |
|
Bhrajaka Shiner Dosha: Pitta Element: Water |
N.A | Skin | Whole body | Maintains skin color, Texture and temperature, Stereognosis |
Normal pigmentation of skin | This pitta keeps the skin warm and is responsible for normal complexion and luster. It also helps in the processing of oils, pastes, and medications applied externally to the skin. When we apply, for instance, sandalwood or ginger paste, the agni principle of bhrajaka absorbs and assimilates the substance. The skin is a gate or door that is kept functional by bhrajaka pitta. Bhrajaka pitta works in connection with ranjaka pitta and pachaka pitta. Skin care is important in Ayurveda. Oil is absorbed through the skin and the quality of the oil penetrates deeply into the connective tissue all the way to the bone. The medium that carries and absorbs that oil is bhrajaka pitta. | Eczema, dermatitis, acne, and anesthesia—loss of sense of touch, tingling, and numbness. |
|
Tarpaka Satisfier Dosha: Kapha Element: Ether |
N.A | Brain (white matter) | Myelin Sheath, Cerebrospinal Fluid |
Subconscious thinking and emotions, memory |
Intelligence | Tarpaka kapha is predominantly present in the white matter of the brain. It is thick, sticky, slimy, and soft. Tarpaka nourishes the brain cells. The liquid qualities of tarpaka kapha are present in the meninges and cerebrospinal fluid, which surround the soft brain tissue and the spinal cord. Tarpaka kapha brings energy to rasa dhatu (plasma) by way of the sweet and salty tastes, creating a feeling of happiness. If a crying child is given sugar, he becomes happy and stops crying. Another important site of tarpaka kapha is the myelin sheath, a protective sheath surrounding most nerve cells. Tarpaka kapha lubricates the sinuses and nasal cavities and is present in the spinal cord, where it governs the reflex arc. The tarpaka kapha in the spinal cord acts as a medium for the completion of the circuit for the reflex arc. If batteries are dry, nothing happens. So tarpaka kapha in the spinal cord acts like a battery solution. Tarpaka kapha helps to create neurological time, which is stimulus and response. Psychological time is thought. There is no space without time. Time is space and space is distance. If tarpaka kapha becomes thick and firm, there is crystallization, rigidity, and callousness, which create confusion. Confusion is conclusion and this conclusion is judgment that is stored in tarpaka kapha. We carry the memory of our parents' illnesses within the DNA molecules, which is tarpaka kapha. If a person’s grandfather had diabetes, taipaka kapha carries, tapaka kapha carries that memory of diabetes in the person's cells. We seek security by retaining memories and tarpaka kapha performs this task. When a child burns his hand in a fire, that memory is recorded. Now when he sees fire, he knows not to play with the flame. There is safety and security in biological memory, which is absolutely necessary for safety. We also have psychological memories of childhood suffering. Whatever treatment received from parents or teachers during the first seven years of life, stays with us through life and shapes our personality. Within tarpaka kapha there is a space beyond time and aging, which can be reached through sensitive awareness. In other words, one can avoid the DNA problems. Within that space, a person will no longer live in the past. To live in the present means to live in a timeless space. To live now means to live in eternity. To live in your relationships with these qualities of taipaka kapha is to live with God. | Stroke paralysis, Parkinson’s disease, or brain tumors. Concussion, compression, or contusion may affect tarpaka kapha and change the entire personality. |
|
Avalambaka Supporter Dosha: Kapha Element: Earth |
N.A | Lungs, Pleural Cavity, Heart, Respiratory Tract, Spine |
Heart | Support, Holds emotions, Supports all kapha systems |
Energy in Limbs | Avalambaka kapha is an important kapha that supports all kapha systems in the body, functionally as well as structurally. It includes the spine as well as the lungs and heart. It carries pranic energy from the lungs to every cell, tissue, and organ. It is supportive to both the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. Avalambaka kapha is present in the respiratory and cardiovascular systems, in the trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. Avalambaka kapha also supports the intracostal muscles and ribs. Because of its liquid quality, avalambaka kapha helps with gaseous exchange by removing unwanted carbon dioxide from the alveoli so that oxygen can enter. In addition, avalambaka kapha provides the liquid quality within the pulmonary trunk so that oxygenated blood can be carried to the heart. Avalambaka kapha protects the lungs and alveoli, and maintains the tone of the muscular layer of the bronchi. In addition, as pericardial fluid it protects the heart muscle. Kledaka kapha and avalambaka kapha have functional integrity. Without kledaka kapha, avalambaka kapha cannot do anything. Avalambaka creates confidence, courage, and ability to face problems so that the chest is expanded. When the chest is contracted, the person is not able to cope with challenges. Psychologically, avalambaka kapha is associated with support, love, and compassion. | When there is excessive grief and sadness, avalambaka kapha becomes sticky, and lung function is affected. The lungs are the seat of grief and sadness. The inferior quality of avalambaka kapha may create pulmonary changes and collapse of the bronchial lumen. Bronchitis, asthma, bronchiectasis, pneumonia, and emphysema are all due to dysfunction of avalambaka kapha. |
|
Kledaka Wetter Dosha: Kapha Element: Fire |
N.A | Stomach, Gastrointestinal Tract |
Stomach | Gastric secretion, Digestion and absorption, Nourishes rasa |
Moistening of food in stomach | Kledaka kapha is present in the gastrointestinal tract. It is liquid, soft, slightly oily, and slimy. This kapha creates a protective lining as the gastric mucous membrane. This membrane can be destroyed when food is consumed. Cayenne pepper, curry pepper, and alcohol dissolve the mucous membrane. Within 72 hours, kledaka kapha provides a fresh, new mucosal lining to protect the wall of the stomach. The stomach is divided into the greater curvature and the lesser curvature. The lesser curvature is the acid bearing area that secretes more hydrochloric acid and other digestive juices, which are pachaka pitta. The greater curvature, or fundus, produces more kledaka kapha. The lesser curvature of the stomach is near the liver, a pitta organ. The greater curvature is near the spleen, whose function is to filter blood. Sleeping on the left side suppresses kapha and builds pitta. The greater curvature of the stomach goes down and the lesser curvature is pressed toward the liver, creating more acid secretion. People who sleep on the left side can increase digestive fire but may have hyperacidity. People who sleep on the right side can calm pitta but might induce kapha aggravation, leading to sinus congestion. Sleeping on the right side brings more spleen energy, while sleeping on the left side suppresses spleen energy and builds more liver energy. When you sleep on the right side, the stomach empties earlier, because the pyloric valve is on the right. However, the food leaving the stomach may not be fully digested. Optimally, one should wait three or more hours after a meal before going to sleep so the stomach has emptied completely. | With excess kledaka: Obesity, obsessive eating habits, hyperglycemia, diabetes, high cholesterol. With insufficient kledaka: hypoglycemia, peptic ulcer. |
|
Bodhaka Perceiver Dosha: Kapha Element: Air |
N.A | Mouth | Mouth | Salivary secretions, Taste, Swallowing, Speech |
Taste | It is located in the mouth and is represented by saliva, which is liquid, sticky, sweet, and slightly unctuous. The liquid quality of bodhaka kapha keeps the mouth wet and soft. The agni of bodhaka kapha, called bodhaka agni, is responsible for maintaining the oral temperature. Any substance that goes into the mouth causes secretion of bodhaka kapha. Bodhaka kapha also lubricates the tonsils, pharynx, and vocal cords. The epiglottis is well lubricated by bodhaka kapha so that foodstuffs can slide over the epiglottis directly into the esophagus without entering the trachea. The pharynx leads to the esophagus and the larynx leads to the lungs. This space within the throat is moistened, and the posterior wall of the pharynx is also well lubricated, by bodhaka kapha. Kledaka kapha works in conjunction with bodhaka kapha in the digestion of protein, starch, and carbohydrates. | Thick saliva indicates dental calculi, diabetes, worms, or Parkinson’s disease. Excess saliva or a sticky mouth may also indicate dehydration or pre-diabetes, because stickiness of the mouth is due to sweet saliva. In a 24-hour period, we swallow about one pint of saliva and in this way bodhaka kapha nourishes kledaka kapha. In addition, through saliva bodhaka kapha helps to maintain water electrolyte balance. |
|
Shleshaka Embracer Dosha: Kapha Element: Water |
N.A | Joints | Joints | Lubricates joints (synovial fluid), Nourishes bones |
Lubrication of joints | Shleshaka kapha is thick, sticky, liquid, oily and slimy. It is present all over the body, and especially in the joint spaces, where two bones come together. It lubricates the joints and nourishes the articular (joint) surfaces and cartilages to promote easy movement. One of the important functions of shleshaka kapha is to support the skeletal system and to strengthen the ligaments. | Degenerative arthritis, Rheumatoid arthritis. |
Dhatus
Go to top| Name | Functions | Superior Byproduct | Inferior Byproduct | Description | Causes of Increase | Causes of Decrease | Signs of Increase | Signs of Decrease | Signs of Disturbed | Signs of Disturbed by Vata | Signs of Disturbed by Pitta | Signs of Disturbed by Kapha |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Rasa Plasma, Blood Serum, Lymph Preparation Time: 5 days Size: 9 anjali |
Nutrition, Affection, Immunity |
Top layer of skin, Lactation, Menstruation |
Kapha (Poshaka kapha) | Rasa dhatu is the first and foremost juice of all life—from the amoeba to the human being and is associated with plasma, serum, and lymph. Ahara rasa is the immature form of rasa dhatu and forms within 12 hours of the intake of food. Rasa agni, the fire principle of rasa, transforms ahara rasa into Mature Rasa and Immature Rakta. This transformation, from food to plasma, takes five days. Rasa dhatu contains both hot and cold molecules. The hot molecules are red blood cells and the cold molecules are white blood cells. Rasa—which includes white blood cells—and rakta (red blood cells) function together. White blood cells and red blood cells bathe and breathe in plasma, which is rasa dhatu. Plasma also includes blood serum and lymph, the circulating fluid of the lymphatic system. In fact, the entire lymphatic system is part of rasa dhatu. Kledaka Kapha, Vyana Vayu, and a small amount of Pachaka Pitta are present in rasa dhatu. Because of the presence of Vyana vayu, rasa dhatu is mobile, active, and keeps flowing. Pachaka pitta gives rasa a yellowish color. Without pachaka pitta, which contains agni, the transformation of asthayi (immature/raw) into sthayi (mature) rasa is impossible. |
Excessive water intake, Hydrophilic substances, such as salt and watermelon, Dairy products - such as milk, cheese and yogurt, Alcoholic drinks, Sleeping during the daytime, Insufficient exercise, Repression of emotions. | Insufficient water intake, Profuse perspiration, Eating dry fruits, Post-influenza dehydration, Leftover food, Nausea, Hot/Dry Spicy food, Vomiting, Excessive amounts of pungent, bitter and astringent substances, Diarrhea, Fluid loss, Beans, Polyuria (excess urination), Excessive exercise, Over-exposure to hot sun, Emotional reactions, such as anger and fear. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rakta Red blood cells Preparation Time: 10 days Size: 8 anjali |
Life function, Oxygenation, Enthusiasm |
Blood vessels, granulation tissues, Small tendons and sinews |
Pitta (Poshaka Pitta) | Rakta dhatu is the red blood cells in the heart and blood vessels, and it provides a bridge between the body’s internal and external environments by carrying nutrients to the tissues. It transports nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract, prana from the lungs and vyana from the heart to the cells of the body. The waste products from the cells in the form of carbon dioxide are carried to the lungs. Other waste products are carried by the blood to other excretory organs and are related to apana vayu. Although rasa and rakta dhatus are integrated and function together, they are considered separate systems in Ayurvedic theory. From ahara rasa (the nutrient precursor), it takes five days for Mature Rasa dhatu to be formed. Mature rasa and Immature/Raw Rakta are formed at the same time. After 10 days, Mature rakta is formed. Rasa and rakta dhatus regulate temperature by distributing heat from the skeletal muscles and active organs to all body parts. This distribution of heat is an important function of rasa and rakta dhatus together. Ranjaka pitta is present in rakta dhatu, as is Prana Vayu and Vyana Vayu, and together they are responsible for circulation. |
Low dhatu agni, Large amounts of jaggary, Hot spicy food and drinks, Excessive consumption of oily or fried, Iron or folic acid supplements, Meat, Alcohol, especially red wine, Intravenous blood transfusion, Sour substances, Working under the hot sun, Anger, hate and envy. | Anemia, Severe blood loss in traumatic situation, Iron, folic acid or vitamin B12 deficiency, Pinworms or hookworms, Hemorrhage, Excessive menstrual bleeding, Hemorrhoids, Insufficient sunlight. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mamsa Muscle Preparation Time: 15 days Size: It varies |
Plastering, Form, Movement, Support, Strength, Protection |
Six layers of skin, Subcutaneous fat |
Ear wax, Nasal crust, Sebaceous secretions, Tooth tartar, Smegma |
The next dhatu is mamsa. The fully processed sthayi (mature) mamsa is created from asthayi (immature/raw) mamsa, which is formed at the same time as sthayi rakta. The transformation from ahara rasa to sthayi mamsa takes about 15 days. Mamsa dhatu is the muscle tissue. The muscular system accounts for nearly half of the body weight. Mamsa dhatu is closely connected to the tonsils; they regulate the immunity of mamsa dhatu. |
Low dhatu agni, Kapha foods, such as wheat and dairy products, Heavy food, Excessive consumption of food, Red meat, Sleeping during daytime, Suddenly stopping heavy exercise, High protein diet. | Excessive exercise with insufficient nutrition, Vata provoking diet, Old age, Chronic illness and consumptive diseases, Multiple sclerosis, Neuromuscular disorders, Malabsorption, Lack of protein |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Meda Adipose Preparation Time: 20 days Size: 2 anjali |
Lubrication, Bulk to body, Insulation, Beauty, Personal love |
Tendons, sinews, ligaments, flat muscles |
Sweat | Meda is adipose tissue, a loose connective tissue that includes fat, phospholipids, steroids such as cholesterol, and other types of lipids. Meda dhatu is connected to the adrenals. | Fatty, fried food Excessive water intake, Hydrophilic substances - such as salt, yogurt and watermelon, Insufficient exercise, Sedentary lifestyle, Underactive thyroid, Low Mamsa and Meda agni. | Excessive exercise, Chronic consumptive diseases, Insufficient water intake, Insufficient oil in the diet, Lack of food, Poverty, Fear, anxiety and nervousness. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Asthi Bone Preparation Time: 25 days Size: Approx. 365 bones |
Support, Structure, Protection of vital organs |
Teeth, Cartilage |
Hair, Nails |
It is the densest tissue in the body. This dhatu also conducts sound waves that aid in hearing. Asthi dhatu also acts as an excretory tissue. The unwanted molecules of toxic heavy metals, such as arsenic, mercury, and lead are retained in asthi dhatu, and the body tries to eliminate them in the nails and hair. In hair analysis, some people show excessive amounts of these metals, which come from the bone. Predominately made of Earth, Air and Water. |
Low dhatu agni, Metabolic bone disorders, Endocrine disorders, Thyroid and parathyroid disorders Kapha disorders, Excessive consumption of calcium, magnesium, zinc and other minerals. | Lack of calcium, magnesium, zinc and other minerals, Heavy metal toxicity, Exposure to radiation, Malabsorption, Trauma, Excessive exercise, Too much jogging or jumping, Vata disorders, Menopause, Chronic illness (TB, typhoid, etc.), Insufficient milk during childhood, Broad-spectrum antibiotics. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Majja Bone marrow, Nervous tissue Preparation Time: 35 days Size: 2 anjali |
Reproduction, Produce ojas, Emotional release |
Lacrimal secretions | Oily secretions in eyes | Majja dhatu includes both the nerve tissue and the bone marrow. Bone marrow is a soft jelly-like tissue within the cavity of the bone. Every bone has a little foramen, a small hole, through which the nerves and blood vessels enter the bone tissue. Therefore, the bone tissue has a sense of pain, pressure and position of the joint. Whenever your joint is flexed or extended, you know its position because of majja dhatu. Majja dhatu is the seat of the conscious and subconscious mind. The frontal lobe of the brain governs the emotional brain. According to Ayurveda, the superior area governs vata, the middle governs pitta and the inferior governs kapha. Anxiety, fear and nervousness are located more in the vata area. Anger, judgment and criticism are in the pitta area. Attachment, greed and possessiveness are found in the kapha area. |
Excessive sleep, Sedentary lifestyle, Excessive fats and oils in the diet, Excessive water intake, Kapha aggravating foods. | Vata-provoking diet, Overexertion, Excessive exercise, Emotional reactions, such as fear and anxiety, Prolonged exposure to radiation, Heavy metal toxicity, Malabsorption or malnutrition, Trauma, Alcohol, tobacco, marijuana and other drugs, Incompatible food combining, Broken bones, Cerebral concussion/compression, Laceration of the brain, Head or spinal injury, Whiplash. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Shukra and Artava Reproductive Preparation Time: 40 days Size: Half anjali |
Reproduction, Produce ojas, Emotional release |
Ojas | None | Shukra dhatu is the male and artava the female reproductive tissue. Both male and female reproductive tissues have as their primary function the continuation of human life. | Low dhatu agni, Sedentary lifestyle, Lack of exercise, Rich, oily foods, Dairy products, Meat, Heavy food, Excessive water intake, Attachment, greed and possessiveness, Anger, irritability, envy or jealousy, Steroidal and hormonal therapy, Pitta aggravating factors, Meat and fish, Working in a hot room or under the sun. | Low dhatu agni, Excessive exercise, Fear, anxiety, worry and nervousness, Intense joy, excitation, happiness, fear, anxiety, grid and sadness, Chronic illness, Excessive dry, hot, spicy food, Lack of good fats in the diet, Dehydration, Parasites, Trauma, Venereal diseases, Over-indulgence in sex, Excessive masturbation, Vata aggravation, Anemia, Severe blood loss. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ayurvedic Medicines
Go to topIn order of power they can be arranged as Prabhava > Virya > Vipaka > Rasa
| Medicine Name | Prabhava/Special Action | Virya/Potency | Vipaka/Post Digestion Taste | Rasa/Taste | Guna/Quality | Karma/Actions | TherapeuticUsages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Flaxseed/Linseed Alsi Linum Usitatissimum Atasi, Uma |
V-P+K+ Special Action:Alleviates vitiated blood. Warning: It reduces semen and eye-sight. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vaataghna) Removing disorders of Wind |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Siroroga) Diseases of head, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Cardamom - Green Elaichi - Chhoti Elettaria Cardamomum Ela, Suksmaila |
V*P*K- |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Mutra Virechaniya) Diuretic, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Arsa) Piles, (Mutrakrcchra) Dysuria, (Aruci) Tastelessness |
|
Fennel Seeds Saunf Foeniculum Vulgare Miller Misreya, Madhurika |
V-P-K- Special Action:Cures weakened digestive fire. |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Amadosahara) Restorer of impaired digestion and metabolism |
(Kasa) Cough, (Sula) Pain, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Pravahika) Dysentery, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Arsa) Piles |
|
Carom seeds/Bishop's weed Ajwain Trachyspermum Ammi Yavani, Dipya |
V-P+K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Sulahara) Pain killer, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Pacana) Carminative, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Sula) Pain, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Black Pepper Kali Mirch Piper Nigrum Marica |
V-P+K- Special Action:Green variety of Marica is sweeet in vipika and heavy. It eliminates Kapha. It does not increase Pitta. White variety of Marica is neither hot nor cold in potency. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Chedana) Chedana, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Chedi) Cleanses Channel, (Jantunasana) Anti biotic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Medohara) Fat Remove |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Sula) Pain, (Tvagroga) Skin disease, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Clove Laung Syzygium Aromaticum Lavanga |
V*P-K- Special Action:Useful for Heart and Eyes. |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Sulahara) Pain killer, (Pacana) Carminative, (Kasahara) Expectorant, (Rucya) Stimulate taste |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Sula) Pain, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Trsna) Thirst |
|
Cinnamon Dalchini Cinnamomum Zeylanicum/Cassia Tvak |
V-P+K- Description: There are 3 main varities of Cinnamon: 1. Cinnamomum Cassia (Indian/Chinese). It is the perfect for medicines. Its has a thick and harder bark. It is also used topically as anti-inflammatory agent in traditional systems of medicine. 2. Cinnamomum Zeylanicum/Verum/True/Ceylon. It has a thinner bark than Cassia cinnamon. It is sweeter than Cassia cinnamon and less bitter in taste. 3. Cinnamomum Tamala (Indian): It has a thick bark which is not very pungent. When it is ground with water it becomes mucilaginous. Its leaves are called Tejpatra. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Visaghna) Anti poison |
(Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Arsa) Piles, (Trsna) Thirst, (Basti roga) Diseases due to urinary system, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Kanthamukharoga) Diseases of Mouth and Throat, (Mukhasosa) Dry Mouth, (Sukradosa) Diseases of Semen |
|
Indian Cinnamon Tejpatra Cinnamomum Tamala Tvakpatra, Tamala |
V-P*K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Tikshna) Sharp, (Pichchila) Cloudy/Slimy |
(Rucya) Stimulate taste |
(Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Arsa) Piles, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Hrllasa) Angina pectoris (Heart issue) |
|
Caraway Black Jira - Kala/Shah Carum Carvi Krsnajiraka |
V-P+K- Special Action:It is Constipative. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Jvarahara) Febrifuge/Anti Pyretic/Refrigerant, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Sothahara) Anti Inflammatory |
(Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Grahaniroga) Malabsorption syndrome/Diseases of Small Intestine, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Jirnajvara) Fever (Chronic), (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Uterus Clean) Cleans uterus |
|
Cumin Seed Jira - Chitta Cuminum Cyminum Svetajiraka, Ajaji |
V-P+K- Special Action:It is Constipative. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Pacana) Carminative, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Garbhashaya Vishodhana) Uterus Function Improver, (Pittala) Bilious |
(Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Uterus Clean) Cleans uterus |
|
Small Fennel Jira - Mota Kala (Kalonji) Nigella Sativa Kalvanji, Upakuncika |
V-P+K- Special Action:It is Constipative. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Garbhashaya Vishodhana) Uterus Function Improver, (Pittala) Bilious, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Uterus Clean) Cleans uterus |
|
Fenugreek Methi seed Trigonella Foenum-graecum Linn Methika |
V-P-K- Special Action:It specifically decreases Vayu. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Tikka) Bitter | (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Recana) Laxative |
(Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Sula) Pain, (Jvara) Fever, (Grahaniroga) Malabsorption syndrome/Diseases of Small Intestine, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Arsa) Piles, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Sukradosa) Diseases of Semen |
|
Coriander, Cilantro Dhania Coriandrum Sativum Linn Dhanyaka |
V-P-K- Special Action:Green dhania leaves are similar in properties to dried dhania. It has sweet taste. Specially, it alleviates/decreases Pitta. So, Green Coriander is NOT tridosha. Warning: It reduces virility. It causes constipation. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Mutra Virechaniya) Diuretic, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Jvara) Fever, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Arsa) Piles, (Daha) Burning Sensation, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Trsna) Thirst, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Saffron Kesar Crocus Sativus Kunkuma |
V-P-K- Special Action:Happiness, It is constipative. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Jantunasana) Anti biotic, (Visaghna) Anti poison, (Harsana) Exhilaration |
(Kasa) Cough, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Mutraghat) Urinary obstruction, (Udavarta) Upward movement of gases, (Siroroga) Diseases of head, (Suryavarta) Sinusitis, (Kantharoga) Diseases of throat, (Vyanga) Pigmentation disorder, (Sidma) Pityriasis versicolor, (Ardhava Bhedaka) Migraine, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Turmeric Haldi Curcuma Longa Haridra, Nisa |
V*P-K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Kushthaghna) Cure Skin Diseases., (Visaghna) Anti poison |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Pandu) Anaemia, (Sopha) Oedema, (Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Apaci) Chronic Lymphadenopathy/Scrofula, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Tvagroga) Skin disease, (Sitapitta) Urticaria, (Madhumeha) Diabetes |
|
Ginger Root Dried Adrak Dried/Sund Zingiber Officinale Roxb Sunthi, Nagara |
V-P*K- Special Action:Promotes voice and sex desire. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Amadosahara) Restorer of impaired digestion and metabolism |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Sula) Pain, (Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Pandu) Anaemia, (Sopha) Oedema, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Arsa) Piles, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Amavata) Rheumatism, (Slipada) Filariasis |
|
Ginger Root Green Adrak Fresh Zingiber Officinale Rosc Ardraka |
V-P*K- Special Action:* It is always useful if taken before food. * If taken along with kdhjika (vinegar) and (rock-salt), it works as a good dipana (digestive stimulant) and pacana (carminative). * If taken along with lavana (rock-salt), it alleviates vitiated and causes harsana (exhileration). Description: It shares the attributes of Dry Ginger (Sund). If it is taken with rock-salt (lavana), then it alleviates vitiated vayu. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Katu) Pungent |
(Guru) Heavy, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Bhedana) Purgative, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Harsana) Exhilaration, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Sula) Pain, (Sopha) Oedema, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Kantharoga) Diseases of throat |
|
Long Pepper Dried Magha/Pippalimula Piper Longum Linn Pippali/Kana |
V-P-K- Special Action:It has excessively hot potency (virya). But Green Pippali has sweet taste, oily, and heavy. It's potency is cold and increases kapha. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Recana) Laxative |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Sula) Pain, (Jvara) Fever, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Arsa) Piles, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Amavata) Rheumatism, (Trsna) Thirst, (Amadosa) Impaired digestion and metabolism, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Salt - Rock/HimalayanPink Loon - Dali wala Rock Salt Saindhava Lavana |
V-P-K- |
Cold Potency | --- | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Laghu) Light, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Sukshma) Subtle, (Abhishyandi) Obstructs channels of circulation., (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Srstamala) Elimination of waste products |
(Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound |
|
Salt - Black Loon - Kala Black salt Sanchal Lavana |
V-P+K* |
Hot Potency | --- | (Patu/Lavana) Salty |
(Laghu) Light, (Tikshna) Sharp, (Vishada) Clear/Non-Slimy |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Sukshma) Subtle, (Abhishyandi) Obstructs channels of circulation., (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Srstamala) Elimination of waste products |
(Sula) Pain, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools |
|
Salt - Sea Loon - Samudra Sea Salt Samudra Lavana |
V-P+K+ |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Bhedana) Purgative, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Sukshma) Subtle, (Abhishyandi) Obstructs channels of circulation., (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (Srstamala) Elimination of waste products |
|
|
Water - Sun/Moon Charged Pani - Sun/Moon Hamsodaka Hamsodaka |
V-P-K- Special Action:1. It is like antariksa jala (water collected directly from the sky). 2. It is free from defects. 3. It is ANabhisyandi (which does not obstruct the channels of circulation). 4. It is like an ambrosia. Description: Water which is exposed to the sun's rays during the day time and to the moon's rays at night is called hamsodaka. |
Cold Potency | --- |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
||
|
Water- Boiled Pani - Boiled Boiled Water Boiled Water |
V-P-K- Special Action:HOT WATER AFTER BOILING 1. When hot water is taken at night, it clears the adhesion of Kapha, help in the elimination of Vayu and removes indigestion immediately. 2. Water Reduced to 3/4 after boiling: Decreases Vayu. 3. Water Reduced to 1/2 after boiling: Decreases Pitta. It is useful in early winter, late winter, rainy season and spring season. 4. Water Reduced to 1/4 after boiling: Decreases Kapha. It is light, stimulates the power of digestion but constipative. It is useful in summer and autumn. 5. It is useful for Chronic Rhinitis (Pinasa), Cleans urinary tract (Cleans Basti), Flatulance with gurgling sound (Adhmana), Hiccup (Hikka), Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia (Parsva sula). 6. The water which is boiled and warm takes 48 minutes for digestion. COLD WATER AFTER BOILING 1. This water is always wholesome. 2. This water is harmful if stale (kept over night) and it becomes full of impurities (or polluted). It aggravates all the three dosas. If the water is boiled during the day time and kept over night, it becomes heavy. Similarly, if water is boiled at night and taken next day, it excessively aggravates/increases all the dosas. 3. The water which is boiled and cooled gets digested in one and a half hour. Description: The water which is boiled, free from foam and movement. |
--- | --- | (Laghu) Light |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative, (Stimulates power of digestion) Stimulates power of digestion |
(Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Parsva sula) Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia, (Cleans Basti) Cleans urinary tract |
|
|
Arjuna Arjon Terminalia Arjuna Kakubha |
V*P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Kasaya) Astringent | (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous | (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic |
(Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Medoroga) Obesity, (Visa) Poison, (Trsna) Thirst, (Vyanga) Pigmentation disorder, (Asthibhagna) Bone fracture |
|
Emblic Myrobalan Aula/Amla Emblica officinalis Amalaka |
V-P-K- Special Action:Increases Plasma (Rasa) |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Amla) Sour, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic |
(Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Daha) Burning Sensation |
|
Myrobalan Harar Terminalia Chebula Retz Abhaya/Haritaki |
V-P-K- Special Action:It cures ALL diseases. Effects According to Different Modes of Use * If taken after meals, it quickly cures diseases caused by the aggravation of vayu, pitta and kapha as a result of unwholesome food and drinks. * When Haritaki is taken by chewing, it promotes the power of digestion. * When used in paste form it cleanses the bowels. * When used after boiling it produces constipative effect. * When used after roasting it cures the ailments caused by the intake of unwholesome food. Description: Use in Different Seasons * Summer season, it should be used with equal quantity of (jaggery). * Rainy season, it should be used by adding the sufficient quantity of saindhava (rock-salt). * Autumn season it should be taken with equal quantity of purified sarkara (sugar). * Beginning of Winter, it should be used with dry-ginger powder. * Late winter, it should be taken by adding long-pepper powder. * Spring season, it should be used with honey. Good Qualities of Dried Haritaki: * When put in water, it should sink * Freshness (freshly collected) * Dry * Compactness * Round in shape * Heaviness Good Qualities of Fresh Haritaki: * Matured but green * If the pulp is scraped with the help of a knife and taken, it should have taste sweet like jaggery with slightly astringent taste * Which has thick outer skin * Juicy * Have small seed It has 7 varieties: Jivanti: Life-promoting effects; golden in color and useful in all types of diseases. Putana: Purifying effect; it has a bigger seed and is useful in external application. Amrta: Ambrosia like properties; it has 3 segments and it is useful for purgation. Vijaya: Endows user with victory over diseases; it is like a tumba (elongated gourd) in shape. It cures all diseases. Abhaya: Takes away fear of diseases; it has 5 segments and it is useful in eye-diseases. Rohini: Exceeds in therapeutic utility; round in shape and it helps in healing ulcers. Cetaki: Conscious-promoting property; it has 3 segments. It is useful in recipes used in the form of powder. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Amla) Sour, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Kushthaghna) Cure Skin Diseases., (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kamala) Jaundice, (Kasa) Cough, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Sula) Pain, (Pandu) Anaemia, (Inflammation) Sotha, (Grahaniroga) Malabsorption syndrome/Diseases of Small Intestine, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Svarabheda) Hoarseness of voice, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Arsa) Piles, (Kandu) Itching, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Jirnajvara) Fever (Chronic), (Visamajvara) Fever (Intermittent), (Udavarta) Upward movement of gases, (Siroroga) Diseases of head, (Tamaka Svasa) Asthma (Bronchial Asthma), (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Beleric Myrobalan Bahera Terntinalia Belerica Roxb Bibhitaka |
V*P-K- Special Action:Its seed-pulp is intoxicating. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Bhedana) Purgative, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Kasahara) Expectorant, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Kesya) HairTonic |
(Kasa) Cough, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Svarabheda) Hoarseness of voice, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Withania somnifera Dunal Asgandh Withania somnifera Dunal Ashwagandha, Hayagandha |
V-P*K- |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator |
(Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Inflammation) Sotha, (Daurbalya) Weakness, (Klaibya) Male impotence |
|
Cardamom - Black Elaichi - Wadi/Moti Amomum subulatum Sthulaila |
V-P+K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Angamarddaprasamana) Bodyache Relievers, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Kandu) Itching, (Trsna) Thirst, (Hrllasa) Angina pectoris (Heart issue), (Basti roga) Diseases due to urinary system, (Kanthamukharoga) Diseases of Mouth and Throat |
|
Asfoetida Hing Ferula foetida Hingu/Ramaha |
V-P+K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent | (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste |
(Sula) Pain, (Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Sularoga) Gastric Ulcer/Duodenal ulcer/Colic, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Licorice Root Mulathi/Jethimadh Glycyrrhiza glabra Yasti/Madhuka |
V-P-K* |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic |
(Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Svarabheda) Hoarseness of voice, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Trsna) Thirst |
|
Indian Senna Sarnapatta/Sanaya Cassia angustifolia Svarnapatri |
V*P-K* |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Recana) Laxative |
(Vibandha) Constipation, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites) |
|
Nardus root Billilotan/Balchhar Nardostachys jatamansi Jatamamsi/Mamsi |
V-P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Nidrakara) Hypnotic, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Kushthaghna) Cure Skin Diseases., (Tridosha) Tridosha, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Daha) Burning Sensation, (Visarpa) Erysepales, (Manasroga) Mental disorders, (Anidra) Insomnia |
|
Asparagus Satavar Asparagus racemosus Satavari/Atirasa |
V-P-K* |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Medhya) Brain Tonic, (Stanya Kara) Milk Increase, (KaphaVatAghna) Kapha & Vata Balance, (AgniPustiKara) Nourishment to Agni |
(Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Svarabheda) Hoarseness of voice, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Arsa) Piles, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Visarpa) Erysepales, (Parinamsula) Duodenal ulcer, (Stanya dosa) Aversion to breast milk, (Stanya ksaya) Decrease in breast milk, (Vaata Jvara) Fever (due to Vaata |
|
Gum-gugul/Indian Bdellium Guggal Commiphora mukul Guggulu |
V-P-K- Special Action:Fresh Guggulu is nourishing and aphrodisiac. Fresh guggulu is golden in color and has a fragrance. Old Guggulu is exceedingly lekhana (depleting). Old guggulu emits a foul smell and is devoid of its natural color. Warning: The patient who is using guggulu should refrain from sour things, sharp things, things that are indigestible, sexual act, exhaustion, exposure to sun, alcoholic drinks and anger if he desires to have the prescribed therapeutic effects of this drug. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Sara) Mobile, (Vishada) Clear/Non-Slimy |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Medohara) Fat Remove |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Sopha) Oedema, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Arsa) Piles, (Apaci) Chronic Lymphadenopathy/Scrofula, (Medoroga) Obesity, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Amavata) Rheumatism, (Gandamala) Cervical Lymphadenitis, (Vatavyadi) Diseases due to Vata dosha/ Neurological disorders, (Granthi) Cyst, (Asthibhagna) Bone fracture |
|
The Sweet Flag Varch/Ghodavaca Acarus calamus Vacha/Vaca |
V-P*K- Special Action:1-2 gm. of the drug in powder form is used to induce vomiting. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Kanthya) Useful for Throat, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Sula) Pain, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Apasmara) Epilepsy, (Unmada) Mania, (Karnasrava) Ottotthoea, (Smrti daurbalya) Weak memory, (Bhuta) Attacks by evil spirits |
|
Hellebore Karru, Kutki Picrorhiza kurroa Katuka |
V*P-K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light |
(Bhedana) Purgative, (Jvarahara) Febrifuge/Anti Pyretic/Refrigerant, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Recana) Laxative |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kamala) Jaundice, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Jvara) Fever, (Daha) Burning Sensation, (Visamajvara) Fever (Intermittent) |
|
Thyme Leaved Gratiola Brahmibuti Bacopa monnieri Brahmi/Sarasvati |
V-P*K- |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Sara) Mobile |
(Prajasthapana) Anebolic, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Visaghna) Anti poison, (Recana) Laxative, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Kasa) Cough, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Jvara) Fever, (Pandu) Anaemia, (Sopha) Oedema, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Visa) Poison, (Smrti vardhaka) Memory enhancer |
|
Camphor (Natural) Karpur Cinnamomum camphora Kapura |
V-P-K- Description: There are 2 kinds of Karpura: Pakva and Apakva. Pakva is from Cinnamomum camphora and the Apakva from Dryobalanops aromatica. Both are used in Ayurveda. Apakva was used more in medicine than Pakva. Warning: Kapura is toxic in large doses; sometimes even 2 grams. |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Lekhaniya) Reducing Corpulency, (Madaka) Intoxicant, (Vedanasthapana) Anodyne/Analgesic, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Kandu) Itching, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Visa) Poison, (Daha) Burning Sensation, (Klaibya) Male impotence, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Amavata) Rheumatism, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Dantasula) Toothache, (Trsna) Thirst, (Parsva sula) Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia, (Danatapuya) Pyorrhoea, (Jirnapratisyaya) Chronic sinusitis, (Kantharoga) Diseases of throat, (Sanshisula) Joint pain, (Vicarcika) Eczema, (Visucika) Gastro-enteritis with peircing pain, (Vrkkaroga) Renal disorder, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Cowhage Tatgajuli, Kewanch Mucuna prurita Kapikacchu, Atmagupta |
V-P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Brimhaneeya) Nutritives, (Balya) Strength Promoter |
(Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Daurbalya) Weakness, (Vatavyadi) Diseases due to Vata dosha/ Neurological disorders, (Dustavrana) Non-healing ulcer |
|
Indian Maddar Manjistha Rubia cordifolia Manjistha |
V-P-K* |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Guru) Heavy |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Visha) Toxic, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Kushthaghna) Cure Skin Diseases., (Sonitasthapana) Alterative/Blood-Purifier, (Stambhana) Constipative |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Sopha) Oedema, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Yonidosa) Disorder of female genital tract, (Arsa) Piles, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Visarpa) Erysepales, (Vyanga) Pigmentation disorder, (Sarpadansha) Snake bites, (Slesmaja sotha) Inflammation due to kapha dosa |
|
Cork Swallow-wort Jivanti Leptadenia reticulata Jivanti |
V-P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Stanya Janana) Galactagogue, (Brimhaneeya) Nutritives, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Visaghna) Anti poison |
(Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Jvara) Fever, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Daha) Burning Sensation, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Trsna) Thirst, (Mukharoga) Diseases of mouth, (Sosa) Cachexia |
|
Symplocos bark Lodhar Symplocos racemosa Lodhara |
V*P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Kasaya) Astringent | (Laghu) Light |
(Bhedana) Purgative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Recana) Laxative |
(Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Jvara) Fever, (Sopha) Oedema, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Atisara) Diarrhoea |
|
Castor oil plant Erand Ricinus communis Eranda |
V*P+K* |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Sukshma) Subtle, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Bhedana) Purgative, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Anulomana) Downward Vayu movement, (Medohara) Fat Remove, (Sroto Shodhana) Channel cleanser, (Vayasthapana) Anti aging |
(Yakrdroga) Disease of liver, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Amavata) Rheumatism, (Katigraha) Stiffness of lumbar region, (Sitanga) Coldness in the body |
|
Holy Basil Tulsi Ocimum sanctum Tulasi |
V-P+K- Special Action:* Wild Tulsi is best among Ram, Krishna, and Wild. * Whole plant is Pittavardhini (Pitta increase). * Leaves are Pittahara (Decrease) * Seeds are Kaphahara, Vatahara, Pittahara (Decrease). Warning: It causes burning sensation (daha). |
Hot Potency | --- |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Arsa) Piles, (Visa) Poison, (Mutrakrcchra) Dysuria, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Parsva sula) Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia, (Pratisyaya) Sinusitis, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Parsva Ruk) Pain in side of chest |
|
Caltrops Bhakhra Tribulus terrestris Gokshura |
V-P*K* |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Mutrakrcchra) Dysuria, (Cleans Basti) Cleans urinary tract |
|
|
The lemon of India Nimbu Citrus limon Nimbu, |
V-P+K- |
Hot Potency | (Amla) Sour | (Amla) Sour | (Laghu) Light |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Pacana) Carminative |
(Sula) Pain, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Trsna) Thirst, (Visucika) Gastro-enteritis with peircing pain, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Celery Valjawain, Ajmod Apium graveolens Ajmoda, Kharahva |
V-P*K- Special Action:Ther Usage: 1164 pdf of main. Mastiskadaurbalya (Neurosthenia), Prsthasula (Lumbago), Fever due to Kapha dosa. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant |
(Sula) Pain, (Sopha) Oedema, (Yakrdroga) Disease of liver, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Mutraghat) Urinary obstruction, (Siroroga) Diseases of head, (Asmari) Calculus, (Grdhrasi) Sciatica, (Parsva sula) Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia, (Yakrtplihavrddhi) Enlargement of liver and spleen, (Basti roga) Diseases due to urinary system, (Pliha Vrddhi) Enlargement of spleen, (Yakrt Vrddhi) Enlargement of liver, (Jalodara) Ascites |
|
Sesame, Gingelly-oil Seeds Til Sesamum indicum Tila |
V-P+K+ Special Action:Among the different types of tila, the black variety is the best, the white variety is middling and other varieties are inferior in quality. Description: - Menorrhagia (Pradara) - Yoni sula - Dantaharsa (Morbid sensitiveness of the teeth) |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Sukshma) Subtle |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Mutra Sangrahaniya) Antidiuretic, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Snehopaga) Udvartana/Unction Helpers, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Kesya) HairTonic, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Visaghna) Anti poison, (Pittala) Bilious, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Sirah sula) Headache, (Pravahika) Dysentery, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Asmari) Calculus, (Granthi) Cyst, (Trsna) Thirst, (Parsva sula) Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia, (Mukharoga) Diseases of mouth, (Unmada) Mania, (Pratisyaya) Sinusitis, (Visarpa) Erysepales, (Nadi vrana) Sinus, (Galaganda) Goiter, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Tamarind Imli Tamarindus indica Amlika, Cinca |
V-P*K* Special Action:Unripe Imli is heavy. It decreases Vaata but vitiates/disturbs pitta, kapha and blood. Ripe Imli is laxative and appetizer. It is a digestive stimulant and it cleanses the urinary bladder. Dried Imli is hrdya (cardiac tonic). It cures srama (exhaustion), bhrtinti (giddiness), trstla (morbid thirst) and klama (mental fatigue). It is light. |
Hot Potency | (Amla) Sour |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Amla) Sour, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Guru) Heavy, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Sara) Mobile |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic |
(Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Nadi vrana) Sinus, (Karna sula) Otalgia, (Cleans Basti) Cleans urinary tract |
|
Garlic Lasan Allium sativum Lasuna, Rasona |
V-P+K- Warning: * It suppresses power of digestion. * Anyone using garlic should avoid exercise, exposure to sun, anger, water in excess, milk and jiggery. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Sara) Mobile, (Tikshna) Sharp, (Pichchila) Cloudy/Slimy |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Pacana) Carminative, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Jantunasana) Anti biotic, (Recana) Laxative, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Sula) Pain, (Hrdroga) Heart diseases, (Jvara) Fever, (Sopha) Oedema, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Arsa) Piles, (Medoroga) Obesity, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Visamajvara) Fever (Intermittent), (Vatavyadi) Diseases due to Vata dosha/ Neurological disorders, (Apasmara) Epilepsy, (Unmada) Mania, (Kantharoga) Diseases of throat, (Visucika) Gastro-enteritis with peircing pain, (Karna sula) Otalgia, (Trika sula) Pain in sacral region, (Pliha Vrddhi) Enlargement of spleen, (Asthibhagna) Bone fracture, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Onion Piyaj Allium cepa Palandu, Sukanda |
V-P*K- Special Action:* It has properties similar to Garlic but it (onion) does not increase pitta in excess. * It alleviates vaata (which is not combined with other aggravated doshas). * It is NOT very hot potency. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Katu) Pungent |
(Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Jvara) Fever, (Sopha) Oedema, (Vidradhi) Abscess |
|
Spearmint Pahari pudina Mentha viridis Pudinah, Rocani |
V-P-K- |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent |
(Laghu) Light, (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Mutra Virechaniya) Diuretic, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Rocana) Stimulate appetite |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kasa) Cough, (Sula) Pain, (Jvara) Fever, (Agnimandya) Digestive impairment, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Grahaniroga) Malabsorption syndrome/Diseases of Small Intestine, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Adhmana) Flatulance with gurgling sound, (Mutrakrcchra) Dysuria, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Jirnajvara) Fever (Chronic), (Visucika) Gastro-enteritis with peircing pain, (Kasthaartava) Dysmenorrhoea, (Prasutijvara) Fever (Puerperal), (Mada) Intoxication, (Hanustambha) Lockjaw, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Psyllium seed Isabgol Plantago Ovota Ashwagolam |
V-P-K* Special Action:* Psyllium can be taken in buttermilk (lassi) in case of diarrhea. * Psyllium can be taken in warm milk in case of constipation. Description: The seeds swell with mucilage in the colon, which absorbs bacteria and toxins, soothes inflamed mucous membranes and moistens dryness. Psyllium seeds, however, may cause griping. They may be replaced with psyllium husks, which are a superior medicinal, or balanced by an aromatic like ginger or fennel. Warning: The heavy property of psyllium tends to reduce Agni, and so for long term usage balancing it out with a digestive stimulant would be recommended anyway. |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Pichchila) Cloudy/Slimy |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dahaprasamana) Curatives of Burning syndrome, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Recana) Laxative |
(Jvara) Fever, (Pravahika) Dysentery, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Amatisara) Diarrhoea due to indigestion |
|
Indian Aloe Mussabar Aloe barbadensis Kumari, Kanyasara |
V*P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Katu) Pungent | (Sheeta) Cold | (Bhedana) Purgative |
(Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Jvara) Fever, (Yakrdroga) Disease of liver, (Vibandha) Constipation, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Tvagroga) Skin disease, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Granthi) Cyst, (Visphota) Blister, (Kasthaartava) Dysmenorrhoea, (Yakrtplihavrddhi) Enlargement of liver and spleen, (Pliha Vrddhi) Enlargement of spleen, (Yakrt Vrddhi) Enlargement of liver |
|
Rose Gulab Rosa centifolia Satapatrika, Devataruni |
V-P-K- Special Action:* It is pleasing to Mind. * It removes foul smell of body. * It also removes inauspiciousness. * The water (after distillation) of rose alleviates/decreases exhaustion. |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Pacana) Carminative, (Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Sukrala/Sukra Utpattikara) Semen Generator |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara) Vitiation of blood and its components, (Visa) Poison, (Daha) Burning Sensation |
|
Clarified butter Ghee Clarified butter Ghrta |
V-P-K+ Special Action:* Ghee prepared from Cow's milk is the best. * Ghee prepared from Buffalo's milk cures Raktapitta (Bleeding disorder). * Ghee prepared directly from milk is refreshing. It cures eye diseases and daha (burning sensation), Raktapitta (Bleeding disorder), Fainting. * Preserved ghee (10 or more years) alleviates/decreases all 3 doshas (Vaata, Pitta, and Kapha). It is purgative, cures ulcers, cataract,chronic cold, asthma, fainting, obstinate skin diseases Including leprosy, poisoning, unmada (insanity), burning syndrome, epilepsy, colic pain in female genital tract, ear, eye and head, oedema, and fever. It is purgative. Preserved Ghee of 100 years cures afflictions by evil spirits. Warning: Ghee is not very useful in tuberculosis, young age, old age, in diseases caused by kapha, in the Ama stage of diseases, cholera, constipation, alcoholism, fever and in the suppression of the power of digestion. |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Mrudu) Soft |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Vishaghna) AntiToxic, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Abhishyandi) Obstructs channels of circulation., (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Rucya) Stimulate taste, (AgniDipana) Digestive stimulant Agni, (Ojas/Tejas) VitalFluid/Semen |
(Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Sula) Pain, (Amlapitta/Ajirna) Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Visa) Poison, (Udavarta) Upward movement of gases, (Unmada) Mania, (Visarpa) Erysepales |
|
Oil - Sesamum/Gingelly Taila - Tila Sesamum indicum oil Tila taila |
V-P*K* Special Action:* Useful for people with Vaata prakriti. * It is used in the form of sprinkling, massage, bath, enema, drinking through mouth, inhalation, ear drop, and pouring over eyes. It is used in food and drinks for the alleviation of vayu. * It is useful in excised, incised, dislocated, macerated, lacerated, ulcerated, pressed, fractured, broken, perforated, burnt, separated and scraped wounds and injury and eating away by wild animals. |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Sara) Mobile, (Sukshma) Subtle |
(Sandhaneeya) Wound Healer, (Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Vyavayi) Vyavayi, (Stanya Janana) Galactagogue, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Vikasi) Vikasi, (Chakshusya) EyeTonic, (Kesya) HairTonic, (Recana) Laxative, (Medhya) Brain Tonic |
(Sula) Pain, (Sirah sula) Headache, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Yonidosa) Disorder of female genital tract, (Kandu) Itching, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Daurbalya) Weakness, (Dantasula) Toothache, (Agnidagdha) Burn injury, (Ardita) Facial palsy, (Karna sula) Otalgia, (Vranashodhaka and Ropaka) Wound healing property, (Asthibhagna) Bone fracture, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation, (Paksaghata) Paralysis, (Puyameha) Gonorrhoea, (Ear disease) Ear diseases |
|
Oil - Coconut Taila - Nariyal Cocos nucifera Narikela taila |
V-P-K+ Special Action:* Useful for people with Pitta prakriti. |
Cold Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Kesya) HairTonic | (Pama) Eczema |
|
Oil - Mustard Taila - Sarson Brassica campestris Sarsapa taila |
V-P*K- Special Action:* It vitiates pitta and blood. * Useful for people with Kapha prakriti. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Katu) Pungent, (Tikka) Bitter |
(Laghu) Light, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous, (Tikshna) Sharp |
(Angamarddaprasamana) Bodyache Relievers, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Krmighna) Anthelmintic/Parasiticide, (Lekhaniya) Reducing Corpulency, (Mutra Virechaniya) Diuretic, (Vedanasthapana) Anodyne/Analgesic |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga) Eye disease, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Arsa) Piles, (Kandu) Itching, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Siroroga) Diseases of head, (Kotha) Urticaria, (Danatapuya) Pyorrhoea, (Sveta Pradara) Leucorrhoea, (Slipada) Filariasis, (Pliha Vrddhi) Enlargement of spleen, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
|
Oil - Castor Taila - Erand Ricinus communis Eranda taila |
V-P*K- |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet | (Madhura) Sweet | (Sukshma) Subtle |
(Vrishya/Vajikarana) Aphrodisiac, (Bhedana) Purgative, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Sukra Sodhana) Spermato Purificators, (Ama pacana) Detoxicant |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Sula) Pain, (Sopha) Oedema, (Gulma) Phantom Tumor, (Hikka) Hiccup, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Udararoga) Diseases of abdomen (Ascites), (Anaha) Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools, (Pliha) Splenic disease, (Vatasonita) Gout, (Granthi) Cyst, (Balya) Increase stamina and endurance, (Vidradhi) Abscess, (Asthila) Hard tumor in abdomen, (Katigraha) Stiffness of lumbar region, (Sitanga) Coldness in the body |
|
Curd Dahi Curd Dadhi |
V*P*K+ Special Action: Based upon the Stage: * Immature (Manda) [V+P+K+]; causes burning sensation. It helps in elimination of stool and urine. * Sweet variety [V-P-K+]; when taken in early morning. It is aphrodisiac and reduces fat. It produces more of blood and pitta. It slightly obstructs the channels of circulation. * Both sweet and sour variety has all general properties. * Sour variety [V*P+K+]; increases blood. It stimulates digestion. * Excessively sour produces bleeding disorders. Based upon Source: * Curd prepared from Boiled milk [V-P-K*]; promotes all the dhatus, power of digestion, strength, appetite.It is exceedingly useful. * Curd prepared from Cow's milk [V-P*K*]; is excellent. It is appetizer, digestive stimulant, nourishing. * Curd prepared from Buffalo's milk [V-P-K+]; It vitiates blood (impair the quality) of blood. It obstructs the channels of circulation, but aphrodisiac. Based upon Combination: * Curd added with sugar [V*P-K*]; is very useful. It cures morbid thirst, burning syndrome, vitiation of blood. * Curd added with jaggery [V-P*K*]; is heavy, aphrodisiac, nourishing, refreshing. Based upon Season: * Beneficial in first part of winter, later part of winter, and in rainy season. * Not useful in autumn, summer and spring season. Based upon Part of curd: * Sara (Upper layer of curd which is dense) is [V-P+K+]; heavy, laxative, aphrodisiac, cleans urinary bladder. But it suppresses the power of digestion. * Masru (watery portion) is [V-P*K-]; light, promotes strength, appetite, refreshing, instant laxative and giver of happiness. It cleanses channels of circulation. But it is NOT aphrodisiac. Description: There are 5 states of curd: 1. First state of curd is: Manda (Immature) in which there is no manifested taste. 2. Second state of curd is: Svadu (Sweet) in which curd is sweet in taste. 3. Third state of curd is: Svadvamla: both sweet and sour in taste. 4. Fourth state of curd is: Amla (Sour) in which curd is sour taste. 5. Fifth state of curd is: Atyamla (excessively sour). Warning: * Dadhi should not be taken at night, nor should it be taken without ghee, sugar, honey. |
Hot Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Madhura) Sweet, (Amla) Sour |
(Guru) Heavy, (Snigdha) Oily/Unctuous |
(Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Varnya) Complexion Promoter, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Stambhana) Constipative, (Sukrala/Sukra Utpattikara) Semen Generator |
(Pinasa) Chronic Rhinitis, (Mutrakrcchra) Dysuria, (Atisara) Diarrhoea, (Aruci) Tastelessness, (Visamajvara) Fever (Intermittent), (Balya) Increase stamina and endurance, (Karsya) Emaciation |
|
Vasaka Vansa, Bhekar Adhatoda vasica Vasaka, Atarusaka |
V+P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent |
(Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Hridya) Cardiac Tonic, (Recana) Laxative |
(Svasa) Asthma, (Kamala) Jaundice, (Kasa) Cough, (Ksaya) Phthisis/Wasting, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Raktapitta) Bleeding disorder, (Jvara) Fever, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Meha) Excessive flow of urine |
|
Guduchi Gilo Tinospora cordifolia Guduchi, Amrta |
V-P-K- Special Action:* If taken along with Cow Ghee, it alleviates Vayu. * If taken along with jaggery it alleviates Pitta. * If taken along with honey it alleviates Kapha. * If taken along with castor oil it cures acute type of gout. * If taken along with sunthi, it cures amavata (rheumatism). |
Hot Potency | (Madhura) Sweet |
(Tikka) Bitter, (Kasaya) Astringent |
(Laghu) Light |
(Dahaprasamana) Curatives of Burning syndrome, (Dipana) Digestive Stimulant, (Rasayana) Rejuvenator, (Balya) Strength Promoter, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative, (Tridosha) Tridosha, (Ama pacana) Detoxicant |
(Kamala) Jaundice, (Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Jvara) Fever, (Pandu) Anaemia, (Chardi/Vami) Vomit, (Vatarakta/Adhyavata) Gout, (Trsna) Thirst, (Ama) Metabolic waste/toxinx, (Amavisha) Reactive toxins generated inside the body from Ama, (Garavisha) Environment toxins |
|
Margosa Tree Nim/Neem Azadirachta Indica Arista/Picumarda |
V*P-K- |
Cold Potency | (Katu) Pungent | (Tikka) Bitter | (Ruksha) Dry/Ununctuous |
(Kandughna) Anti Psoric, (Sangrahi/Grahi) Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative |
(Kustha) Diseases of Skin, (Prameha) Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine), (Jvara) Fever, (Vranas) Ulcer, (Krmiroga) Parasitic Infestation |
Homeopathic Medicines
Go to top
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Homeopathic | Details |
|---|---|
|
Calcarea Fluorica (12 Tissue Salts) |
Calcarea Fluorica (CALC-F)
Calcium Fluoride, Fluor Spar, Fluoride of Lime, Calcii fluorica; Calcium fluoride, Fluor spar, Fluorite, CaF2 Calcaria Fluorica (Fluoride of Lime). The quality of this chemical is to draw distant places together. It draws and establishes communication in terms of the subjective mind. The human personalities unite within it. It is the feminine or receptive aspect of the Life Power. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Connective tissue, Bones, Vein walls, Tendons, Sinews, Glands, Eastic fibers, Periosteum (bone covering), Tooth enamel, Throat, Larynx, Thyroid, Binding of tissues, Elasticity of tissues Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Around the eye sockets, translucent tips of teeth, cracked lips. Skin Appearance: Reflective, especially in acute conditions. Color: Blue lips, brownish-black shading, white flakes, transparent tips of teeth. Texture: Raised wrinkles, fan-shaped wrinkles, furrows, white scales, cracked lips, translucent tips of teeth. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Cornea problems, Brittle/Splitting/Soft-nails, Low body temperature, Chapping, Cracked skin, Cavities, Varicose veins, Osteoporosis, Deficient teeth enamel, Sweaty feet Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Tongue is cracked, inflammation, and swelling, hardness, can be painful or not Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Indecisiveness, weakness, low self-esteem, stress regarding financial matters Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Grass-green discharges or thick yellow-greenish discharges, that smell offensive Foods Rich in Salt: Whole grain foods, dairy foods, raw vegetables, soybeans, sesame seeds, spinach, broccoli, mushrooms Potential Diseases: Bone problems, Cataracts, Tooth enamel problems, Hardening glands, Gas, Tumors, Weak connective tissue, Scoliosis, Scar tissue, Splinters, Smelly feet |
|
Calcarea Phosphorica (12 Tissue Salts) |
Calcarea Phosphorica (CALC-P)
Phosphate of Calcium, Calcium Phosphate, Phosphate of Lime, Ivory, Tri-Calcium Phosphate, Calcii phosphas precipitatus, calcium phosphoricum, Precipitated phosphate of calcium, Tribasic calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2 Calcarea Phosphorica (Phosphate of Lime). Without the proper amount of calcarea phos, no bone could be constructed. It is a worker in albumen and carries it to the bone and uses it as cement. Bright's disease is simply an overflow of albumen by the way of the kidneys due to a deficiency of Phosphate of Lime. The deficiency of this chemical in the gastric juices results in undigested foods from which acids form and this deprives the joints of the arms and legs of the cartilage necessary to oil; yet the term used to denote this deficiency is known to us as rheumatism. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Nutrition, Bones, Muscles, Tendons, Teeth, Spine, Blood, Periosteum (bone covering), Cartilage, Glands, Protein binder, Cartilage, Chest Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Ears, nose, skin under eyebrows, cheekbone, small lips, translucent tips of teeth. Skin Appearance: Ears, nose, skin under eyebrows, cheekbone, small lips, translucent tips of teeth. Color: White waxy appearance, transparent tips of teeth. Texture: Waxy appearance, white flakes in teeth or fingernails, translucent tips of teeth, stretched skin on cheekbones, small lips Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Muscles are sensitive to cold, White marks on fingernails and teeth, Tips of teeth are translucent, Osteoporosis, Nosebleeds, Bone growth, Late teeth, Heart palpitations, Nose polyps, Headaches (in children), Growing pains Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Bitter taste in mouth with blister or pimples on the tip of the tongue, the tongue is swollen, stiff and numb Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Desire to travel, loss of motivation, mental weakness, difficulty handling bad news Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Thick clear discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Almonds, cucumbers, oats, soybeans, white beans, dandelions, cherries, spinach, dairy foods, dates Potential Diseases: Bone problems, Weak ankles, Teething problems, Osteoporosis, Spinabifida, Stiff neck, Rickets |
|
Calcarea Sulphuricum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Calcarea Sulphuricum (CALC-SUL)
Calcium Sulphate, Gypsum, Plaster of Paris, Calcii sulphas; Sulphate of calcium, CaSO4 Calcarea Sulphurica (Sulphate of Lime--Plaster of Paris) These elements - lime and sulphur, are in no way beneficial to the human body in their crude forms. It is only when nature steps up their vibration through plant life, that they can be utilized in body chemistry. The aggressive urges here are entirely capable of resurrecting every dead cell in the body and revitalizing all conditions. It is the crucible for relaxing, fluxing and transmuting the great vibratory forces that we need. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Liver, Gallbladder, Heart muscle, Connective tissue, Glands, Mucus membranes, Bones, Skin Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Jaw line Skin Appearance: Glassy or polished Color: Alabaster-white appearance, paleness Texture: Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Chronic pus, Open infections, Fibroids, Yellow mucus discharges, Boils, Contact dermatitis, Burning, Itching, Inflammation Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Inflammation, infected sores. Flabby with yellow coating at back Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Fatigue, laziness, inactivity, worries about imaginary problems Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Yellow thick and lumpy discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Oats, almonds, cucumbers, lentils, peanuts, soybeans, cauliflower Potential Diseases: Abcesses, Boils, Inflammation, Acne, Eczema, Yellow discharges, Tonsillitis, Tumors, Ulcers |
|
Ferrum Phosphoricum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Ferrum Phosphoricum (FERR-P)
Phosphate of Iron, Iron (III) phosphate dihydrate Ferrum phosphoricum (Phosphate of Iron). This chemical has an affinity for oxygen which is carried into the circulation and diffused throughout the organism by the chemical force of this phosphate of iron. Just as the feet are the foundation of the body, so iron is the foundation of the blood. Through this foundation of the blood is ignited cells of both red and white. Iron is known as a magnetic mineral and magnetism is made possible by the body's knowledge. In the blood stream we find both red and white corpuscles and due to the chemical value of iron, they carry on the process of wheels within wheels or the interlocking cycles and rotations of metabolic activity. Lack of iron in the blood results in an over lymphatic condition. When the red corpuscles are short the result is a severe acid condition and generally results in anemia. This cell salt builds both the magnetism and the body's ability to utilize both nature and art. When iron is tempered to a high potency, it provides that stamina needed. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Blood, Arterial system, Hemoglobin, Nerves, Circulation, Colon, Lungs, Ears (eustachian tubes), Heart, Mucus membranes, Bones Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Chronic: whole-face paleness, bluish-black circles under eyes; acute: red cheek, forehead, ears. Skin Appearance: Color: Bluish-black shade, red ears. Texture: Shading in corners of the eyes, furrows, hung-over or sleepless appearance, red ears, inflamed skin. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: First stages of fever (99–101 deg), Fatigue, Weak immune system, Red face, Pulsing and throbbing headaches, Inflammations, Anemia, Hemorrhages, Sore throat, Nosebleeds, Colds, Flus Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Red to dark red with inflammation and swelling with no coating Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: At first, stimulation and overheating, followed by dullness and listlessness Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Hemorrhages of blood from inflammatory conditions anywhere in the body Foods Rich in Salt: Spinach, hazelnuts, whole rice, soy, sesame seeds, tomatoes, oats, red and blue berries Potential Diseases: Anemia, Nosebleeds, Sore throats, Hemorrhages, Low-to-moderate fevers, Blood problems |
|
Kali Muriaticum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Kali Muriaticum (KALI-MUR)
Potassium Chloride, Kali Chloratum, Chloride of Potash Kali Mur (Chloride of Potassium). It is believed that this chemical joins the positive and negative elements in the body. The perfect balance between the brain and nerves. The top of the nerves connected with the Pineal Gland and is the male electric current of the spinal system. The top of the nerve connects with the Pituitary gland and is the female electric current of the spinal system. These are the male and female electric current joined together at the cerebellum. This chemical signifies the personality and individuality on the mental planes of the individual. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Fibrin (fibrous protein), Glands, Bronchials, Throat, Eustachian tubes, Ears, Muscles, Joints, Mucus membranes, Shoulders Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Cheeks, eyelids Skin Appearance: Color: Milky red, or blue, or purple shading; acne rosacea; red spider veins. Texture: Milky appearance, acne rosacea, chicken skin. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Second stages of fever (101–103 deg), Coughing, Eustachian tube blockage, White mucus discharges, Allergies, Varicose veins, Glandular problems, Chicken skin on the arms Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Tongue can be coated grayish-white, dry or slimy Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Family issues, irritability, apathy, homesickness, tendency to hypochondria Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Thick white discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Cucumber, peanuts, hazelnuts, lentils, spinach, pork, soybeans, sesame seeds, potatoes Potential Diseases: Eustachian tube blockage, Sinus problems, Acne rosacea, Varicose veins, White discharges, Tonillitis, Fat digestion problems |
|
Kali Phosphorica (12 Tissue Salts) |
Kali Phosphorica (KALI-P)
Potassium Phosphate, Phosphate of Potash, Di-Potassium Phosphate, Di-Potassium Hydrogen Orthophosphate Kali phosphoricum (Phosphate of Potassium). The optic thalamus is in the center of the head and connects the pineal gland to the pituitary body. These are thought to correspond to the reason and intuition. Potassium phosphate produces the highest rate of vibration. It is thought to be the invisible fire of Nature and is the greatest healing agent known. This yellow-green salt accelerates the cerebrospinal system and effects the use of heat in the body. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Spleen, Nerves, Brain, Muscles, Mucus membranes, Skin, Temples Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Sunken temples and cheeks, overall gray coloring, dull eyes Skin Appearance: Color: Ash-gray Texture: Ash-gray appearance, frosted look of eyes, sunken cheeks, bad breath Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Poor gum and dental health, Nervousness, Depression, Bad breath, Nerve and sleep problems, Anxiety Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Coated dark yellow to brown, dry and inflamed and swollen. Creeping paralysis Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Nervous irritability, weak memory, test anxiety, tension, moody depression, anger, self-pity, feeling of being insulted and disgraced by family Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Profuse orange discharges from rectum or vagina. Yellowish creamy discharges in general Foods Rich in Salt: White beans, soybeans, cucumbers, almonds, spinach, pork, hazelnuts, peanuts, lentils Potential Diseases: Neurasthenia, Fatigue, Anxiety, Panic attacks, Sciatica, Bedweeting, Tinnitis, Bad breath, Yellow discharges |
|
Kali Sulphuricum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Kali Sulphuricum (KALI-SUL)
Potassium Sulphate, Sulphate of Potash, K2SO4 Kali Sulphuricum (Potassium Sulphate). The abdominal cavity and its contents. Emotional and intellectual conciliation is the working order of complete assimilation. It is the psychic realm, perfectly neutral until effected by exterior conditions. This chemical helps select that material which is useful to the body and separate it from the waste which is to be rejected. Kali Sulph creates the proper activity for the oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen and carbon which depend on its predominant green color. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Pancreas, Liver, Skin, Mucus membranes, Glands, Respiratory organs, Pancreas, Pigmentation Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Brown to yellow entire face, typically around the mouth. Skin Appearance: Color: Brownish-yellow or ocher pigmentation, liver spots, age spots, vitiligo, freckles. Texture: Craves fresh air, brownish-yellow appearance, pigmentation, freckles, vitiligo, pregnancy mask. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Third stage of fever (103–105 deg), Hyper or hypo pigmentation, Freckles, Liver or old-age spots, Browness of skin coloring, Cravings for fresh air, Skin dandruff, Thick yellow discharges, Constantly changing symptoms Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Coated yellow and slimy with a dull taste in mouth Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Fearful dreams, need for self-validation, sensitivity to noises, irritability, anger Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: General yellow to green slimy discharges. Profuse and thin discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Pork, hazelnuts, peanuts, almonds, spinach, lentils, peas, nuts Potential Diseases: High fevers, Vitiligo (lack of pigmentation), Freckles, Eczema, Sinusitis, Psoriasis, Asthma |
|
Magnesia Phosphorica (12 Tissue Salts) |
Magnesia Phosphorica (MAG-P)
Phosphate of Magnesia Magnesia Phosphorica (Phosphate of Magnesia). This chemical is the fluid that is the remedy for all spasmodic and impulsive deficiencies. It is the pot that forever filters and scatters the Elixir of life. All the blood in the body passes through the heart. It becomes the Alchemical Vase. As in the Tarot card, the energy that rising up in the sympathetic system, as the strong lion, becomes tamed in the heart and therefore closes and controls the mouth of that energy. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Heart, Colon, Nerves, Muscles, Glands, Smooth muscles Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Facial redness or acute blushing. Skin Appearance: Color: Redness (chronic) Texture: Chronic redness, nerve spots, alcohol redness. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Chocolate or sugar cravings, Blushing, Cramping and shooting pains, Muscle paralysis Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Swollen clean tongue (a swollen tongue usually has teeth marks on the edge) Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Sensitivity, outgoing nature, complaints regarding physical problems, impulsivity, quick action Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: White thin discharges of the nose and dark stringy vaginal discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Brazil nuts, white beans, wheat, soybeans, corn, walnuts, peanuts, peas Potential Diseases: Cramps, Painful cramping menses, Right sided sciatica, Teethaches (hyperisum), Neuralgic pains, Gas pains etc. |
|
Natrum Muriaticum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Natrum Muriaticum (NAT-MUR)
Sodium Chloride, Common Table Salt, Halite, NaCl Natrum Muriaticum (Chloride of Sodium). Although this is table salt, it is used in the body as the basis of the blood, which is salty without the other ingredients. It is the basic chemical value of the circulatory system and it could be called the Great Sea in the body. It is "Living water" and carries true spiritual knowledge in the highest vibration when perfectly balanced. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Digestion, Connective tissue, Upper stomach, Kidneys, Bladder, Blood, Muscles, Glands, Mucus membranes, Cartilage, Brain, Heart, Spleen, Liver Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: Lower eyelashes, nose, cheek, chin or forehead. Skin Appearance: Gelatinous. This is often found on the upper eyelid or the edge of the eyelashes on the lower eyelid. When the greasy part of the skin is wiped clean, this quality will reappear after 20-30 minutes. Color: Red border at hairline Texture: Inflamed eyelids, large pores, dandruff, dry skin, puffy cheeks, spongy or bloated appearance, bell-shaped nose, sweat, greasy skin. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Dandruff, Dryness, Loss of smell or taste, High blood pressure, Cracking joints, Sinus, Must have sun glasses, Head cold and congestion; Clear/Watery discharges; Sun sensitivity; Cold sores Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Frothy coating, bubbles on the sides. Numbness and tingling. Peeled appearance on sides Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Isolation, control issues, sun sensitivity, deep grief, forgiveness issues Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Clear thin watery discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Red beets, lentils, radishes, tomatoes, sea salt, milk, celery, celery seeds, goat whey Potential Diseases: Depression, Grief, Herpes, (facial or genital), Infertility, M.S, Sun problems, Vaginal dryness, Clear runny nasal or Sinus discharges |
|
Natrum Phosphoricum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Natrum Phosphoricum (NAT-P)
Sodium Phosphate, Phosphate of Soda Natrum Phosphoricum (Phosphate of Soda) - The purpose of this chemical is to balance the difference between alkaline and acid. This alkaline tissue-builder is made from bone-ash by neutralizing phosphoric acid with carbonate of sodium. Natrum phos holds the balance between the acids and the normal fluids of the human body. A certain amount of acid is necessary and is always present in the stomach and liver fluids, but an excess of acid is due to a deficiency in alkaline chemicals. An absence of Sodium Phosphate allows the acids to run riot in the body. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Stomach, Tissues, Lymphatics, Genitals, Intestines, Mucus membranes, Lower stomach, Bile ducts, Nerves Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: general yellow to red coloring: nose, mouth, forehead, chin, and cheeks. Skin Appearance: Greasy. It has a greasy feel Color: Red chin Texture: Combination skin, cholesterol deposits (raised yellow pimple-like growths around the eyes), blackheads, pimples, acne, upper lip wrinkles, fatty deposits, red chin, acid spots, dry skin, dry or greasy hair, greasy sweat. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Acne, Hearburn, Digestion, Hypoglycemia, Blackheads, Swollen glands, Sugar cravings, Sour smell, Greasy or brittle hair, Split ends, Over acidic conditions, Candida Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Yellow creamy coating on back of tongue. Blisters on the tip with stinging; hairlike sensation on tongue Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Depression from overly sensitive nerves, sleeplessness, low self-esteem Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Sour, creamy or honey colored thin discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Lentils, pork, asparagus, spinach, rose hips, oats, olives, carrots Potential Diseases: Parasites, Creamy yellow discharges, Acidity, Jaundice, Candida, Acne, Blackheads |
|
Natrum Sulphuricum (12 Tissue Salts) |
Natrum Sulphuricum (NAT-SUL)
Sodium Sulphate, Sulphate of Soda, Glauber Salts Natrum Sulphuricum (Sulphate of sodium). This lemon-colored salt aids in transmitting impulses from the cerebellum, the idea area of the brain to the action area of the body, the vocal chords. Thus, ideas become spoken and moved into action. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
Cell SaltOrgans and Tissues Affected: Liver, Gallbladder, Pancreas, Colon, Head Facial Signs of Deficiency: Location: General green coloring to a chronic red; indications on the nose; bags under the eyes Skin Appearance: Color: Greenish-yellow, bluish-red, yellowish Texture: Greenish-yellowish coloring, swollen lower eyelid sacks, yellowish sclera, bad-smelling gas. Physical Symptoms of Deficiency: Foul-smelling gas, Swollen feet or hands, Head injuries, Depression, Suicidal feelings, Itching skin, Skin has a greenish tinge, Lower eyelid sacks. Worse in wet, cold or damp weather Tongue Symptoms of Deficiency: Greenish-brown swelling or gray coating on the back of tongue or slimy thick white mucus coating Emotional Symptoms of Deficiency: Depression from wet weather or head injuries Discharges Indicative of Deficiency: Watery yellowish to greenish discharges Foods Rich in Salt: Lentils, pork, spinach, oats Potential Diseases: Head injuries, Bad gas, Epilepsy after head injury, Spinal meningtis, Diabetes, Photophobia, Asthma especially in children, Bitter taste, Yellowish discharges |
|
Silicea (12 Tissue Salts) |
Silicea (SIL)
Silica, Silex, Acidium Silicicum, Flint, Silicon Dioxide, SiO2 Silicea (Silica, pure flint). The sciatic nerve carries the steel-like temper of long-range endurance. It is purity in this form; in others, it is quartz or crystal. (It is made by fusing silica with carbonate of soda; dissolve the residue, filter, and precipitate by hydrochloric acid.) The bio-chemic process which occurs when run through plant life makes it accessible to the blood stream. Silica is called the surgeon of the body. It supplies materials for nails, hair and, what we know as periosteum membrane covering and protecting bone. Also the nerve sheath called neurilemma, and a trace is found in the bone tissue. In the last analysis it supplies the polish, or gloss, for the nails and hair. In its powdered form, under the microscope, it takes the shape of arrowheads. This point is pertinent to "the archer" Sagittarius. Decaying organic matter must be discharged from the body to clear the hips, thighs, and the sciatic nerve. MANIFESTATIONS INDICATING CELL SALT USE:
|
|
Adamas (Crystal Kingdom) |
Adamas (ADAM)
Diamond Dust As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Aphrodisiac, Brain, Circulatory System, Cranial Plates, Endorphins, Nervous System, Sexual Region, Testicles, Vitality Cellular Level Chart: Nervous System, RNA, Synapsess Nutrients Chart: Protein, Vitamin B, Vitamin E Diseases Chart: Cerebral Homorrhage, Detoxification, Dyslexia, Autism, Brain, Epilepsy, Eye Problems, Jaw, Left-Right Brain, Muscle System, Nervous System, Physical Coordination, Pineal Gland, Pituitary Gland, Sexual Disorders, Shoulders, Syphilis, Testicles, TMJ problem Psychological Chart: Anxiety/Stress, Dreams, Envy-Jealously, Insecurity, Mental Clarity, Nervous Tension, Personality Balanced, Self-Esteem, Sexual Conflicts Chakra Chart: Crown, ThirdEye Chakra, Sex Subtle Body Chart: All Subtle Bodies, Etheric Body, Mental Body Miasm Chart: All Miasms, Radiation Miasm, Syphilitic Miasm Tips Chart: When using diamond there should be some caution because it is so powerful. It can radiate too much energy and deplete one’s energy. For instance, there can be too much drainage of the self if diamond is used in conjunction with the throat and heart chakra |
|
Quartz Crystal (Crystal Kingdom) |
Quartz Crystal (QUAR)
SiO4 As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Abdomen-Stomach, Cell Salts, Circulatory System, Crystalline Properties, Fatty Tissue, Intestinal Tract, Lymphs, Nervous System, Pineal Gland, Pituitary Gland, Red Corpuscles, Vitality, White Corpuscles Cellular Level Chart: General Strengthening, Pituitary Gland, White Corpuscles Nutrients Chart: Protein Diseases Chart: Cataracts, Digestive Ills, Bubonic Plague, Environmental Pollutants, Eye Problems, Intestinal Tract, Leukemia, Nutrient Deficiency, Radiation (Artificial and Natural), Ulcers, X-Ray exposure Psychological Chart: Emotional Balance, Expressive Ability, Hysteria, Inner Perception Chakra Chart: ThirdEye Chakra, Crown, Emotional, Sex Subtle Body Chart: Emotional, Etheric Miasm Chart: Petrochemical Miasm Tips Chart: |
|
Helianthus annuus (Flower Kingdom) |
Helianthus annuus (HELIA)
Sunflower As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Cellular Level Chart: Nutrients Chart: Diseases Chart: Psychological Chart: Chakra Chart: Subtle Body Chart: Miasm Chart: Tips Chart: |
|
Nelumbo Nucifera (Flower Kingdom) |
Nelumbo Nucifera (NELU-N)
Lotus As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Heart, Kundalini, Liver, Longevity, Pineal gland, Spleen Cellular Level Chart: Tissue Regeneration Nutrients Chart: All Nutrients, Germanium Diseases Chart: Aids, Caffeine Problems, Jet lag Psychological Chart: Past Life Problems, Stress Chakra Chart: All Chakras, Seventh Chakra, All Meridians, All Nadis Subtle Body Chart: All Subtle Bodies Miasm Chart: All Miasms Tips Chart: Enables the entire body to assimilate any form of healing. If it were given in combination with other flower essences or vibrational remedies, lotus always acts like a booster to other remedies in the combination. Lotus balances nearly any negative astrol |
|
Aurum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Aurum Metallicum (AUR-MET)
Gold As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Abdomen-Stomach, Biomagnetic Properties, Brain, Breath Regulated, Circulatory System, Electrical Properties, Endocrine System, Heart, Immune System, Life Force Enhanced, Longevity, Lungs, Metabolism, Muscle System, Nervous System, Pineal Gland, Pituitary Cellular Level Chart: Biomelecular Functions, Brain Neurons, Capillary Action, Cell Mitosis, Chromosomal Damage, General Strengthening, Heart, Muscle System, Nervous System, Pancreas, Skin, Spleen Nutrients Chart: All Nutrients, Gold, Magensium, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Silver, Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin D, Vitamin E Diseases Chart: Cancer-Precancer, Childhood Diseases, Chilly-Warmth, Circulation, Detoxification, Digestive Ills, Dyslexia, Anemia, Arthritis, Autism, Blood Sugar Level Off, Brain, Bronchial, Environmental Pollutants, Epilepsy, Eye Problems, Fever, Flu-Colds, Headaches, Psychological Chart: Anger, Anxiety/Stress, Autism, Depression, Eentric behavior, Ego, Emotional Balance, Excited, Family Affairs, Fear (Unnatural), Frustration, Harmony, Inferiority, Lethargy, Manic-Depressive, Mental Imbalances, Nervous Tension, Overaggresion, Oversensitive Chakra Chart: Five Chakras above head, Crown, ThirdEye Chakra, Heart Subtle Body Chart: Emotional Body, Ethereal Fluidium, Mental Body, Spiritual Body, All Nadis Miasm Chart: All Miasms, Heavy Metal Miasm, Petrochemical Miasm, Radiation Miasm Tips Chart: All the meridians and nadis are strengthened. Using gold with copper and silver aids in balancing the personality and one's sexuality. Gold and silver accentuate the feminine accord, while gold and copper balance the masculine. If all three elixirs are ta |
|
Argentum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Argentum Metallicum (ARG-MET)
Silver As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Biomagnetic Properties, Brain, Circulatory System, Electrical Properties, IQ Increases, Nervous System, Pineal Gland, Pituitary Gland, Sense of Movement, Vertebrae Cellular Level Chart: General Strengthening Nutrients Chart: Silver Diseases Chart: Cyst, Digestive Ills, Disinfectant, Dropsy-Edema, Dyslexia, Ear Hearing, Allergies, Anorexia Nervosa, Autism, Bladder, Brain, Bulimia, Burns, Environmental Pollutants, Epilepsy, Eye Problems, Female Problems, Fever, Fistulae, Headaches, Hemorrhaging, Infe Psychological Chart: Anxiety/Stress, Autism, Childhood Pressures, Compulsive, Expressive Ability, Hysteria, Imagination, Mental Balance, Mental Clarity, Mental Imbalances, Schizophrenia, Sexual Conflicts, Shock, Sleep Better, Subconscious Cleansed Chakra Chart: Five Chakras above head Subtle Body Chart: Miasm Chart: Astral Body, Etheric Body Tips Chart: |
|
Cuprum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Cuprum Metallicum (CUPR-MET)
Copper As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Glandular Functions, Heart, Metabolism, Pineal Gland, Pituitary Gland, Red Corpuscles, Sexual Region, Sinuses Cellular Level Chart: Genetic code Nutrients Chart: Copper, Molybdenum Diseases Chart: Cerebral Cortex, Chilly-Warmth, Cholera, Circulation, Constipation, Convulsions, Cramps, Diaphragm, Digestive Ills, Dizziness, Dropsy-Edema, Dysentery, Dyslexia, Ear Hearing, Anemia, Arthritis, Autism, Brain, Environmental Pollutants, Epilepsy, Eye Proble Psychological Chart: Apathy, Emotional Balance, Excited, Fear of Death, Hysteria, Memory, Mental Balance, Mental Imbalances, Schizophrenia, Self-awareness, Self-confidence, Self-Esteem, Biomagnetic Properties, Breath Regulated, Capillary Action, Electrical Properties Chakra Chart: Root Chakra, ThirdEye Chakra, Emotional, Heart, Sex, Throat Subtle Body Chart: All Subtle Bodies, Astral Body Miasm Chart: Tips Chart: |
|
Platina Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Platina Metallicum (PLAT-MET)
Platinum As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Biomagnetic Properties, Brain, Electrical Properties, Endocrine System, Heart, Nervous System, Synapses, Thymus, Vertebrae Cellular Level Chart: Nutrients Chart: All Nutrients Diseases Chart: Constipation, Ear Hearing, Endocrine System, Environmental Pollutants, Female Problems, Female Pelvic Problems, Headaches, Menstruation, Muscle System, Nervous System, Numb, Paralysis, Spasmodic Disorders Psychological Chart: Excited, Fear (Unnatural), Hysteria, Irritability, Memory, Passions Controlled, Pride (false), Protection, Receptivity, Sexual Conflicts, Shock, Superiority (sense of) Chakra Chart: Five Chakras above head, All Nadis Subtle Body Chart: Miasm Chart: Petrochemical Miasm, Tuberculosis Miasm Tips Chart: |
|
Magnesia Metallica (Mineral Kingdom) |
Magnesia Metallica (MAG-MET)
Magnesium As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Crystalline Properties, Heart Cellular Level Chart: Detoxification (cellular) Nutrients Chart: Enzymes, Protein Diseases Chart: Cancer-Precancer, Cholesterol, Circulation, Colic, Constipation, Convulsions, Cyst, Detoxification, Diarrhea, Digestive Ills, Alcholism, Body Odor, Bowel, Epilepsy, Female Problems, Gallstones, Heart, Hyperreflexia, Intestinal Tract, Jaundice, Kidneys, La Psychological Chart: Anxiety/Stress, Depression, Irritability, Mental Imbalances, Nervous Tension, Oversensitive Chakra Chart: Emotional Chakra Subtle Body Chart: Etheric Body Miasm Chart: All Miasms Tips Chart: |
|
Sandstone (Mineral Kingdom) |
Sandstone (SANDS)
As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Blood Vessels, Skin Cellular Level Chart: Skin Nutrients Chart: Silica, Silicon, Zinc, Vitamin B Diseases Chart: Arteriosclerosis, Arthritis, Burns, Environmental Pollutants, Hardening Diseases, Liver, Radiation (Artificial and Natural), Rheumatism, Scleroderma, Skin, X-Ray exposure Psychological Chart: Flexibility, Personality Balanced Chakra Chart: Subtle Body Chart: Emotional, Etheric Miasm Chart: Tips Chart: |
|
Clay (Mineral Kingdom) |
Clay (CLAY)
As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Cell Salts, Crystalline Properties, Intestinal Tract, Lymphs, Muscle System, Pineal Gland, Red Corpuscles, Scalp, Skeletal System, Skin, Teeth, Thymus, Uric Acid, Vertebrae, Vitality, White Corpuscles Cellular Level Chart: Detoxification (cellular), General Strengthening Nutrients Chart: Diseases Chart: Cancer-Precancer, Circulation, Detoxification, Digestive Ills, Ear Hearing, Alkalosis, Allergies, Amoebic Dysentery, Anemia, Antiseptic, Arthritis, Bacteria Problems, Burns, Eye Problems, Female Problems, Hemorrhaging, Hernia, Infections, Inflammations, I Psychological Chart: Anxiety/Stress, Resentment Chakra Chart: Emotional Subtle Body Chart: Emotional, Ethereal Fluidium, Etheric Body Miasm Chart: Tips Chart: |
|
Sand (Mineral Kingdom) |
Sand (SIL-M)
As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Skin, Vertebrae, Cardiovascular System, Cell Elasticity, Cell Mitosis, Circulatory System, Heart Cellular Level Chart: Lungs, Skeletal System Nutrients Chart: Diseases Chart: Cardiovascular Ills, Childhood Diseases, Decalcification, Digestive Ills, Dropsy-Edema, Arteriosclerosis, Arthritis, Environmental Pollutants, Gout, Hardening Diseases, Intestinal Tract, Liver, Lungs, Radiation (Artificial and Natural), Scleroderma, Skele Psychological Chart: Chakra Chart: Subtle Body Chart: Emotional Miasm Chart: Tips Chart: |
|
Ferrum Magneticum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Ferrum Magneticum (FERR-MA)
Magnetite, Loadstone As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Biomagnetic Properties, Capillary Action, Cerebrospinal Fluid, Circulatory System, Endocrine System, Nervous System, Vertebrae, Vitality Cellular Level Chart: Blood into Ductless Glands, General Strengthening Nutrients Chart: Iron Diseases Chart: Cancer-Precancer, Cramps, Detoxification, Dizziness, Endocrine System, Bladder, Blood Sugar Level Off, Environmental Pollutants, Female Problems, Female Pelvic Problems, Headaches, Joints, Lumbago, Muscle System, Neck, Nutrient Deficiency, Pain, Pancreas Psychological Chart: Altruism, Draws people to you, Expressive Ability, Insomnia, Sleep Better Chakra Chart: All Chakras Subtle Body Chart: All Subtle Bodies, Aura Cleansed, Ethereal Fluidium, Etheric Body Miasm Chart: Petrochemical Miasm Tips Chart: |
|
Brass (Mineral Kingdom) |
Brass (BRAS-MET)
As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Hair on Scalp, Vertebrae Cellular Level Chart: Skin Nutrients Chart: Diseases Chart: Detoxification, Arthritis, Environmental Pollutants, Scalp, Skeletal System, Skin, Vertebrae Psychological Chart: Chakra Chart: Subtle Body Chart: Miasm Chart: Heavy Metal Miasm Tips Chart: |
|
Succinum (Proven by Nuala Eising) (Mineral Kingdom) |
Succinum (Proven by Nuala Eising) (SUCC)
Amber As per GurudasPhysical Parts Chart: Ear Hearing, Electrical Properties, Life Force Enhanced, Metabolism, Nervous System, Thyroid, Vertebrae Cellular Level Chart: Cell Mitosis, DNA Nutrients Chart: Vitamin B Diseases Chart: Brain, Inflammations, Nervous System, Viral Inflammations Psychological Chart: Altruism, Anxiety/Stress, Decision-Making, Eccentric Behavior, Memory Chakra Chart: ThirdEye Chakra, Emotional Chakra Subtle Body Chart: Mental Body Miasm Chart: Syphilitic Miasm Tips Chart: |
|
Naja (Animal Kingdom) |
Naja (NAJA)
Cobra Snake Venom Uses: |
|
Lachesis (Animal Kingdom) |
Lachesis (LACH)
Bushmaster Snake Venom Uses: |
|
Formica Rufa (Animal Kingdom) |
Formica Rufa (FORM)
Red Ant Uses: |
|
Apis mellifica (Animal Kingdom) |
Apis mellifica (APIS)
Honey Bee Uses: Brings tumour (swelling) any where and every where |
|
Tarentula hispanica (Animal Kingdom) |
Tarentula hispanica (TARE)
Wolf Spider Uses: Overstimulated Nervous System, Repetitive Behavior |
|
Cantharis (Animal Kingdom) |
Cantharis (CANT)
Spanish Fly Uses: All 'burning' issues - medical - physical - urinary - 'doused' by this |
|
Sepia (Animal Kingdom) |
Sepia (SEP)
Uses: |
|
Placenta Humana (Proven by Welsh) (Matridonal) |
Placenta Humana (Proven by Welsh) (PLAC-H)
Uses: |
|
Ferrum Phos (Mineral Kingdom) |
Ferrum Phos (FERR-P)
Uses: |
|
Calcarea Carbonicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Calcarea Carbonicum (CALC)
Uses: |
|
Phosphorus (Mineral Kingdom) |
Phosphorus (PHOS)
Uses: Prostrate, Sleep Disturbances, Violent, Destructive, Anger Increased during Lunar-cycles |
|
Hepar sulph (Mineral Kingdom) |
Hepar sulph (HEPA)
Uses: Irritable Throat, When allergy has settled in throat; be it adenoids or tonsillitis, Throat with Thyroid complaints even the vocal cord cyst. |
|
Kali Bichromicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Kali Bichromicum (KALI-BICH)
Uses: Linings of Stomach, Intestine, Airway passages |
|
Arsenicum album (Mineral Kingdom) |
Arsenicum album (ARS)
Uses: Food Poisoning, Loose motions , Rice watery stools & foetid stools, Asthma, Wheezing |
|
Ferrum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Ferrum Metallicum (FERR-MET)
Iron Uses: |
|
Germanium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Germanium Metallicum (GERM-MET)
Uses: |
|
Ruthenium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Ruthenium Metallicum (RUTH-MET)
Uses: |
|
Rhodium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Rhodium Metallicum (RHOD-MET)
Uses: |
|
Iridium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Iridium Metallicum (IRID-MET)
Uses: |
|
Titanium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Titanium Metallicum (TITA-MET)
Uses: |
|
Zincum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Zincum Metallicum (ZINC-MET)
Zinc Uses: |
|
Boron (Mineral Kingdom) |
Boron (BORO)
Uses: Helps in the Mineral Absorption by Kidneys, Maintains levels of Calcium and Testosterone in body |
|
Selenium (Mineral Kingdom) |
Selenium (SELE-MET)
Uses: |
|
Plumbum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Plumbum Metallicum (PLUM-MET)
Lead Uses: |
|
Stannum Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Stannum Metallicum (STAN-MET)
Tin Uses: |
|
Mercurius Vivus (Mineral Kingdom) |
Mercurius Vivus (MERC-V)
Mercury Uses: |
|
Aluminium Metallicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Aluminium Metallicum (ALUM-MET)
Uses: |
|
Kalium Carbonicum (Mineral Kingdom) |
Kalium Carbonicum (KALI-C)
Uses: |
|
Carbo Vegetabilis (Mineral Kingdom) |
Carbo Vegetabilis (CARB)
Uses: |
|
Lymph Gland (Organo Kingdom) |
Lymph Gland (LYMP-G)
Uses: |
|
China officinalis (Plant Kingdom) |
China officinalis (CHIN)
Uses: Tonic |
|
Chamomilla (Plant Kingdom) |
Chamomilla (CHAM)
Uses: Stomach Issues, Vomit, Anger Issues |
|
Phytolacca (Plant Kingdom) |
Phytolacca (PHYT)
Uses: Cancer |
|
Rhus Tox (Plant Kingdom) |
Rhus Tox (RHUS)
Uses: Arthritis, Cancer |
|
Staphysagria (Plant Kingdom) |
Staphysagria (STAP)
Uses: Low Libido |
|
Lycopodium (Plant Kingdom) |
Lycopodium (LYC)
Uses: Hair |
|
Symphytum (Plant Kingdom) |
Symphytum (SYMP)
Uses: |
|
Aconite Napellus (Plant Kingdom) |
Aconite Napellus (ACON)
Uses: Violence Reduced, Can Activate each and every trillion cells of your body at any stage, Psychological Specialist, Brought down many patient's abuse of psycholeptics and tranquilizers |
|
Arnica Montana (Plant Kingdom) |
Arnica Montana (ARN)
Uses: New Vascularisation, Great capillary calibrator to dissolve clots - brain clots |
|
Belladonna (Plant Kingdom) |
Belladonna (BELL)
Uses: Arthritis, Regulator of Blood Circulation to Brain, When allergy has settled in throat; be it adenoids or tonsillitis, Throat with Thyroid complaints even the vocal cord cyst., Migraine overall |
|
Allium cepa (Plant Kingdom) |
Allium cepa (ALL-C)
Uses: For any Allergy, Reddish Eyes, Itching running nose, Sneezing, Allergic Rhinitis |
|
Aloe Socotrina (Plant Kingdom) |
Aloe Socotrina (ALOE)
Uses: Skin Allergy, Itching, Medicinal Allergy |
|
Nux Vomica (Plant Kingdom) |
Nux Vomica (NUX)
Uses: Piles: in the evening hours - thermal chilly; 1M for AIDS; Post operative cases - I generally give Nux vomica 200 in evening hours to tone up liver and reduce the side effect of all medicines. |
|
Aegle Mar (Plant Kingdom) |
Aegle Mar (AEGL-M)
Uses: |
|
Neem (Plant Kingdom) |
Neem (NEEM)
Uses: |
|
Ocimum canum (Plant Kingdom) |
Ocimum canum (OCIM-C)
Hoary Basil, Krishna Tulsi Uses: |
|
Cina Maritima (Plant Kingdom) |
Cina Maritima (CINA)
Uses: Worms |
|
Colocynth (Plant Kingdom) |
Colocynth (COLO)
Uses: |
|
Thuja occidentalis (Plant Kingdom) |
Thuja occidentalis (THUJ)
Cedar Uses: |
|
Olibanum sacrum (Plant Kingdom) |
Olibanum sacrum (OLIB)
Uses: |
|
Centella Asiatica (Plant Kingdom) |
Centella Asiatica (HYDRO)
Gotu Kola, Hydrocotyle Uses: |
|
Camphor (Plant Kingdom) |
Camphor (CAMP)
Uses: |
|
Ashwagandha (Plant Kingdom) |
Ashwagandha (ASHW)
Uses: |
|
Asparagus racemose (Plant Kingdom) |
Asparagus racemose (ASPA-R)
Shatavari Uses: |
|
Crataegus (Plant Kingdom) |
Crataegus (CRAT)
Hawthorn Berry Uses: |
|
Tinospora Cordifolia (Plant Kingdom) |
Tinospora Cordifolia (TINO-C)
Guduchi Uses: |
|
Tribulus Terrestris (Plant Kingdom) |
Tribulus Terrestris (TRIB)
Bindii Uses: |
|
Ginseng (Plant Kingdom) |
Ginseng (GINS)
Uses: Hormone Balancer |
|
Chelidonium (Plant Kingdom) |
Chelidonium ()
Uses: |
|
Wiesbaden Aqua (Water) |
Wiesbaden Aqua (WIES)
Uses: Hair |
Nadis
Go to top| Nadi | Chakra | Aperture | Location | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yashasvati | --- | Tips of Right Thumb, Big Toe | Runs from root to navel chakra where it branches out. | NA |
| Hastijihva | --- | Tips of Left Thumb, Big Toe | Runs from root to navel chakra where it branches out. | NA |
| Sushhumna | Sahasrara | Eyes | From base of spine to top of head, with many nadis branching out from it in the region of third eye. | NA |
| Shankhini | Ajna | Left Ear | Branches out from third-eye, goes to left ear which is its orifice. | NA |
| Payasvini | Ajna | Right Ear | Branches out from third-eye, goes to right ear which is its orifice. | NA |
| Gandhari | Ajna | Left Eye | Branches out from third-eye, goes to left eye which is its orifice. | NA |
| Pusha | Ajna | Right Eye | Branches out from third-eye, goes to right eye which is its orifice. | NA |
| Ida | Ajna | Left Nostril | Branches out from third-eye, goes to left nostril which is its orifice. | NA |
| Pingala | Ajna | Right Nostril | Branches out from third-eye, goes to right nostril which is its orifice. | NA |
| Sarasvati | Vishuddhi | Mouth and throat | From base of spine to throat chakra. | NA |
| Varuna | Anahata | Skin | From base of spine to heart chakra and from it throughout the entire body. | NA |
| Vishvodhara | Manipura | Navel | From base of spine to the navel and from it throughout the abdomen. | NA |
| Kuhu | Swadhisthana | Penis/Vagina | From base of spine to sex chakra and forward to the end of the urethra. | NA |
| Alambusha | Muladhara | Anus | From center of root chakra to tip of rectum | NA |
Srotas
Go to top| Srota | Srota Type | Root | Passage | Opening | Points | Description | Functions | Signs of excess flow | Signs of deficiency flow | Signs of blocked flow | Signs of flow through wrong channel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Pranavaha LifeForce channel |
Govern the intake of substances into body | Left chamber of Heart | Respiratory system | Nose | PC-8, M-HN-3 |
These carry our life force and run through the entirety of the respiratory system. The prana is absorbed through the lungs and the colon. If there is some issue in the root organ (left chamber of the heart), then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. The pranavaha srotas also connect to and work with the Pranamaya kosha. | Respiratory tract, bronchial tree including alveoli | Rapid breathing and hyperventilation. | Slow or shallow breathing and shortness of breath. | Difficulty in breathing accompanied by coughing, wheezing or asthma. There may also be hiatal hernias. | Lungs could be perforated. |
|
Annavaha Food channel |
Govern the intake of substances into body | Esophagus and greater curvature of stomach | Gastrointestinal tract | Ileocecal valve | TH-9, BL-57 |
These are the channels responsible for carrying our food. These srotas are the main channels in the body. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Digestion, Assimilation, Absorption | Excessive appetite, hyperacidity and possibly diarrhea. | Suppressed apprtite as well as hypoacidity, anorexia and constipation. | Intestinal obstruction and the formation of tumors. | There may be vomiting and perforations of the stomach or intestines, or perforated ulcers. |
|
Ambuvaha Water Metabolism channel |
Govern the intake of substances into body | Pancreas | Gastrointestinal mucous membrane | Kidneys, Tongue, Sweat glands | LI-14, PC-2, BL-40, CV-3 |
These channels carry water and other fluids throughout the body, including the cerebrospinal fluid, saliva, and the gastric mucosal and pancreatic secretions. This is the fluid-absorbing aspect of digestion. These srotas govern the assimilation of water and foods that contain water. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Body temperature, Lubrication, Energy, Electrolyte balance, Selection of wastes | Excessive thirst, a sharp taste in the mouth and hypoglycemia. | Lack of taste in the mouth, nausea and hyperglycemia. | Diabetes or other serious problems of the pancreas such as cancer. | Vomiting and anorexia. |
|
Rasavaha Plasma channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Right chamber of heart and ten great blood vessels | Network of blood vessels and Lymphatic systems | Arteriole venous junction in capillaries | TH-9 | These are the channels of the lymph (rasa) dhatu that carry the plasma. They are connected to the lymphatic and circulatory systems. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Nutrition, Affection (prlnana), Immunity, Faith, Regulation of blood pressure and volume | Edema, as well as swelling of the glands and lymph glands. | Dehydration and emaciation. | Overly swollen glands, major lymphatic obstructions and lymphatic cancer. | Bleeding as well as the coughing up of blood. |
|
Raktavaha Blood channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Liver and Spleen | Circulatory system | Skin | LI-18, ST-8, CV-17 |
These channels carry the blood and relate to the circulatory system. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Life function, Oxygenation, Enthusiasm | Rapid pulse, heart palpitations and hypertension. | Slow pulse with hypotension and varicose veins. | Arrhythmia, an enlarged liver or spleen, clotting of the blood, tumors or heart attacks. | Different types of bleeding disorders. |
|
Mamsavaha Muscle channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Ligaments and skin where the muscle tissues are attached | All muscles of the body | Through all the skin | SP-3 | These channels supply the muscle tissue with nutrients. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Plastering, Form, Movement, Support, Protection, Strength | Hyperactivity of muscles and tremors may occur. | Under activity of the muscles that can cause loss or lack of muscle tone and spasms. | Chronic inflammation in the muscles, as well as tumors. | Muscles that are more easily torn. |
|
Medavaha Fat channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Abdominal fat, Kidneys, Adrenals | Subcutaneous fat tissue | Sebaceous glands | CV-2 | These channels supply fat issue with nutrients. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Lubrication (snehan), Personal love, Beauty, Insulation, Bulk to body | Edema and Obesity. | Emaciation with dryness of the skin. | Tumors in adipose/fat tissue. | May lead to the tearing of fat tissue. |
|
Asthivaha Bone channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Adipose tissue and hips/pelvic girdle/sacrum | Skeletal system | Nails and the hair | ST-8 | These channels nourish the bones and skeletal system. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Support, Structure, Protection of vital organs | Excess of bone tissue. | Weak bones, deficient bone tissue and osteoporosis. | Bone sppurs, calcification of the bones and cancer. | Wrong flow also occurs when a bone is broken. |
|
Majjavaha Nervous or Marrow channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Joints and bones, and secondarily by the brain and spinal cord | Entire nervous system (central, sympathetic and parasympathetic) | Synaptic space | GV-20, GV-25, GV-27 |
These supply the nerve tissue and bone marror with nutrients. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Fills bone spaces, Sensation, Communication, Learning, Memory, Coordination | Hypersensitivity, Pain, Insomnia, Tremors and an oerly heightened sense of perception. | Hyposensivity, numbness (physical and emotional), dulllness, lethargy and a clouded sense of perception. | Convulsions, multiple sclerosis and one may even enter into a coma. | Nerve tissue damage |
|
Shukravaha Reproductive fluid channel |
Supply 7 dhatus or bodily tissues | Testes and nipples | Prostate gland, urethra, epididymus and the urogenital tract. | Opening of the urethra. | GB-29, CV-2 |
These are the channels through which nutrients are transported to the male reproductive system. These srotas are also connected to the secretions that occur during sexual activities. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Reproduction, Produces ojas, Emotional release | Spermatorrhea, involuntary nocturnal emissions, premature ejaculation and leucorrhea. | Difficulty to attain an erection, as well as delayed ejaculation. | Inability to ejaculate, testicular swelling, prostate stones and tumors. | Sperm may enter into the bladder. |
|
Purishavaha Faecal channel |
Govern elimination of metabolic waste materials from body | Cecum, rectum and the colon | Large intestine | Anus | GV-15, GV-16, CV-2 |
These channels carry feces. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Absorption of minerals, Strength, Support, Formation & elimination of feces | Diarrhea | Constipation | Onstructions to the colon and there may be diverticulitis or tumors. | Perforation in the colon. |
|
Mutravaha Urinary channel |
Govern elimination of metabolic waste materials from body | Kidneys | Ureters, urethra and bladder. | Opening of urethra. | BL-30, BL-36, GB-29 |
These channels carry the urine, and include the entire urinary system. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Electrolyte balance, Elimination of urine, Maintenance of blood pressure | Excessive or frequent urination. | Scant urination | Painful and difficult urination, and there may be stones in the urinary tract. | Bladder can bust. |
|
Svedavaha Sweat channel |
Govern elimination of metabolic waste materials from body | Sweat glands | Sweat ducts | Pores of the skin and the sweat glands underneath the skin. | LV-2, LV-3 |
These are the channels that carry sweat, the sebaceous glands. These srotas are intrinsically connected the adipose/fat tissue. The more fat the body has, the more the body sweats. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Elimination of liquid wastes, Perspiration, Electrolyte balance, Body temperature, Lubrication | Profuse sweating will occur. | Temporary lack of sweating. | Complete inability ot sweat. | Sweat will enter into lymphatic system (rasa) dhatu. |
|
Artavavaha Menstruation channel |
Govern female systems | Ovaries and areola | Fallopian tubes, uterus, cervical canal and vagina | Labia | BL-30, BL-36, GB-29, SP-6 |
These are the channels through which nutrients are transported to the female reproductive system. These srotas have some responbility for the menstruation and also nourish the reporductive tissue, or the ova. It goerns the production of hormones and other sexual secretions. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Reproduction, Produces ojas, Emotional release | Spermatorrhea, involuntary nocturnal emissions, premature ejaculation and leucorrhea. | Difficulty to attain an erection, as well as delayed ejaculation. | Inability to ejaculate, testicular swelling, prostate stones and tumors. | Sperm may enter into the bladder. |
|
Stanyavaha Lactation channel |
Govern female systems | Lactation glands | Lactiferous dicts | Nipple (it function only when a women gives birth) | SP-6, CV-17 |
These are the channels that carry breast milk for lactating women. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Lactation | Excess of breast milk | Lack of breast milk | No breast milk, painful and swelling breasts, mastitis, cysts, tumors or cancer. | Injury to the breasts. |
|
Manovaha Mental channel |
Govern mind system | Heart or cardiac plexus and the ten sensory pathways | Whole body | Sense organs | HE-7, GV-20 |
These are the channels of the mind that carry thoughts. They are not only physical channels, but subtle channels as well, and are critical in the development of a balanced mind. These channels are lcoated in the merve tissue and arr part of our emotional process. The Manovaha srotas maske up the subtle body and are part of the Manomaya kosha. The mind is directly connected to the parts of the nervous system and physical body that are resposible for the sensory and motor system. When in its higher state of awareness, the mind transcends physical body consciousness. If there is some issue in the root organ, then the entire srotas will be messed up, which can then cause disease. But if the problem is in srotas, then it is not necessary for root organ to have issue. | Thinking, Feeling, Inquiring, Deciding, Discrimination, Desire, Memory, Communication | Mental unrest, Hyperactive mind and senses and one may worry to have a lot of anger. | Dulled senses and depression, with predominant emotions of gried and sadness. | Blocked or suppressed emotions | Major psychological probles like delirium, delusion (including delusions of grandeur) and schizophrenia. |
Marmas
Go to topSrotas are NOT mapped to Marmas but instead assigned to AcupuncturePoints because in authentic marma (from SouthIndia and also as mentioned in Vasant Lad's), the marma have different names as used in today's world. In reality the smaller marmas/siras are mapped which happens to exctly correspond with AcupuncturePoints.
Marmas for each Chakra
|
Marmas in each Region
|
Marmas in each Category
|
Lethal Marmas
|
All Marmas
| Marma | Chakra | Region/Category/Lethal | Description | Acupuncture Points | Indications/Actions/Contradictions | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Adhipati Overlord Location: Top of the head Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 1 |
Sahasrara |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Mind, Nerves, Epilepsy, Treatment of psychiatric diseases and nervous system disorders, Pranic energy balancer, pineal gland and brain disorders |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Apanga Looking away Location: Outer corner of the eyes Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vision, Reduces nervous stress |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Avarta Disaster Location: Midpoint above the eyes Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Depression, Vision, Posture, Eye disease, Sinusitis (frontal) and temporal headaches |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Krikatika Joint of the neck Location: Joint of the neck Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Tremors, Disability, Stiffness, Neck and shoulder pain |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Manya Honor Location: Side of upper neck Size: 4 anguli Number: 2 |
Vishuddhi |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Speech, Taste, Perception, Blood, Transfer marma |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Nila Dark Blue Location: Base of the throat Size: 4 anguli Number: 2 |
Vishuddhi |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Transfer point. Balances the sense of timing and treats aphonia and loss of taste. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Phana A serpent hood Location: Side of the nostrils Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Smell, Sinus, Ears, Stress, Nosebleed |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Shankha A conch shell Location: Temple Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Asthi (Bone) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Colon, Treats hearing, Temporal headaches |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Shringataka Place where four roads meet Location: Soft palate of the mouth Size: 4 anguli Number: 4 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Dhamani (Channel) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates the Nervous system, Soothe the eyes, ears, nose, tongue. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Simanta Summit Location: Fissures on the skull Size: 4 anguli Number: 5 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Sanity, Grounding, Intelligence, Blood, Migraine, Lacrimation, Fear |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Sira Matrika Mother of the blood vessels Location: Base of the neck Size: 4 anguli Number: 8 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Blood circulation |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Sthapani What gives support or fixes Location: Point between the eyes Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 1 |
Ajna |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vishalyaghna (Death when foreign object is extracted) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Main Vayu marma, Balances mind and nervous sytem including Pituitary gland, Hypothalamus |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Utkshepa What is upwards Location: Above the ears Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vishalyaghna (Death when foreign object is extracted) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Colon, Temporal headaches |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Vidhura Distress Location: Behind and below the ears Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Head and Neck Category: Dhamani (Channel) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Hearing, Head support, Ear disorders, Facial paralysis |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Apalapa Unguarded Location: Armpit or axilla Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Blood, Balances sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Apastambha What stands to the side Location: Upper side of the abdomen Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Dhamani (Channel) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Blood, Lungs, Sympathetic and Parasympathetic Nervous Systems, Asthma, Coughs, Dyspepsia |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Basti Bladder Location: Lower abdomen Size: 4 anguli Number: 1 |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Urinary, Basti |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Guda Anus Location: Anus Size: 4 anguli Number: 1 |
Muladhara |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Dhamani (Channel) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates uro-genito functions (Reproduction, Colon, Urine, Gas, Stool). This is also the local Apana Vayu sira on the torso. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Hridaya Heart Location: Heart Size: 4 anguli Number: 1 |
Anahata |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Controls the centrifugal Pranic flow (Vayu), breast disease, allows balance in circulation and breathing. Main Pitta marma, Vyana vayu, Affects Sadhaka Pitta that causes fantasies and realities to become indistinguishable when vitiated. May treat the Pericardium organ. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Nabhi Navel Location: Navel Size: 4 anguli Number: 1 |
Manipura |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Sadya Pranahara (Death immediately or within 24 hours) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Seat of all Vein, Transfer points, Small Intestines. When massaged may stimulate the small intestine and Pachaka Pitta. May treat hyperacidity and gastric, duodenal ulcers. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Stanamula Root of breast Location: Root of the breast Size: 2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Kapha, Pitta, Blood circulation, Assists with cough and apnea |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Stanarohita Upper region of the breast Location: Upper region of the breast Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Abdomen and Chest Category: Mamsa (Muscle) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Kapha, Pitta, Arm Muscles, Sedates arms |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Amsa Shoulder Location: Shoulder Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Vishuddhi |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Udana vayu, Brain, Stimulates Throat chakra, Thyroid and the endocrine system |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Amsaphalaka Shoulder blade Location: Shoulder blade Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Anahata |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Asthi (Bone) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vayu, Touch/Sensation, Atrophy, Scapular pain and fourth chakra treatment (chest) |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Brihati Wide or large Location: Broad region of the upper back Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Manipura |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Major Pitta accumulation site, Coughing of blood, Heart symptoms. |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Katikataruna What rises from the hip Location: Hip-joint Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Asthi (Bone) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Fat, Constipation, Vayu, Treatment of hip joint |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kukundara What marks the loins Location: On each side of lower iliac spine Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Swadhisthana |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Reproduction, Elimination, Leg Mobility, Local, rear Apana Vayu manna |
|||||||||||||||||
|
Nitamba Buttocks Location: The upper region of the buttocks Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Asthi (Bone) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vayu, Pitta, Digestion, Vitality, Backache, Sciatica, Paralysis of lower limb, Large intestine problems. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Parshvasandhi The side of the waist Location: The upper hips Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Back and Hips Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Pitta, Digestion, Elimination, Circulation. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Ani The point of a needle Location: Lower region of the upper arm Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vayu, Muscle tension, Controls muscle tone |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Bahvi What relates to the arm Location: Inside of upper arm Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Indrabasti Indra arrow Location: Center of forearm Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Mamsa (Muscle) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates Digestive Fire (Jataragni), Small Intestine |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kakshadhara What upholds the flank Location: Top of shoulder joint Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Muscle tension, Affects muscle tone in upper abdomen and chest |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kshipra Quick to give results Location: Between thumb and index finger Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Heart, Lungs, Eye pain, Toothache, Redness and pain in fingers |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kurcha A knot or bundle Location: Bottom of thumb Size: 4 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vision, Treatment of large intestine, pain |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kurchashira The head of kurcha Location: Base of thumb joint Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Rujakara (Causing persistent prolonged pain) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Muscle Spasm, Heart and lung symptoms |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kurpara Elbow joint Location: Elbow joint Size: 3 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Heart, Liver, Spleen, Numbness of arm, Elbow pain, Cardiac pain, Coughs, Asthma |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Lohitaksha Red-jointed Location: Lower frontal end of shoulder joint Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Fluid movement, Arm Blood supply, Assists circulation and pain in arms. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Manibandha Bracelet Location: Wrist Size: 2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Rujakara (Causing persistent prolonged pain) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Relieves stiffness, Treats diseases of the wrist, Carpal tunnel syndrome, Cardiac pain, Mental disorders |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Talahridaya Center of the surface Location: Center of the palm of the hand Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Mamsa (Muscle) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates the Lungs (Vata) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Urvi What is wide Location: The mid-region of the upper arm Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Arms and Hands Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Udakavaha Srota, Fluid movement, Stimulates Ambhu Vaha Srotas, urine retention and swelling and pain in inguinal area. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Ani The point of a needle Location: Lower region of the upper leg Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vayu, Muscle tension, Controls muscle tone |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Gulpha Ankle joint Location: Ankle joint Size: 2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Rujakara (Causing persistent prolonged pain) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Relieves Stiffness, Treatment of leg paralysis and pain (especially in ankle joint) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Indrabasti Indra arrow Location: Center of lower leg Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Mamsa (Muscle) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates Digestive Fire (Jataragni), Small Intestine |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Janu Knee joint Location: Knee joint Size: 3 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Sandhi (Joint) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Heart, Liver, Spleen, Treats the lower back and leg pain including the hip joint |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kshipra Quick to give results Location: Between big toe and second toe Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Heart, Lungs, Swelling, Redness and pain in eye and toes. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kurcha A knot or bundle Location: Bottom of big toe Size: 4 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Vision, High blood pressure, Jaundice, Uterine bleeding |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Kurchashira The head of kurcha Location: Base of big toe joint Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Rujakara (Causing persistent prolonged pain) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Muscle Spasm, Leg and back ache, epilepsy. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Lohitaksha Red-jointed Location: Lower frontal end of the hip joint Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Fluid movement, Leg Blood supply, Assists circulation and pain in legs. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Talahridaya Center of the surface Location: Center of the sole of the foot Size: 1/2 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Mamsa (Muscle) Lethal: Kalantara Pranahara (Death within 2 to 4 weeks) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Stimulates the Kidneys (Vata) |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Urvi What is wide Location: The mid-region of the upper thigh Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Sira (Point on Dhamani) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Udakavaha Srota, Fluid movement, Stimulates Ambhu Vaha Srotas, urine retention and swelling and pain in inguinal area. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Vitapa What is hot or painful Location: Perineum Size: 1 anguli Number: 2 |
Swadhisthana |
Region: Legs and Feet Category: Snayu (Ligaments and Tendons) Lethal: Vaikalyakara (Maiming or deformity when injured) |
|
Indications: Contradictions: Actions: Belly muscle tension, Impotence, Semen, Ovum, urine retention, External genital pain, Seminal emission. Affects muscle tone in lower abdomen |
Meridians
Go to topMeridians
| Meridian | Route | Body Organ | Zodiac Sign | Homeopathy | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Lung Meridian 3am - 5am |
Starts At: Neat armpit, between second and third ribs Runs Via: Upper and lower arms Ends At: Inside of thumb at the root of the nail |
Lungs | Gemini | Carbo Vegetabilis | No description |
|
Large Intestine Meridian 5am - 7am |
Starts At: Base of index fingernails Runs Via: Up inner side of the arms Ends At: Sides of the nostrils |
Large Intestine | Aquarius | Aluminium Metallicum | No description |
|
Heart Meridian 11am - 1pm (13:00) |
Starts At: Base of the armpit Runs Via: Down inner side of arm Ends At: Base of the little fingernail |
Heart | Leo | Aurum Metallicum | No description |
|
Small Intestine Meridian 1pm - 3pm (15:00) |
Starts At: Base of the little fingernail Runs Via: Up the arm and side of face Ends At: Just in front of each ear |
Small Intestine | Virgo | Plumbum Metallicum | No description |
|
Pericardium Meridian 7pm - 9pm (21:00) |
Starts At: The chest muscle Runs Via: Down the arms Ends At: Base of the middle fingernail |
Pericardium | Aries | Staphysagria | No description |
|
Triple Warmer Meridian 9pm - 11pm (23:00) |
Starts At: Ring finger, on the little finger side Runs Via: Up the arm to the head Ends At: Near the eye, under the eyebrow |
Triple Warmer | Pisces | Silicea | No description |
|
Kidney Meridian 5pm - 7pm (19:00) |
Starts At: Soles of feet Runs Via: Up the inside leg, through the center of the body Ends At: Below the collar bone between the clavicle and first rib |
Kidney | Libra | Phosphorus | No description |
|
Bladder Meridian 3pm - 5pm (17:00) |
Starts At: The inside corner of the eye Runs Via: Over the skull, down the spinal column Ends At: Base of the little toenail |
Bladder | Scorpio | Kalium Carbonicum | No description |
|
Liver Meridian 1am - 3am |
Starts At: Base of the nail of the big toe Runs Via: Up the inside of the leg Ends At: Near the nipple |
Liver | Sagittarius | Stannum Metallicum | No description |
|
Gallbladder Meridian 11pm - 1am |
Starts At: Outer corner of the eye Runs Via: Several points on the head Ends At: The second joint of the fourth toe |
Gall Bladder | Capricorn | Colocynth | No description |
|
Spleen Meridian 9am - 11am |
Starts At: The root of the nail of the big toe Runs Via: Up the inside of the legs and torso Ends At: Below the armpit |
Spleen | Taurus | Thuja occidentalis | No description |
|
Stomach Meridian 7am - 9am |
Starts At: Just under the eye Runs Via: Down the body and legs Ends At: Root of the second toenail |
Stomach | Cancer | Nux Vomica | No description |
|
Governing Vessel |
Starts At: In the pelvic cavity between the tip of the coccyx and anus Runs Via: Middle of spinal column, over the skull Ends At: Two front teeth, between the upper lip and gums |
Center of Back. Sea of Yang. | |||
|
Conception Vessel |
Starts At: Pelvic cavity, in the center of the perineum Runs Via: Middleline of the abdomen, through the chest and throat to the mandible Ends At: Two front teeth, between the lower lip and gums |
Center of Torso. Sea of Yin. |
Acupuncture Point Categories
Go to top24 Meridians (12*2) are actually Sushrut's 24 Dhamanis while AcupuncturePoints on meridians are Siras of Sushrut.
700 siras = Lung Meridian (22 points {11+11 for Right and Left}) + .... + Governor channel (only left: 28 points) + Conception channel (only left 24 points) + Extra siras/points (30)
All Solid organ channels always have Ether as their first element point. All Hollow organ channels have Air as their first element point. BUT each channel follws the Wheel of Support.
| Buddhist triangle |
Special combination of Anxiety/Depression |
| Command |
According to 16th century Ming Dynasty physician Gao Wu, these points can be used to treat any kind of disorder in
these regions, whether deficient, excess, hot, cold, chronic
or acute. These are also called "4 command points", the 2 other points are added later. |
| Confluent/Coupled |
The extraordinary vessels run "behind" the 12 main meridians. They interconnect with the 12 meridians and correspondingly allow for broad and deep effects within the body. 6 of the 8 extraordinary vessels has a master and coupled point on a pair of the main meridians. The Governing Vessel and the Conception Vessel, however, have their own points. |
| Confluent/Master |
The extraordinary vessels run "behind" the 12 main meridians. They interconnect with the 12 meridians and correspondingly allow for broad and deep effects within the body. 6 of the 8 extraordinary vessels has a master and coupled point on a pair of the main meridians. The Governing Vessel and the Conception Vessel, however, have their own points. |
| Entry |
Pending |
| Exit |
Pending |
| Five Element (Child) |
It is responsible for taking the food from parent as per the Wheel of Support. |
| Five Element (Mother) |
It is responsible for feeding the child as per the Wheel of Support. |
| Five Shu (He-sea) |
Sea points are related to Flowering and at which the Qi enters Inwards. At the Sea points the Qi of the channel is vast and deep; it collects, comes together and joins the general circulation of the body, like a large river flowing into the sea. Compared to the Well points, the Sea points are much less dynamic and their effect is less quick and dramatic. Sea point are used for all stomach and intestinal diseases (i.e with digestive functions). This applies mostly to Yang channels but also to Yin ones. |
| Five Shu (Jing-river) |
River points are related to Manifestation and at which the Qi Flows. Defensive Qi gathers at the River points. At the River points the Qi of the channel is much bigger, wider and also deeper. The Qi flows like a large current after coming a long distance from its source; Qi is able to flow down a channel. At the River points, exterior pathogenic factors are deviated towards joints, bones and sinews. Jing-river points have to do with many respiratory problems as well as fever and chills, coughs and dyspnoea, diseases that take place in the bones and sinews and finally health problems that affect the vocal cords and serve to alter a persons way of speaking. This applies more to Yin than Yang channels. |
| Five Shu (Jing-well) |
Well points are related to Aggravation and at which the Qi Emanates. The Well is the point of departure of Qi. At this point the channel is the most superficial and thinnest and the energy changes polarity from Yin to Yang or vice versa. The energy is at its most unstable state here, so that it can be easily and readily influenced and changed. The energy at these points has an outward movement, the energy of the channel tends to go outwards in a centrifugal movement at these points. The Well points are used in acute conditions as the Well points tend to be used to eliminate pathogenic factors quickly in acute conditions. The Well points are used for irritability, mental restlessness and anxiety. |
| Five Shu (Shu-stream) |
Stream points are related to Displacement and at which the Qi Pours. At the Stream point the Qi of the channel pours through, it swirls and the flow starts to be bigger and slightly deeper within the channel. Here the flow of Qi is rapid and large enough to carry other things with it hence its name transporting. At the Spring points, on the one hand, exterior pathogenic factors can be transported into the interior and penetrate deeper in the channels. Stream points are used for Painful Obstruction Syndrome (Bi Syndrome) especially from dampness. This applies to Yang channels more then Yin channels. Shu-stream points have to do with pain and discomfort in the tendons and joints as well as intermittent kinds of diseases and a feeling of heaviness in the body as if it is being pulled down. |
| Five Shu (Ying-spring) |
Spring points are related to Overflow and at which the Qi Glides. At the Spring point the Qi of the channel is very powerful and full of potential energy ready to manifest, like the swirling movement of water in a mountain spring. Qi is able to effectively glide or slide down the channel in question. The Spring points have a particularly strong action and are generally used to eliminate pathogenic factor whether they are interior or exterior and in particular to clear Heat. The Spring points are used sparingly. The Spring points of the feet are more powerful then the Spring points of the hands. Spring points are used for febrile diseases or to clear Heat. Virtually all Spring points clear heat in their respective channels. |
| Four Seas |
Pending |
| Ghost |
The most basic of the ways in which possession could be carried out within Chinese medicine. Used in treatment for possession by ghosts. |
| Hui Meeting/Gathering |
Pending |
| Lower He Sea |
These points are located on the Yang meridians and are used to treat their respective yang/hollow organs. These are places where the Qi in the meridians is most vigorous. |
| Luo/Bridge |
There are points which connect between the hollow and solid organ channels and allow Prana to travel between one channel and the next in line. |
| Ma Danyang/12 Star Points |
Points as per the poem of Ma Danyang (originally named Ma Yu) Daoist; which he originally wrote in 1329. |
| Mu/Front |
Pending |
| Shu/Back |
Pending |
| Window of Sky |
The basic functions of the points are to improve the flow of energy between the head and the rest of the body. |
| Xi/Cleft |
These are points where Prana tends to be retained in the channel and forms a type of base. In other words, points are the position on the channel where both the blood as well as the qi come together and once connected, make their way further into the human body. |
| Yuan/Base |
Source points (Mula Marmas) are points where Prana tends to be retained in the channel and forms a type of base. This may be needed as when a blockage of Prana occurs along a channel (as in the case of chronic dis-ease). The Base point will then release energy from the organ into the channel in order to facilitate healing. The Base point of a channel not only reflects the energy of the related organ but is also a minor doshic representative along the channel. That is to say that in the case of the Lung, the base point of the Lung channel reflects Vata in that channel. Additionally, the Base points reflect the condition of their related organs. For instance an imbalance in the Large Intestine may refer tenderness at Large Intestine 4, at the web between thumb and index finger on the outside of the hand. |
Srota Points
|
SubDosha Points
|
Five Shu Points
|
Five Element Points
|
Yuan/Base Points
|
Luo/Bridge Points
|
Command Points
Four Seas
Buddhist Triangle Points
|
Window of Sky Points
Lower He Sea
|
MuShu FrontBack Points
|
Entry/Exit Points
|
Master/Coupled Points
Hui Meeting/Gathering Points
|
Ghost Points
|
Ma Danyang/12 Star Points
Xi/Cleft Points
|
Acupuncture Points
Go to top| Point # | Srota/Dosha/Marma | Category/Function | Location | Indications | Actions | Description | Cautions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CV-1 Huiyin (Meeting of Yin) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: Muladhara/Root |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Guda Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ghost Function: Ghost Store |
At the perineum, midway between the anus and the scrotum in men, and the anus and the posterior labial commissure in women. Landmark: In males the scrotum may need to be lifted away from the point. |
|
|
Pregnancy According to the Great Compendium of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, this point is contraindicated to needling. | |
|
CV-2 Qugu (Curved Bone) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Fat channel, Reproductive fluid channel, Faecal channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Apana (Vaata) |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, at the superior border of the pubic symphysis, 5 cun below the umbilicus. |
|
|
deep insertion will penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment | |
|
CV-3 Zhongji (Middle Pole) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Water Metabolism channel Part of Marma: Basti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Bladder organ |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, 4 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 1 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. |
|
|
Deep insertion will penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment | |
|
CV-4 Guanyuan (Gate of Origin) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Basti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Small Intestine organ |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, 3 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 2 cun superior to the pubic symphysis |
|
|
Deep insertion may penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment | |
|
CV-5 Shimen (Stone Gate) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Basti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Triple Heater organ |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, 2 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 3 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. |
|
|
Several Classical texts, this point is contraindicated to needling and moxibustion during pregnancy.Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-6 Qihai (Sea of Qi) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: Swadhisthana/Sacral |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Basti Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, 1.5 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 3.5 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-7 Yinjiao (Yin Intersection) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower abdomen, 1 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 4 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-8 Shenque (Spirit Gateway) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: Manipura/Solar Plexus |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Nabhi Subdosha: Pachaka (Pitta) |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the centre of the umbilicus. |
|
|
||
|
CV-9 Shuifen (Water Separation) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the abdomen, 1 cun above the umbilicus and 7 cun below the sternocostal angle. |
|
|
This point is contraindicated to needling in cases of water illness, and plentiful moxibustion should rather be used. Moxibustion is contraindicated in pregnancy.In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-10 Xiawan (Lower Cavity) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the abdomen, 2 cun above the umbilicus and 6 cun below the sternocostal angle. |
|
|
Pregnancy In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-11 Jianli (Strengthen the Interior) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the abdomen, 3 cun above the umbilicus and 5 cun below the sternocostal angle. |
|
|
In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
CV-12 Zhongwan (Middle Cavity) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Kledaka (Kapha) |
Category: Mu/Front, Hui Meeting/Gathering Function: Stomach organ, Yang Organs |
On the midline of the abdomen, 4 cun above the umbilicus and midway between the umbilicus and the sternocostal angle. |
|
|
In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-13 Shangwan (Upper Cavity) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the abdomen, 5 cun above the umbilicus and 3 cun below the sternocostal angle. |
|
|
In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
CV-14 Juque (Great Gateway) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Heart organ |
On the midline of the abdomen, 6 cun above the umbilicus and 2 cun below the sternocostal angle. Landmark: In some patients the xiphoid process may extend to this point |
|
|
Deep insertion, especially in thin subjects, may damage the left lobe of the liver or the heart if either is enlarged.Oblique superior insertion towards the heart is contraindicated in all cases. | |
|
CV-15 Jiuwei (Turtledove Tail) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On the midline of the abdomen, 7 cun above the umbilicus and 1 cun below the sternocostal angle. Landmark: i. Many sources locate this point below the xiphoid process. In practice however, the xiphoid process varies considerably in length, and this point may lie on the xiphoid process itself. |
|
|
1. deep insertion, especially in thin subjects, may damage the left lobe of the liver or the heart if either is enlarged. 2. oblique superior insertion towards the heart is contraindicated in all cases. | |
|
CV-16 Zhongting (Central Courtyard) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the sternum at the sternocostal angle. Landmark: This point is level with the fifth intercostal space at the mamillary line. |
|
|
||
|
CV-17 Shanzhong (Chest Centre) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: Anahata/Heart |
Srotas: Blood channel, Lactation channel Part of Marma: Hridaya Subdosha: Vyana (Vaata), Sadhaka (Pitta) |
Category: Mu/Front, Hui Meeting/Gathering, Four Seas Function: Pericardium organ, Qi, Sea of Qi |
On the midline of the sternum, in a depression level with the junction of the fourth intercostal space and the sternum. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it and count down to the fourth space.2. This point can be located directly between the nipples in men. |
|
|
According to several classical texts, this point is contraindicated to needling. | |
|
CV-18 Yutang (Jade Hall) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the sternum, level with the junction of the third intercostal space and the sternum. Landmark: First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it and count down to the third space. |
|
|
||
|
CV-19 Zigong (Purple Palace) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the sternum, level with the junction of the second intercostal space and the sternum. Landmark: Locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it. |
|
|
||
|
CV-20 Huagai (Magnificent Canopy) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the sternum, level with the junction of the first intercostal space and the sternum. Landmark: First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the first intercostal space above it. |
|
|
||
|
CV-21 Xuanji (Jade Pivot) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the manubrium of the sternum, midway between Huagai CV-20 and Tiantu CV-22. |
|
|
||
|
CV-22 Tiantu (Heavenly Prominence) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian Tu (Heavenly Crevice) |
On the midline, in the centre of the suprasternal fossa, 0.5 cun superior to the suprasternal notch |
|
|
||
|
CV-23 Lianquan (Corner Spring) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: Vishuddhi/Throat |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Nila, Sira Matrika Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the anterior midline of the neck, in the depression above the hyoid bone. Landmark: 1. Run a finger gently along the underside of the chin towards the throat until it falls into the deep depression just in front of the hyoid bone.2. the hyoid bone is readily located as the most superior palpable bony structure at the midline of the throat and runs transversely above the laryngeal prominence; this point is located at its superior border. |
|
|
According to several modern texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion. | |
|
CV-24 Chengjiang (Container of Fluids) Meridian: Conception Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ghost Function: Ghost Market |
Above the chin, in the depression in the centre of the mentolabial groove. Landmark: The mentolabial groove runs horizontally, approximately midway between the chin and the lower lip. |
|
|
||
|
GV-1 Changqiang (Long Strong) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Muladhara/Root |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Guda Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On the midline, midway between the tip of the coccyx and the anus. Landmark: This point may be located and needled with the patient either: i. lying on the front, ii. lying on the side with knees drawn up, or iii. first sitting on the heels and then leaning forwards and resting the upper body weight on the elbows with the head on the hands. |
|
|
||
|
GV-2 Yaoshu (Lumbar Shu) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline, in the sacro-coccygeal hiatus. Landmark: The sacro-coccygeal hiatus is located in-between the cornua of the sacrum and coccyx, in the depression inferior to the fourth sacral spinous process if this is palpable. Note, however, that the sacro-coccygeal hiatus may sometimes extend as high as the level of the third sacral foramina. |
|
|
||
|
GV-3 Yaoyangguan (Lumbar Yang Gate) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Swadhisthana/Sacral |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower back, in the depression below the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra. Landmark: This point is located one intervertebral space below the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-4 Mingmen (Gate of Life) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower back, in the depression below the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra. Landmark: This point is located one intervertebral space above the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-5 Xuanshu (Suspended Pivot) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower back, in the depression below the spinous process of the first lumbar vertebra. Landmark: This point is located two intervertebral spaces above the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-6 Jizhong (Centre of the Spine) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Manipura/Solar Plexus |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located four intervertebral spaces above the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build.According to a number of classical texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion. | |
|
GV-7 Zhongshu (Central Pivot) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the tenth thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located five intervertebral spaces above the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-8 Jinsuo (Sinew Contraction) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located six intervertebral spaces above the line connecting the highest points of the two iliac crests (level with the lower border of L3). |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-9 Zhiyang (Reaching Yang) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located seven intervertebral spaces below C7. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-10 Lingtai (Spirit Tower) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Anahata/Heart |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the back, in the depression below the spinous process of the sixth thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located six intervertebral spaces below C7. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-11 Shendao (Spirit Pathway) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the upper back, in the depression below the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located five intervertebral spaces below C7. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-12 Shenzhu (Body Pillar) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the upper back, in the depression below the spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located three intervertebral spaces below C7. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-13 Taodao (Way of Happiness) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the upper back, in the depression below the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra. Landmark: This point is located one intervertebral space below C7. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. | |
|
GV-14 Dazhui (Great Vertebra) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Vishuddhi/Throat |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas Function: Sea of Qi |
On the midline at the base of the neck, in the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra. Landmark: The spinal canal lies between 1.25 and 1.75 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. |
|
|
||
|
GV-15 Yamen (Gate of Muteness) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Faecal channel Part of Marma: Krikatika, Sira Matrika Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas Function: Sea of Qi |
On the midline at the nape of the neck, in the depression 0.5 cun inferior to Fengfu GV-16, below the spinous process of the first cervical vertebra (impalpable). Landmark: The posterior hairline is measured as 1 cun inferior to Fengfu GV-16. Locate Yamen GV-15 at the midpoint, i.e. 0.5 cun above the posterior hairline. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.5 and 2 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. Deep perpendicular insertion is therefore strictly contraindicated, as is superior oblique insertion towards the brain. | |
|
GV-16 Fengfu (Palace of Wind) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Ajna/Third Eye |
Srotas: Faecal channel Part of Marma: Krikatika Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas, Window of Sky, Ghost Function: Sea of Marrow, Feng Fu (Wind Palace), Ghost Pillow |
On the midline at the nape of the neck, in the depression immediately below the external occipital protuberance. Landmark: 1. The external occipital protuberance is found as the bony prominence at the base of the skull on the midline, though in some individuals it may be difficult to feel. 2. This point lies approximately 1 cun above the posterior hairline. |
|
|
The spinal canal lies between 1.5 and 2 cun deep to the skin surface, varying according to body build. Deep perpendicular or superior oblique insertion is therefore strictly contraindicated. | |
|
GV-17 Naohu (Brain Door) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the back of the head on the midline, 1.5 cun directly above Fengfu GV-16, in the depression directly superior to the external occipital protuberance. Landmark: This point may be located at the junction of the lower quarter and the upper three quarters of the line connecting Fengfu GV-16 and Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
GV-18 Qiangjian (Unyielding Space) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the back of the head on the midline, 1.5 cun directly superior to Naohu GV-17, midway between Fengfu GV-16 and Baihui GV-20. Landmark: This point may be located at the midpoint of the line connecting Fengfu GV-16 and Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
GV-19 Houding (Behind the Crown) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the back of the head on the midline, 1.5 cun directly superior to Qiangjian GV-18 and 1.5 cun posterior to Baihui GV-20. Landmark: This point may be located at the junction of the lower three quarters and the upper quarter of the line connecting Fengfu GV-16 and Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
GV-20 Baihui (Hundred Meetings) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: Sahasrara/CrownSahasrara/Crown |
Srotas: Nervous or Marrow channel, Mental channel Part of Marma: Adhipati Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas Function: Sea of Marrow |
At the vertex on the midline, in the depression 5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline and 7 cun superior to the posterior hairline. This point may also be measured as 8 cun posterior to the glabella and 6 cun superior to the external occipital protuberance. Landmark: 1. Place the heels of the hands on the anterior and posterior hairlines and extend the middle fingers towards each other; Baihui GV-20 is located 1 cun anterior to where the middle fingers meet.2. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, place the heels of the hands on the glabella and external occipital protuberance and extend the middle finsers towards each other; Baihui GV-20 is located 1 cun posterior to where the middle fingers meet. 3. Extend a line along the long axis of the ear (from the midpoint of the lobe to the midpoint of the apex) in its slightly posterior direction to the top of the head where Baihui GV-20 may be found. |
|
|
||
|
GV-21 Qianding (In Front of the Crown) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the top of the head on the midline, 1.5 cun directly anterior to Baihui GV-20 and 3.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Baihui GV-20 and the anterior hairline into thirds. Qianding GV-21 lies slightly posterior to the junction of the first and middle thirds. 2. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, locate it 3 cun superior to the glabella and 5 cun anterior to Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
This point should not be needled in infants whose fontanelle has not yet closed. | |
|
GV-22 Xinhui (Fontanelle Meeting) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the top of the head on the midline, 2 cun posterior to the anterior hairline. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Baihui GV-20 and the anterior hairline in half and locate Xinhui GV-22 at 0.5 cun anterior to this midpoint. 2. Locate 1 cun posterior to Shangxing GV-23. 3. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, locate it 3 cun superior to the glabella and 5 cun anterior to Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
This point should not be needled in infants whose fontanelle has not yet closed. | |
|
GV-23 Shangxing (Upper Star) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ghost Function: Ghost Hall |
At the top of the head on the midline, 1 cun posterior to the anterior hairline and 0.5 cun posterior to Shenting GV-24. Landmark: If the anterior hairline is indistinct, locate it 3 cun superior to the glabella and 5 cun anterior to Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
GV-24 Shenting (Courtyard of the Spirit) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the top of the head on the midline, 0.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline and 0.5 cun anterior to Shangxing. Landmark: If the anterior hairline is indistinct, locate it 3 cun superior to the glabella and 5 cun anterior to Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
GV-25 Suliao (White Crevice) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Nervous or Marrow channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline at the tip of the nose. |
|
|
||
|
GV-26 Renzhong (Man Middle) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Command, Ghost Function: Fainting & Collapse, Ghost Place |
Above the upper lip on the midline, at the junction of the upper third and lower two thirds of the philtrum. Landmark: The philtrum is the marked indentation found on the midline between the root of the nose and the margin of the upper lip. |
|
|
Single most important point to revive consciousness and re-establish yin-yang harmony. | |
|
GV-27 Duiduan (Extremity of the Mouth) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Nervous or Marrow channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline, at the junction of the margin of the upper lip and the philtrum. Landmark: The philtrum is the marked indentation found on the midline between the root of the nose and the margin of the upper lip. |
|
|
||
|
GV-28 Yinjiao (Gum Intersection) Meridian: Governing Vessel Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Inside the mouth, in the superior frenulum, at the junction of the upper lip and the gum. Landmark: The superior frenulum is the midline band of fibrous tissue connecting the upper lip and gum. |
|
|
||
|
ST-1 Chengqi (Container of Tears) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Entry Function: NA |
With the eyes looking directly forwards, this point is located directly below the pupil between the eyeball and the infraorbital ridge. |
|
|
||
|
ST-2 Sibai (Four Whites) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
With the eyes looking directly forwards, this point is located 1 cun directly below the pupil, in the depression at the infraorbital foramen. Landmark: The infraorbital foramen can be felt by palpating downwards from the edge of the orbital bone, about 0.3 cun below the edge. |
|
|
||
|
ST-3 Juliao (Great Crevice) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
With the eyes looking directly forwards, this point is located directly below the pupil, level with the lower border of the ala nasi, on the lateral side of the naso-labial groove. |
|
|
||
|
ST-4 Dicang (Earth Granary) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.4 cun lateral to the corner of the mouth Landmark: This point lies in the continuation of the naso-labial groove; ask the patient to smile if the groove is not visible. |
|
|
||
|
ST-5 Daying (Great Welcome) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly anterior to the angle of the jaw, in a depression at the anterior border of the masseter muscle. Landmark: Ask the patient to clench the jaw before locating. |
|
|
Vigorous manipulation is contraindicated to avoid the risk of damaging the facial artery and vein. | |
|
ST-6 Jiache (Jaw Bone) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ghost Function: Ghost Bed |
Approximately 1 fingerbreadth anterior and superior to the angle of the jaw at the prominence of the masseter muscle. Landmark: Ask the patient to clench the jaw before locating. |
|
|
||
|
ST-7 Xiaguan (Below the Joint) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the lower border of the zygomatic arch, in the depression anterior to the condyloid process of the mandible Landmark: Although this point is needled with the mouth closed, it is helpful to ask the patient to open the mouth to better locate the condyloid process. If the finger rests on the condyloid process when the mouth is open, it will fall into Xiaguan ST-7 when the mouth is closed. |
|
|
||
|
ST-8 Touwei (Head Binding) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Blood channel, Bone channel Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the corner of the forehead, 4.5 cun lateral to Shenting GV-24 and 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline Landmark: There are three methods to locate this point: 1. Find the meeting point of a horizontal line drawn 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, and a vertical line drawn 0.5 cun posterior to the hairline of the temple.2. Locate Toulinqi GB-15 which lies directly above the pupil when the patient is looking directly forwards, and Shenting GV-24 which lies on the midline, 0.5 cun posterior to the anterior hairline. Touwei ST-8 lies on the continuation of a line drawn between these two points and twice its distance.3. 0.5 cun superior to the upper line of origin of the temporalis muscle, 0.5 cun posterior to a vertical line drawn directly above Taiyang (M-HN-9). |
|
|
||
|
ST-9 Renying (Man welcome) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Nila Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas, Window of Sky Function: Sea of Qi, Ren Ying (Humanities Welcome) |
Level with the tip of and 1.5 cun lateral to the laryngeal prominence, in the depression between the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle and the lateral border of the thyroid cartilage. Note: the carotid artery lies just deep to, and can be readily palpated at, the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. This point therefore lies between the carotid artery and the lateral border of the thyroid cartilage. Landmark: 1. Ask the patient to lie flat and remove any pillow. Palpate the laryngeal prominence, and then, laterally, the lateral border of the thyroid cartilage. A little more laterally than this, the carotid artery may be felt. Use the index finger of one hand to define and enlarge the space between the lateral border of the thyroid cartilage and the artery and needle into this space with the other hand.2. In females the laryngeal prominence is not as pronounced as in males. If it is indistinct, palpate the depression formed by the lower border of the hyoid bone and the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at the midline. The laryngeal prominence lies just below this. |
|
|
Care should be taken to avoid puncturing the carotid artery which must be palpated and then held laterally during needling, by using the index finger and thumb of one hand, above and below the point. This needling method should not be attempted by those who have not had appropriate clinical supervision. | |
|
ST-10 Shuitu (Water Prominence) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
To identify the anterior border of the muscle, ask the patient to turn their head away from the side to be needled, whilst you apply resistance at the chin. |
|
|
Care should be taken to avoid puncturing the carotid artery which must be palpated and then held laterally during needling, by using the index finger and thumb of one hand, above and below the point. This needling method should not be attempted by those who have not had appropriate clinical supervision. | |
|
ST-11 Qishe (Abode of Qi) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the root of the neck, superior to the medial end of the clavicle, directly below Renying ST-9 in the depression between the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Landmark: Palpation of the sternal and clavicular heads is made easier if the patient turns their head away from the side to be needled, whilst you apply resistance at the chin. |
|
|
||
|
ST-12 Quepen (Empty Basin) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the supraclavicular area, posterior to the superior border of the clavicle and at its midpoint, 4 cun lateral to the midline, on the mamillary line. Landmark: This point should be located and needled behind the clavicle. |
|
|
Deep or posterior insertion may injure the subclavian vessels or puncture the lung. | |
|
ST-13 Qihu (Qi Door) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the top of the chest, directly below Quepen ST-12, on the inferior border of the clavicle, 4 cun lateral to the midline, on the mamillary lin |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular insertion carries a substantial risk of puncturing the lung or injuring the subclavian vessels. | |
|
ST-14 Kufang (Storehouse) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the chest, in the first intercostal space, 4 cun lateral to the midline (Huagai CV-20), on the mamillary line. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the first intercostal space above it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. Note that the intercostal space curves upwards laterally, so that Kufang ST-14 will lie superior to the level of Huagai CV-20. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular insertion carries a substantial risk of puncturing the lung | |
|
ST-15 Wuyi (Room Screen) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the chest, in the second intercostal space, 4 cun lateral to the midline (Zigong CV-19), on the mamillary line. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. Note that the intercostal space curves upwards laterally, so that Wuyi ST-15 will lie superior to the level of Zigong CV-19. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular insertion carries a substantial risk of puncturing the lung | |
|
ST-16 Yingchuang (Breast Window) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the chest, in the third intercostal cun lateral to the midline (Yutang CV-18), on the mamillary line. Landmark: 1. First locate the second intercostal space (see Wuyi ST-15 above), then find the third intercostal space below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular insertion carries a substantial risk of puncturing the lung | |
|
ST-17 Ruzhong (Middle of the Breast) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Stanamula Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the centre of the nipple, in the fourth intercostal space, 4 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: Directly below the nipple, in the fifth intercostal space. |
||||
|
ST-18 Rugen (Root of the Breast) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Stanamula Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly below the nipple, in the fifth intercostal space. Landmark: 1. First locate the second intercostal space (see Wuyi ST-15 above), then find the fifth intercostal space, three spaces below it.2. In males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. On a woman, this point lies at the ,root of the breast, inferior to the breast tissue itself; in females the nipple is unlikely to lie 4 cun lateral to the midline and should not be used as a reference point |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular insertion carries a substantial risk of puncturing the lungs | |
|
ST-19 Burong (Not Contained) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 6 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Juque CV-14. Landmark: 1. The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle.2. In some patients with a narrow subcostal angle, this point may fall on the costal margin. The options then are to a. locate more medially, b. needle transversely on the costal margin, c. select a different point. |
|
|
Deep insertion may injure the heart on the left or the liver on the right if either of these organs is enlarged | |
|
ST-20 Chengman (Supporting Fullness) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 5 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Shangwan CV-13. Landmark: 1. The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle.2. In some patients with a narrow subcostal angle, this point may fall on the costal margin. The options then are to a. locate more medially, b. needle transversely on the costal margin, c. select a different point. |
|
|
1. In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity.2. deep needling at right Chengman ST-20 may penetrate an enlarged liver | |
|
ST-21 Liangmen (Beam Gate) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 4 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Zhongwan CV-12. Landmark: 1. The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle.2. In some patients with a narrow subcostal angle, this point may fall on the costal margin. The options then are to a. locate more medially, b. needle transversely on the costal margin, c. select a different point. |
|
|
1. In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity.2. deep needling at right Liangmen ST-21 may penetrate an enlarged liver. | |
|
ST-22 Guanmen (Pass Gate) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 3 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Jianli CV-11. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
ST-23 Taiyi (Supreme Unity) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 2 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Xiawan CV-10. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
ST-24 Huaroumen (Slippery Flesh Gate) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 1 cun superior to the umbilicus, level with Shuifen CV-9. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdorninis muscle. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
ST-25 Tianshu (Heaven Pivot) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Large Intestine organ |
On the abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the umbilicus Landmark: The 2 cun line on the abdomen is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
|
|
Single most important point for the treatment of the widest variety of intestinal disorders. | In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. |
|
ST-26 Wailing (Outer Mound) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 1 cun inferior to the umbilicus, level with Yinjiao CV-7. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
ST-27 Daju (The Great) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 2 cun inferior to the umbilicus, level with Shimen CV-5. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
ST-28 Shuidao (Water Passage) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 3 cun inferior to the umbilicus, level with Guanyuan CV-4. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
Deep insertion may penetrate the peritoneal cavity in thin patients or may penetrate a full bladder; the patient should therefore be asked to empty the bladder before needling. | |
|
ST-29 Guilai (Return) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline and 4 cun inferior to the umbilicus, level with Zhongji CV-3. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
Deep insertion may penetrate the peritoneal cavity in thin patients or may penetrate a full bladder; the patient should therefore be asked to empty the bladder before needling. | |
|
ST-30 Qichong (Rushing Qi) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Four Seas Function: Sea of Water & Grain |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline, level with the superior border of the pubic symphysis (Qugu CV-2). Landmark: The 2 cun line is located halfway between the midline and the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
Single most important point in the treatment of running piglet qi. | In thin patients, i. deep insertion in a superior direction may penetrate the peritoneal cavity or a full bladder (the patient should therefore be asked to empty the bladder before needling); ii. deep insertion in an inferior direction in the male may penetrate the spermatic cord. |
|
ST-31 Biguan (Thigh Gate) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper thigh, in a depression just lateral to the sartorius muscle, at the junction of a vertical line drawn downward from the anterior superior iliac spine, and a horizontal line drawn level with the lower border of the pubic symphysis. Landmark: The horizontal level may also be taken as approximately the most prominent point of the greater trochanter. |
|
|
||
|
ST-32 Fufu (Crouching Rabbit) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Urvi Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the thigh, on a line drawn between the lateral border of the patella and the anterior superior iliac spine, in a depression 6 cun proximal to the superior border of the patella. Landmark: Divide the distance between the prominence of the greater trochanter and the upper border of the patella into thirds; this point is located just superior to the junction of the lower and middle thirds. |
|
|
||
|
ST-33 Yinshi (Yin Market) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the thigh, on a line drawn between the lateral border of the patella and the anterior superior iliac spine, in a depression 3 cun proximal to the superior border of the patella. Landmark: 1. Locate Yinshi ST-33 one handbreadth proximal to the upper border of the patella.2. Locate Yinshi ST-33 midway between Futu ST-32 and the upper border of the patella. |
|
|
||
|
ST-34 Liangqiu (Ridge Mound) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the thigh, on a line drawn between the lateral border of the patella and the anterior superior iliac spine, in a depression 2 cun proximal to the superior border of the patella. Landmark: Since the height of the patella is measured as 2 cun, this point may be located one patella length above its superior border. |
|
|
||
|
ST-35 Dubi (Calf Nos) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Janu Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the knee, in the hollow formed when the knee is flexed, immediately below the patella and lateral to the patellar ligament. Landmark: This point is also known as lateral Xiyan, forming a pair with medial Xiyan (MN-LE-16) [see Extra points] which lies immediately below the patella and medial to the patellar ligament. |
|
|
||
|
ST-36 Zusanli (Leg Three Miles) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Avalambaka (Kapha), Kledaka (Kapha) |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Command, Lower He Sea, Four Seas, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Abdomen, Stomach organ, Sea of Water & Grain |
Below the knee, 3 cun inferior to Dubi ST-35, one finger breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. Landmark: 1. First locate Yanglingquan GB-34. Zusanli ST-36 lies one cun inferior to Yanglingquan GB-34 and one finger breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia.2. Locate one handbreadth below Dubi ST-35. |
|
|
Single most important point to treat disorders of stomach. | |
|
ST-37 Shangjuxu (Upper Great Void) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Lower He Sea, Four Seas Function: Large Intestine organ, Sea of Blood |
On the lower leg, 3 cun inferior to ST-36, one finger breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. Landmark: Locate one handbreadth below ST-36. |
|
|
||
|
ST-38 Tiaokou (Lines Opening) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower leg, midway between the tibioul femoral joint line (level with the popliteal crease) and the prominence of the lateral malleolus, one fingerbreadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. |
|
|
||
|
ST-39 Xiajuxu (Lower Great Void) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Lower He Sea, Four Seas Function: Small Intestine organ, Sea of Blood |
On the lower leg, 3 cun inferior to Shangjuxu ST-37, one finger-breadth lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia. Landmark: Divide the distance between the tibiofemoral joint line (level with the popliteal crease) and the prominence of the lateral malleolus into two equal parts. The midpoint is Tiaokou ST-38; Xiajuxu ST-39 is located 1 cun below Tiaokou ST-38. |
|
|
||
|
ST-40 Fenglong (Abundant Bulge) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On the lower leg, midway between the tibiofemoral joint line (level with the popliteal crease) and the lateral malleolus, two finger-breadths lateral to the anterior crest of the tibia (i.e. one finger-breadth lateral to Tiaokou ST-38). |
|
|
Single most important acupuncture point to transform phlegm in the body, whatever its origin. | |
|
ST-41 Jiexi (Stream Divide) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
On the ankle, level with the prominence of the lateral malleolus, in a depression between the tendons of extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus. Landmark: Ask the patient to extend the big toe against resistance in order to define the tendon of extensor hallucis longus, and locate Jiexi ST-41 lateral to this tendon and level with the prominence of the lateral malleolus. If in doubt, ask the patient to extend the remaining toes against resistance to define the tendon of extensor digitorum longus; Jiexi ST-41 is located between the two tendons. |
|
|
Anterior tibia1 vessels and nerve lie deep to this point. | |
|
ST-42 Chongyang (Rushing Yang) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurchashira Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base, Exit Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, in the depression formed by the junction of the second and third metatarsal bones and the cuneiform bones (second and third), 1.5 cun distal to Jiexi ST-41, on the line drawn between Jiexi ST-41 and Xiangu ST-43, at the point where the pulsation of the dorsalis pedis artery may be palpated. Landmark: 1. Run the finger proximally from Xiangu ST-43 towards Jiexi ST-41; the point is located in a depression approximately halfway between these two points.2. This point may lie either side of the medial slip of the extensor digitorum longus tendon, which runs to the second toe. |
|
|
Care should be takennot to puncture the dorsalis pedis artery which lies beneath this point | |
|
ST-43 Xiangu (Sunken Valley) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream) Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, between the second and third metatarsal bones, in a depression 1 cun proximal to Neiting ST-44. |
|
|
||
|
ST-44 Neiting (Inner Courtyard) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, between the second and third toes, 0.5 cun proximal to the margin of the web. |
|
|
||
|
ST-45 Lidui (Strict Exchange) Meridian: Stomach Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the second toe, at the junction of lines drawn along the lateral border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
SP-1 Yinbai (Hidden White) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Entry, Ghost Function: Ghost Fortress |
On the dorsal aspect of the big toe, at the junction of lines drawn along the medial border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
SP-2 Dadu (Great Metropolis) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
On the medial side of the big toe, in the depression distal and inferior to the first metatarso-phalangeal joint. Landmark: In the depression located by sliding the fingertip distally over the side of the ball of the foot. |
|
|
||
|
SP-3 Taibai (Supreme White) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Muscle channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base Function: NA |
On the medial side of the foot in the depression proximal and inferior to the head of the first metatarsal bone. Landmark: In the depression located by sliding the fingertip proximally over the side of the ball of the foot. |
|
|
||
|
SP-4 Gongsun (Grandfather Grandson) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled Function: Thrusting Vessel, Yin Wei Vessel |
On the medial side of the foot, in the depression distal and inferior to the base of the first metatarsal bone. Landmark: First locate Taibai SPC-3, then slide the finger proximally along the shaft of the first metatarsal bone until it reaches the depression at the base of the bone (approximately 1 cun). |
|
|
||
|
SP-5 Shangqiu (Shang Mound) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurchashira Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the medial side of the ankle, in the depression which lies at the junction of straight lines drawn along the anterior and inferior borders of the medial malleolus. |
|
|
||
|
SP-6 Sanyinjiao (Three Yin Intersection) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Menstruation channel, Lactation channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Apana (Vaata) |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the medial side of the lower leg, 3 cun superior to the prominence of the medial malleolus, in a depression close to the medial crest of the tibia. Landmark: This point is most readily located one handbreadth superior to the prominence of the medial malleolus. |
|
|
Single most important distal point in the treatment of any gynaecological, obstetrical or post-partum disorder whether characterised by deficiency of qi, blood, yin, yang or Kidney essence, failure of Spleen qi to hold the blood, or stagnation of qi, blood, dampness, damPC-heat or phlegm. | Pregnancy |
|
SP-7 Lougu (Dripping Valley) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the medial side of the lower leg, 3 cun superior to Sanyinjiao SPC-6, in a depression just posterior to the medial crest of the tibia. Landmark: This point is most readily located one handbreadth superior to Sanyinjiao SPC-6 |
|
|
||
|
SP-8 Diji (Earth Pivot) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the medial side of the lower leg, 3 cun inferior to Yinlingquan SPC-9, in a depression just posterior to the medial crest of the tibia. Landmark: 1. This point is most readily located one handbreadth inferior to Yinlingquan SPC-9.2. Alternatively, it may be located at the junction of the upper third and the lower two thirds of a line drawn between the popliteal crease and the prominence of the medial malleolus. |
|
|
||
|
SP-9 Yinlingquan (Yin Mound Spring) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea) Function: NA |
On the medial side of the lower leg, in a depression in the angle formed by the medial condyle of the tibia and the posterior border of the tibia. Landmark: 1. Run the finger in the groove posterior to the medial border of the tibia until it falls into the depression below the tibia1 condyle.2. This point lies at the same level as Y anglingquan GB-34. |
|
|
||
|
SP-10 Xuehai (Sea of Blood) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
2 cun proximal to the superior border of the patella, in the tender depression on the bulge of the vastus medialis muscle, directly above Yinlingquan SPC-9. Landmark: 1. Place the heel of your right palm on the inferior border of the patient left patella, with the fingers and thumb fully extended and the thumb at 45" to the index finger. This point is found beneath the tip of the thumb, directly above Yinlingquan SPC-9.2. Locate one patella height (2 cun) above the superior border of the patella, in the tender depression directly above Yinlingquan SPC-9. |
|
|
||
|
SP-11 Jimen (Winnowing Gate) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the medial side of the upper leg, 6 cun proximal to Xuehai SPC-10, on a line connecting Xuehai SPC-10 with Chongmen SPC-12. Landmark: 1. Locate two handbreadths superior to Xuehai SPC-10.2. Locate midway between the tibiofemoral joint line and Chongmen SPC-12. |
|
|
Deep needling may puncture the femoral artery | |
|
SP-12 Chongmen (Rushing Gate) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3.5 cun lateral to Qugu CV-2, on the lateral side of the femoral artery. Landmark: Palpate to locate the pulsation of the femoral artery, just over one handbreadth lateral to the midline, at the level of the upper border of the pubic symphysis. Locate Chongmen SPC-12 in the depression immediately lateral to this pulsation. |
|
|
Deep needling in a medial direction may puncture the femoral artery, and in a lateral direction, the femoral nerve. | |
|
SP-13 Fushe (Abode of the Fu) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 0.7 cun superior and 0.5 cun lateral to Chongmen SPC-12,4 cun lateral to the midline. This point is also defined as lying 4.3 cun inferior to Daheng SPC-15. Landmark: The 4 cun line is determined by the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
SP-14 Fujie (Abdomen Knot) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
The 4 cun line is determined by the palpable lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle at the level of the umbilicus. |
|
|
In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
SP-15 Daheng (Great Horizontal) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, in the depression at the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle level with the umbilicus. Landmark: This point is normally defined as 4 cun lateral to the midline, and on the abdomen the 4 cun line is located at the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
|
|
1. In thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity.2. Deep needling at this point may penetrate a substantially enlarged spleen or liver. | |
|
SP-16 Fuai (Abdomen Sorrow) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, in the depression at the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle, 3 cun superior to Daheng SPC-15. Note: in some patients with a narrow subcostal angle, this point may fall on the costal margin; the options then are to i. locate more medially, ii. needle transversely on the costal margin, iii. select a different point. Landmark: This point is normally defined as 4 cun lateral to the midline, and on the abdomen the 4 cun line is located at the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle. |
|
|
1. in thin patients deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity.2D deep needling at this point may penetrate an enlarged spleen. | |
|
SP-17 Shidou (Food Cavity) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Stanamula Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the chest, in the fifth intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. The intercostal spaces are most reliably counted downwards from the second intercostal space which lies immediately below the sternal angle. In males, the nipple almost invariably lies in the fourth intercostal space.2. The six cun line is located two cun lateral to the mamillary line. |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SP-18 Tianxi (Heavenly Stream) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the chest, in the fourth intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. The intercostal spaces are most reliably counted downwards from the second intercostal space which lies immediately below the sternal angle. In males, the nipple almost invariably lies in the fourth intercostal space.2. The six cun line is located two cun lateral to the mamillary line. |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SP-19 Xiongxiang (Chest Village) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Apastambha Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the chest, in the third intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. The intercostal spaces are most reliably counted downwards from the second intercostal space which lies immediately below the sternal angle. In males, the nipple almost invariably lies in the fourth intercostal space.2. The six cun line is located two cun lateral to the mamillary line. |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SP-20 Zhourong (Encircling Glory) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Stanarohita Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the chest, in the second intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it.2. The six cun line is located two cun lateral to the mamillary line.3. This point lies one intercostal space directly below Zhongfu LU-1. |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SP-21 Dabao (Great Wrapping) Meridian: Spleen Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Exit Function: NA |
On the mid-axillary line, in the seventh intercostal space. Note: some sources locate this point in the sixth intercostal space. Landmark: 1. The intercostal spaces are most reliably counted downwards from the second intercostal space which lies immediately below the sternal angle. In males, the nipple almost invariably lies in the fourth intercostal space.2. The mid-axillary line is drawn vertically down from the apex of the axilla (Jiquan HT-1). |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
GB-1 Tongziliao (Pupil Crevice) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Apanga Subdosha: NA |
Category: Entry Function: NA |
In the hollow on the lateral side of the orbital margin, approximately 0.5 cun lateral to the outer canthus. |
|
|
According to several modern texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion | |
|
GB-2 Tinghui (Meeting of Hearing) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the hollow between the intertragic notch posteriorly and the condyloid process of the mandible anteriorly. Locate this point with the mouth wide open. Landmark: In order to locate this point, ask the patient to open the mouth so that the condyloid process of the mandible slides forwards to reveal the depression. |
|
|
||
|
GB-3 Shangguan (Above the Joint) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Anterior to the ear, in a hollow above the upper border of the zygomatic arch, directly superior to Xiaguan ST-7. Landmark: First locate Xiaguan ST-7 at the lower border of the zygomatic arch, in the depression anterior to the condyloid process of the mandible. Then run the palpating finger superiorly over the zygomatic arch into the hollow. |
|
|
Traditionally emphasised that deep needling should be avoided at this point. | |
|
GB-4 Hanyan (Jaw Serenity) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the temporal region, within the hairline, one quarter of the distance between Touwei ST-8 and Qubin GB-7. |
|
|
||
|
GB-5 Xuanlu (Suspended Skull) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the temporal region, within the hairline, half the distance between Touwei ST-8 and Qubin GB-7. |
|
|
||
|
GB-6 Xuanli (Suspended Hair) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the temporal region, within the hairline, three quarters of the distance between Touwei ST-8 and Qubin GB-7. |
|
|
||
|
GB-7 Qubin (Crook of the Temple) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the temporal region, within the hairline, level with and one finger-breadth anterior to Jiaosun TH-20. Landmark: Jiaosun TH-20 is located directly level with the apex of the ear, when the ear is folded forwards. Fold the ear so that the posterior part of the upper helix directly covers the anterior part of the upper helix. Take care not to push the whole of the ear forwards. |
|
|
||
|
GB-8 Shuaigu (Leading Val ley) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the temporal region, in the slight depression 1 cun directly above the apex of the ear. Landmark: Fold the ear forward to define the apex. Fold the ear so that the posterior part of the upper helix directly covers the anterior part of the upper helix. Take care not to push the whole of the ear forwards. |
|
|
||
|
GB-9 Tianchong (Heavenly Rushing) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Above the ear, in the depression 0.5 cun posterior to Shuaigu GB-8. |
|
|
||
|
GB-10 Fubai (Floating White) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Posterior to the ear, along a curved line drawn from Tianchong GB-9 to Wangu GB-12 running within the hairline and more or less parallel to the line of the rim of the ear, in a depression about one third of the distance between Tianchong GB-9 and Wangu GB-12. |
|
|
||
|
GB-11 Touqiaoyin (Yin Portals of the Head) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Posterior to the ear, along a curved line drawn from Tianchong GB-9 to Wangu GB-12 running within the hairline and more or less parallel to the line of the rim of the ear, in a depression slightly greater than two thirds of the distance between Tianchong GB-9 and Wangu GB-12. |
|
|
||
|
GB-12 Wangu (Mastoid Process) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression just posterior and inferior to the mastoid process. Landmark: Place a finger on the prominence of the mastoid process then slide it posteriorly into the depression. |
|
|
||
|
GB-13 Benshen (Root of the Spirit) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the forehead, 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, two thirds of the distance between Shenting GV-24 and Touwei ST-8. Landmark: Some sources locate this point on the line directly above the outer canthus of the eye. |
|
|
||
|
GB-14 Yangbai (Yang White) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Avarta Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the forehead, 1 cun superior to the middle of the eyebrow, directly above the pupil when the eyes are looking straight ahead. Landmark: The distance between the glabella and the anterior hairline at the midline is measured as 3 cun. |
|
|
||
|
GB-15 Toulinqi (Head Governor of Tears) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the forehead, directly above Yangbai GB-14,0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, midway between Shenting GV-24 and Touwei ST-8. Landmark: The distance between the anterior and posterior hairlines in the midline is measured as 12 cun. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, the distance is measured as 15 cun between the glabella [point Yintang (M-HN-3)] and the posterior hairline; the location of the anterior hairline would thus be defined as one fifth of this distance. If the posterior hairline is indistinct, it can be measured as 1 cun inferior to Fengfu GV-16 which lies immediately below the external occipital protuberance. Note that the line of the anterior hairline away from the midline usually curves somewhat posteriorly, and this should be taken. into account when locating the Gall Bladder points on the scalp (Toulinqi GB-15 to Naokong GB-19). |
|
|
||
|
GB-16 Muchuang (Window of the Eye) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Toulinqi GB-15 and Fengchi GB-20, following the contour of the cranium, 1.5 cun posterior to Toulinqi GB-15. Landmark: 1. See location note for Toulinqi GB-15.2. First locate Toulinqi GB-15 0.5 cun posterior to the hairline and then locate Chengling GB-18 directly lateral to Baihui GV-20, on the line of the Gall Bladder channel. Muchuang GB-16 is then located one third of the distance between Toulinqi GB-15 and Chengling GB-18 |
|
|
||
|
GB-17 Zhengying (Upright Nutrition) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the parietal region, on a curved line drawn between Toulinqi GB-15 and Fengchi GB-20, following the contour of the cranium, 1.5 cun posterior to Muchuang GB-16. Landmark: 1. See location note for Toulinqi GB-15.2. First locate Toulinqi GB-15,0.5 cun posterior to the hairline, and then locate Chengling GB-18 directly lateral to Baihui GV-20, on the line of the Gall Bladder channel. Zhengying GB-17 is then located two thirds of the distance between Toulinqi GB-15 and Chengling GB-18. |
|
|
||
|
GB-18 Chengling (Support Spirit) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the parietal region, on a curved line drawn between Toulinqi GB-15 and Fengchi GB-20, following the contour of the cranium, 1.5 cun posterior to Zhengying GB-17. Landmark: Locate directly lateral to Baihui GV-20, on the line of the Gall Bladder channel (2.25 cun from the midline). |
|
|
||
|
GB-19 Naolong (Brain Hollow) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the occipital region, directly above Fengchi GB-20, level with Naohu GV-17. Landmark: 1. Locate Naohu GV-17 1.5 cun directly above Fengfu GV-16, in the depression directly superior to the external occipital protuberance.2. Alternatively (if the external occipital protuberance is indistinct) locate Naokong GB-19 one quarter of the distance between Fengchi GB-20 and Chengling GB-18. |
|
|
||
|
GB-20 Fengchi (Wind Pool) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Sira Matrika Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Below the occiput, approximately midway between Fengfu GV-16 and Wangu GB-12, in the hollow between the origins of the sternomastoid and trapezius muscles. Landmark: i. Locate close to the base of the skull; ii. This point is normally located as the most tender point of the hollow. |
|
|
Single most important point in the treatment of headache, whatever the aetiology and whichever the involved channels. | Deeper needling may damage the spinal cord; iii. Joined by through-needling to contralateral Fengchi GB-20,2 to 3 cun. |
|
GB-21 Jianjing (Shoulder Well) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Sira Matrika, Amsa Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Midway between Dazhui GV-14 and the tip of the acromion, at the crest of the trapezius muscle. Landmark: i. The crest refers to the highest point of the trapezius muscle on the sagittal (anterior-posterior) plane; ii. This point is normally located at the point of maximum tenderness. |
|
|
PregnancyPerpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax | |
|
GB-22 Yuanye (Armpit Abyss) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the mid-axillary line, in the fifth intercostal space, approximately 3 cun inferior to the apex of the axilla, at the level of the nipple. Landmark: 1. The mid-axillary line is drawn vertically down from the apex of the axilla (Jiquan HT-1).2.. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, locate the second intercostal space below it and then locate the fifth intercostal space, three spaces below that; in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. Some sources locate this point in the fourth intercostal space. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular needling may induce a pneumothoraxAccording to several classical texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion | |
|
GB-23 Zhejin (Flank Sinews) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Below the axilla in the fifth intercostal space, 1 cun anterior to Yuanye GB-22, approximately at the level of the nipple. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular needling may induce a pneumothorax. | |
|
GB-24 Riyue (Sun and Moon) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Gallbladder organ |
On the anterior chest wall, in the seventh intercostal space, directly below the nipple, 4 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, locate the second intercostal space below it and then locate the seventh intercostal space, five spaces below that. In males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space. |
|
|
Deep or perpendicular needling may induce a pneumothorax. | |
|
GB-25 Jingmen (Capital Gate) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front Function: Kidney organ |
Below the lateral aspect of the ribcage, anterior and inferior to the free end of the 12th rib. Landmark: To locate the free end of the twelfth rib, first place the entire hand on the upper abdomen and with gentle finger pressure palpate downwards along the costal margin, until the end of the eleventh rib is located just above the level of the umbilicus. Then palpate further along the inferior margin of the ribcage until the free end of the twelfth rib is located in the lateral lumbar region. |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
GB-26 Daimai (Girdling Vessel) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Parshvasandhi Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly below Zhangmen LV-13 (anterior and inferior to the free end of the eleventh rib), level with the umbilicus. Landmark: 1. To locate the free end of the eleventh rib, place the entire hand on the upper abdomen and with gentle finger pressure palpate downwards along the costal margin, until the end of the eleventh rib is located just above the level of the umbilicus.2. The free end of the eleventh rib usually lies on or near the mid-axillary line which is drawn vertically down from the apex of the axilla (Jiquan HT-1). |
|
|
In thin subjects, deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
GB-27 Wushu (Five Pivots) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression just anterior to the anterior superior iliac spine, approximately level with Guanyuan CV-4 (3 cun below the umbilicus). Landmark: To locate the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), place the hand on the lateral part of the lower abdomen, below the level of the umbilicus. The ASIS is then readily palpated as the pronounced bony prominence. Alternatively, follow the ridge of the iliac crest and palpate the ASIS as its anterior prominence. |
|
|
||
|
GB-28 Weidao (Linking Path) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 cun anterior and inferior to Wushu GB-27 Landmark: To locate the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS), place the hand on the lateral part of the lower abdomen, below the level of the umbilicus. The ASIS is then readily palpated as the pronounced bony prominence. Alternatively, follow the ridge of the iliac crest and palpate the ASIS as its anterior prominence. |
|
|
||
|
GB-29 Juliao (Stationary Crevice) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Reproductive fluid channel, Urinary channel, Menstruation channel Part of Marma: Kukundara, Nitamba Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the hip joint, at the midpoint of a line drawn between the anterior superior iliac spine and the prominence of the greater trochanter. Landmark: 1. To locate the anterior superior iliac spine see Wushu GB-27.2. To accurately palpate the prominence of the greater trochanter place one hand over the lateral aspect of the hip joint at the level of the perineum, and with the other hand rotate the foot in order to feel the movement of the prominence of the greater trochanter. 3. Alternatively, flex the hip joint and locate Juliao GB-29 at the lateral end of the crease thus formed. |
|
|
||
|
GB-30 Huantiao (Jumping Circle) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
On the postero-lateral aspect of the hip joint, one third of the distance between the prominence of the greater trochanter and the sacro-coccygeal hiatus (Yaoshu GV-2). Landmark: 1. This point may most readily be located (and needled) with the patient lying on their side.2. To accurately palpate the prominence of the greater trochanter place one hand over the lateral aspect of the hip joint at the level of the perineum, and with the other hand rotate the foot in order to feel the movement of the prominence of the greater trochanter; iii. The sacro-coccygeal hiatus is located in-between the cornua of the sacrum and coccyx, in the depression inferior to the fourth sacral spinous process if this is palpable. Note, however, that the sacrococcygeal hiatus may sometimes extend as high as the level of the third sacral foramina |
|
|
Single most important point for the treatment of sciatica. | |
|
GB-31 Fengshi (Wind Market) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the thigh, directly below the greater trochanter, 7 cun superior to the popliteal crease. Landmark: 1. To palpate the prominence of the greater trochanter place a hand over the lateral aspect of the hip joint at the level of the perineum.2. The distance between the prominence of the greater trochanter and the popliteal crease is 19 cun, thus Fengshi GB-31 is located at the tender point approximately 1 cun proximal to the junction of the upper two thirds and lower third of this line.3. This point is traditionally described as being located where the tip of the middle finger reaches when a person stands erect with their arms extended by their sides, although the significant differences found in body proportions render this unreliable. |
|
|
||
|
GB-32 Zhongdu (Middle Ditch) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the thigh, 2 cun inferior to Fengshi GB-31. Landmark: 1. First locate Fengshi GB-31 (see above) and then locate Zhongdu GB-32, 2 cun inferior to it.2. The distance between the prominence of the greater trochanter and the popliteal crease is 19 cun, thus Zhongdu GB-32 is located at the tender point just proximal to the junction of the upper three quarters and the lower quarter of this line. |
|
|
||
|
GB-33 Xiyangguan (Knee Yang Gate) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the knee, in the depression above the lateral epicondyle of the femur, between the femur and tendon of biceps femnrk. Landmark: Starting above the knee joint, run a finger down the lateral aspect of the thigh in the groove between the femur and the tendon of biceps femoris, until the finger falls into the depression just proximal to the lateral epicondyle of the femur. |
|
|
According to several classical texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion | |
|
GB-34 Yangglingquan (Yang Mound Spring) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Janu Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Hui Meeting/Gathering, Lower He Sea, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Sinews, Gallbladder organ |
Below the lateral aspect of the knee, in the tender depression approximately 1 cun anterior and inferior to the head of the fibula. Landmark: To avoid confusing the head of the fibula with the tibia1 condyle, slide your fingers up the lateral aspect of the lower leg until the soft tissue of the musculature gives way to the bony prominence of the head of the fibula. |
|
|
Single most important point to treat disorders of gallbladder. | |
|
GB-35 Yangjiao (Yang Intersection) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: Yang Wei Vessel |
On the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 7 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, in the depression at the posterior border of the fibula. Landmark: 1. The distance between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the popliteal crease is 16 cun; locate Yangjiao GB-35 one cun distal to the midpoint of this line2. Above the region of Xuanzhong GB-39, the fibula is not easily palpable because it is covered by the peroneus brevis muscle; therefore feel for the posterior border of the fibula above the malleolus where it is easily palpable and extend a line towards the head of the fibula. |
|
|
||
|
GB-36 Waiqiu (Outer Hill) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 7 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, at the anterior border of the fibula. Landmark: 1. The distance between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the popliteal crease is 16 cun; locate Waiqiu GB-36 one cun distal to the midpoint of this line.2. Above the region of Xuanzhong GB-39, the fibula is not easily palpable because it is covered by the peroneus brevis muscle; therefore feel for the anterior border of the fibula above the ankle joint where it is easily palpable and extend a line towards the head of the fibula. |
|
|
||
|
GB-37 Guangming (Bright Light) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 5 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, at the anterior border of the fibula. Landmark: 1. The distance between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the popliteal crease is 16 cun; locate Guangming GB-37 just distal to the junction of the upper two thirds and lower third of this line.2. Above the region of Xuanzhong GB-39, the fibula is not easily palpable because it is covered by the peroneus brevis muscle; therefore feel for the anterior border of the fibula above the ankle joint where it is easily palpable and extend a line towards the head of the fibula. |
|
|
||
|
GB-38 Yangfu (Yang Assistance) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the lateral aspect of the lower leg, 4 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, at the anterior border of the fibula. Landmark: 1. The distance between the tip of the lateral malleolus and the popliteal crease is 16 cun; locate Yangfu GB-38 at the junction of the upper three quarters and lower quarter of this line.2. Above the region of Xuanzhong GB-39, the fibula is not easily palpable because it is covered by the peroneus brevis muscle; therefore feel for the anterior border of the fibula above the ankle joint where it is easily palpable and extend a line towards the head of the fibula. |
|
|
||
|
GB-39 Xuanzhong (Suspended Bell) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Gulpha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Hui Meeting/Gathering Function: Marrow |
Above the ankle joint, 3 cun superior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus, between the posterior border of the fibula and the tendons of peroneus longus and brevis. Landmark: Locate one handbreadth proximal to the prominence of the lateral malleolus. |
|
|
||
|
GB-40 Qiuxu (Mound of Ruins) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base Function: NA |
At the ankle joint, in the depression anterior and inferior to the lateral malleolus. Landmark: Locate at the junction of lines drawn along the anterior and inferior borders of the lateral malleolus. |
|
|
||
|
GB-41 Zulinqi (Foot Governor of Tears) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Exit, Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled Function: Belt Vessel, Yang Wei Vessel |
In the depression distal to the junction of the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones, on the lateral side of the tendon of m. extensor digitorumlongus (branch to little toe). Landmark: Ask the patient to abduct their little toe in order to make the branch of m. extensor digitorum longus more prominent. Run a finger from Xiaxi GB-43 towards the ankle, along the interspace between the fourth and fifth metatarsals until it passes over this branch into the significant depression immediately beyond the tendon. |
|
|
||
|
GB-42 Diwuhui (Earth Five Meetings) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurcha Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Between the 4th and 5th metatarsal bones, in the depression proximal to the metatarsal heads, on the medial side of the tendon of m. extensor digitorum longus (branch to little toe). Landmark: Ask the patient to abduct their little toe in order to make the branch of m. extensor digitorum longus more prominent. Run a finger from Xiaxi GB-43 towards the ankle, along the interspace between the fourth and fifth metatarsals, until it encounters the significant depression immediately before the tendon. |
|
|
Classical sources say that this point should not be treated by moxibustion otherwise emaciation and death will follow within three years. Modern sources however agree that there are no contraindications to moxibustion. | |
|
GB-43 Xiaxi (Clamped Stream) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
Between the fourth toe and the little toe, 0.5 cun proximal to the margin of the web. |
|
|
||
|
GB-44 Zuqiaoyin (Yin Portals of the Foot) Meridian: Gallbladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well) Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the 4th toe, at the junction of lines drawn along the lateral border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
LV-1 Dadun (Big Mound) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Entry Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the big toe, at the junction of lines drawn along the lateral border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. Landmark: Some sources (including the Spiritual Pivot) locate this point on the dorsal aspect of the big toe, midway between the lateral corner of the nail (i.e. the location above) and the interphalangeal joint, 0.4 cun proximal to the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
LV-2 Xingjian (Moving Between) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Sweat channel Part of Marma: Kshipra Subdosha: Ranjaka (Pitta) |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, between the first and second toes, 0.5 cun proximal to the margin of the web. |
|
|
||
|
LV-3 Taichong (Great Rushing) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Sweat channel Part of Marma: Kshipra, Kurcha Subdosha: Alochaka (Pitta) |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, in the hollow distal to the junction of the first and second metatarsal bones. Landmark: Run a finger from Xingjian LV-2 along the interspace between the first and second metatarsal bones towards the ankle, into the pronounced depression before the junction of the bases of the first and second metatarsals. |
|
|
||
|
LV-4 Zhongfeng (Middle Seal) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
On the ankle, anterior to the prominence of the medial malleolus, in the significant depression just medial to the tendon of tibialis anterior when the ankle is extended (dorsiflexed). Landmark: 1. It is important to extend (dorsiflex) the ankle (by drawing the toes upwards towards the shin) before locating this point.2. This point is also described as midway between Shangqiu SPC-5 and Jiexi ST-41; iii. The distance of this point from the prominence of the medial malleolus is given variously in classical sources as either 1 or 1.5 cun. |
|
|
||
|
LV-5 Ligou (Woodworm Canal) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
5 cun above the prominence of the medial malleolus, immediately posterior to the medial crest of the tibia, in the depression between the medial crest of the tibia and the gastrocnemius muscle. Landmark: Divide the distance between the tip of the medial malleolus and the popliteal crease into thirds; Ligou LV-5 is located at the junction of the distal third and proximal two thirds. |
|
|
||
|
LV-6 Zhongdu (Central Capital) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
7 cun above the prominence of the medial malleolus, immediately posterior to the medial border of the tibia, in the depression between the medial border of the tibia and the gastrocnemius muscle. Landmark: Divide the distance between the tip of the medial malleolus and the popliteal crease into half and locate Zhongdu LV-6 at 0.5 cun distal to the midpoint. |
|
|
||
|
LV-7 Xiguan (Knee Joint) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Posterior and inferior to the medial condyle of the tibia, 1 cun posterior to Yinlingquan SPC-9. Landmark: Locate Yinlingquan SPC-9 in the depression in the angle formed by the medial condyle of the tibia and the posterior border of the tibia, and then locate Xiguan LV-7 one cun posterior to it. |
|
|
||
|
LV-8 Ququan (Spring at the Crook) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
Just superior to the medial end of the popliteal crease, in the depression anterior to the tendons of m. semitendinosus and m. semimembranosus, about 1 cun anterior to Yingu KD-10. Landmark: 1. It is helpful to flex the knee to locate the popliteal crease and identify the tendons of m. semitendinosus and m. semimembranosus, although the point may subsequently be needled with a pillow under the leg to semi-flex it.2. The tendon of semitendinosus, which lies posteriorly to semimembranosus, is the most prominent of the two tendons. |
|
|
||
|
LV-9 Yinbao (Yin Wrapping) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly superior to the medial epicondyle of the femur, 4 cun superior to Ququan LV-8, in the cleft between m. vastus medialis and m. sartorius. Landmark: Locate one patella height (2 cun) above the superior border of the patella, in the tender depression between m. vastus medialis and m. sartorius, directly above Ququan LV-8. |
|
|
||
|
LV-10 Zuwuli (Leg Five Miles) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun inferior to Qichong ST-30 on the anterior border of m. adductor longus. Landmark: 1. Qichong ST-30 is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline, level with the superior border of the pubic symphysis (Qugu CV-2).2. Measure the 3 cun as one handbreadth inferior to Qichong ST-30.3. The tendon of origin of adductor longus arises from the pubic bone and is identified as the most prominent tendon in the groin. |
|
|
||
|
LV-11 Yinlian (Yin Corner) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Lohitaksha Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
2 cun inferior to Qichong ST-30 on the anterior border of m. adductor longus Landmark: 1. Qichong ST-30 is located on the lower abdomen, 2 cun lateral to the midline, level with the superior border of the pubic symphysis (Qugu CV-2).2. The tendon of origin of adductor longus arises from the pubic bone and is identified as the most prominent tendon in the groin. |
|
|
||
|
LV-12 Jimai (Urgent Pulse) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1 cun inferior and 2.5 cun lateral to Qugu CV-2, in the crease of the groin, medial to the femoral vein. Landmark: Locate the pulsation of the femoral artery in the groin, approximately midway between the pubic symphysis and the anterior superior iliac spine. The femoral vein runs along the medial side of the artery and is approximately one fingerbreadth in diameter. Jimai LV-12 is then located just medial to the vein on the groin crease. |
|
|
Care should be taken to avoid penetrating the femoral vein. The Essential Questions advises that this point should be treated by moxibustion rather than needling. Modern texts, however, say that moxibustion is contraindicated due to the proximity of this point both to the femoral vessels and to the pubic hair, and that the point should rather be treated by needling. | |
|
LV-13 Zhangmen (Completion Gate) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front, Hui Meeting/Gathering Function: Spleen organ, Yin Organs |
Directly anterior and inferior to the free end of the eleventh rib Landmark: 1. To locate the free end of the eleventh rib, first place the entire hand on the upper abdomen and with gentle finger pressure palpate downwards along the costal margin, until the end of the eleventh rib is located just above the level of the umbilicus.2. This point usually lies on or near the mid-axillary line which is drawn vertically down from the apex of the axilla (Jiquan HT-I). |
|
|
||
|
LV-14 Qimen (Cycle Gate) Meridian: Liver Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front, Exit Function: Liver organ |
On the mamillary line, in the sixth intercostal space, 4 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it and count down to the sixth space.2. Note that there is another point known as lower Qimen located on the mamillary line, 4 cun lateral to the midline, on the lower border of the tenth rib. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique insertion carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-1 Jingming (Bright Eyes) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Entry Function: NA |
0.1 cun medial and superior to the inner canthus of the eye, near the medial border of the orbit. |
|
|
||
|
BL-2 Zanzhu (Gathered Bamboo) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Superior to the inner canthus, in a depression on the eyebrow, close to its medial end. Landmark: Palpate laterally along the eyebrow from its medial end and feel for the hollow directly above Jingming UB-1. This point is often found to be tender on palpation. |
|
|
||
|
BL-3 Meichong (Eyebrows Pouring) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly superior to Zanzhu UB-2, 0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, level with Shenting GV-24. Landmark: The distance between the anterior and posterior hairlines is measured as 12 cun. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, the distance is measured as 15 cun between the glabella [point Yintang (M-HN-3)] and the posterior hairline; the location of the anterior hairline would thus be defined as one fifth of this distance. If the posterior hairline is indistinct, it can be measured as 1 cun inferior to Fengfu GV-16 which lies immediately below the external occipital protuberance. |
|
|
||
|
BL-4 Quchai (Crooked Curve) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 cun within the anterior hairline, 1.5 cun lateral to Shenting GV-24 and one third of the distance between Shenting GV-24 and Touwei ST-8. Landmark: To locate the anterior hairline if indistinct, see location note for Meichong UB-3. |
|
|
||
|
BL-5 Wuchu (Fifth Place) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shringataka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 cun directly posterior to Quchai UB-4, l cun anterior hairline, and 1.5 cun lateral to Shangxing GV-23. Landmark: 1. To locate the anterior hairline if indistinct, see location note for Meichong UB-32. Note that the distance from the anterior hairline at the midline to Baihui GV-20 is 5 cun. |
|
|
||
|
BL-6 Chengguang (Receiving Light) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cun posterior to Wuchu UB-5,2.5 cun within the anterior hairline and 1.5 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. To locate the anterior hairline if indistinct, see location note for Meichong UB-3.2. Note that the distance from the anterior hairline at the midline to Baihui GV-20 is 5 cun. |
|
|
||
|
BL-7 Tongtian (Heavenly Connection) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cun posterior to Chengguang UB-6 and 4 cun within the anterior hairline, 1.5 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. The distance between the glabella (Yintang M-HN-3) and the lower border of the occipital protuberance (Fengfu GV-16) is measured as 14 cun. Tongtian UB-7 is located 1.5 cun lateral to the midpoint of this line.2. Tongtian UB-7 can also be located 1 cun anterior and 1.5 cun lateral to Baihui GV-20. |
|
|
||
|
BL-8 Luoque (Declining Connection) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cun posterior to Tongtian UB-7, and 5.5 cun within the anterior hairline, 1.5 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. Luoque UB-8 is most easily located 1.5 cun lateral to and 0.5 cun posterior to Baihui GV-20.2. To locate the anterior hairline if indistinct, see location note for Meichong UB-3.3. Note that the distance from the anterior hairline at the midline to Baihui GV-20 is 5 cun |
|
|
||
|
BL-9 Yuzhen (Jade Pillow) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.3 cun lateral to Naohu GV-17 (which is located in the depression superior to the external occipital protuberance, 1.5 cun superior to Fengfu GV-16). |
|
|
||
|
BL-10 Tianzhu (Celestial Pillar) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian Zhu (Heavens Pillar) |
On the lateral aspect of the trapezius muscle, 1.3 cun lateral to Yamen GV-15. Landmark: First locate Fengfu GV-16 directly below the occipital protuberance in a depression between the trapezius on both sides. Then locate Yamen GV-15 which is 0.5 cun below Fengfu GV-16 in the depression 0.5 cun within the hairline. Now locate Tianzhu UB-10, 1.3 cun lateral to Yamen GV-15. |
|
|
||
|
BL-11 Dazhu (Great Shuttle) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Amsaphalaka Subdosha: NA |
Category: Hui Meeting/Gathering, Four Seas Function: Bones, Sea of Blood |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the first thoracic vertebra (T1). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax | |
|
BL-12 Fengmeng (Wind Gate) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra (T2). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-13 Feishu (Lung Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Lung organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra (T3). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-14 Jueyinshu (Jueyin Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Pericardium organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-15 Xinshu (Heart Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Heart organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of fhe fifth thoracic vertebra (T5). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-16 Dushu (Governor Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Governing Vessel |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the sixth thoracic vertebra (T6). Landmark: Locate at the visible hghest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-17 Geshu (Diaphragm Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back, Hui Meeting/Gathering Function: Diaphragm organ, Blood |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra (T7). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Single most important point for the treatment of any disorder arising from blood heat, blood stasis or blood deficiency. | Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. |
|
BL-18 Ganshu (Liver Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Brihati Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Liver organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vertebra (T9). Landmark: Locate at the visible hghest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-19 Danshu (Gall bladder Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Gallbladder organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the tenth thoracic vertebra (T10). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-20 Pishu (Spleen Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Spleen organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-21 Weishu (Stomach Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Stomach organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the twelfth thoracic vertebra (T12). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-22 Sanjiosshu (Sanjiao Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Triple Heater organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the first lumbar vertebra (Ll). Landmark: Locate at the visible lughest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-23 Shenshu (Kidney Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Kidney organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra (L2). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular needling carries a risk of injuring the kidney. | |
|
BL-24 Qihaishu (Sea of Qi Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Sea of Qi |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the third lumbar vertebra (L3). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
Perpendicular needling or oblique needling away from the spine carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-25 Dachangshu (Large Intestine Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Large Intestine organ |
1.5 cunlateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth lumbar vertebra (L4). Landmark: Locate at the visiblehghest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
||
|
BL-26 Guanyuanshu (Gate of Origin Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Gate of Source |
1.5 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the fifth lumbar vertebra (L5). Landmark: Locate at the visible lughest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
||
|
BL-27 Xiaochangshu (Small Intestine Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Small Intestine organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the midline, at the level of the first posterior sacral foramen Landmark: As the inner line of the Bladder channel on the back descends towards the sacrum, it runs closer to the midline; the 1.5 cun measurement in this area, therefore, will be relatively shorter. |
|
|
||
|
BL-28 Pangguangshu (Bladder Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Basti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Bladder organ |
1.5 cun lateral to the midline, at the level of the second posterior sacral foramen. Landmark: As the inner line of the Bladder channel on the back descends towards the sacrum, it runs closer to the midline; the 1.5 cun measurement in this area, therefore, will be relatively shorter. |
|
|
||
|
BL-29 Zhonglusu (Mid-Spine Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Center Back Muscles |
1.5 cun lateral to the midline, at the level of the third posterior sacral foramen. Landmark: As the inner line of the Bladder channel on the back descends towards the sacrum, it runs closer to the midline; the 1.5 cun measurement in this area, therefore, will be relatively shorter. |
|
|
||
|
BL-30 Baihuanshu (White Ring Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Urinary channel, Menstruation channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: White Ring |
1.5 cun lateral to the midline, at the level of the fourth posterior sacral foramen. Landmark: As the inner line of the Bladder channel on the back descends towards the sacrum, it runs closer to the midline; the 1.5 cun measurement in this area, therefore, will be relatively shorter. |
|
|
||
|
BL-31 Shangliao (Upper Crevice) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Katikataruna Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Over the first posterior sacral foramen. |
|
|
||
|
BL-32 Ciliao (Second Crevice) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Over the second posterior sacral foramen. |
|
|
||
|
BL-33 Zhongliao (Middle Crevice) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Over the third posterior sacral foramen. |
|
|
||
|
BL-34 Xialiao (Lower Crevice) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Over the fourth posterior sacral foramen. |
|
|
||
|
BL-35 Huiyang (Meeting of Yang) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Apana (Vaata) |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 cun lateral to the Governing vessel, level with the tip of the coccyx. |
|
|
||
|
BL-36 Chengfu (Hold and Support) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Urinary channel, Menstruation channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Just below the buttock, on a line directly superior to Weizhong UB-40, in the centre of the transverse gluteal crease in a depression between the hamstring muscles. |
|
|
||
|
BL-37 Yinmen (Gate of Abundance) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Urvi Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the back of the thigh, in the depression between the hamstring muscles, 6 cun distal to Chengfu UB-36, and 8 cun proximal to Weizhong UB-40, on the line connecting Chengfu UB-36 and Weizhong UB-40. Landmark: 1. Locate two handbreadths distal to Chengfu UB-36.2. Find the midpoint between Chengfu UB-36 and Weizhong UB-40 and locate Yinmen UB-37 in the depression 1 cun proximal to this. |
|
|
||
|
BL-38 Fuxi (Floating Cleft) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the back of the knee, 1 cun superior to Weiyang UB-39, on the medial side of the tendon of biceps femoris. Landmark: Locate with the knee slightly flexed |
|
|
||
|
BL-39 Weiyang (Outside of the Crook) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Lower He Sea Function: Triple Heater organ |
At the back of the knee, on the popliteal crease and towards its lateral end, in the depression medial to the tendon of biceps fernoris. Landmark: Locate with the knee slightly flexed. |
|
|
||
|
BL-40 Weizhong (Middle of the Crook) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Water Metabolism channel Part of Marma: Janu Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Command, Lower He Sea, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Lumbar Region, Bladder organ |
At the back of the knee, on the popliteal crease, in a depression midway between the tendons of biceps femoris and semitendinosus. Landmark: Locate with the knee slightly flexed. |
|
|
Tibia1 nerve and the popliteal artery and vein lie deep to this point. | |
|
BL-41 Fufen (Attached Branch) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Amsaphalaka Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the second thoracic vertebra (T2) and level with Fengmen UB-12 Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-42 Pohu (Door of the Corporeal Soul) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra (T3) and level with Feishu UB-13. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-43 Gaohuangshu (Vital Region Shu) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Shu/Back Function: Vital Region |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the fourth thoracic vertebra (T4) and level with Jueyinshu UB-14. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-44 Shentang (Hall of the Spirit) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebra (T5) and level with Xinshu UB-15. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-45 Yixi (Yixi) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the sixth thoracic vertebra (T6) and level with Dushu UB-16 Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax | |
|
BL-46 Geguan (Diaphragm Gate) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the seventh thoracic vertebra (T7) and level with Geshu UB-17. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax | |
|
BL-47 Hunmen (Gate of the Ethereal Soul) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Brihati Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 curt lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the ninth thoracic vertebra (T9) and level with Ganshu UB-18. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
||
|
BL-48 Yanggang (Yang Key Link) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the tenth thoracic vertebra (T10) and level with Danshu UB-19. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
||
|
BL-49 Yishe (Abode of Thought) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the eleventh thoracic vertebra (T11) and level with Pishu UB-20. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-50 Weicang (Stomach Granary) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the twelfth thoracicvertebra (T12) and level with WeishuUB-21. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or deep oblique needling in a medial direction carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax. | |
|
BL-51 Huangmen (Vitals Gate) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the first lumbar vertebra (Ll) and level with Sanjiaoshu UB-22. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular needling carries a risk of injuring the kidney | |
|
BL-52 Zhishi (Residence of the Will) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, level with the lower border of the spinous process of the second lumbar vertebra (L2) and level with Shenshu UB-23. Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular needling carries a risk of injuring the kidney. | |
|
BL-53 Baohuang (Bladder Vitals) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Katikataruna Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the midline, at the level of the spinous process of the second sacral vertebra. Landmark: 1. When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula.2. Alternatively this point may be located midway between the midline and the lateral edge of the buttock, when the lateral edge is firmly pressed in with the palm of the hand. |
|
|
||
|
BL-54 Zhibian (Order Limit) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Nitamba Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the buttock, in the depression 3 cun lateral to the sacro-coccygeal hiatus. Landmark: 1. The sacro-coccygeal hiatus is the depression between the bony prominences of the sacral and coccygeal cornua (just below the spinous process of the fourth sacral vertebra if this is palpable).2. When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula.3. Alternatively this point may be located midway between the midline and the lateral edge of the buttock, when the lateral edge is firmly pressed in with the palm of the hand. |
|
|
||
|
BL-55 Heyang (Confluence of Yang) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower leg, 2 cuninferior to Weizhong UB-40, on the line connecting Weizhong UB-40 and Chengshan UB-57, in the depression between the two heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. Landmark: First locate Chengshan UB-57. Then locate Heyang UB-55 at one quarter of the distance between Weizhong UB-40 and Chengshan UB-57. |
|
|
||
|
BL-56 Chengjin (Support the Sinews) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower leg, 5 cun below Weizhong UB-40 and midway between Heyang UB-55 and Chengshan UB-57, in the centre of the belly of the gastrocnemius muscle. Landmark: First locate Chengshan UB-57 then Heyang UB-55. Chengjin UB-56 is located midway between these two points. |
|
|
||
|
BL-57 Chenshan (Support the Mountain) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Food channel Part of Marma: Indrabasti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
On the lower leg, in the depression formed below the bellies of the gastrocnemius muscle when the muscle is flexed, approximately 8 cun distal to Weizhong UB-40, i.e. midway between Weizhong UB-40 and Kunlun UB-60. Landmark: Run your finger upwards from the Achilles tendon along the midline until it falls into the depression formed between the two origins of the gastrocnemius muscle bellies; this depression may be easier to palpate if you ask the patient to press the ball of their foot against the resistance of your hand. |
|
|
||
|
BL-58 Feiyang (Soaring Upwards) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On the lower leg, 7 cun directly superior to Kunlun UB-60, lateral to and approximately 1 cun inferior to Chengshan UB-57. |
|
|
||
|
BL-59 Fuyang (Instep Yang) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Gulpha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: Yang Qiao Vessel |
On the lower leg, 3 cun directly superior to Kunlun UB-60. Landmark: 1. Locate one handbreadth proximal to Kunlun UB-60.2. This point is located in the depression between the Achilles tendon and the peroneal tendons. |
|
|
||
|
BL-60 Kunlun (Kunlun Mountains) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river), Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
Behind the ankle joint, in the depression between the prominence of the lateral malleolus and the Achilles tendon. Landmark: Locate in the centre of the depression, midway between the prominence of the lateral malleolus and the posterior border of the Achilles tendon. |
|
|
Pregency | |
|
BL-61 Pucan (Servants Request) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the foot, 1.5 cun inferior to Kunlun UB-60, in a tender depression on the calcaneum. Landmark: The distance between the prominence of the lateral malleolus and the sole of the foot is 3 cun; locate Pucan UB-61 directly below Kunlun UB-60 and midway between this point and the sole. |
|
|
||
|
BL-62 Shenmai (Extending Vessel) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled, Ghost Function: Yang Qiao Vessel, Governing Vessel, Ghost Path |
On the lateral side of the foot, approximately 0.5 cun inferior to the inferior border of the lateral malleolus, in a depression posterior to the peroneal tendons. Landmark: Locate this point directly inferior to the prominence of the lateral malleolus. |
|
|
||
|
BL-63 Jinmen (Golden Gate) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the foot, in the depression posterior to the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal bone. Landmark: The tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal bone is the most palpable landmark on the lateral side of the foot. |
|
|
||
|
BL-64 Jingju (Capital Bone) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the foot, in the depression anterior and inferior to the tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal bone. Landmark: The tuberosity of the fifth metatarsal bone is the most palpable landmark on the lateral side of the foot. |
|
|
||
|
BL-65 Shugu (Restraining Bone) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the foot, in the depression posterior and inferior to the head of the fifth metatarsal bone. Landmark: Run a finger distally along the lateral side of the foot from Jinggu UB-64 until it falls into the depression. |
|
|
||
|
BL-66 Zutonggu (Foot Connecting Valley) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the foot, in the depression anterior and inferior to the fifth metatarso-phalangeal joint. Landmark: First locate Shugu UB-65, then run the finger over the prominence of the metatarso-phalangeal joint until it falls into the depression at the base of the little toe. |
|
|
||
|
BL-67 Zhiyin (Reaching Yin) Meridian: Bladder Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Five Element (Mother), Exit Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the little toe, at the junction of lines drawn along the lateral border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
KD-1 Yongquan (Gushing Spring) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Talahridaya Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Five Element (Child), Entry Function: NA |
By the side of the foot, between second and third metatarsal bones, approximately one third of the distance between the base of the second toe and the heel, in a depression formed when the foot is plantar flexed. |
|
|
||
|
KD-2 Rangu (Blazing Valley) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
On the medial side of the foot, distal and inferior to the medial malleolus, in the depression distal and inferior to the navicular tuberosity. Landmark: The navicular tuberosity is the prominence found superior to the midpoint between the ball of the foot and the heel. |
|
|
||
|
KD-3 Taixi (Supreme Stream) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base Function: NA |
In the depression between the medial malleolus and the Achilles tendon, level with the prominence of the medial malleolus. Landmark: Locate in the centre of the depression, midway between the prominence of the medial malleolus and the posterior border of the Achilles tendon. |
|
|
||
|
KD-4 Dazhong (Great Bell) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
Approximately 0.5 cun posterior to the midpoint of the line drawn between Taixi KD-3 and Shuiquan KD-5, on the anterior border of the Achilles tendon. Landmark: First locate Shuiquan KD-5, 1 cun directly inferior to Taixi KD-3, then locate Dazhong KD-4 halfway between and 0.5 cun posterior to these two points. |
|
|
||
|
KD-5 Shuiquan (Water Spring) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
1 cun inferior to Taixi KD-3 in a depression anterior and superior to the calcaneal tuberosity (the site of insertion of the Achilles tendon into the calcaneum). |
|
|
||
|
KD-6 Zhaohai (Shining Sea) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled Function: Yin Qiao Vessel, Conception Vessel |
1 cun below the prominence of the medial malleolus, in the groove formed by two ligamentous bundles Landmark: This point lies between the tibialis posterior tendon anteriorly and the flexor digitorurn longus tendon posteriorly. These tendons may be highlighted by flexing and inverting the foot. |
|
|
||
|
KD-7 Fuliu (Returning Current) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
On the medial aspect of the lower leg, in the depression 2 cun superior to Taixi KD-3, on the anterior border of the Achilles tendon. |
|
|
||
|
KD-8 Jiaoxin (Exchange Belief) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: Yin Qiao Vessel |
On the medial aspect of the lower leg, 2 cun superior to Taixi KD-3 and 0.5 cun anterior to Fuliu KD-7, posterior to the medial border of the tibia. |
|
|
||
|
KD-9 Zhubin (Guest House) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: Yin Wei Vessel |
On the medial aspect of the lower leg, 5 cun superior to Taixi KD-3, on the line drawn between Taixi KID3 and Yingu KD-10, about 1 cun posterior to the medial border of the tibia. Landmark: Locate at the junction of the lower third and upper two thirds of the distance between Taixi KD-3 and Yingu KD-10. Note that this point is on the same level as Ligou LV-5. |
|
|
||
|
KD-10 Yingu (Yin Valley) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Shleshaka (Kapha) |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea) Function: NA |
At the medial end of the popliteal crease, between the semitendinosus and semimembranosus tendons. Locate and needle with the knee slightly flexed. Landmark: 1. In order to accentuate the tendons, ask the patient to tighten the hamstrings.2. The tendon of semitendinosus, which lies posteriorly to semimembranosus, is the most prominent of the two tendons. |
|
|
||
|
KD-11 Henggu (Pubic Bone) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Vitapa Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 5 cun below the umbilicus, at the superior border of the symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Qugu CV-2). Landmark: The Great Compendium of Acupuncture and Moxibustion locates the points Henggu KD-11 to Shangqu KD-17 one cun lateral to the midline. |
|
|
Deep insertion will penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment | |
|
KD-12 Dahe (Great Luminance) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 4 cun below the umbilicus, 1 cun superior to the superior border of the symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Zhongji CV-3). See location note for Henggu KD-11. |
|
|
Deep insertion will penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment. | |
|
KD-13 Qixue (Qi Cave) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 3 cun below the umbilicus, 2 cun superior to the superior border of the symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Guanyuan CV-4). See location note for Henggu KD-11. |
|
|
Deep insertion will penetrate a full bladder which should therefore be emptied before treatment | |
|
KD-14 Siman (Four Fullnesses) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 2 cun below the umbilicus, 3 cun superior to the superior border of the symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (ShimenCV-5). See location note for Henggu KD-11. |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
KD-15 Zhongzhu (Middle Flow) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 1 cun below the umbilicus,.4 cun superior to the superior border of the symphysis pubis, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Yinjiao CV-7). See location note for Henggu KD-11. |
|
|
deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
KD-16 Huangshu (Vitals Shu) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the abdomen, 0.5 cun lateral to the centre of the umbilicus. See location note for Henggu KD-11 |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
KD-17 Shangqu (Shang Bend) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper abdomen, 2 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Xiawan CV-10). See location note for Henggu KD-11 |
|
|
deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
KD-18 Shiguan (Stone Pass) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper abdomen, 3 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Jianli CV-11). Landmark: The Great Compendium of Acupuncture and Moxibustion locates the points Shiguan KD-18 to Youmen KD-21,1.5 cun lateral to the midline. |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
KD-19 Yindu (Yin Metropolis) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper abdomen, 4 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Zhongwan CV-12). |
|
|
deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity. | |
|
KD-20 Futonggu (Abdomen Connecting Valley) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper abdomen, 5 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Shangwan CV-13). |
|
|
Deep needling may penetrate the peritoneal cavity | |
|
KD-21 Youmen (Hidden Gate) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper abdomen, 6 cun above the umbilicus, 0.5 cun lateral to the midline (Juque CV-14). |
|
|
||
|
KD-22 Bulang (Walking Corridor) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Stanamula Subdosha: NA |
Category: Exit Function: NA |
In the fifth intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the second intercostal space (see Shencang KD-25), then find the fifth intercostal space, three spaces below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung and/or liver. | |
|
KD-23 Shenfeng (Spirit Seal) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the fourth intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the second intercostal space (see Shencang KD-25), then find the fourth intercostal space, two spaces below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung | |
|
KD-24 Lingxu (Spirit Rui) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the third intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the second intercostal space (see Shencang KD-25), then find the third intercostal space, one space below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung | |
|
KD-25 Shencang (Spirit Storehouse) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the second intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the second intercostal space below it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung. | |
|
KD-26 Yuzhong (Comfortable Chest) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the first intercostal space, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: 1. First locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the first intercostal space above it.2. Note that in males the nipple lies in the fourth intercostal space.3. The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung. | |
|
KD-27 Shufu (Shu Mansion) Meridian: Kidney Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression on the lower border of the clavicle, 2 cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: The 2 cun line is located midway between the midline and the mamillary line. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular or oblique needling may puncture the lung. | |
|
TH-1 Guanchong (Rushing Pass) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Entry Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the ring finger, at the junction of lines drawn along the ulnar border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
TH-2 Yemen (Fluid Gate) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Shleshaka (Kapha) |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
Between the ring and little fingers, 0.5 cun proximal to the margin of the web. Landmark: This point is usually located and needled with the hand resting in a loose fist; the point may then be located at the proximal end of the visible crease formed by the web space. |
|
|
||
|
TH-3 Zhongzhu (Central Islet) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurcha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the hand, in the depression just proximal to the fourth and fifth metacarpo-phalangeal joints. Landmark: 1. Locate and needle with the hand resting in a loose fist.2. This point may be located at the apex of an equilateral triangle formed by this point and the prominences of the metacarpo-phalangeal joints of the ring and little fingers. |
|
|
||
|
TH-4 Yangchi (Yang Pool) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurchashira Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the wrist, at the level of the wrist joint, in the depression between the tendons of extensor digitorum communis and extensor digiti minimi. Landmark: Follow the interspace between the fourth and fifth metacarpals proximally from Zhongzhu TH-3 into the depression at the level of the wrist joint. This depression may be more clearly defined by extending the wrist and fingers, but the point should subsequently be needled with the tendons relaxed. |
|
|
||
|
TH-5 Waiguan (Outer Pass) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Manibandha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled Function: Yang Wei Vessel, Belt Vessel |
2 cun proximal to Yangchi TH-4, in the depression between the radius and the ulna, on the radial side of the extensor digitorum communis tendons. Landmark: The point is located between the radius and the extensor digitorum communis tendons, close to the border of the radius. |
|
|
Movement of the patient arm or hand after needling this point can result in a bent needle | |
|
TH-6 Zhigou (Branch Ditch) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
3 cun proximal to Yangchi TH-4, in the depression between the radius and the ulna, on the radial side of the extensor digitorum communis muscle. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Yangchi TH-4 and the lateral epicondyle into half and then halve the distance between this midpoint and Yangchi TH-4.2. The point is located between the radius and the extensor digitorum communis muscle, close to the border of the radius. |
|
|
Movement of the patient arm or hand after needling this point can result in a bent needle. | |
|
TH-7 Huizong (Ancestral Meeting) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
3 cun proximal to Yangchi TH-4, level with and on the ulnar side of Zhigou TH-6, in the depression between the ulna and the extensor digitorum communis muscle. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Yangchi TH-4 and the lateral epicondyle into half and then halve the distance between this midpoint and Yangchi TH-4.2. The point lies approximately one fingerbreadth to the ulnar side of Zhigou TH-6, close to the border of the ulna. |
|
|
||
|
TH-8 Sanyanglao (Three Yang Luo) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
4 cun proximal to Yangchi TH-4, in the depression between the radius and the ulna, on the radial side of the extensor digitorum communis muscle. Landmark: Divide the distance between Yangchi TH-4 and the lateral epicondyle into three equal parts. Sanyangluo TH-8 is located at the junction of the distal third and middle third. |
|
|
||
|
TH-9 Sidu (Four Rivers) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Food channel, Plasma channel Part of Marma: Indrabasti Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression between the radius and the ulna, on a line drawn between Yangchi TH-4 and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, 7 cun proximal to Yangchi TH-4. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Yangchi TH-4 and the lateral epicondyle into half and then locate Sidu TH-9 1 cun proximal to this midpoint.2. The point is located in the depression between the muscle bellies of extensor digitorum communis and extensor carpi ulnaris. |
|
|
||
|
TH-10 Tianjing (Heavenly Well) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurpara Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
With the elbow flexed, this point is located in the depression 1 cun proximal to the olecranon. |
|
|
||
|
TH-11 Qinglengyuan (Clear Cold Abyss) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
With the elbow flexed, this point is located 1 cun proximal to Tianjing TH-10. |
|
|
||
|
TH-12 Xiaoluo (Dispersing Luo River) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper arm, on a line drawn between Tianjing TH-10 and Jianliao TH-14,4 cun proximal to Tianjing TH-10 and 6 cun distal to Jianliao TH-14. Landmark: 1. Divide the distance between Tianjing TH-10 and Jianliao TH-14 into half and locate this point 1 cun distal to this midpoint.2. Locate in the depression within the triceps muscle, posterior to the shaft of the humerus (between the muscle bellies of the long and lateral heads of the triceps). |
|
|
||
|
TH-13 Naohui (Upper Arm Meeting) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper arm, where the line drawn between Tianjing TH-10 and Jianliao TH-14 meets the posterior border of the deltoid muscle, approximately two thirds of the distance between these two points. Landmark: i. Locate in the depression within the triceps muscle, posterior to the shaft of the humerus (between the muscle bellies of the long and lateral heads of the triceps).2. Although most sources specify both a distance of 3 cun from Jianliao TH-14 and a location at the posterior border of the deltoid muscle, these do not usually correspond. In practice, palpate the region of this point to find the most tender location. |
|
|
||
|
TH-14 Jianliao (Shoulder Crevice) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kakshadhara Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the origin of the deltoid muscle, in the depression which lies posterior and inferior to the lateral extremity of the acromion. Landmark: 1. Locate with the arm abducted in order to enhance the depression.2. Note that Jianyu LI-15 is located in the depression which lies anterior and inferior to the lateral extremity of the acromion. |
|
|
||
|
TH-15 Tianliao (Heavenly Crevice) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the suprascapular fossa, in the depression midway between Jianjing GB-21 and Quyuan SI-13 (at the medial end of the suprascapular fossa). Landmark: This point may also be located midway between the lateral extremity of the acromion and Dazhui GV-14, and 1 cun posterior to Jianjing GB-21 (the highest point of the trapezius muscle). |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
TH-16 Tianyou (Window of Heaven) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Sira Matrika, Vidhura Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian You (Window of Heaven) |
On the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, approximately 1 cun inferior to Wangu GB-12, on a line drawn between Tianzhu UB-10 and Tianrong SI-17. |
|
|
||
|
TH-17 Yifeng (Wind Screen) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Vidhura Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Behind the earlobe, between the ramus of the mandible and the mastoid process, in the depression just superior to the palpable transverse process of the first cervical vertebra. Landmark: Fold the earlobe forwards to reveal this point. |
|
|
If the needle is directed too anteriorly or posteriorly, pain will ensue and may cause discomfort on opening and closing the mouth for some while after treatment. | |
|
TH-18 Qimai (Spasm Vessel) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Posterior to the ear, in a small depression on the mastoid bone, one third of the distance along a curved line drawn from Yifeng TH-17 to Jiaosun TH-20 following the line of the rim of the ear. |
|
|
||
|
TH-19 Luxi (Skull Rest) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
two thirds of the distance along a curved line drawn from Yifeng TH-17 to Jiaosun TH-20 following the line of the rim of the ear. |
|
|
||
|
TH-20 Jiansun (Minute Angle) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the side of the head, directly level with the apex of the ear when the ear is folded forwards. Landmark: Fold the ear so that the posterior part of the upper helix directly covers the anterior part of the upper helix. Take care not to push the whole of the ear forwards. |
|
|
||
|
TH-21 Ermen (Ear Gate) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression anterior to the supratragic notch and slightly superior to the condyloid process of the mandible. Landmark: In order to locate this point, ask the patient to open the mouth so that the condyloid process of the mandible slides forwards to reveal the depression. This point is needled with the mouth open. Following needling the mouth can be closed. |
|
|
Many classical sources prohibit moxibustion at this point in cases of discharge of pus from the ear. | |
|
TH-22 Erheliao (Ear Harmony Crevice) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Exit Function: NA |
Approximately 0.5 cun anterior to the upper border of the root of the ear, in a slight depression on the posterior border of the hairline of the temple. Landmark: This point lies just posterior to where the superficial temporal artery can be palpated. |
|
|
||
|
TH-23 Sizhukong (Silken Bamboo Hollow) Meridian: Triple Warmer Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Apanga Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression on the supraorbital margin, at the lateral end of the evebrow. Landmark: According to several classical texts, this point is contraindicated to moxibustion. |
|
|
||
|
PC-1 Tianchi (Heavenly Pool) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Entry, Window of Sky Function: Tian Chi (Pool of Heaven) |
1 cun lateral and slightly superior to the nipple, in the 4th intercostal space. Landmark: The level of the fourth intercostal space at this point is more or less the same as that of the fourth intercostal space at its junction with the sternum. |
|
|
Deep needling carries a substantial risk of causing a pneumothorax | |
|
PC-2 Tianquan (Heavenly Spring) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Water Metabolism channel Part of Marma: Bahvi, Urvi Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the anterior aspect of the arm, 2 cun below the anterior axillary fold, between the two heads of the biceps brachii muscle. |
|
|
||
|
PC-3 Quze (Marsh at the Crook) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Tarpaka (Kapha) |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea) Function: NA |
On the transverse cubital crease, in the depression immediately to the ulnar side of the aponeurosis of the biceps brachii muscle. Landmark: This point should be located and needled with the elbow slightly bent. |
|
|
Brachial artery and veins lie deeply, just medial to this point | |
|
PC-4 Ximen (Xi-Cleft Gate) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Indrabasti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the flexor aspect of the forearm, 5 cun proximal to Daling PC-7, on the line connecting Daling PC-7 and Quze PC-3, between the tendons of palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis. Landmark: 1. In the absence of the tendon of palmaris longus, locate this point on the ulnar side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis.2. Divide the distance between the cubital crease and Daling PC-7 into half and locate this point 1 cun distal to this midpoint. |
|
|
||
|
PC-5 Jianshi (Intermediate Messenger) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
On the flexor aspect of the forearm, 3 cun proximal to Daling PC-7, between the tendons of palmaris longus, and flexor carpi radialis. Landmark: 1. In the absence of the tendon of palmaris longus, locate this point on the ulnar side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis.2. Divide the distance between the cubital crease and Daling PC-7 into quarters and locate this point at the junction of the proximal three quarters and the distal quarter. |
|
|
||
|
PC-6 Neiguan (Inner Pass) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Indrabasti Subdosha: Udana (Vaata) |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Command, Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled, Buddhist triangle Function: Heart, Chest & Epigastrium, Yin Wei Vessel, Thrusting Vessel |
On the flexor aspect of the forearm, 2 cun proximal to Daling PC-7, between the tendons of palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis. Landmark: In the absence of the tendon of palmaris longus, locate this point on the ulnar side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis. |
|
|
Single most important distal point for disorders of the chest (e.g pain of the Heart) and it is one of the primary points in acupuncture analgesia for chest surgery. Its range of actions extends not only to the Heart, but also to the Lung. | the median nerve lies directly under this point and needling commonly induces a significant electric sensation. This is an acceptable manifestation of deqi (arrival of qi), but once elicited, further manipulation is inappropriate and may damage the nerve. |
|
PC-7 Daling (Great Mound) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Sadhaka (Pitta) |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base, Five Element (Child), Ghost Function: Ghost Heart |
At the wrist joint, between the tendons of palmaris longus and flexor carpi radialis, level with Shenmen HT-7. Landmark: 1. This point is commonly described as being at the wrist crease, which is variable. It is more reliably located level with Shenmen HT-7 which lies at the proximal border of the pisiform bone.2. In the absence of the tendon of palmaris longus, locate this point on the ulnar side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis. |
|
|
the median nerve lies directly under this point and needling commonly induces a significant electric sensation. This is an acceptable manifestation of deqi (arrival of qi), but once elicited, further manipulation is inappropriate and may damage the nerve. | |
|
PC-8 Laogong (Palace of Toil) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: LifeForce channel Part of Marma: Talahridaya Subdosha: Prana (Vaata) |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Exit, Ghost Function: Ghost Cave |
Between the second and third metacarpal bones, proximal to the metacarpo-phalangeal joint, in a depression at the radial side of the third metacarwal bone. Landmark: 1. This point may be located at the place where the tip of the middle finger lands when a fist is made.2. Some classical sources locate this point on the ulnar side of the third metacarpal bone, where the tip of the ring finger lands when a fist is made. |
|
|
||
|
PC-9 Zhongchong (Middle Rushing) Meridian: Pericardium Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Five Element (Mother) Function: NA |
In the centre of the tip of the middle finger. Alternatively, this point is sometimes located at the radial side of the middle finger, at the junction of lines drawn along the radial border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
SI-1 Shaoze (Lesser Marsh) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Entry Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the little finger, at the junction of lines drawn along the ulnar border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
SI-2 Qiangu (Front Valley) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
On the ulnar border of the little finger, in a depression just distal to the metacarpo-phalangeal joint. |
|
|
||
|
SI-3 Houxi (Back Stream) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Five Element (Mother), Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled Function: Governing Vessel, Yang Qiao Vessel |
On the ulnar border of the hand, in the substantial depression proximal to the head of the fifth metacarpal bone. Landmark: This point is easier to locate when the hand is made into a loose fist. |
|
|
||
|
SI-4 Wangu (Wrist Bone) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base Function: NA |
On the ulnar border of the hand, in the depression between the base of the fifth metacarpal bone and the triquetral bone. |
|
|
||
|
SI-5 Yanggu (Yang Valley) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurchashira, Manibandha Subdosha: Samana (Vaata), Pachaka (Pitta) |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
At the ulnar border of the wrist, in the depression between the head of the ulna and the triquetral bone. Landmark: Most sources locate this point between the styloid process of the ulna and the triquetral bone, but in practice, the styloid process of the ulna may not be palpable and where it is palpable it often lies slightly posterior to Yanggu SI-5. |
|
|
||
|
SI-6 Yanglao (Support the Aged) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
When the palm of the hand is placed on the chest, this point is located on the dorsal aspect of the head of the ulna, in a cleft level with and to the radial side of the high point of the styloid process of the ulna. Landmark: This point may be located in the following way. Ask the patient to lie with their arm by their side and the hand prone (palm on the couch). If the practitioner places a finger on the high point of the ulnar styloid and asks the patient to place their palm on their chest, the point is found in the cleft where the practitioner finger then rests. |
|
|
||
|
SI-7 Zhizheng (Branch of the Upright) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
On a line connecting Yanggu SI-5 and Xiaohai SI-8,5 cun proximal to Yanggu SI-5, in the groove between the anterior border of the ulna and the muscle belly of flexor carpi ulnaris. Landmark: This point should be located and needled with the patient lying on their back and with their arm either in the supine position or resting on the chest. |
|
|
||
|
SI-8 Xiaohai (Small Sea) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurpara Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
In the depression between the tip of the olecranon process of the ulna and the tip of the medial epicondyle of the humerus. |
|
|
||
|
SI-9 Jianzhen (True Shoulder) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the posterior aspect of the shoulder, 1 cun superior to the posterior axillary crease when the arm hangs in the adducted position. Landmark: This point lies in the depression just below the posterior border of the deltoid. |
|
|
||
|
SI-10 Naoshu (Upper Arm Shu) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the posterior aspect of the shoulder, in the depression inferior to the scapular spine, directly superior to the posterior axillary crease when the arm hangs in the adducted position. Landmark: Slide a finger directly upwards from Jianzhen SI-9 until it falls into the depression just below the scapular spine. |
|
|
||
|
SI-11 Tianzong (Heavenly Gathering) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the scapula, in a tender depression one third of the distance from the midpoint of the inferior border of the scapular spine to the inferior angle of the scapula. Landmark: In practice it may be difficult to palpate the inferior angle of the scapula. An alternative method of location is to draw an equilateral triangle with Jianzhen SI-9 and Naoshu SI-10, after first ensuring that the patients shoulder is relaxed. |
|
|
||
|
SI-12 Bingfeng (Grasping the Wind) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the centre of the suprascapular fossa, directly above Tianzong SI-11, in a depression formed when the arm is raised. |
|
|
Deep perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SI-13 Quyuan (Crooked Wall) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the tender depression superior to the medial end of the scapular spine, midway between Naoshu SI-10 and the spinous process of T2. Landmark: Slide a fingertip medially along the superior border of the scapular spine until it falls into the tender depression just lateral to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
This point is located close to the medial border of the scapula. Too medial an insertion or deep medialoblique needling may puncture the lungs. | |
|
SI-14 Jianwaishu (Outer Shoulder Shu) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun lateral to the lower border of the spinous process of T1 (Taodao GV-13). Landmark: When the shoulder is relaxed, the three cun line corresponds to the medial border of the scapula. |
|
|
Perpendicular insertion, especially in thin patients, carries a substantial risk of inducing a pneumothorax. | |
|
SI-15 Jianzhoungzhu (Middle Shoulder Shu) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
2 cunlateral to the lower border of the spinous process of C7 (Dazhui GV-14). Landmark: 1. This point may be found two thirds of the distance between the midline and the medial border of the scapula, when the shoulder is in a relaxed position |
|
|
||
|
SI-16 Tianchuang (Heavenly Window) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian Chuang (Heavenly Window) |
On the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle, level with the laryngeal prominence. Landmark: 1. Palpation of the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is made easier if the patient turns their head away from the side to be needled, whilst you apply resistance at the chin.2. In females the laryngeal prominence is not as pronounced as in males. If it is indistinct, palpate the depression formed by the lower border of the hyoid bone and the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at the midline. The laryngeal prominence lies just below ths. |
|
|
||
|
SI-17 Tianrong (Heavenly Appearance) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Sira Matrika Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian Rong (Heavenly Manifestation) |
In the depression between the angle of the mandible and the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Landmark: 1. Palpation of the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle is made easier if the patient turns their head away from the side to be needled, whilst you apply resistance at the chin.2. If the transverse process of C2 is palpable, locate and needle this point anterior to it. |
|
|
||
|
SI-18 Quanliao (Cheek Bone Crevice) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Directly below the outer canthus, in the depression at the lower border of the zygomatic bone. |
|
|
||
|
SI-19 Tinggong (Palace of Hearing) Meridian: Small Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Exit Function: NA |
With the mouth open, this point is located in the depression between the middle of the tragus and the condyloid process of the mandible. Landmark: In order to locate this point, ask the patient to open the mouth so that the condyloid process of the mandible slides forwards to reveal the depression. |
|
|
||
|
HE-1 Jiquan (Summit Spring) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Lohitaksha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Entry Function: NA |
In the depression at the centre of the axilla. Landmark: This point is located with the arm abducted. Slide your finger up the lateral wall of the chest between the two muscle groups (latissimus dorsi posteriorly and pectoralis major anteriorly) into the depression at the highest point of the axillary hollow. |
|
|
Medial insertion towards the chest may puncture the lung. | |
|
HE-2 Qingling (Green Spirit) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun proximal to the medial end of the transverse cubital crease, on the line connecting Jiquan HT-1 and Shaohai HT-3 Landmark: 1. Locate with the elbow flexed.2. This point is located in the groove medial to the biceps brachii muscle, one handbreadth proximal to Shaohai HT-3. |
|
|
Many early classics only discuss moxibustion in relation to this point, implying that needling was contraindicated, perhaps because of the danger of damaging the brachial artery, whilst the Introduction to Medicine specifically contraindicates needling at this point. | |
|
HE-3 Shaohai (Lesser Sea) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea) Function: NA |
Midway between Quze PC-3 and the medial epicondyle of the humerus, at the medial end of the transverse cubital crease when the elbow is fully flexed. |
|
|
||
|
HE-4 Lingdao (Spirit Path) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
On the radial side of the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, 1.5 cun proximal to Shenrnen HT-7. |
|
|
||
|
HE-5 Tongli (Penetrating the Interior) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: NA |
On the radial side of the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, 1 cun proximal to Shenmen HT-7. |
|
|
||
|
HE-6 Yinxi (Yin Cleft) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the radial side of the tendon of flexor carpi ulnaris, 0.5 cun proximal to Shenmen HT-7. |
|
|
||
|
HE-7 Shenmen (Spirit Gate) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Mental channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base, Five Element (Child), Buddhist triangle Function: NA |
At the wrist joint, on the radial side of flexor carpi ulnaris, in the depression at the proximal border of the pisiform bone. Landmark: 1. The location of this point is normally given in relation to the crease of the wrist. Since wrist creases are a superficial and variable anatomical feature, it is better to locate this point in relation to the underlying pisiform bone.2. When it is necessary to needle a patient in the prone position with the arms towards the head, this point may be located and needled on the ulnar side of flexor carpi ulnaris, very close to the tendon insertion; the needle is then directed beneath the tendon towards its radial side. |
|
|
Ulnar artery and ulnar nerve lie adjacent to this point. | |
|
HE-8 Shaofu (Lesser Palace) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
On the palm, in the depression between the 4th and 5th metacarpal bones, where the tip of the little finger rests when a fist is made. Landmark: This point generally lies between the two transverse palmar creases. |
|
|
||
|
HE-9 Shaochong (Lesser Rushing) Meridian: Heart Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Five Element (Mother), Exit Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the little finger, at the junction of lines drawn along the radial border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
LI-1 Shangyang (Shang Yang) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well) Function: NA |
On the dorsal aspect of the index finger, at the junction of lines drawn along the radial border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
LI-2 Erjian (Second Space) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the radial border of the index finger, in a depression just distal to the metacarpo-phalangeal joint. Landmark: This point will be easier to find if the index finger is relaxed in a slightly flexed position. |
|
|
||
|
LI-3 Sanjian (Third Space) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream) Function: NA |
On the radial side of the index finger, in the substantial depression proximal to the head of the second metacarpal bone. Landmark: This point is easier to locate when the hand is made into a loose fist. |
|
|
||
|
LI-4 Hegu (Joining Valley) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kshipra Subdosha: NA |
Category: Yuan/Base, Entry, Command, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Face & Mouth |
On the dorsum of the hand, between the first and second metacarpal bones, at the midpoint of the second metacarpal bone and close to its radial border. Landmark: Ask the patient to squeeze the thumb against the base of the index finger, and locate Hegu LI-4 at the highest point of the bulge of the muscle and approximately level with the end of the crease. |
|
|
Single most important point to treat disorders of the face and sense organs. | |
|
LI-5 Yangxi (Yang Stream) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurcha Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
On the radial side of the wrist, in the centre of the hollow formed by the tendons of extensor pollicis longus and brevis (anatomical snuffbox). Landmark: 1. Ask the subject to extend the thumb to emphasise the hollow of the anatomical snuffbox.2. Look carefully to locate the cephalic vein which runs through the anatomical snuffbox in order to avoid needling through the vein. |
|
|
||
|
LI-6 Pianli (Veering Passage) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Luo/Bridge Function: NA |
3 cun proximal to Yangxi LI-5 on the line connecting Yangxi LI-5 with Quchi LI-11. Landmark: i. Locate with the elbow flexed and with the radial side of the arm upwards; ii. Divide the distance between Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11 into half, and then halve the distance between this midpoint and Yangxi LI-5. |
|
|
||
|
LI-7 Wenliu (Warm Flow) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
5 cun proximal to Yangxi LI-5 on the line connecting Yangxi LI-5 with Quchi LI-11. Landmark: 1. Locate with the elbow flexed and with the radial side of the arm upwards.2. Divide the distance between Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11 into two equal parts, then locate Wenliu LI-7 one cun distal to this midpoint. |
|
|
||
|
LI-8 Xialian (Lower Angle) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the radial side of the forearm, 4 cun distal to Quchi LI-11, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 with Yangxi LI-5. Landmark: 1. Locate with the elbow flexed and with the radial side of the arm upwards.2. Divide the distance between Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11 into three equal parts. Xialian LI-8 is located at the junction of the proximal and middle thirds. |
|
|
||
|
LI-9 Shanglian (Upper Angle) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the radial side of the forearm, 3 cun distal to QuchiLI-11, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 with Yangxi LI-5. Landmark: 1. Locate with the elbow flexed and with the radial side of the arm upwards.2. Divide the distance between Yangxi LI-5 and Quchi LI-11 into half, and then halve the distance between this midpoint and Quchi LI-11. |
|
|
||
|
LI-10 Shousanli (Arm Three Miles) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the radial side of the forearm, 2 cun distal to Quchi LI-11, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 with Yangxi LI-5. Landmark: 1. Locate with the elbow flexed and with the radial side of the arm upwards. 2. First locate Shanglian LI-9, then locate Shousanli LI-10 one cun proximal to it; iii. This point is usually significantly tender to palpation. |
|
|
||
|
LI-11 Quchi (Pool at the Crook) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Kurpara Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Five Element (Mother), Ghost, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Ghost Leg |
At the elbow, midway between Chize LU-5 and the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, at the lateral end of the transverse cubital crease. Landmark: This point should be located with the elbow flexed. |
|
|
||
|
LI-12 Zhouliao (Elbow Crevice) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
When the elbow is flexed, this point is located in the depression 1 cun proximal to and 1 cun lateral to Quchi LI-11 Landmark: When the elbow is flexed, this point may be found directly above the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, just anterior to the lateral supracondylar ridge. |
|
|
||
|
LI-13 Shouwuli (Arm Five Miles) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the upper arm, 3 cun proximal to Quchi LI-11, on the line connecting Quchi LI-11 with Jianyu LI-15. Landmark: 1. Locate approximately one handbreadth superior to Quchi LI-11, in the depression between the lateral border of biceps brachii and the humerus.2. Locate at one third of the distance between Quchi LI-11 and the axillary fold |
|
|
||
|
LI-14 Binao (Upper Arm) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Water Metabolism channel Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the upper arm, in the visible and tender depression formed between the distal insertion of the deltoid muscle and the brachialis muscle, approximately three fifths of the distance along the line drawn between Quchi LI-11 and Jianyu LI-15. Landmark: This point is easier to locate if the muscles of the upper arm are tensed. |
|
|
||
|
LI-15 Jianyu (Shoulder Bone) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression which lies anterior and inferior to the acromion, at the origin of the deltoid muscle. (Note: Jianliao TH-14 is located in the depression which lies posterior and inferior to the acromion). Landmark: If the arm is abducted, the two hollows will be more easily palpable and are often visible. |
|
|
||
|
LI-16 Jugu (Great Bone) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the upper aspect of the shoulder, in the depression medial to the acromion process and between the lateral extremity of the clavicle and the scapular spine. |
|
|
||
|
LI-17 Tianding (Heaven Tripod) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Sira Matrika Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lateral side of the neck, 1 cun inferior to Futu LI-18, on the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. |
|
|
||
|
LI-18 Futu (Support the Prominence) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: Blood channel Part of Marma: Manya, Nila Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Fu Tu (Supporting Prominence) |
On the lateral side of the neck, level with the tip of the laryngeal prominence, between the sternal and clavicular heads of the sternocleidomastoid muscle. Landmark: 1. Palpation of the sternal and clavicular heads is made easier if the patient turns their head away from the side to be needled, whilst you apply resistance at the chin.2. In females the laryngeal prominence is not as pronounced as in males. If it is indistinct, palpate the depression formed by the lower border of the hyoid bone and the upper border of the thyroid cartilage at the midline. The laryngeal prominence lies just below this.3. This point may be located approximately 3 cun (one handbreadth) lateral to the laryngeal prominence. |
|
|
||
|
LI-19 Kouheliao (Mouth Grain Crevice) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Phana Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Below the lateral margin of the nostril, 0.5 cun lateral to Renzhong GV-26 Landmark: Renzhong GV-26 is located above the upper lip on the midline, at the junction of the upper thrd and lower two thirds of the philtrum. |
|
|
||
|
LI-20 Yingxiang (Welcome Fragrance) Meridian: Large Intestine Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Phana Subdosha: NA |
Category: Exit Function: NA |
In the naso-labial groove, at the level of the midpoint of the lateral border of the ala nasi. |
|
|
||
|
LU-1 Zhongfu (Middle Palace) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Apalapa Subdosha: NA |
Category: Mu/Front, Entry Function: Lung organ |
On the lateral aspect of the chest, in the first intercostal space, 6 cun lateral to the midline, 1 cun inferior to Yunrnen LU-2. Landmark: 1. Ask the patient to extend their hand forwards whilst you apply resistance to their hand, in order to emphasise the delto-pectoral triangle. First locate Yunmen LU-2 in the centre of the triangle, then locate Zhongfu LU-1 in the intercostal space approximately one cun inferior and slightly lateral to it. 2. To locate the first intercostal space, first locate the costal cartilage of the second rib which is level with the sternal angle, then locate the first intercostal space above it. |
|
|
||
|
LU-2 Yunmen (Cloud Gate) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the antero-lateral aspect of the chest, below the lateral extremity of the clavicle, 6 cun lateral to the midline, in the centre of the hollow of the delto-pectoral triangle. Landmark: Ask the patient to extend their hand forwards whilst you apply resistance to their hand, in order to emphasise the delto-pectoral triangle, and locate Yunmen LU-2 at its centre. |
|
|
||
|
LU-3 Tianfu (Palace of Heaven) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Window of Sky Function: Tian Fu (Mansion of Heaven) |
On the antero-lateral aspect of the upper arm, 3 cun inferior to the axillary fold and 6 cun superior to Chize LU-5, in the depression between the lateral border of the biceps brachii muscle and the shaft of the humerus. Landmark: Divide the distance between the axillary fold and the cubital crease of the elbow into equal thirds. Tianfu LU-3 is at the junction of the upper and middle third. |
|
|
||
|
LU-4 Xiabai (Clasping the White) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Ani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the antero-lateral aspect of the upper arm, 4 cun inferior to the axillary fold and 5 cun superior to Chize LU-5, in the depression between the lateral border of the biceps brachii muscle and the shaft of the humerus. Landmark: Divide the distance between the axillary fold and the cubital crease of the elbow into equal thirds and locate Xiabai LU-4 one cun inferior to the junction of the upper and middle third (Tianfu LU-3). |
|
|
||
|
LU-5 Chize (Cubit Marsh) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Avalambaka (Kapha), Bodhaka (Kapha) |
Category: Five Shu (He-sea), Five Element (Child) Function: NA |
On the cubital crease of the elbow, in the depression at the radial side of the tendon of biceps brachi Landmark: 1. Locate slightly lateral to the tendon rather than immediately next to it. 2. Locate and needle with the elbow slightly flexed, avoiding the cubital vein. |
|
|
||
|
LU-6 Kongzui (Maximum Opening) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Indrabasti Subdosha: NA |
Category: Xi/Cleft Function: NA |
On the flexor aspect of the forearm, 7 cun proximal to Taiyuan LU-9, on the line connecting Taiyuan LU-9 with Chize LU-5. Landmark: Divide the distance between Taiyuan LU-9 and Chize LU-5 into half. Kongzui LU-6 is in a palpable depression 1 cun proximal to this midpoint |
|
|
||
|
LU-7 Lieque (Broken Sequence) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: Bhrajaka (Pitta) |
Category: Luo/Bridge, Exit, Command, Confluent/Master, Confluent/Coupled, Ma Danyang/12 Star Points Function: Head & Posterior Neck, Conception Vessel, Yin Qiao Vessel |
On the radial aspect of the forearm, approximately 1.5 cun proximal to Yangxi LI-5, in the cleft between the tendons of brachioradialis and abductor pollicis longus. Landmark: If the forefinger is placed at Yangxi LI-5, in the anatomical snuffbox, and moved directly proximally over the full extent of the styloid process of the radius, the finger falls into the cleft between the two tendons. |
|
|
||
|
LU-8 Jingqu (Channel Gutter) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-river) Function: NA |
Above the wrist, 1 cun proximal to Taiyuan LU-9, on the line connecting Taiyuan LU-9 with Kongzui LU-6, in the depression at the base of the styloid process of the radius and on the radial side of the radial artery. Landmark: If the forefinger is placed on Taiyuan LU-9 and moved proximally over the palpable styloid process of the radius, it will naturally fall into the depression where Jingqu LU-8 is located. |
|
|
||
|
LU-9 Taiyuan (Supreme Abyss) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Shu-stream), Yuan/Base, Five Element (Mother), Hui Meeting/Gathering, Buddhist triangle Function: Vessels |
At the wrist joint, in the depression between the radial artery and the tendon of abductor pollicis longus, level with Shenmen HT-7 (the proximal border of the pisiform bone). Landmark: The location of this point is normally given in relation to the crease of the wrist. Since wrist creases are a superficial and variable anatomical feature, it is better to locate this point in relation to the nearby pisiform bone: first locate ACTIONS Shenmen HT-7 at the lower (proximal) border of the Descends Lung qi and alleviates cough and wheezing pisiform bone, then find Taiyuan LU-9 at the same level. |
|
|
Single most important point on the Lung channel to tonify the Lung qi or yin, the two principal patterns of Lung deficiency. | |
|
LU-10 YujiLu (Fish Border) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Ying-spring) Function: NA |
On the thenar eminence of the hand, in a depression between the midpoint of the shaft of the first metacarpal bone and the thenar muscles. Landmark: Locate and needle close to the border of the metacarpal bone. |
|
|
||
|
LU-11 Shaoshang (Lesser Shang) Meridian: Lung Meridian Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: Five Shu (Jing-well), Ghost Function: Ghost Faith |
On the extensor aspect of the thumb, at the junction of lines drawn along the radial border of the nail and the base of the nail, approximately 0.1 cun from the corner of the nail. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-1 Sishencong (Four Alert Spirit) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Simanta Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Four points at the vertex of the scalp, grouped around GV-20 and located 1 cun anterior, posterior and lateral to it. Landmark: The distance between GV-20 and the anterior hairline is 5 cun. If the anterior hairline is indistinct, the distance between GV-20 and the glabella is measured as 8 cun. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-3 Yintang (Hall of Impression) Meridian: NA Chakra: Ajna/Third Eye |
Srotas: LifeForce channel Part of Marma: Sthapani Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the glabella, at the midpoint between the medial extremities of the eyebrows. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-6 Yuyao (Fish Waist) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the centre of the eyebrow, in the depression directly above the pupil when the eyes are looking straight forwards. Landmark: It is traditionally located lateral to the supraorbital notch from which the supraorbital nerve emerges. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-8 Qiuhou (Behind the Ball) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Along the inferior border of the orbit, at the junction of the lateral one quarter and medial three quarters of the infra-orbital margin. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-9 Taiyang (Supreme Yang) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Shankha Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the temple, in the tender depression approximately 1 cunposterior to the midpoint between the lateral extremity of the eyebrow and the outer canthus of the eye. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-10 Erjian (Tip of the Ear) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: Utkshepa Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
When the ear is folded forwards, this point lies at the apex of the ear. Landmark: Fold the ear so that the posterior part of the upper helix directly covers the anterior part of the upper helix. Take care not to push the whole of the ear forwards. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-14 Bitong (Penetrating the Nose) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the highest point of the naso-labial groove. Landmark: Run the finger along the naso-labial groove into the depression immediately below the nasal bone. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-30 Bailao (Hundred Taxations) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
At the back of the neck, 2 cun superior to GV-14, l cun lateral to the midline. Landmark: The distance between the inferior border of the spinous process of C7 and the posterior hairline is 3 cun. |
|
|
||
|
N-HN-54 Anmian (Peacefu1 Sleep) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Behind the ear, midway between Fengchi GB-20 and TH-17. Landmark: This point is found close to GB-12, but posterior and slightly superior to it. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-18 Jiachengjian (Adjacent to Container of Fluids) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1 cun lateral to CV-24, over the mental foramen. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-20 Jinjinand Yuge (Golden Liquid and Jade Fluid) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
These paired points are located on the 1 veins either side of the frenulum of the tongue, Jinjin to the left and Yuye to the right. Landmark: The tongue should be rolled back to locate and treat these points. If required the practitioner should roll the tongue back using a gauze swab or wooden spatula. |
|
|
||
|
M-HN-37 Haiquan (Sea Spring) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the centre of the frenulum of the tongue between Jinjin and Yuye. Landmark: The tongue should be rolled back to locate and treat this point. If required the practitioner should roll the tongue back using a gauze swab or wooden spatula. If the deeper needling method is used, the tongue then rests on the needle with the mouth closed. |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-1 Dincchuan (Calm Dyspnoea) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 to 1 cun lateral to the depression below the spinous process of the seventh cervical vertebra GV-14). |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-6 Huamen (Gate of Suffering) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cun lateral to the prominence of the spinous process of the fifth thoracic vertebra (T5). |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-1 Weiguanxiashu (Stomach Controller Lower Shu) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
1.5 cunlateral to the lower border of the spinous process of the eighth thoracic vertebra (T8). Landmark: Locate at the visible highest point of the paraspinal muscles. |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-2 Yaoyan (Lumbar Eyes) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression approximately 3.5 cun lateral to the lower border of L4 (GV-3). Landmark: The eyes referred to in the point name are the visible hollows found in many people, just over one handbreadth either side of the lumbar spine, below the level of the iliac crest. |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-25 Shiqizhuixia (Below the Seventeenth Vertebra) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the midline of the lower back, in the -. depression below the spinous process of the fifth lumbar vertebra. Landmark: Slide a finger upwards along the midline of the sacrum until it meets the significant depression inferior to the lumbar spine. |
|
|
||
|
M-BW-35 Huatuojiaji (Huatuojiaji Points) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
0.5 to 1 cun lateral to the depressions below the spinous processes of the 6 neck, 12 thoracic and 5 lumbar vertebrae. Landmark: In clinical practice, the points located 0.5 to 1 cun lateral to the depressions below the spinous processes of the seven cervical vertebrae are used as additional Huatuojiaji points. |
|
|
||
|
M-CA-23 Sanjiaoji (Triangle Moxibustion) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen. Construct an equilateral triangle of which the apex is the umbilicus (CV-8), and the sides are equal to the length of the patient smile. These points are located at the three points of the triangle. Landmark: It is helpful to describe this location to the patient. This will invariably induce a smile which can then be measured. |
|
|
||
|
M-CA-18 Zigong (Place of child uterus) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 3 cun lateral to the midline, level with CV-3. Landmark: CV-3 lies on the midline of the lower abdomen, 4 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 1 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. Zigong (Place of child) is located one handbreadth lateral to this point. |
|
|
||
|
N-CA-4 Tituo (Life and Support) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the lower abdomen, 4 cun lateral to the midline, level with CV-4 Landmark: CV-4 lies on the midline of the lower abdomen, 3 cun inferior to the umbilicus and 2 cun superior to the pubic symphysis. Locate Tituo 4 cun lateral to this point, medial to the anterior superior iliac spine. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-1 Shixuan (Ten Diffusions) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the tips of the ten fingers, approximately 0.1 cun from the fingernail. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-9 Sifenc (Four Seas) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the palmar surface of the hand, at the midpoints of the transverse creases of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the index, middle, ring and little fingers. Landmark: In most subjects two creases will be found at the proximal interphalangeal joints. In this case, Sifeng is located on the crease which is more prominent on flexion of these joints. |
|
|
It is an important and commonly used point grouping in the treatment of a wide range of childhood digestive disorders. It is indicated for two important patterns known as chldhood nutritional impairment and childhood accumulation disorders. | |
|
M-UE-22 Baxie (Eight Pathogens) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
When the hand is made into a fist, six of these points lie in the depressions between the metacarpal heads, proximal to the web margins. The remaining two points lie equidistant between the thumb and index metacarpals, proximal to the web margins. Landmark: To assist location of the first six points described above, with the hand held in a fist draw an equilateral triangle between the prominences of the metacarpal heads and the proximal end of the visible crease formed by the web space. The points lie at the centre of these triangles. |
|
|
||
|
N-UE-1 Yaotoncxue (Lumbar Pain Point) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the hand, two points located between the second and third and the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, in the depressions lying immediately distal to the bases of the metacarpals. Landmark: Slide a finger proximally along the back of the hand towards the wrist, in the groove between the metacarpal bones until it reaches the tender depression just proximal to the junction of the metacarpals. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-24 Luozhen (Stiff Neck) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the hand, in the depression just proximal to the second and third metacarpo-phalangeal joints Landmark: This point may be located at the apex of an equilateral triangle formed by this point and the prominences of the metacarpo-phalangeal joints of the index and middle fingers. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-29 Erbai (Two Whites) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the flexor aspect of the forearm, 4 cun proximal to Daling PC-7, either side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis Landmark: There are two points; one lies on the ulnar side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis, and between this tendon and the tendon of palmaris longus if this is present, whilst the other lies on the radial side of the tendon of flexor carpi radialis; ii. Divide the distance between the cubital crease and Daling PC-7 into thirds and locate this point at the junction of the proximal two thirds and the distal third. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-46 Zhoujian (Elbow Tip) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the tip of the olecranon process of the ulna. |
|
|
||
|
M-UE-48 Jianqian (Front of the Shoulder) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the anterior aspect of the shoulder joint, midway between the anterior axillary crease and LI-15 Landmark: This point is usually found to be tender on palpation |
|
|
||
|
M-LE-34 Baichonwo (Hundred Insect Burrow) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
3 cun proximal to the superior border of the patella, in a tender depression on the bulge of the vastus medialis muscle Landmark: This point lies 1 cun proximal to SPC-10. |
|
|
||
|
M-LE-27 Heding (Crane Submit) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
In the depression at the midpoint of the superior border of the patella |
|
|
||
|
MN-LE-16 Xiyan (Eyes of the Knee) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the knee, in the hollows formed when the knee is flexed, immediately below the patella and both medial and lateral to the patellar ligament. Landmark: This point is identical with ST-35 |
|
|
||
|
M-LE-13 Lanweixue (Appendix Point) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Approximately 2 cun distal to Zusanli ST-36 on the right leg Landmark: The exact location of this point is determined by careful palpation to identify the point of maximum tenderness. |
|
|
||
|
M-LE-23 Dannangxue (Gallbladder Point) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
Between 1 and 2 cun distal to GB-34 on the right leg. Landmark: The exact location of this point is determined by careful palpation to identify the point of maximum tenderness. |
|
|
||
|
M-LE-8 Bafeng (Eight Winds) Meridian: NA Chakra: NA |
Srotas: NA Part of Marma: NA Subdosha: NA |
Category: NA Function: NA |
On the dorsum of the foot, between the toes, 0.5 cun proximal to the margin of the web. Landmark: These eight points include LV-2, ST-44 and GB-43 |
|
|
Shariras
Go to top| Sharira | Kosha | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Physical Sthul |
Pranamaya, Annamaya | Pind |
| Astral Sukshma |
Vijnanamaya, Manamaya, Pranamaya | Aand |
| Causal Karan |
Anandamaya | Brahmund (it further contains multiple Mental planes) |
Koshas
Go to top| Kosha | Sharira | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Annamaya Food |
Physical | It is the outermost of the koshas "the sheath of food". We take care of it, nurture it, so that we can both enjoy our external lives and go inward without it being an obstacle during meditation time. In meditation, we become aware of Annamaya kosha, explore it, and then go inward, to and through the other koshas. |
| Pranamaya Energy |
Physical, Astral | It is the vital force that produces the subtle vibrations related to breath, and which are the driving force behind the physical aspect of the senses and the operation of the physical body. It is very useful, or essential that this level of our being be trained, regulated, and directed, so that it flows smoothly. In meditation, we become aware of Pranamaya kosha, explore it, and then go inward, to and through the other koshas. |
| Manamaya Mental |
Astral | It is the level of processing thoughts and emotions. It is in direct control of the operation, through the prana, of the physical body and senses. It is like a supervisor in a factory, in that it gives instructions, but is not supposed to be the manager of the factory of life. Because of this, it naturally has doubts, and created illusions. When it receives clear instructions from the deeper level, it functions quite well. However, when it is clouded over by its illusions, the deeper wisdom is clouded over. After taking care of the physical body and training the energy flow of prana, the most important part to be trained in positive ways is this level of mind. In meditation, we become aware of Manamaya kosha, explore it, and then go inward, to and through the remaining koshas. |
| Vijnanamaya Wisdom |
Astral | It is the sheath of wisdom that is underneath the processing, thinking aspect of mind. It knows, decides, judges, and discriminates between this and that, between useful and not useful. It is also the level of ego consciousness, meaning the powerful wave of I-am-ness. This I-am-ness itself is a positive influence, but when it gets co-mingled with the memories, and is clouded over by the manas, it loses its positive strength. A major part of sadhana (spiritual practice) is gaining ever increasing access to this level of our being. It is the level that has the higher wisdom to seek Truth, to go within, in search of the eternal center of consciousness. |
| Anandamaya Bliss |
Causal | It is the most interior of the koshas, the first of the koshas surrounding the Atman, the eternal center of consciousness. Yet, even this bliss, however wonderful it is, is still a covering, a sheath, a lampshade covering the pure light of consciousness. It is the subtle most of the five koshas. In the silence of deep meditation, this too is let go of, so as to experience the center. |
Malas
Go to top| Name | Causes of Increase | Causes of Decrease | Signs of Increase | Signs of Decrease | Signs of Disturbed by Vata | Signs of Disturbed by Pitta | Signs of Disturbed by Kapha | Signs of Disturbed by Multiple Doshas |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutra Urine |
Excessive fluid intake, Coffee, Alcohol, Hydrophilic substances, Diaphoretic herbs, Diabetes, Anxiety. | Insufficient water intake, Excessive consumption of tomatoes, spinach or other foods high in oxalic acid, Dehydration, Heavy sweating, Suppression of urination, Sex with a full bladder, Kidney diseases, Post-influenza perspiration, Chronic illness, Parasites and bacteria. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Purisha Feces |
Suppression of natural urges to pass flatus and feces, Parasites such as amoebae or giardiasis, Chronic indigestion, Incompatible food combining, Dysfunctional agni, Malabsorption, Liver or spleen dysfunction. | Excessive exercise, Prolonged fasting, Insufficient food intake, Lack of nutrition, Chronic illness. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Sveda Sweat |
Excessive exercise, Working in hot conditions, Summer, Hot, spicy food, Hot drinks, Excessive water intake, Excess salt, Alcohol, Anger, Anxiety or grief, Fever, Obesity, Pitta disorders. | Insufficient water intake, Insufficient exercise, Dehydration, Vata disorders, Emotional factors such as greed and attachment, Cold weather, dry climate. |
|
|
|
|
|
Not available |
Rasas
Go to top| Rasa/Taste | Vipaka/Post-Digestion Taste | Virya/Potency | Elements | Gunas | Dosha Effect | Charactertics | Description | ActionsOnTissueElements | ActionsOnWasteProducts | AffectsOfOvereat | Exceptions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Madhura Sweet |
Madhura Sweet |
Cold Potency | Water, Earth | V- P- K+ | Sticks to the tongue, is tasty and creates desire for it, provide a feeling of contentment (pleasure) to the body and comfort to the sense organs. | It causes softening of the body, promotion of brain activities, healing of ulcers, beneficial for reducing burning sensation, thirst and it is useful for the diseases of heart, throat, skin and hair. Drugs having this taste are generally used in the case of general debility and for rejuvenation of the body. | In general promote the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. | It promotes elimination of the waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat). | If used in excess, it causes fatness, heaviness, loss of appetite, parasitic infestation, cough, asthma, digestive disorders, suppression of digestive power, obstinate urinary disorders including diabetes, fever, hoarseness of voice, goitre, lymphadenitis, tumours and conjunctivitis. | Generally, substances of sweet taste cause increase of kapha except Honey, Old Rice (more than one year old), Wheat. | |
|
Amla Sour |
Amla Sour |
Hot Potency | Fire, Earth | V- P+ K+ | Makes the mouth watery, causes horripilations (the erection of hairs on the skin) and tingling of the teeth, and leads to closing of the eyes and brows. | It promotes salivation, appetite, carmil1ative and digestion. It is It is, therefore, used in patients suffering from dyspepsia, indigestion and anorexia. It reduces semen and eyesight. | In general promote the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. | It promotes elimination of the waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat). | If used in excess, it causes giddiness, cataract, fever, itches, anemia, ocdema, obstinate skin diseases including leprosy, morbid thirst, laxity of muscles, inflammation and burning sensation, loss of strength, blindness, giddiness, itching, and fevers. | Generally substances of sour taste cause increase of pitta, except dhatri, dadima, and amalaka. | |
|
Patu/Lavana Salty |
Madhura Sweet |
Hot Potency | Fire, Water | V- P+ K+ | Causes more moisture in the mouth (increase salivation) and burning sensation in the cheeks and throat. | It is cleansing, appetizer, carminative. It removes the rigidity, clears the obstructions (of the channels and pores). It causes moistening and promotes digestion, appetite and expectoration. It is, therefore, useful in indigestion, dyspepsia and cough. It causes slothfulness and softness of the body. It reduces strength. | In general promote the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. Saline taste produces slothness of the body. | It promotes elimination of the waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat). | If taken in excess, it causes thirst, fever, skin diseases, ascites, impotency, impairment of sense organs, premature greying of hair, falling of hair, premature wrinkling, gastritis skin diseases, conjunctivitis, bleeding from different parts of body. | Generally salts are bad for the eyes except Rock Salt (Saindhava). | |
|
Katu Pungent |
Katu Pungent |
Hot Potency | Air, Fire | V+ P+ K- | Stimulates (excites) the tip of the tongue, causes irritation, brings out secretions from the eyes, nose and mouth, and causes burning sensation of the cheeks. | It stimulates digestive system, nervous system, cleans mouth and kills intestinal parasites, eliminates the doshas, breaks up hard masses, dilates (expands) the channels i.e opens up the channels of circulation. It is used in case of indigestion, dyspepsia, dysentery, sprue, obesity, diabetes, cough, asthma and parasitic infestation. | In general reduce the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. | It cause their retention of waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat) in the body. | If consumed in excess, it causes impotency, debility, emaciation, burning sensation, morbid thirst, fainting, trembling and neurotic pains, giddiness, dryness of mouth. It reduces strength and semen. | Generally pungents are non-aphrodisiacs and increase vata except for Guduchi, Dry Ginger, Pippali/Long-Pepper, Pointed Gourd, Garlic. | |
|
Tikka Bitter |
Katu Pungent |
Cold Potency | Ether, Air | V+ P- K- | Cleanses the mouth and destroys the organs of taste (makes perception of other tastes impossible). | It is anthelmintic, blood purifier and anti-pyretic. It cures morbid thirst, fainting, parasitic infestation, skin diseases, fever, obesity, diabetes, poisoning, nausea, burning sensation, ulcers and pus formation in the body. It cleanses the throat, lactation and mouth. It stimulates agni. | In general reduce the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. Bitter taste has specific action to cause depletion of fat tissues, bone marrow and lymph. | It cause their retention of waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat) in the body. | If consumed in excess, it causes emaciation, roughness, weakness, depression, dryness in the body, headache, torticollis, exhaustion, pain, tremor, fainting, morbid thirst. It reduces strength and semen. | Generally pungents are non-aphrodisiacs and increase vata except for Guduchi, Dry Ginger, Pippali/Long-Pepper, Pointed Gourd, Garlic. | |
|
Kasaya Astringent |
Katu Pungent |
Cold Potency | Air, Earth | V+ P- K- | Inactivates the tongue (diminishes capacity of taste perception) and causes obstructions of the passage in the throat. | It causes healing and is anti-diuretic. It is, therefore, useful in diarrhoea, haemorrhage and wounds. | In general reduce the quantity of all the 7 tissue elements. | It cause their retention of waste products/malas (stool, urine, and sweat) in the body. | If consumed in excess, it causes heart diseases, causes stasis of food without digestion, flatulence, hoarseness of voice, constipation, impotency, weakness, emaciation and stiffness of the body. | All astringent things are generally constipative; but Haritaki is an exception to this rule. |
Vipakas/Post-Digestion-Tastes
Go to top| Name | Elements | Dosha Effects | Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Madhura Sweet |
Water, Earth | V- P- K+ | Builds the Dhatus, helps heal wounds, moisten the skin and create well-formed stools and clear urine. It promotes tissues in general and semen in particular and works as a laxative as well as diuretic. |
| Amla Sour |
Fire, Earth | V- P+ K+ | Forms Rakta Dhatu, strenghens Agni, reduces Ama, decrease Vata (reduces pain), creates sweat and cleanses the mouth and tongue. It reduces tissue elements and works as laxative and diuretic. |
| Katu Pungent |
Air, Fire | V+ P+ K- | Reduces Meda Dhatu and excessive fluids from the body, depletes the Dhatus, causes constipation and blocks sweat glands. |
Viryas/Potencies
Go to top| Name | Elements | Dosha Effects | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot Potency | Fire | V- P+ K- | It produces heating effect in the body, promotes digestion, causes sweating, thirst and emaciation. |
| Cold Potency | Water, Earth | V+ P- K+ | Cold/Soma-Principle. Produces cooling and moistening effects. Promotes life, increases tissue elements, especially the semen, produces tonic effect and causes revitalisation. |
Gunas
Go to top| Guna/Quality | Doshas | Elements | Rasas/Tastes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guru (Heavy) | Kapha | Water, Earth | Sweet, Salty, Astringent |
| Laghu (Light) | Vaata, Pitta | Ether, Air, Fire | Sour, Pungent, Bitter |
| Snigdha (Oily/Unctuous) | Pitta, Kapha | Water | Sweet, Sour, Salty |
| Ruksha (Dry/Ununctuous) | Vaata | Air, Fire, Earth | Pungent, Bitter, Astringent |
| Sara (Mobile) | Vaata | Air, Water | Sour |
| Sthira (Stable) | Kapha | Earth | |
| Shlakshna (Smooth) | Kapha | Fire | |
| Khara (Rough) | Vaata | Air | |
| Sthula (Gross) | Kapha | Earth | |
| Sukshma (Subtle) | Vaata | Ether, Air, Fire | |
| Ushna (Hot) | Pitta | Fire | Sour, Salty, Pungent |
| Sheeta (Cold) | Vaata, Kapha | Water | Sweet, Bitter, Astringent |
| Tikshna (Sharp) | Pitta | Fire | Sour |
| Manda (Dull) | Kapha | Water, Earth | |
| Kathina (Hard) | Vaata | Earth | |
| Mrudu (Soft) | Kapha | Ether, Water | |
| Sandra (Dense) | Kapha | Earth | |
| Drava (Liquid) | Pitta | Water | |
| Pichchila (Cloudy/Slimy) | Kapha | Water | Sweet |
| Vishada (Clear/Non-Slimy) | Vaata | Ether, Air, Fire, Earth |
Karmas
Go to top| Karma (Sanskrit Name) | Karma (English Name) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Angamarddaprasamana | Bodyache Relievers | Bodyache Relievers. |
| Arshoghna | Anti Haemorroidals | Helps in piles. |
| Sandhaneeya | Wound Healer | Not available |
| Vrishya/Vajikarana | Aphrodisiac | These are herbs that correct conditions of impotence and impure sex power. It causes excitement and passionate sex desire. |
| Avrishya | Anti Aphrodisiac | These are herbs that depress the sexual organs. |
| Bhedana | Purgative | That which eliminates both the solid and disintegrated excreta through the downward tract without dissolving or liquefying them. It causes rapid evecuation. |
| Chhardinigrahana | Anti Emetic | These are medicines which have the effect of relieving and suspending sickness of the stomach and thus preventing vomiting. |
| Chedana | Chedana | The drug which by force, uproots the adhered dosas is called chedana dravya. |
| Dahaprasamana | Curatives of Burning syndrome | Relieve burning sensation. or Relieve heat of body. |
| Jvarahara | Febrifuge/Anti Pyretic/Refrigerant | These are herbs that are cooling to the system and are used to reduce fevers. |
| Dipana | Digestive Stimulant | They stimulate the power of digestion, and cause (digestion) of ama (undigested or improperly metabolised product of food). They are dominated by agni mahabhuta. |
| Hikkanigrahana | Anti Hiccup | Relieve hicups. |
| Kandughna | Anti Psoric | Destroy itching. |
| Kanthya | Useful for Throat | Useful for Throat |
| Krmighna | Anthelmintic/Parasiticide | These are herbs which have the capacity to destroy intestinal worms and parasites; there are two categories of anthelmintics: Vermicides are agents which destroy worms without necessarily causing their expulsion from the bowels. Vermicides should be followed by or combined with laxative or cathartic herbs. Vermifuges are agents which expel worms from the bowels, usually having cathartic properties. |
| Lalotpadaka | Sialagogues | These are the agents that promote an increased flow of saliva. |
| Lalaghna | Anti Sialagogues | These are the agents that reduce the flow of saliva. |
| Lekhaniya | Reducing Corpulency | That which remove fat from the body by scraping the nonessential adipose/fat tissue. |
| Madaka | Intoxicant | That which is intoxicating and which is effective in destroying the wisdom. |
| Mutra Sangrahaniya | Antidiuretic | Reduce secretion of urine. |
| Mutra Virechaniya | Diuretic | These are herbs that increase the flow of urine. They are usually combined with demulcents to soothe any irritation from acids or gravel. |
| Nidrahara | Antihypnotic | Antihypnotic. |
| Nidrakara | Hypnotic | Hypnotic. |
| Prajasthapana | Anebolic | Which eliminate procreational defects and thus restores embryo. Cure Barreness or Sterility. |
| Pramathi | Pramathi | That which by its own potency eliminates the dosas located in the channels of circulation. |
| Purisha Sangrahaniya | Anti Diarrhoeal | Those which relieve losseness of the bowels and make the stools consistent. |
| Purisha Virajaniya | Bowel Anti Discoloring agent | Alter the colour of the faeces. |
| Rasayana | Rejuvenator | The drug which destroys the process of aging as well as diseases is called rasayana dravya. |
| Visha | Toxic | They are regarded as possessed of five properties. Vyavayi (Capable of affecting the entire system); Sukshma (Capable of penetrating the minutest nerves of the body); Vikasi (Capable of drying the humors, depressing the organism, and causing a relaxation of the joints); Agneya (Capable of heating or stimulating the system); Madavha (Intoxicants or Capable of robbing consciousness). Taken in large doses, poisons destroy life; but in small or judicious doses, their action is beneficial, for they restore health and cure many diseases. |
| Vishaghna | AntiToxic | Acts as antidotes to poison. |
| Vyavayi | Vyavayi | That which pervades the entire body before getting digested e.g poisons, narcotics, opium etc. |
| Vedanasthapana | Anodyne/Analgesic | Which relieve pain produced by external causes such as wounds etc. These are herbs that relieve pain by lessening the excitability of the nerves and nerve centers. These are closely allied to the antispasmodics. |
| Vamana | Emetic | Produce Vomiting. Being dominated by Air and Fire elements; by nature, they have tendency to move upwards, and they help in the elimination of undigested kapha, pitta etc. They are usually administered in tincture and tea form. |
| Varnya | Complexion Promoter | Improve complexion. |
| Trishna Nigrahana | Thirst Restraining | Relieve thirst. |
| Svedopayoga | Diaphoretic/Sudorific | Allow for easier sweating/perspiration. These are herbs that increase perspiration. The diaphoretics influence the entire circulatory system; there are three categories of diaphoretics: Stimulating, Neutral, Relaxing. |
| Stanya Janana | Galactagogue | These herbs favor the secretion of milk from the nursing mother. |
| Snehopaga | Udvartana/Unction Helpers | Used in combination with other powders to bind them in making pills or may be applied externally to soften and soothe. They are applied in salves, fomentations and poultices. |
| Svasahara | Anti Asthmatic/Broncho Dilator | Cure difficult breathing or Asthma. |
| Sukra Janana | Spermatopoietic | Increase the secretion of semen. |
| Sirovirechanopayoga | Cerebral Purgative | Adjuvents of for elimination of Doshas from head. Cerebral purgatives. Possibly through snezzing? |
| Sanjnasthapana | Restorative of Conciousness | Restore consciousness. |
| Sankochana | Constringent | Constringent |
| Sitaprasamana | Curatives of cold | Which relieve sense of coldness or stop shivering. |
| Sulahara | Pain killer | Relieve Colic pains anywhere in the body. |
| Sramsana | Laxative | The drug which eliminates the excreta that is pakva (digested) after disintegrating their solid state is called sramsana dravya. |
| Jeevaniya | Invigorator | Promote longevity |
| Brimhaneeya | Nutritives | Promote nutrition and increase corpulency. These supply a substantial amount of nutrients and aid in building and toning the body. These are mostly dominated by Water element. |
| Anulomana | Downward Vayu movement | The drug which causes downward movement of vayu is called anulomana dravya. |
| Sandhana | Sandhana | That which promotes the union of broken bones. |
| Pacana | Carminative | These drugs help in the paka (digestion) of ama (product of undigested food and improper metabolism). These are NOT necessarily Digestive Stimulants. |
| Balya | Strength Promoter | They promote strength and are dominated by prthvi mahabhuta. |
| Hridya | Cardiac Tonic | Which produces tonic effect on the heart. |
| Tripthighna | Removal of Pseudo Contentment | Kapha, when vitiated gives rise to a sense of pseudocontentment which tells upon normal health. Drugs, which remove that sort of pseudo-contentment are known as Triptighnas. |
| Kushthaghna | Cure Skin Diseases. | Cure all skin diseases. |
| Stanya Sodhana | Galacto Purificators | Purifies milk. |
| Sukra Sodhana | Spermato Purificators | Purify the semen. |
| Asthapanopayoga | Enema Non-oily | Used in non-oily/decoction enemas. |
| Anuvasanopayoga | Enema Oily | Used in oily enemas. |
| Mutra Vivarjaneeya | Urinary Anti Discoloring agent | Urinary anti- discoloring agents. |
| Sukra pravartaka | Semen ejaculator | Semen ejaculator. |
| Sukra Soshaka | Semen dehydrant | Semen dehydrant. |
| Sukra Sthambhaka | Semen anti-ejaculator | Semen anti-ejaculator |
| Kasahara | Expectorant | Promotes the thinning and ejection of mucus or exudate from the lungs, bronchi, and trachea; sometimes the meaning is extended to all remedies that quiet a cough. |
| Svayathuhara | Anti Inflammatory | Anti inflammatory. |
| Udarddaprasamana | Curatives of urticaria | Curatives of urticaria. |
| Sonitasthapana | Alterative/Blood-Purifier | These are herbs which alter (purify) the blood after eliminating its vitiating doshas. Most herbs for blood purification promote the cleaning action of the spleen, liver, kidneys and bowels. These herbs should be used over a long period of time, allowing gradual detoxification of the entire blood stream which in turn, will improve digestion, assimilation and glandular secretions. |
| Sukshma | Subtle | That which has the ability to enter through the thin and subtle channels of the body. |
| Samana | Alleviation of Doshas | These drugs help in the alleviation of dosas, and are generally, dominated by akasa mahabhuta |
| Stambhana | Constipative | The drug which is light for digestion, and which because of its astringent taste causes constipation is called stambhana dravya. |
| Vikasi | Vikasi | That which loosens the ligaments of the joints, which causes slackness of the hands and legs. These drugs after reaching the body, cause depletion of oja (essence of taste, energy during digestion and post digestive taste, i.e. essence of a product after digestion). These dravyas cause loosening of major joints between the constituents of various dhatus and bones, ligaments and also of numerous minor joints within the body, thus these dravyas bring about considerable decrease in the strength of the body, e.g. Tobacco, supari etc. |
| Abhishyandi | Obstructs channels of circulation. | That which obstructs the channels of circulation carrying rasa (plasma), and which produces heaviness in the body. |
| Romasnjanana | Hair growth promoters | Hair growth promoters. |
| Chakshusya | EyeTonic | Eye tonics. |
| Kesya | HairTonic | Hair tonics. |
| Dantya | DantyaTonic | Tooth and Gum tonics. |
| Shodhaniya | Antiseptic | That which prevents decay or putrefaction. A substance that inhibits the growth and development of microorganisms without necessarily destroying them. |
| Sugandhi Tadravya | Aromatics | These are herbs which have a fragrant smell and an agreeable, pungent taste. Aromatic herbs have a stimulating effect on the gastrointestinal mucus membrane because of their essential oils. They have a spicy taste and are used to aid digestion and expel wind from the stomach and bowels. They are also used to cover the taste of bitter herbs. Aromatic herbs are also carminatives. If inflammation of the stomach or bowels is present, aromatic herbs should be avoided. |
| Not available | Deobstruent | These herbs remove obstructions. Also see Aperients and Laxatives for treating the intestines. |
| Virechana | Purgative | These are purgative drugs and are dominated by prthvi as well as jala mahabhutas. By nature, they have tendency to move downwards. They help in the elimination of both pakva (digested) and apakva (undigested) excreta after dissolving them. |
| Sangrahi/Grahi | Digestive Stimulant, Carminative, and Constipative | That which as a result of its heating nature works as Dipana (Digestive Stimulant) And Pacana (Carminative) And which simultaneously causes Constipation |
| Yogavahi | Enhancers | That which when added to another drug enhances the effect of the latter. |
| Tridosha | Tridosha | That which balances all the doshas. |
| Vaataghna | Removing disorders of Wind | That which removes disorders of Wind. |
| Chedi | Cleanses Channel | That which cleans channels. |
| Jantunasana | Anti biotic | That which acts as antibiotic. |
| Rucya | Stimulate taste | Stimulate taste |
| Medohara | Fat Remove | That which removes fat. |
| Sothahara | Anti Inflammatory | That which reduces inflammation. |
| Visaghna | Anti poison | That which removes poison. |
| Garbhashaya Vishodhana | Uterus Function Improver | That which improves the function of uterus. |
| Pittala | Bilious | That which causes secretion of bile. |
| Amadosahara | Restorer of impaired digestion and metabolism | That which restores impaired digestion and metabolism. |
| Harsana | Exhilaration | That which restores impaired digestion and metabolismThat which causes feeling of excitement, happiness, or elation. |
| Srstamala | Elimination of waste products | That which eliminates waste products. |
| Recana | Laxative | Gentle Laxative. |
| Rocana | Stimulate appetite | Stimulate appetite. |
| Medhya | Brain Tonic | Brain Tonic |
| Stimulates power of digestion | Stimulates power of digestion | Stimulates the power of digestion |
| Wholesome | Wholesome | Wholesome |
| Sukrala/Sukra Utpattikara | Semen Generator | It increases semen i.e Ojas |
| Stanya Kara | Milk Increase | It increases milk. |
| KaphaVatAghna | Kapha & Vata Balance | It balances Kapha and Vaata. |
| AgniPustiKara | Nourishment to Agni | It provides nourishment to digestive agni. |
| Ama pacana | Detoxicant | Removes ama. |
| Sroto Shodhana | Channel cleanser | Drugs having properties of cleansing the channel block |
| Vayasthapana | Anti aging | Anti aging |
| AgniDipana | Digestive stimulant Agni | Promoter of digestive power/agni. |
| Ojas/Tejas | VitalFluid/Semen | Promoter of both Ojas and Tejas. |
Therapeutic Usages
Go to top| Name (Sanskrit) | Name (English) |
|---|---|
| Svasa | Asthma |
| Kamala | Jaundice |
| Kasa | Cough |
| Ksaya | Phthisis/Wasting |
| Kustha | Diseases of Skin |
| Prameha | Urinary disorders (Increased frequency and turbidity of urine) |
| Raktapitta | Bleeding disorder |
| Sula | Pain |
| Hrdroga | Heart diseases |
| Jvara | Fever |
| Agnimandya | Digestive impairment |
| Amlapitta/Ajirna | Dyspepsia/Hyperacidity |
| Pandu | Anaemia |
| Mutraroga | Urinary disorders |
| Sopha | Oedema |
| Manasavikara | Psychological disorders |
| Inflammation | Sotha |
| Yakrdroga | Disease of liver |
| Sirah sula | Headache |
| Pravahika | Dysentery |
| Grahaniroga | Malabsorption syndrome/Diseases of Small Intestine |
| Gulma | Phantom Tumor |
| Yaksma/Rajayaksma | Tuberculosis |
| Pinasa | Chronic Rhinitis |
| Hikka | Hiccup |
| Raktadosa/Raktisara/Raktavikara | Vitiation of blood and its components |
| Nertaroga/Drstiroga/Aksiroga | Eye disease |
| Vranas | Ulcer |
| Vibandha | Constipation |
| Chardi/Vami | Vomit |
| Svarabheda | Hoarseness of voice |
| Vatarakta/Adhyavata | Gout |
| Yonidosa | Disorder of female genital tract |
| Udararoga | Diseases of abdomen (Ascites) |
| Arsa | Piles |
| Apaci | Chronic Lymphadenopathy/Scrofula |
| Kandu | Itching |
| Medoroga | Obesity |
| Meha | Excessive flow of urine |
| Sularoga | Gastric Ulcer/Duodenal ulcer/Colic |
| Adhmana | Flatulance with gurgling sound |
| Anaha | Distension of abdomen due to obstruction to passage of urine and stools |
| Kesa Patana | Falling of hair |
| Tvagroga | Skin disease |
| Jara | Senility/Progeriasis |
| Napumsakata | Impotency |
| Pliha | Splenic disease |
| Visa | Poison |
| Rasayana | Nutrient of mind and body with adapto-immuno-neuroendocrino-modulator properties. |
| Daha | Burning Sensation |
| Asargdara | Menorrhagia |
| Mutrakrcchra | Dysuria |
| Mutraghat | Urinary obstruction |
| Daurbalya | Weakness |
| Klaibya | Male impotence |
| Atisara | Diarrhoea |
| Amavata | Rheumatism |
| Vatasonita | Gout |
| Visavikara | Morbidity due to Poisonous substance |
| Gandamala | Cervical Lymphadenitis |
| Aruci | Tastelessness |
| Jirnajvara | Fever (Chronic) |
| Visamajvara | Fever (Intermittent) |
| Udavarta | Upward movement of gases |
| Siroroga | Diseases of head |
| Tamaka Svasa | Asthma (Bronchial Asthma) |
| Sitapitta | Urticaria |
| Asmari | Calculus |
| Dantasula | Toothache |
| Grdhrasi | Sciatica |
| Udarakrmi | Intestinal worms |
| Pitta Jvara | Fever (due to Pitta dosa) |
| Vatavyadi | Diseases due to Vata dosha/ Neurological disorders |
| Granthi | Cyst |
| Trsna | Thirst |
| Pilahayakritroga | Hepato-splenic affections |
| Antrasula | Intestinal colic |
| Suryavarta | Sinusitis |
| Parsva sula | Intercostal neuralgia and pleurodynia |
| Dosa Traya | Aggrevated Vayu, Pitta and Kapha |
| Apatantraka | Convulsion |
| Mukharoga | Diseases of mouth |
| Amatisara | Diarrhoea due to indigestion |
| Karnaroga | Diseases of ear |
| Apasmara | Epilepsy |
| Kotha | Urticaria |
| Unmada | Mania |
| Pitika/Pidaka | Carbuncle |
| Pratisyaya | Sinusitis |
| Balaroga | Diseases of children |
| Danatapuya | Pyorrhoea |
| Jirnapratisyaya | Chronic sinusitis |
| Kantharoga | Diseases of throat |
| Sanshisula | Joint pain |
| Vicarcika | Eczema |
| Visucika | Gastro-enteritis with peircing pain |
| Vrkkaroga | Renal disorder |
| Kampa | Tremor |
| Dustavrana | Non-healing ulcer |
| Balya | Increase stamina and endurance |
| Visarpa | Erysepales |
| Karsya | Emaciation |
| Kstaksina | Debility due to chest injury |
| Sphota | Boil |
| Rajyakshma | Tuberculosis |
| Karnasrava | Ottotthoea |
| Parinamsula | Duodenal ulcer |
| Vyanga | Pigmentation disorder |
| Sidma | Pityriasis versicolor |
| Ardhava Bhedaka | Migraine |
| Sarpadansha | Snake bites |
| Kumbhakamala | Hepatitis |
| Mukhapaka | Mouth ulcer |
| Sukra meha | Spermatorrhoea |
| Manasroga | Mental disorders |
| Anidra | Insomnia |
| Sangrahani | Diarrhea |
| Stanya vikara | Breast milk disorder |
| Prasveda | Excessive sweating |
| Sveta Pradara | Leucorrhoea |
| Smrti daurbalya | Weak memory |
| Vaatapitta Jvara | Fever (due to Vaata and Pitta dosa) |
| Prasdara | Excessive vaginal discharge |
| Pitta Daha | Burning sensation due to Pitta dosa |
| Musika Visa | Rat poisoning |
| Ksata sotha | Wound inflammation |
| Madya trsna | Alcoholism |
| Bastisotha | Cystitis |
| Agnidagdha | Burn injury |
| Visphota | Blister |
| Ardita | Facial palsy |
| Rakarsa | Bleeding piles |
| Ksayaja Kasa | Cough due to Phthisis/Wasting |
| Hrtkampa | Cardiac fibrillation |
| Asthisosa | Osteoporosis |
| Mutrasada | Oligouria |
| Kasthaartava | Dysmenorrhoea |
| Prasutijvara | Fever (Puerperal) |
| Mada | Intoxication |
| Urahkasata | Chest wound |
| Vidradhi | Abscess |
| Smrti vardhaka | Memory enhancer |
| Yakrtplihavrddhi | Enlargement of liver and spleen |
| Hrllasa | Angina pectoris (Heart issue) |
| Raktatisara | Diarrhoea with blood |
| Stanya dosa | Aversion to breast milk |
| Stanya ksaya | Decrease in breast milk |
| Nadi vrana | Sinus |
| Karna sula | Otalgia |
| Pama | Eczema |
| Netrabhiasanda | Conjunctivitis |
| Urastoya | Pleural effusion |
| Mudha Garbha | Malpresentation of the foetus |
| Rakta Gata Vata | Rakta affected by Vata doas |
| Basti roga | Diseases due to urinary system |
| Urustambha | Stiffness in thigh muscles |
| Tilaka | Non elevated mole |
| Arbuda/Karkata | Tumor |
| Sosa | Cachexia |
| Jirna carma roga | Chronic skin diseases |
| Galaganda | Goiter |
| Asrgdara Ruja | Dysmenorrhoea |
| Nashtartava | Ammenorrhoea |
| Rajadosa | Menstrual disorder |
| Garbhasya dosa | Uterine disorder |
| Madhumeha | Diabetes |
| Sravahar | Decongestant |
| Ksobhahar | Soothing |
| Vranashodhaka and Ropaka | Wound healing property |
| Slesmaja sotha | Inflammation due to kapha dosa |
| Dantodbhava | Fever (Dentitional) |
| Hrddaurbalya | Weakness of heart |
| Basti sula | Pain in urinary system |
| Medodosa | Disorder of adipose tissue |
| Slipada | Filariasis |
| Vrddhi | Inguino-scrotal sweelings |
| Amadosa | Impaired digestion and metabolism |
| Stanya pida | Diseases of breast |
| Trika sula | Pain in sacral region |
| Pliha Vrddhi | Enlargement of spleen |
| Yakrt Vrddhi | Enlargement of liver |
| Raktaksya | Blood loss |
| Badhiratva | Deafness |
| Pangutva | Paraplegia |
| Gartra Kampa | Tremors |
| Manyastambha | Neck rigidity/Torticollis |
| Hanustambha | Lockjaw |
| Ekangasosa | Wasting of one limb |
| Sukra akasya | Deficiency of semen |
| Vandhyatva | Infertility |
| Jihvastambha | Glossal palsy |
| Snayubhagna | Rupture of ligament |
| Asthibhagna | Bone fracture |
| Sthavara visa | Poisoning by plant or mineral |
| Jalodara | Ascites |
| Koshta sula | Abdominal pain |
| Krmiroga | Parasitic Infestation |
| Uterus Clean | Cleans uterus |
| Kanthamukharoga | Diseases of Mouth and Throat |
| Mukhasosa | Dry Mouth |
| Sukradosa | Diseases of Semen |
| Cleans Basti | Cleans urinary tract |
| Vaata Jvara | Fever (due to Vaata |
| Bhuta | Attacks by evil spirits |
| Parsva Ruk | Pain in side of chest |
| Paksaghata | Paralysis |
| Puyameha | Gonorrhoea |
| Ear disease | Ear diseases |
| Asthila | Hard tumor in abdomen |
| Katigraha | Stiffness of lumbar region |
| Sitanga | Coldness in the body |
| Ama | Metabolic waste/toxinx |
| Amavisha | Reactive toxins generated inside the body from Ama |
| Garavisha | Environment toxins |
Trigrams
Go to top| Name (Chinese) | Name (English) | Element | Number as per Early Heaven | Number as per Later Heaven | Direction as per Early Heaven | Direction as per Later Heaven | Family | Body Part | Tao Pillar | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qian | Heaven | Air (Metal) | 1 | 6 | South | Northwest | Father | Head | Tao of Philosophy, which comprise political, family, military, economic, business, amour, and many other philosophies. | |
| Dui | Lake | Air (Metal) | 2 | 7 | Southeast | West | Youngest Daughter | Mouth | Tao of Success. | |
| Li | Fire | Fire (Fire) | 3 | 9 | East | South | Second Daughter | Eye | Tao of Sex Wisdom (Taoist Sexology) | |
| Zhen | Thunder | Ether (Wood) | 4 | 3 | Northeast | East | Eldest Son | Foot | Tao of FOrgotten Food Diet(Taoist Herbology) | |
| Xun | Wind | Ether (Wood) | 5 | 4 | Southwest | Southeast | Eldest Daughter | Thigh | Tao of Healing Art (Acupuncture, Acupressure, and other Spiritual healing methods). | |
| Kan | Water | Water (Water) | 6 | 1 | West | North | Second Son | Ear | Tao of Revitalization. | |
| Gen | Mountain | Earth (Earth) | 7 | 8 | Northwest | Northeast | Youngest Son | Hand | Tao of Balanced Diet | |
| Kun | Earth | Earth (Earth) | 8 | 2 | North | Southwest | Mother | Stomach | Tao of Mastery (Personology, Fingerprint system, Numerology, Astrology, Directionology, and Symbology). |
Special Frequencies
Go to topFrequencies which are divisible by 3, 6, and 9 and whose sum is 9.
| Frequency | Categories | Indications | Descriptions |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.18 | Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer | Soft Tissue Sarcoma. |
| 1.44 | Spooky2 CAFL | AIDS 2 | Acquired immune deficiency. See HIV. Use Human T Lymphocyte Virus3.Immune System |
| 1.8 | Spooky2 XTRA | Sinus Congestion | inus congestion occurs when fluid becomes trapped in the sinuses. Home remedies including hydration, steam inhalation |
| 2.88 | Spooky2 CAFL | AIDS 3 | Acquired immune deficiency. See HIV. Use Human T Lymphocyte Virus3.Immune System |
| 3.6 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Anger and Irritability, Dog and Cat Hostility 1, Inflammation 1, Inflammation 2, Inflammation General, Insomnia 1, Irritability and Whining, Lymph Drain Circulation | Inflammation (from Latin: inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators., Interspecies agression, Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment. The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli. It is usually used to refer to anger or frustration.Mind, Irritability is the excitatory ability that living organisms have to respond to changes in their environment.The term is used for both the physiological reaction to stimuli and for the pathological, abnormal or excessive sensitivity to stimuli. It is usually used to refer to anger or frustration. In individuals with autism disorder for example, they tend to be marked by aggression patterns.Irritability can be a growing response to the objective stimuli of hunger or thirst in animals or humans which then reaches some level of awareness of that need. Irritability may be demonstrated in behavioral responses to both physiological and behavioral stimuli including environmental, situational, sociological, and emotional stimuli.The emotion, anger, also known as wrath or rage, is an intense emotional state. It involves a strong uncomfortable and hostile response to a perceived provocation, hurt or threat.A person experiencing anger will often experience physical conditions, such as increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and increased levels of adrenaline and noradrenaline.Some view anger as an emotion which triggers part of the fight or flight brain response. Anger becomes the predominant feeling behaviorally, cognitively, and physiologically when a person makes the conscious choice to take action to immediately stop the threatening behavior of another outside force.The English term originally comes from the term anger of Old Norse language.Anger can have many physical and mental consequences. The external expression of anger can be found in facial expressions, body language, physiological responses, and at times public acts of aggression. Facial expressions can range from inward angling of the eyebrows to a full frown. While most of those who experience anger explain its arousal as a result of what has happened to them, psychologists point out that an angry person can very well be mistaken because anger causes a loss in self-monitoring capacity and objective observability.Modern psychologists view anger as a primary, natural, and mature emotion experienced by virtually all humans at times, and as something that has functional value for survival. Uncontrolled anger can, however, negatively affect personal or social well-being and impact negatively on those around them. While many philosophers and writers have warned against the spontaneous and uncontrolled fits of anger, there has been disagreement over the intrinsic value of anger. The issue of dealing with anger has been written about since the times of the earliest philosophers, but modern psychologists, in contrast to earlier writers, have also pointed out the possible harmful effects of suppressing anger.Mind, See Infections programs., The lymph is moved through the body in its own vessels making a one-way journey from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck. Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to pump it, its upward movement depends on the motions of the muscle and joint pumps., Use Parasites General program. |
| 9.18 | Spooky2 XTRA | Blood Hypertension, Blood Pressure High Renin Induced, Brain Tumor 1, Brain Tumor 2, Congestive Heart Failure, Convulsions 1, Convulsions with Spasticity, Deafness 1, Dermatitis, Detox All Purpose, Detox Respiratory, Detox Toxins Elimination 2, Ear Conditions Various 2, Ear Discharge, Eczema 2, Eczema Vascular and Lung, High Blood Pressure Hypertension, Hypertension 3, Hypertension 4, Kidney Infection 1, Languorous Paralysis, Locomotor Convulsions, Lumbago 1, Lumbago 2, Tumor Brain 2, Tumor Brain 3 | A variety of conditions may affect your hearing or balance:Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children.Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes.Ear, Also called Dermatitis. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches. Can also cause blood vessel and lung problems., Also called Dermatitis. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches.Skin, Also called Eczema. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches., Also called low back pain. Also see Back programs, and Pain programs., Also see Cancer programs., detoxification means cleansing the blood. This is done by removing impurities from the blood in the liver, where toxins are processed for elimination. The body also eliminates toxins through the kidneys, intestines, lungs, lymphatic system, and skin., Drink lots of pure water., Ear discharge, also known as otorrhea, is any fluid that comes from the ear. Most of the time, your ears discharge earwax., Epileptic seizures, High blood pressure., Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated., Inability of heart to pump blood efficiently enough to meet the bodys needs. Other use: deafness due to Otosclerosis., Kidney renin high., May refer to hypotonia, an intense muscle weakness. Also see Amyotonia Congenita., Rapid contraction and relaxation of muscles, leading to uncontrolled shaking., See Blood Pressure High., See Cancer Astrocytoma, Gliomas, Glioblastoma, and Astrocytoma programs., The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in animals and plants. The anatomy and physiology that make this happen varies greatly, depending on the size of the organism, the environment in which it lives and its evolutionary history. In land animals the respiratory surface is internalized as linings of the lungs. Gas exchange in the lungs occurs in millions of small air sacs called alveoli in mammals and reptiles, but atria in birds. These microscopic air sacs have a very rich blood supply, thus bringing the air into close contact with the blood. These air sacs communicate with the external environment via a system of airways, or hollow tubes, of which the largest is the trachea, which branches in the middle of the chest into the two main bronchi. These enter the lungs where they branch into progressively narrower secondary and tertiary bronchi that branch into numerous smaller tubes, the bronchioles. In birds the bronchioles are termed parabronchi. It is the bronchioles, or parabronchi that generally open into the microscopic alveoli in mammals and atria in birds. Air has to be pumped from the environment into the alveoli or atria by the process of breathing which involves the muscles of respiration.Lung, The source of many health issues arise when these toxins build up in the body over years.The liver is one of the bodys most essential organs that helps get rid of unwanted substances and toxins. The liver filters blood and metabolizes nutrients in order to keep us healthy., This occurs when a person cannot understand speech through hearing, even when sound is amplified. |
| 10.8 | Spooky2 XTRA | Tumor Benign | Also see Cancer programs. |
| 14.4 | Spooky2 XTRA | Multiple Sclerosis Myelin Sheath Repair | Demyelinating disease. Aspartame, mercury, benzene, lead, and toluene can cause same symptoms. Use Chlamydia General, Herpes Type 6, and see ALS, Herpes General, Blastocystis Hominis, Parasites Flukes, Shigella, Nocardia, and Herpes Zoster programs. |
| 18 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Acupuncture Disturbance Field, Emotions and Sleep 1, Joint Mobility, Memory Reading Spelling Improve | Emotions play a key role in overall mental health, and sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal homeostasis of emotional functioning.Mind, Improve your mental ability to read and spell, Joint Mobility is defined as the degree to which an articulation (where two bones meet) can move before being restricted by surrounding tissues (ligaments/tendons/muscles etc.). Otherwise known as the range of uninhibited movement around a joint., Meridian disruption due to scarring. |
| 31.32 | Spooky2 XTRA | Insomnia Secondary/Hypoglycemia | Experimental. All program settings defaults except Wave=sine, Amplitude=4, Repeat Prog=0. Start 30 mins before bedtime. |
| 36 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Cramps General, Emotions and Sleep 2 | Emotions play a key role in overall mental health, and sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal homeostasis of emotional functioning. Deficient sleep, both in the form of sleep deprivation and restriction, adversely impacts emotion generation, emotion regulation, and emotional expression.Mind, Overuse of a muscle, dehydration, muscle strain or simply holding a position for a prolonged period can cause a muscle cramp. In many cases, however, the cause isnt known. Although most muscle cramps are harmless, some may be related to an underlying medical condition, such as: Inadequate blood supply. |
| 54 | Spooky2 XTRA | Emotions and Sleep 3 | Emotions play a key role in overall mental health, and sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining the optimal homeostasis of emotional functioning. Deficient sleep, both in the form of sleep deprivation and restriction, adversely impacts emotion generation, emotion regulation, and emotional expression.Mind |
| 72 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Abdominal Inflammation, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 3, Allergies 1, Anal Itching, Aneurysm, Angina Pectoris, Apoplexy, Appendicitis, Appetite Lack Of, Asthma, Asthma 1, Ataxia General, Bells Palsy, Bells Palsy 1, Bells Palsy 2, Bells Palsy 3, Bilirubinemia, Black Vomit, Bladder Infection, Blood Hypertension, Bronchial Asthma, Bronchial Asthma 1, Bronchial Asthma 3, Bronchial Asthma 4, Bronchitis, Bronchitis 2, Cancer Basic 1, Cancer Breast 3, Cancer General 2, Cancer General program 2, Cancer Prostate, Cancer Prostate 2, Cancer Prostate 3, Candida Albicans 2, Candida and Organ Support 2, Candida Secondary, Cervical Inflammation, Chest Infection Secondary, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 1, Cold 1, Coordination Difficulties, Coughing, Cramping and Nausea, Croup, Detox 1 Toxins in the Intestines, Detox 3 Toxins in the Kidneys and Liver, Detox 4 Toxins Throughout the Body, Detox Mental Disorders, Diabetes 2, Diabetic Foot Infection, Disc Slipped, Dizziness 1, Dyspepsia, Emotional Spectrum, Emotions General Aid, Epstein Barr Virus 1, Fat Burn 3, Fatigue 1, Fatigue 2, Fatigue 3, Fatigue General, Frigidity, Fungus General, Gonads Inflammation 1, Head Injuries 1, Head Injuries 2, Head Injury Follow-up, Headaches Parasites 2, Heartburn Chronic, Hepatitis C 4, Hepatitis C 6, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, Impotence, Impotence 2, Indigestion, Indigestion 1, Indigestion 3, Infections 1, Infections General, Infectious Mononucleosis 1, Inflammation Urethra, Influenza 2003/2004 1, Itching, Itching 2, Jaundice, Kidney, Kidney Function Balance, Kidney Infection 2, Kidney Insufficiency, Kidney Stimulation, Languorous Paralysis, Locomotor Dysfunction Incoordination, Low Blood Sugar, Lumbago, Lumbago 1, Lumbago 2, Lung General 1, Lung General 3, Lung General Conditions, Lyme Herxheimer Helper 1, Lyme Herxheimer Helper 2, Meningitis 2, Meningitis 3, Meningitis Tertiary, Mental Disorders, Motion Sickness, Nerve Disorders 1, Nerve Disorders and Neuropathy, Orchitis, Otitis Medinum, Paralysis from Stroke, Paralysis Nonspastic, Paralysis Spastic, Parasites, Parasites and Amoebas 4, Parasites General, Parasites General 2, Parasites General Comprehensive, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Pericarditis, Pleurisy, Prostate Complaints, Prostate Problems General, Prostatitis, Sexual Dysfunction Men, Sinusitis, Sinusitis 1, Slipped Discs, Stomach Disorders, Stroke Follow Up, Systemic Conditions, Thrombosis Infective Herpes Type, Urethritis, Varicoses 2, Xanthemia, Yeast General, Yeast General V, Yeast Ultimate | A cold or the flu runs its course in a couple weeks, if youre lucky. After that, youre back to normal. But sometimes you may get bronchitis, too.Thats when your bronchial tubes, which carry air to your lungs, get infected and swollen. You end up with a nagging cough and a lot more mucus.You can get bronchitis in other ways, too, and there are actually two types of it:Acute bronchitis: This is the more common one. Symptoms last for a few weeks, but it doesnt usually cause any problems past that.Chronic bronchitis: This one is more serious, in that it keeps coming back or doesnt go away at all. Its one of the conditions that makes up whats called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, A cough, also known as tussis, is a voluntary or involuntary act that clears the throat and breathing passage of foreign particles, microbes, irritants, fluids, and mucus; it is a rapid expulsion of air from the lungs., A parasite is an organism that lives in or on another organism. It depends on its host for survival, and it might cause disease., A variety of different types of autoimmune diseases can produce symptoms of nerve pain and nerve damage. These include: multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barr syndrome (a rare condition in which the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves), myasthenia gravis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease., Acute inflammation of meningeal membranes, due to viral, bacterial (including Lyme spirochetes), or other organisms., Acute inflammation of meningeal membranes, due to viral, bacterial (including Lyme spirochetes), or other organisms. Bacterial: use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Influenza Haemophilus Type B, and see Listeriose, and Leptospirosis. Viral: use Echo, Coxsackie, and Meningococcus programs., Also called carotenemia. High levels of carotene in blood, causing skin discoloration., Also called glandular fever. Symptoms vary with age. Also see Mononucleosis, Epstein Barr Virus, and EBV., Also called low back pain. Also see Back programs, and Pain programs., Also called low back pain. Also see Back programs, and Pain programs.Back, Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs., Also see Blood Purify programs., Also see Disc Herniated, Disc Slipped, Hernia Disc, Herniated Disc Reduce Swelling, and Intervertebral Disc Displacement., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Gastroenteritis programs.Stomach, Also see General Antiseptic programs., Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Also see Stroke programs.Nerve, An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder, or urethra., Appetite stimulant., Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi), the air passages between the mouth and nose and the lungs.More specifically, bronchitis describes a condition where the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes inflamed.Individuals with bronchitis have a reduced ability to breathe air and oxygen into their lungs; also, they cannot clear heavy mucus or phlegm from their airways.This article will cover the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention of bronchitis. Symptoms of bronchitisMan coughingBronchitis is characterized by persistent coughing.Signs and symptoms of both acute and chronic bronchitis include:Persistent cough, which may produce mucusWheezingLow fever and chillsChest tighteningSore throatBody achesBreathlessnessHeadachesBlocked nose and sinusesOne of the main symptoms of acute bronchitis is a cough that lasts for several weeks. It can sometimes last for several months if the bronchial tubes take a long time to heal fully.It is common for the symptoms of chronic bronchitis to get worse two or more times every year, and they are often worse during the winter months.However, a cough that refuses to go away could also be a sign of another illness such as asthma or pneumonia., Bulge in weak blood vessel wall., Chest pain indicative of cardiac problems.Heart, Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs.Lung, Combination treatment and support., Diabetic foot infection, defined as soft tissue or bone infection below the malleoli, is the most common complication of diabetes mellitus leading to hospitalization and the most frequent cause of nontraumatic lower extremity amputation., Disorders which affect a number of organs and tissues, or the body as a whole., Drink lots of pure water., Drink lots of pure water.Kidney, Enlarged and twisted veins, usually on leg, due to valve defects., Excessive muscle contraction leading to movement problems.Nerve, Fatigue is a term used to describe an overall feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. It isnt the same as simply feeling drowsy or sleepy. When youre fatigued, you have no motivation and no energy. Being sleepy may be a symptom of fatigue, but its not the same thing.Fatigue is a common symptom of many medical conditions that range in severity from mild to serious. Its also a natural result of some lifestyle choices, such as lack of exercise or poor diet.If your fatigue doesnt resolve with proper rest and nutrition, or you suspect its caused by an underlying physical or mental health condition, see your doctor. They can help diagnose the cause of your fatigue and work with you to treat it., Formation of blood clot affecting blood flow, associated with Herpesviridae infections. Not to be used with Arrhythmia., Forty adult patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis were prospectively studied and randomized into two groups (control n = 20 and treatment n = 20). The treatment group underwent bilateral femoral quadriceps muscles electrical stimulation for 30 minutes during hemodialysis, three times per week, for two months. The patients were evaluated by pulmonary function test, maximum respiratory pressures, maximum one-repetition test, and six-minute walk test (6MWT), before and after the treatment protocol., Frigidity: Failure of a female to respond to sexual stimulus; aversion on the part of a woman to sexual intercourse; failure of a female to achieve an orgasm (anorgasmia) during sexual intercourse.This disorder can stem from psychological or emotional problems such as stress, anxiety, depression, fatigue, worry, guilt, fear of painful intercourse and fear of pregnancy. It can also develop from the undesirability of a partner, the undesirability of the setting, and the use of alcohol or drugs.Frigid- is derived from the Latin word frigidus (cold.) The suffix -ity is derived from the Latin -itas (condition, state)., General aid, especially if toxins are the cause. Use a good mineral supplement.Mind, General program., Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs., High blood pressure., If micro-perforation has occurred, infection must be eliminated before drinking any water. A few drops may be fatal., Incoordination of muscles. Slow results in some cases.Nerve, Increased presence of bilirubin in blood. See Jaundice programs., Infection of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and inside of pelvis, usually by Neisseria Gonorrheae, or Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Fallopian Tube Infection, Salpingitis, Gonorrhea, and General Antiseptic programs., Infectious inflammation of liver (from blood-to-blood contact). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Inflammation of mucous membrane that lines paranasal sinuses. Also see Lung Sinus Bacteria, and Sinus Bacteria. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and appropriate Sinusitis and Rhinitis programs., Inflammation of mucous membrane that lines paranasal sinuses. Also see Lung Sinus Bacteria, and Sinus Bacteria. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and appropriate Sinusitis and Rhinitis programs. Other use: head cold., Inflammation of ovaries or testes - also see Hydrocele, Orchitis, Gonads, Testicular Diseases, Testicle Fluid, or appropriate organ programs.Testicle, Inflammation of pericardium, the sac that surrounds the heart. Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable. This program was developed for animal research only., Inflammation of prostate., Inflammation of testes due to TB, Mumps, Gonorrhea, Cancer, bacteria, etc. See causative condition if known. See Gonads inflammation, Testicle Fluid, Testicular Diseases, and Hydrocele programs., Inflammation of the lung membrane and abdominal lining. Use Bronchitis, Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and General Antiseptic programs., Inflammation of urethra. See Vaginosis, and Chlamydia Trachomatis programs., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Should be run once a month as maintenance. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itch leads to a scratch reflex., Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Locomotor dysfunction., May be slow results. See Schumann Resonance program., May refer to hypotonia, an intense muscle weakness. Also see Amyotonia Congenita., Mental illness, also called mental health disorders, refers to a wide range of mental health conditions N disorders that affect your mood, thinking and behavior. Examples of mental illness include depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, eating disorders and addictive behaviors., micropredation.Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Middle ear swelling and/or infection and fever. See Ear Cholesteatoma and Ears programs. Always use Streptococcus Pneumonia with this. If uncomfortable, lower Amplitude.Ear, Most Lyme disease symptoms are actually excess inflammatory cytokine symptoms. Therefore, a die-off reaction consists of a worsening of many Lyme disease symptoms including: fatigue, brain fog, muscle and nerve pain, chills and sweats, and/or memory and thinking., Most of the time fatigue can be traced to one or more of your habits or routines, particularly lack of exercise. Its also commonly related to depression., Muscle weakness/paralysis not caused by excessive muscle contraction.Nerve, Not sterility but failure to achieve or maintain erection. See Erectile Dysfunction, Nitric Oxide Generate, Sacral, Zinc Etc., and use Circulatory Stasis., One-sided facial paralysis due to nerve dysfunction., One-sided facial paralysis due to nerve dysfunction.Nerve, OverviewThe common cold is a viral infection of your nose and throat (upper respiratory tract). Its usually harmless, although it might not feel that way. Many types of viruses can cause a common cold.Children younger than 6 are at greatest risk of colds, but healthy adults can also expect to have two or three colds annually.Most people recover from a common cold in a week or 10 days. Symptoms might last longer in people who smoke. If symptoms dont improve, see your doctor.SymptomsSymptoms of a common cold usually appear one to three days after exposure to a cold-causing virus. Signs and symptoms, which can vary from person to person, might include:Runny or stuffy noseSore throatCoughCongestionSlight body aches or a mild headacheSneezingLow-grade feverGenerally feeling unwell (malaise)The discharge from your nose may become thicker and yellow or green in color as a common cold runs its course. This isnt an indication of a bacterial infection., Peripheral nerves disorder - see Peripheral Nervous System Diseases., Peripheral nerves disorder - see Peripheral Nervous System Diseases.Nerve, Positive emotions feel good.Existing evidence suggests that positive emotions reliably alter peoples thinking and actions. Together with this past work, the experiments described in this article suggest that one reason positive emotions are worth pursuing is that they can help regulate negative emotions.Mind, Pruritis. Have a hot bath and drink a cup of apple cider vinegar after. If chronic and no long-term relief, use Parasites programs including General and Blood Flukes., Pruritis. Use Parasites Enterobiasis, and see Parasites General program., Respiratory condition due to viral infection of upper airway., Run Streptococcus pneumonia and General Antiseptic programs. See Chemtrail Detox program.Chest, See Strongyloides programs., See Candida and Yeast programs as well as other specific types., See Candida, and Candidiasis programs. Use Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris programs if no lasting relief achieved., See Chemtrail detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Chemtrail Detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Dyspepsia, Acidosis, Heartburn, and Hernia. If chronic or with bloating, use appropriate Parasites General program(s)., See Erectile Dysfunction, Impotence, Nitric Oxide Generate, and Sacral, Zinc Etc. Also see Circulation, and Circulatory programs, and Orchitis., See High Blood Sugar program., See Hyperglycemia programs., See Hypoglycemia, and Hyperinsulism., See Indigestion, Acidosis, Heartburn, and Hernia. If chronic or with bloating, use appropriate Parasites General program(s).Stomach, See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, See Liver Support, Gallbladder, Leptospirosis, Parasites General, and Flukes programs. Also see Icterus Haemolytic., See Low Blood Sugar program., See Mal de Debarquement, Nausea and Cramping, Parasites Enterobiasis, Roundworm, Round Worms, and Parasites Roundworm General programs., See Parasites Enterobiasis, Roundworm, Round Worms, and Roundworm General., See Prostatitis and other prostate programs. Use Streptococcus General, and Propionibacterium Acnes, and practise metals avoidance., See Pullularia Pullulans and Sorghum Smut programs., See Streptococcus, and Propionibacterium Acnes programs, and practise metals avoidance., See Vertigo, and Giddiness., See Yellow Fever., Seek immediate medical attention for this., Short program., Spinal disc pain. Also see Intervertebral Disc Displacement., Stroke paralysis. See Stroke Follow Up., Take a good calcium/magnesium supplement and use the Water Cure. See Acidosis, Hernia, Hyperacidity, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus General, and Heliobacter programs., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, The cervix is the lowest part of the uterus. It extends slightly into the vagina. This is where menstrual blood exits the uterus. During labor, the cervix dilates to allow a baby to pass through the birth canal (endocervical canal).Like any tissue in the body, the cervix can become inflamed for a variety of reasons. Inflammation of the cervix is known as cervicitis.Some women with cervicitis experience no symptoms. When symptoms are present, they can include:abnormal vaginal bleedingpersistent gray or white vaginal discharge that may have an odorvaginal painpain during intercoursea feeling of pelvic pressurebackachesThe cervix can become very inflamed if cervicitis progresses. In some cases, it can develop an open sore. Pus-like vaginal discharge is a symptom of severe cervicitis.Womb, The Emotional Electromagnetic Spectrum is an energy field that is fueled by the emotions of all sentient beings.Mind, The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder., Use appropriate E coli program, and Parasites General program if no lasting relief., Use Blood Cleanser., Use Chronic Fatigue V, EBV, Fatigue General, Parasites General, Roundworm, and Flukes programs. If no response, try Cancer Leukemia Hairy Cell., Warning: can cause large drop in blood sugar level. Can be caused by Cytomegalovirus, Hepatitis C virus, Enteroviruses and Ljungan virus., What is urethritis? Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body, becomes inflamed and irritated. Semen also passes through the male urethra. Urethritis typically causes pain while urinating and an increased urge to urinate, Yeast species. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 90 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Airsickness, Analgesic Pain Relief, Arrhythmia Cardiac, Craniofacial Dysostosis, Diphtheria, Embryopathies, Feel Good Overall, Granulomatosis Wegeners, Mange, Mange Follicular, Mange Follicular 1, Parasites Scabies, Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy, Romberg Disease, Scabies, Silicosis, Stroke, Well-being Sense of | A positive state of mind that enables a person to function effectively within society. Individuals who have good mental health are well-adjusted to society, are able to relate well to others, and basically feel satisfied with themselves and their role in society.Mind, Airsickness is a type of motion sickness, caused by conflicting signals your senses tell your brain. Your eyes adjust to the lack of movement around you and send a message to your brain that you are sitting still. Your inner ear, however, senses the actual movement., Also called Facial Hemiatrophy. Neurocutaneous disorder with tissue degeneration beneath skin, usually on one side of the face., Also called Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA). Serious systemic vasculitis that involves granulomatosis and polyangiitis., Also see Parasites Scabies, and Sarcoptes Scabiei Itch. Also use Psorinum., Bacteria causing sore throat, fever, rapid heartbeat, nausea, chills, and headache. Toxins may damage heart and nerves. See Corynebacterium Diphtheriae., Chronic systemic disease with severe pain, swelling, and skin changes. Also called Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, and Causalgia., Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange., Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange.Hair Skin, Developmental disorders or diseases in embryos., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., Irregular heartbeat, including tachycardia and bradycardia., Lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust, marked by inflammation and scarring with lesions in upper lobes of lungs., Now called Crouzon Syndrome. Malformation of skull and facial bones., Other uses: balance, security., Pain relief., Parry-Romberg syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by slowly progressive deterioration (atrophy) of the skin and soft tissues of half of the face (hemifacial atrophy), usually the left side. It is more common in females than in males., Sarcoptic mange is a contagious dermatitis found in many animals caused by scabies mites. Also see Scabies, and Sarcoptes Scabiei Itch programs.Skin |
| 108 | Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies, Spooky2 CAFL | Large Intestine Meridian, Liver Meridian, Streptococcus Mutant Strain Secondary | , Species causing dental caries and Endocarditis - see appropriate programs. |
| 126 | Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies, Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | CMV, CMV 1, Cytomegalovirus CMV 1, Cytomegalovirus CMV 2, Detox 3 Toxins in the Kidneys and Liver, Heart Meridian, Herpes Type 5, Lung Meridian | , Also see Blood Purify programs., Causes Infectious Mononucleosis, and retinitis. Also see Cytomegalovirus, CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, and HHV5 programs., Cytomegalovirus, also known as Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5., Herpes Type 5. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs., Herpes Type 5. Duty Cycle=72. Dr. H Clarks frequencies included. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs. |
| 144 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 2, Borrelia Lyme B, Coxsackie, Coxsackie General, Enterovirus, Headaches 1, Headaches 2, Headaches Comp, Influenza 2003/2004 1, Tonsillitis | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Generic term meaning small virus. Includes Echo, Coxsackie, and Polio., Headache From Computer. Headaches from computers are often caused by computer vision syndrome (CVS). If you spend extended periods of time on your computer you might get a headache due to glare on the screen, poor lighting in your workspace, improper computer brightness and color, or a combination of these factors., Headache is the symptom of pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It occurs in migraines (sharp, or throbbing pains), tension-type headaches, and cluster headaches. Frequent headaches can affect relationships and employment.There is also an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions whether serious or not. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society. Causes of headaches may include dehydration, fatigue, sleep deprivation, stress, the effects of medications, the effects of recreational drugs, viral infections, loud noises, common colds, head injury, rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage, and dental or sinus issues.Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication. A headache is one of the most commonly experienced of all physical discomforts.About half of adults have a headache in a given year.Tension headaches are the most common, affecting about 1.6 billion people (21.8% of the population) followed by migraine headaches which affect about 848 million (11.7%)., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis. Also see Mumps., Inflammation of tonsils, caused by viruses or bacteria., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease. |
| 144.72 | Spooky2 ALT, Spooky2 CAFL | Planet - Mars, Planetary Orbits | Brainwave frequencies, from Mercury to Pluto., Mars. Other uses: increase activity, energy, humor, freedom. |
| 161.82 | Spooky2 XTRA | Spine Problems A=432 | From Songs of the Spine, based on A=432Hz tuning. Waveform=square. Repeat Program=0. |
| 162 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Chelidonium, Heart General, Heart Tonic, Heart Tonic Animals, Sars 1 | Also use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program.Respiratory, Homeopathic remedy., it supports restorative, circulation, elevated cholesterol levels, arrhythmia, angina, atherosclerosis, high blood pressure for all species, Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable., Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable. Lab animals only. See Chlamydia, Staphylacoccus, Circulatory Stasis, and Kidney programs. |
| 180 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Adenoviridae Infections, Afibrinogenemia, AIDS/HIV, Amaurosis Fugax, Amniotic Band Syndrome, Aprosodia, Arm Injuries, Awakening Epilepsy, Babesiosis, Barotrauma, Barth Syndrome, Bedsores, Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome, Cancer, Cancer Digestive System, Cancer Endometrium, Cancer Neuroblastoma, Cancer Sezary Syndrome, Cancer Skin, Cancer Stomach, Candida, Candidiasis, Candidiasis Vulvovaginal, Carbohydrate-Deficient Glycoprotein Syndrome, Carcinoma Non-Small Cell Lung, Cardiac Tamponade, Central Core Disease, Chondroectodermal Dysplasia, Chromosome 16 Abnormalities, Coloboma, Coma, Cranial Nerve II Diseases, Cysts, Detox Liver Kidneys Lymph Intestine, Duodenal Ulcer, Dyslexia Symptoms, Dyspareunia, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Enchondromatosis, End Stage Renal Disease, Endometrial Cancer, Entropion, Ependymoma, Epilepsy, Fat Burn 3, Filariasis, Fusobacterium Infections, Gassers Syndrome, Hair Diseases, Hemoptysis, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis Viral Human, HIV Infections, HIV Related Infections, Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Coma, Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome, Hypoxia Brain, Ichthyosis, Jacobsen Syndrome, Jaw Diseases, Kidney Calculi, Kidney Diseases, Kidney Diseases Cystic, Kidney Tubular Necrosis Acute, Leiomyosarcoma, Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus, Lymphangioleiomyomatosis, Macular Degeneration, Madura Foot, Melanoma Amelanotic, Migraine Disorders, Neuronal Ceroid-Lipofuscinoses, Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma, Noonan Syndrome, Nose Diseases, Ophthalmoplegia Progressive Supranuclear, Optic Nerve Diseases, Pain Back, Parasites Flukes Liver, Parasites Flukes Lymph, Parasites Schistosoma haematobium, Pemphigoid Bullous, Polyhydramnios, Rabies, Ranula, Rhabdomyolysis, Rickettsia Infections, Royer Syndrome, Salmonella Enteriditis Gut, Salmonella Infections, Salmonella Paratyphi, Samters Syndrome, Shock Septic, Short Bowel Syndrome, Smegma, Spina Bifida Occulta, Spinal Cord Diseases, Spinal Muscular Atrophies of Childhood, Spondylitis Ankylosing, Syphilis Congenital, Torticollis, Toxocariasis, Tympanic Membrane Perforation, Varicose Veins, Vestibular Neuronitis | A hole in one of the eyes structures., Acquired immune deficiency., Acute kidney failure. Death of renal tubule cells due to drugs, low BP, or Renal Artery Obstruction.Kidney, Acute or chronic autoimmune skin disease, involving the formation of blisters., Age-related diminution or blurring of center of visual field. Use with Cataract programs., Also called Ellis-van Creveld Syndrome. Genetic skeletal and cardiac disorder., Also called Hemolytic-uremic Syndrome. Disease with hemolytic anemia, acute kidney failure, and low platelet count, usually in children. Also use E Coli and Shigella programs., Also called Kidney Stones. Also see Gravel in Urine, and Gravel Deposits., Also called Prader-Willi Syndrome. Rare genetic disorder with low muscle tone, short stature, incomplete sexual development, cognitive disabilities, behavior problems, and chronic insatiable hunger., Also called Pressure ulcers., Also called Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD). Also see Renal Dialysis and appropriate kidney programs.Kidney, Also called Vaginal Thrush., Also known as hydrophobia. See Lyssavirus, and Lyssinum programs., Also known as Maduromycosis, caused by Madurella fungus. Implicated in Morgellons Disease. Also use Staphylococcus Aureus, S. Coagulae Positive, S. Haemolyticus, and S. General., Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs., Also see Cancer and Carcinoma programs., Also use Parasites Strongyloides, and Parasites General programs., Bacteria causing food poisoning or blood infections in sub-Saharan Africa., Bacteria causing periodontal disease, Lemierres Syndrome, and skin ulcers - see appropriate programs. Implicated in colon cancers., Blood clotting disorder.Blood, Blood flukes. Associated with bladder problems. Also see Schistosoma Haematobium, and Blood Fluke programs., Can cause paratyphoid fever (similar to typhoid). See Typhoid Fever., Can cause upper respiratory and ear infections, tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, or croup., Cancer arising from wombs lining, most commonly after menopause, and associated with obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and excess estrogen., Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread., Candida infection, commonly called Thrush., Causes can include Glaucoma, Optic Neuritis, tumors, trauma, and other eye problems., Central nervous system tumor, usually intracranial in children and spinal in adults. See Cancer programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of spinal and sacroiliac joints. Also see Ankylosing Spondylitis programs., Closed sac with abnormal walls containing air, fluids, or semi-solids., Combination of shed skin cells, skin oils, and moisture occurring in female and male mammalian genitalia., Condition where asthma is induced by aspirin or other NSAIDs. Also see Asthma and related programs., Condition where damaged skeletal striated muscle breaks down rapidly, which can lead to kidney failure. Caused by trauma, strenuous exercise, and statin or fibrate drugs., Condition where eyelid folds inward, causing eyelash friction with cornea., Congenital - due to trapping of fetal limbs by fibrous bands while in utero., Congenital disorder with heart defects, short stature, learning and blood clotting problems., Congenital muscle disorder. Anesthesia may be contraindicated., Coughing up blood., Cutaneous T Cell Lymphomas. Sometimes considered to be late Mycosis Fungoides with Lymphadenopathy., Diseases of the inner ear. See Labyrinthitis, and Labyrinth Diseases., Disorder of development of bone and cartilage., Disorder with white patches of skin, mostly around genitals. Affects both sexes. Cause unknown. See Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus., Dyslexia is a learning disorder that involves difficulty reading due to problems identifying speech sounds and learning how they relate to letters and words (decoding). Also called reading disability, dyslexia affects areas of the brain that process language., Dystonic neck muscle condition with abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position., Enlarged and twisted veins, usually on leg, due to valve defects., Epilepsy is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.Anyone can develop epilepsy. Epilepsy affects both males and females of all races, ethnic backgrounds and ages.Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people with epilepsy simply stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure, while others repeatedly twitch their arms or legs. Having a single seizure doesnt mean you have epilepsy. At least two unprovoked seizures are generally required for an epilepsy diagnosis.Treatment with medications or sometimes surgery can control seizures for the majority of people with epilepsy. Some people require lifelong treatment to control seizures, but for others, the seizures eventually go away. Some children with epilepsy may outgrow the condition with age., Epilepsy with grand mal seizures on awakening., Excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac, seen in about 1% of pregnancies., Genetic disorder affecting multiple body systems, found only in males., Genetic disorder causing predisposition to kidney cancer, cysts, and fibrofolliculomas., Genetic disorder with progressive muscle wasting and mobility impairment., Gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain, with many different symptoms., Group of genetic cutaneous conditions with dry, thickened, scaly, or flaky skin., Hair diseases are disorders primarily associated with the follicles of the hair.A few examples areAlopeciaBubble hair deformityHair castsHair losshypertrichosisIngrown hairMonilethrixPremature greying of hairPattern hair lossTrichorrhexis invaginataMany hair diseases can be associated with distinct underlying disorders.Piedra are fungal diseases.Hair disease may refer to excessive shedding or baldness (or both). Balding can be localised or diffuse, scarring or non-scarring. Increased hair can be due to hormonal factors (hirsutism) or non-hormonal (hypertrichosis). Scalp disorders may or may not be associated with hair loss., Impaired functioning of optic nerve.Eyes, Includes Trisomy 16, FMF, Crohns Disease, Thalassemia, PKD-1, Autism, Schizophrenia, ADHD, and Synesthesia., Infection in humans of dog, cat, or fox roundworm., Infectious inflammation of liver (from blood or body fluids). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver., Inherited connective tissue disorder with six different types., Kidney disease means your kidneys are damaged and cant filter blood the way they should.If you experience kidney failure, treatments include kidney transplant or dialysis. Other kidney problems include acute kidney injury, kidney cysts, kidney stones, and kidney infections., Lining of womb. See Cancer Cervical, and Cancer Carcinoma Uterine Fermentative. Use Blood Cleanser., Liver flukeis a collective name of apolyphyleticgroup of parasitictrematodesunder the phylumPlatyhelminthes.They are principally parasites of theliverof variousmammals, including humans. Capable of moving along the blood circulation, they can occur also inbile ducts,gallbladder, and liverparenchyma. In these organs, they produce pathological lesions leading to parasitic diseases., Low oxygen. Use Circulatory Stasis, and see Cyanosis., Mainly a childhood neuroendocrine cancer. Use Blood Cleanser., Malabsorption disorder mainly caused by surgical removal of small intestine., Malaria-like illness caused by Babesia., Mildest form of spina bifida. Also see Spinal Dysraphism., Minor arm injuries are common. Symptoms often develop from everyday wear and tear, overuse, or an injury. Arm injuries are often caused by:Sports or hobbies.Work-related tasks.Work or projects around the home.Your child may injure his or her arm during sports or play or from accidental falls. The chance of having an injury is higher in contact sports (such as wrestling, football, or soccer) and in high-speed sports (such as biking, in-line skating, skiing, snowboarding, and skateboarding). Forearms, wrists, hands, and fingers are injured most often. An injury to the end of a long bone near a joint may harm the growth plate and needs to be checked by a doctor.Older adults have a greater chance for injuries and broken bones because they lose muscle mass and bone strength (osteoporosis) as they age. Older adults also have more problems with vision and balance, which increases their chances of having an accidental injury.Most minor injuries will heal on their own, and home treatment is usually all that is needed to relieve symptoms and promote healing., Multiple neurodegenerative disorders that result from excessive accumulation of lipopigments (lipofuscin) in tissues. Also see Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Neurological language/speech disorder.Brain, Now called Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation. Can cause serious organ system failure in infants., Organ detox, Painful sexual intercourse due to medical or psychological causes., Parasitic infection of roundworm spread by blood-feeding flies., Peptic ulcer in first part of small intestine., Physical discomfort occurring anywhere on the spine or back, ranging from mild to disabling., Pleomorphic bacteria transmitted by many arthropods, including chiggers, ticks, fleas, mites, and lice, as well as leeches and protists, causing Typhus, and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Also see Febris Wolhynia., Pressure on hearts sac due to build-up of fluid., Punctured eardrum. Causes include Otitis Media, trauma, ear surgery, extremely loud noises, or flying., Rare congenital defect where the left side of the heart is underdeveloped., Rare congenital disorder with intellectual disabilities, facial/skeletal and heart defects, and a variety of other problems., Rare, progressive, systemic disease that typically results in cystic lung destruction., Retrovirus causing HIV Infection and AIDS. Also see Human T Lymphotropic Virus., See also Cancer Lung Non-Small Cell, and Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma., See Cancer Basal Cell Skin Carcinoma, Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Cancer Melanoma. Use Blood Cleanser., See Heliobacter Pylori. Use Blood Cleanser., Serious complication that can arise when diabetes is not being properly controlled., Serious condition that occurs when Sepsis leads to dangerously low blood pressure and cell metabolism abnormalities., Smooth muscle malignant tumor most commonly found in uterus, intestines, blood vessels and skin., Some protozoa and parasitic flukes are also capable of causing infections of the human circulatory system. Although these infections are rare in the US, they continue to cause widespread suffering in the developing world today. Fungal infections of the circulatory system are very rare., Swelling of connective tissue on floor of mouth composed of mucin (mucocele) from ruptured salivary gland., The digestive or gastrointestinal (G.I.) system is made up of the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. These organs work together to break down the food you eat into nutrients that are absorbed by the bloodstream and carried to all of the cells in your body. This is what gives your body the vital fuel it needs to function.Facts about Digestive CancersColorectal cancer is the #3 diagnosed cancer in the US and the #2 cause of cancer related death in men and women. Many digestive cancers are found in later stages, but colorectal cancer can be found and treated in earlier stages or even prevented due to screening exams.The American Cancer Society reports that even though colorectal cancer is found more often in people ages 50 and older, its on the rise in people under age 50. A study from 1974-2013 found a 1% increase per year in the colon cancer incidence of people 20-49; and an increase per year in the new cases of rectal cancer in adults 20-39 (3%) and 40-54 (2%).The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network reports that pancreatic cancer is expected to be the second cause of cancer-related death by 2020.According to the Esophageal Cancer Action Network, Esophageal cancer caused by long-time GERD (adenocarcinoma) is one of the fastest growing cancers in the US.The CDC reports that liver cancer is increasing approximately 2.3% per year and the death rate is growing rapidly at 3% per year. The cause of this increase is credited mostly to an increase in the cases of Hepatitis C especially in the baby boomer generation., There are many problems that can affect the nose including a deviated septum, nasal polyps, nosebleeds, rhinitis, and nasal fractures., These disorders include fluid-filled cavities (syrinxes), blockage of the blood supply, inflammation (as occurs in acute transverse myelitis), tumors, abscesses, bleeding (hemorrhage), vitamin B12 or copper deficiency, infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), multiple sclerosis, and syphilis., Tissue injury caused by pressure differences between gas and liquid., Transient loss of sight in one eye., Type of skin cancer where cells do not make melanin, making them more difficult to recognise., Unconsciousness from which a person cant be awakened., Use Treponema Pallidum, and see Luesinum and Syphilinum programs., Usually this is the result of clenching your jaw or grinding your teeth over a long time, usually at night. Direct damage to the joint can also be caused from certain injuries or arthritis., Wide range of hereditary, developmental, and acquired kidney conditions involving cysts. Also see Polycystic Kidney Diseases and Medullary Sponge Kidney., Yeast. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 207.36 | Spooky2 XTRA | Independence | OriginalityPlanet - Uranus. Other uses: originality, spontaneity, independence. |
| 210.42 | Spooky2 ALT | Chakra Sacral, Sacral, Zinc Etc | Frequency of the Synodic Moon.Spirit, Impotence support (males). |
| 212.22 | Spooky2 XTRA | Vanadium 50v | Metal, trace element. |
| 216 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Bubonic Plague Yersinia Pestis, Dengue Fever 1, Healing Special, Influenza 1989, Tuberculosis General, Yersinia Pestis 1 | Also called breakbone fever. Mosquito-borne viral disease with fever, headache, muscle and joint pain., Also called Pasteurella pestis. Causes Bubonic Plague. Spread primarily by rats and their fleas. May also be involved in arthritis., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., General healing program, Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum.Lung, Spread primarily by rats and their fleas. Also called Black Death. See Plague, and Yersinia Pestis programs. |
| 228.78 | Spooky2 XTRA | Vanadium 50v | Metal, trace element. |
| 234 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Canker Sore 3, Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever, Ebola Virus, Lockjaw Tetanus, Stomatitis | Also called Hemorrhagic Shock., Also see Stomatitis Aphthous. Painful recurrent benign mouth ulcers., Due to wound infection with Clostridium Tetani. Also see Tetanus programs., inflammation of mouth and lips. See Candida, Herpes Simplex i, Stomatitis Aphthous, Pyorrhea, and Gingivitis programs., Virus causing Ebola, also called Hemorrhagic Shock. |
| 270 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer, Cancer Rhabdomyosarcoma, Corticobasal CBGD, Hot Flashes, Sexual Libido Boost | Also called RMS. Connective tissue cancer. May arise from progenitor cells. Use Blood Cleanser., Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread., Rare progressive neurodegenerative condition with marked movement disorders and cognitive dysfunction, Sexual desire is complex, with both psychological and physical components. Even when a person has a physical condition that affects libido, such as diabetes, improving the emotional and psychological response to sex can improve libido and sexual functioning., Type of flushing due to low levels of estradiol, common in menopause. |
| 270.54 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hydrogen 3h | Hydrogen and pH balance. |
| 288 | Spooky2 ALT, Spooky2 CAFL | Cervical Polyp, Chakra 2 3rd Eye, Chakra 2 Chain | 432Hz basis.Spirit, 432Hz-based. From Dr. Pankaj K Mishra.Spirit, Benign, often asymptomatic growth in cervical canal. |
| 306 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Lyme 2, Borrelia Lyme Tertiary, Borreliosis 1, Detox and Lymphs, Detox Heavy Metals 2, Detox Matrix, Lyme Dougs, Lyme Tertiary | Also called Lyme Disease., Also known as Borreliosis., Also see Blood Purify programs., Detox extracellular mesenchymal matrix., Heavy metal toxicity has proven to be a major threat and there are several health risks associated with it. The toxic effects of these metals, even though they do not have any biological role, remain present in some or the other form harmful for the human body and its proper functioning. They sometimes act as a pseudo element of the body while at certain times they may even interfere with metabolic processes. Few metals, such as aluminium, can be removed through elimination activities, while some metals get accumulated in the body and food chain, exhibiting a chronic nature. Various public health measures have been undertaken to control, prevent and treat metal toxicity occurring at various levels, such as occupational exposure, accidents and environmental factors. Metal toxicity depends upon the absorbed dose, the route of exposure and duration of exposure, i.e. acute or chronic. This can lead to various disorders and can also result in excessive damage due to oxidative stress induced by free radical formation., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease. |
| 324 | Spooky2 ALT, Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 3, Borrelia Spirochete B, Disc Herniated 1, Francisella Tularensis, Herniated Disc Reduce Swelling, High Blood Sugar, Hyperglycemia, Hypertension 2, Hypertension 3, Hypertension 4, Influenza V2 Grippe, Joint Pain Basic, Leukoencephalitis, Leukoencephalitis 2, Lymph Drain Circulation, Mickies Magic Three, Multiple Sclerosis V, Sacral, Zinc Etc, Tularemia | Also see Disc Herniated, Disc Slipped, Hernia Disc, Intervertebral Disc Displacement, and Slipped Discs., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Chain after Borrelia Spirochete A in a Program., Demyelinating disease. Aspartame, mercury, benzene, lead, and toluene can cause same symptoms. Use Chlamydia General, Herpes Type 6, and see ALS, Herpes General, Blastocystis Hominis, Parasites Flukes, Shigella, Nocardia, and Herpes Zoster programs.Nerve, From Bruce Stenulson. Reputed to help arthritis, diabetes, hypertension, muscle spasms and more., Impotence support (males)., Inflammation of brains white matter, usually in infants and children, but also found in horses as a result of forage poisoning. Also see Leuco Encephalitis, and Leucoencephalitis programs., Inflammation of brains white matter, usually in infants and children, but also found in horses as a result of forage poisoning. Also see Leuco Encephalitis, and Leucoencephalitis programs.Brain, Joint pain can be caused by injury affecting any of the ligaments, bursae, or tendons surrounding the joint., See Blood Pressure High., See High Blood Sugar program., See Hyperglycemia programs., Serious tick and arthropod borne infection with lesions and fever, spreading to lungs, lymphatic system, liver, and spleen. Use Francisella Tularensis., Spinal disc pain. Also see Intervertebral Disc Displacement., The lymph is moved through the body in its own vessels making a one-way journey from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck. Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to pump it, its upward movement depends on the motions of the muscle and joint pumps., Tick, deer fly, and arthropod borne highly virulent pathogen causing Tularemia. Found in lagomorphs, rodents, galliformes, and deer. Easily aerosolized, so likely weaponized. |
| 342 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 3, Autism, Bronchiectasis, Canker Sore 1, Fluor Alb, German Measles 1, Measles, Measles Rubeola, Multiple Sclerosis V, Rubeola, Tuberculosis Aviare | 9-Day Measles. Infectious disease with rash, cough, runny nose, eye inflammation, and fever. Also see Measles Rubeola, and Measles., Also called 9-Day Measles. Infectious disease with rash, cough, runny nose, eye inflammation, and fever. Also see Rubeola., Also called Rubella, or 3-Day Measles. Infectious disease with rash, sore throat, itching, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. See Measles Rubella, and Rubella programs., Also called Rubeola. Highly contagious condition with fever, cough, rhinitis, red eyes, followed by white oral spots and red skin rash., Also see Stomatitis Aphthous. Painful recurrent benign mouth ulcers., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Chronic dilatation of the bronchi., Demyelinating disease. Aspartame, mercury, benzene, lead, and toluene can cause same symptoms. Use Chlamydia General, Herpes Type 6, and see ALS, Herpes General, Blastocystis Hominis, Parasites Flukes, Shigella, Nocardia, and Herpes Zoster programs.Nerve, Homeopathic cell salt., Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum.Lung, See Autistic disorder. |
| 343.8 | Spooky2 XTRA | Meridians - Bladder | Abbreviated as BL or UB (urinary bladder), described in Chinese as The Bladder channel of Foot Taiyang |
| 352.26 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hydrogen 2h | Hydrogen and pH balance. |
| 360 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Bladder Infection, Bladder TBC, Cancer Bladder TBC, Cancer Lymphogranuloma Lymphoma 2, Cataract, Eye Disorders, Eye General Ailments, Eyesight to Improve, Healing, Herpes General 5, Herpes Type 2A Secondary, Inflammation Urethra, Influenza Virus 1991/1992 Secondary, Smallpox Secondary, Vision Acuity, Vision Poor | Abnormal lymphatic growths due to Chlamydia Trachomatis, and use Blood Cleanser., Also called Variola. Extremely contagious viral disease marked by fever, prostration, and a rash of small blisters. Also see Herpes Simplex RTI program., Also see Bladder TBC, Cancer Bladder TBC, Cancer Urethral, Parasites, and Schistosoma. Use Blood Cleanser., Also see Esotropia, Exotropia, and Strabismus., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Vision Poor, and Vision Acuity., Also see Vision Poor, and Vision Acuity.Eyes, An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder, or urethra., Blurred vision, cataracts, crossed eyes, diplopia, infections, etc. Also use Macular Degeneration.Eyes, Clouding of lens of eye. Also see Eye and Eyes programs., healing is a complex and dynamic process of replacing devitalized and missing cellular structures and tissue layers., Primarily genital., Primarily genital. Also use General Antiseptic program., See Eye Disorders, Eyesight to Improve, and Macular Degeneration and Visual Acuity programs., See Eye Disorders, Eyesight to Improve, and Macular Degeneration and Visual Acuity programs.Eyes, Transitional Bladder Cancer. Can also cause kidney cancer. Also see Cancer Bladder and Cancer Urethral.Bladder, What is urethritis? Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body, becomes inflamed and irritated. Semen also passes through the male urethra. Urethritis typically causes pain while urinating and an increased urge to urinate |
| 378 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Campylobacter, Campylobacter 1, Campylobacter 2, Trichophyton Nagel Secondary | Bacteria causing food poisoning, usually found in poultry., Fungus that mostly infects nails. See Onchomycosis, Fungus General, Trichophyton General, and other Trichophyton programs. |
| 396 | Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies, Spooky2 XTRA | Emotional Patterns Release, Root Chakra, Solfeggio Frequencies | Fear and guilt. Solfeggio Frequency.Mind, Liberate guilt, fear, release emotional patterns, undo situations, facilitate change, transformation, miracles, DNA repair, connecting, relationships, whole-brain interconnection, awaken intuition, non-linear knowing, return to spiritual order, unconditional love., This is a low and smooth frequency that helps cleanse feelings of guilt, fear, and trauma. It is associated with Root Chakra. |
| 414 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Anthrax, Bacillus Anthracis 2, Borrelia Hatchlings and Eggs, Cancer Basic 1, Cancer General 3, Cancer General program 3, Cancer Leukemia Feline, Candida 1, Candida Albicans, Candida Albicans 1, Candida Albicans 2, Feline Cat Leukemia 1, Fungus and Mold 2, Hepatitis A 1, Hepatitis A 2, Lyme Hatchlings Eggs, Mold and Fungus General, Mold and Fungus General V, Sinusitis 3, Thrush, Tonsillar Pfropfe, Trichophyton Mentagrophytes, Vaginosis, Yeast General | Also called tonsillar plugs. Actinomyces-like granules in tonsils., Also known as Borreliosis., Also see specific types. See Mold, and Fungus programs., Candidiasis, usually oral, with white or light brown tongue coating, or vaginal. Also see Stomatitis programs., Cat. Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser.Blood, Feline leukemiavirus (FeLV) is a retrovirus that infectscats. FeLV can be transmitted from infectedcatswhen the transfer of saliva or nasal secretions is involved. If not defeated by the animals immune system, the virus can cause diseases which can be lethal., Fungus causing Tinea/Ringworm in humans and animals. See Trichophyton General, and Fungus General programs., General program. See Candida and Yeast programs as well as other specific types., Infectious inflammation of liver (from feces-contaminated food or water). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver (from feces-contaminated food or water). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary.Liver, Inflammation of mucous membrane that lines paranasal sinuses. Also see Lung Sinus Bacteria, and Sinus Bacteria. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and appropriate Sinusitis and Rhinitis programs., Non-specific infection. See Gardnerella, Urea Plasma, Candida, and Trichomonas programs., See Candida, and Candidiasis programs. Use Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris programs if no lasting relief achieved., Serious disease of lungs, intestines, and skin. Weaponised., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., Use Blood Cleanser., Weaponised bacteria that causes Anthrax., Yeast species. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if no long-term result., Yeast species. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term., Yeast. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 419.4 | Spooky2 XTRA | HERV | Human Endogenous Retroviruses. |
| 425.88 | Spooky2 XTRA | Iodine 1 | Iodine is a chemical element with the symbol I and atomic number 53. The heaviest of the stable halogens, it exists as a lustrous, purple-black non-metallic solid at standard conditions that melts to form a deep violet liquid at 114 degrees Celsius, and boils to a violet gas at 184 degrees Celsius. |
| 432 | Chakra Frequencies, General, Spooky2 ALT, Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Babesia, Babesiosis, Bacillinum, Bacillus Subtilis, Backache 2, Black Vomit, Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme, Borrelia Lyme 2, Borrelia Lyme B, Borrelia Lyme Tertiary, Borreliosis, Borreliosis 1, Borreliosis 2, Chakra 2 Chain, Chakra 2 Crown, Cholecystitis Chronic, Conjunctivitis, Corynebacterium Diphtheriae, Corynebacterium Diphtheriae 1, Cosmic Healing, Coughing, Cryptosporidium Parvum, Diphtheria, Diphtheria 1, Euglena, Immune System Stimulation 1, Immune System Stimulation 3, Immune System Stimulation 4, Influenza Swine, Kieferosteitis, Lyme Disease, Lyme Disease 6, Lyme Dougs, Lyme General, Lyme Tertiary, Morgellons Disease 1, Morgellons Disease 2, Protozoa, Pullularia Pullulans, Rhodococcus, Root Chakra, Sinusitis 3, Swine Flu, White Blood Cell Stimulation, Yellow Fever | , 432Hz basis. Other uses: chronic cholecystitis, gallbladder inflammation.Spirit, 432Hz-based. From Dr. Pankaj K Mishra.Spirit, A cough, also known as tussis, is a voluntary or involuntary act that clears the throat and breathing passage of foreign particles, microbes, irritants, fluids, and mucus; it is a rapid expulsion of air from the lungs., Also called Borreliosis. Relapsing fever in humans and animals caused by parasitic spirochetes from ticks. Use Borreliosis, Babesia, and Parasites blood flukes programs., Also called Lyme Disease., Also called Lyme Disease.Joints, Also known as Borreliosis., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see H1N1 - Swine Flu, and Spanish Flu., Bacteria causing sore throat, fever, rapid heartbeat, nausea, chills, and headache. Toxins may damage heart and nerves. See Corynebacterium Diphtheriae., Bacteria that causes Diphtheria., Bacteria that causes Diphtheria.Respiratory, Bacteria which can infect the immunocompromised. Also see Mycobacterium Infections programs, and try Diphtheria programs., Can cause conjunctivitis and disease in the immunocompromised, but also functions as a probiotic - as in natto., Group of unicellular eukaryotic organisms., Homeopathic allergy remedy.Lung, Homeopathic nosode.Respiratory, If no relief, use Kidney Insufficiency program, take magnesium and B6 supplements, drink plenty of water.Back, Inflammation of mucous membrane that lines paranasal sinuses. Also see Lung Sinus Bacteria, and Sinus Bacteria. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and appropriate Sinusitis and Rhinitis programs., Long-term inflammation of the gallbladder. See Gallbladder programs.Gallbladder, Malaria-like illness caused by Babesia., Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin., Natural frequency from the universe having cosmic healing abilities., Normalize. Also see Leukocytogenesis Stimulate., Normalize. Also see Leukocytogenesis Stimulate. NB: minimum of 5 treatments.Immune system, Parasitic protozoa causing diarrhea. See Cryptosporidiosis., Protozoan causing malaria-like symptoms. Mostly tick-borne, but has been found in blood products.Blood, See Immune System Stimulation, Leukocytogenesis Stimulate, and Leukopenia programs., See Yellow Fever., Severe viral infection which can damage the liver, kidneys, heart, and entire GI tract., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., Type of bone inflammation marked by enlargement and pain., Type of bone inflammation marked by enlargement and pain.Bone, Use Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Bacillus Subtilis., Water-dwelling unicellular flagellate protist. |
| 438.12 | Spooky2 XTRA | Selenium 34 | Trace mineral element essential for cardiac health. |
| 450 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Abdominal Inflammation, Abscesses 3, Abscesses Secondary, Acne 1, Acne 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 3, Antiseptic General, Appendicitis, Attention Deficit Disorder, Bronchial Pneumonia 3, Cancer Leukemia 2, Cancer Melanoma 1, Cancer Melanoma 2, Candida 1, Candida and Organ Support 2, Cholera 2, Cholera 3, Cholera Secondary, Cold 6, Dental Abscess, Detox Antiseptic Effect, General Antiseptic, General Antiseptic 1, General Antiseptic 3, General Comprehensive, Geniculate Herpes Zoster, H1N1 - Swine Flu, H5N1 - Bird Flu, Hansens Disease, Healing Acceleration, Herpes General 3, Herpes General V, Herpes Zoster, Herpes Zoster Oticus, HIV, Infections General Secondary, Influenza A, Klebsiella Pneumoniae 2, Leprosy Secondary Infection, Lung General 1, Lung General 3, Lung General Conditions, Lyme Disease 6, Lyme Disease 9, Lyme Pain and Repair Organs 1, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Pleurisy, Pneumonia, Pneumonia General, Stomach Disorders, Systemic Conditions, Virus Comprehensive | A cold begins when avirus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat.Your immune system -- the bodysdefense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., A dental abscess is a collection of pus that can form inside the teeth, in the gums, or in the bone that holds the teeth in place. Its caused by a bacterial infection. An abscess at the end of a tooth is called a periapical abscess. An abscess in the gum is called a periodontal abscess., Also called ADD. May be important to avoid preservatives, aspartame, dyes, and other toxins., Also known as Borreliosis., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Gastroenteritis programs.Stomach, Also see General Antiseptic programs., Also see Hansens Disease., Also see Infections General programs., Also see Leprosy programs., Also see Pneumonia Bronchial., Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser., Build-up of pus caused by bacterial infection. Many types may be involved. Use Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA), and see Listeriose.Skin, Combination treatment and support., Common pathogens., Disorders which affect a number of organs and tissues, or the body as a whole., ETDFL Includes H1N1, H5N1, Ebola, Rhinoviruses, Rotaviruses, Influenza A-B, Extremely contagious and serious bacterial infection of small intestines., Gram-negative bacteria normally present in mouth, skin, and intestines that causes serious lung conditions when inhaled - see Pneumonia programs., If micro-perforation has occurred, infection must be eliminated before drinking any water. A few drops may be fatal., Image result for Antisepticwww.dermnetnz.orgAn antiseptic is a substance that stops or slows down the growth of microorganisms. Theyre frequently used in hospitals and other medical settings to reduce the risk of infection during surgery and other procedures., inclusive, extensive, exhaustive, broad, wide, compendious, synoptic, sweeping, widespread, far-reaching, comprising, containing, all-embracing, all-inclusive, complete, thorough, discursive, encyclopedic, full, general, expansive, overall, blanket, umbrella; see also absolute 1, general 1, large 1, 2, whole 1., Infection of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and inside of pelvis, usually by Neisseria Gonorrheae, or Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Fallopian Tube Infection, Salpingitis, Gonorrhea, and General Antiseptic programs., Inflammation of the lung membrane and abdominal lining. Use Bronchitis, Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and General Antiseptic programs., Influenza A virus subtype H5N1, also known as A(H5N1) or simply H5N1, is a subtype of the influenza A virus which can cause illness in humans and many other animal species. A bird-adapted strain of H5N1, called HPAI A(H5N1) for highly pathogenic avian influenza virus of type A of subtype H5N1, is the highly pathogenic causative agent of H5N1 flu, commonly known as avian influenza (bird flu). It is enzootic (maintained in the population) in many bird populations, especially in Southeast Asia. One strain of HPAI A(H5N1) is spreading globally after first appearing in Asia. It is epizootic (an epidemic in nonhumans) and panzootic (affecting animals of many species, especially over a wide area), killing tens of millions of birds and spurring the culling of hundreds of millions of others to stem its spread. Many references to bird flu and H5N1 in the popular media refer to this strain.According to the World Health Organization and United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization, H5N1 pathogenicity is gradually continuing to rise in endemic areas, but the avian influenza disease situation in farmed birds is being held in check by vaccination, and so far there is no evidence of sustained human-to-human transmission of the virus. Eleven outbreaks of H5N1 were reported worldwide in June 2008 in five countries (China, Egypt, Indonesia, Pakistan and Vietnam) compared to 65 outbreaks in June 2006, and 55 in June 2007. The global HPAI situation significantly improved in the first half of 2008, but the FAO reports that imperfect disease surveillance systems mean that occurrence of the virus remains underestimated and underreported. In July 2013, the WHO announced a total of 630 confirmed human cases which resulted in the deaths of 375 people since 2003.Several H5N1 vaccines have been developed and approved, and stockpiled by a number of countries, including the United States (in its National Stockpile),Britain, France, Canada, and Australia, for use in an emergencyResearch has shown that a highly contagious strain of H5N1, one that might allow airborne transmission between mammals, can be reached in only a few mutations, raising concerns about a pandemic and bioterrorism., Kidney, lung, ovary, pancreas., Mostly affects skin, but can appear in mouth, intestines, or eyes. Use Blood Cleanser., Mostly affects skin, but can appear in mouth, intestines, or eyes. Use Blood Cleanser.Skin, Pimples, white/blackheads, greasy skin, possible scars. Also see Propionibacterium Acnes.Skin, Primarily orofacial., Reactivation of Herpes Zoster virus in ganglion of facial nerve, causing paralysis, pain, and taste loss. Also see Geniculate Herpes Zoster., Reactivation of Herpes Zoster virus in ganglion of facial nerve, causing paralysis, pain, and taste loss. Also see Herpes Zoster Oticus., Retrovirus causing HIV Infection and AIDS. Also see Human T Lymphotropic Virus., See Chemtrail detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Chemtrail Detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Pneumonia Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, Bronchial, Pneumocytis Carinii, and Bronchial Pneumonia programs. Always use Streptococcus Pneumoniae., See Pneumonia Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, Bronchial, Pneumocytis Carinii, and Bronchial Pneumonia programs. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program.Lung, Swine influenza is an infection caused by any one of several types of swine influenza viruses. Swine influenza virus (SIV) or swine-origin influenza virus (S-OIV) is any strain of the influenza family of viruses that is endemic in pigs. As of 2009, the known SIV strains include influenza C and the subtypes of influenza A known as H1N1, H1N2, H2N1, H3N1, H3N2, and H2N3.The Swine flu was initially seen in humans in Mexico in 2009, where the strain of the particular virus was a mixture from 3 types of strains. Six of the genes are very similar to the H1N2 influenza virus that was found in pigs around 2000.Swine influenza virus is common throughout pig populations worldwide. Transmission of the virus from pigs to humans is not common and does not always lead to human flu, often resulting only in the production of antibodies in the blood. If transmission does cause human flu, it is called zoonotic swine flu. People with regular exposure to pigs are at increased risk of swine flu infection.Around the mid-20th century, identification of influenza subtypes became possible, allowing accurate diagnosis of transmission to humans. Since then, only 50 such transmissions have been confirmed. These strains of swine flu rarely pass from human to human. Symptoms of zoonotic swine flu in humans are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general, namely chills, fever, sore throat, muscle pains, severe headache, coughing, weakness, shortness of breath, and general discomfort., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, This process of wound healing has four distinct phases that overlap with each other; haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and remodelling., Use appropriate E coli program, and Parasites General program if no lasting relief., Use for Chicken Pox and Shingles - see programs for both, and for Varicella., Yeast. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 468 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer 4 W1, Candida Robusta, Crohns and Other Bowel Problems, Influenza Virus B 1, Rickettsia Rickettsii 1, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., From Dr. Richard Loyd. Candida robusta is rarely identified in humans, but has been reported as a cause of VVC in pregnant women., Inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of GI tract. Also see Ileocolitis Colon Inflammation.Intestines, Potentially lethal tick-borne rickettsial illness with sudden onset of fever, headache, and muscle pain, followed by rash. Also see Lyme programs., See Cancer programs., Tick-transmitted causative agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. |
| 504 | Spooky2 XTRA | Yersinia Pestis 1 | Also called Pasteurella pestis. Causes Bubonic Plague. Spread primarily by rats and their fleas. May also be involved in arthritis. |
| 520.2 | Spooky2 XTRA | Morgellons Nancy DB | Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin. Dowsed by Nancy Sliwa. |
| 522 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Abdominal Pain, Acute Pain, Adnexitis, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 3, Allergies 1, Apoplexy, Appendicitis, Asthma, Asthma 1, Auto Intoxication, Autoimmune Disorders, Autointoxication, Back Spasms, Bronchial Asthma, Bronchial Asthma 1, Bronchial Asthma 3, Bronchial Asthma 4, Cancer Cervical 2, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 2, Cerebral Palsy, Cold 2, Coughing, Cryptococcus Neoformans, Dental 2, Detox 1, Detox 1 Toxins in the Intestines, Detox 3 Toxins in the Kidneys and Liver, Detox 4 Toxins Throughout the Body, Detox All Purpose, Detox and Lymphs, Detox Anesthesia 1, Detox Anesthesia 2, Detox Autointoxication, Detox Headache Toxicity 1, Detox Headache Toxicity 2, Detox Heavy Metals 2, Detox Lymphs, Detox Matrix, Detox Mental Disorders, Detox Toxins Elimination 1, Detox Toxins Elimination 2, Dizziness 1, Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy DMD, Echinococcus Granulosus 2, Edema 1, Edema 2, Edema and Swelling, Edema Swelling, Emotions General Aid, Fallopian Tube Infection, Fat Burn, Fat Burn 3, Fat Burn Hypophyseal Lymph Detox, Fibromyalgia 2, Food Allergies 2, Gingivitis 1, Gum Disease, Hangover, Head Injuries 1, Head Injuries 2, Head Injury Follow-up, Headaches Comp, Headaches Due to Toxicity, Herpes Simplex RTI, High Blood Sugar, Hives, Hives 1, Hives 2, Hyperglycemia, Hyperosmia, Iatrogenic Infections, Immune System Balance, Influenza 1979, Influenza 1993, Kidney 4, Kidney Function Balance, Kidney Infection 2, Lyme Herxheimer Helper 1, Lyme Herxheimer Helper 2, Lymph Drain Circulation, Lymph Stasis 1, Lymph Stasis Secondary, Lymphedema, Lymphs and Detox, Mental Disorders, Motion Sickness, Muscular Dystrophy 2, Muscular Dystrophy 3, Muscular Dystrophy 6, Oral Lesions, Otitis Medinum, Palsy Cerebral, Paralysis from Stroke, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Pharyngitis, Pneumonia General V, Polyp General, Prostatitis, Pyorrhea, Rhinitis, Stroke Follow Up, Sunstroke, Surgery Anaesthesia Detox, Surgery Pre-op Post-op Prevent Infections, Swelling, Swelling Edema 2, Tapeworm, Throat and Lymph Nodes, Torulopsis, Toxin Elimination, Tuberculinum, Urticaria, Yeast General | A cold begins when a virus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat. Your immune system -- the bodys defense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., A cough, also known as tussis, is a voluntary or involuntary act that clears the throat and breathing passage of foreign particles, microbes, irritants, fluids, and mucus; it is a rapid expulsion of air from the lungs., A food allergy is a condition in which certain foods trigger an abnormal immune response (2Trusted Source).Its caused by your immune system wrongly recognizing some of the proteins in a food as harmful. Your body then launches a range of protective measures, including releasing chemicals like histamine, which causes inflammation.For people who have a food allergy, even exposure to very small amounts of the problem food can cause an allergic reaction.Symptoms can occur anywhere from a few minutes after exposure to a few hours later, and they may include some of the following:Swelling of the tongue, mouth or faceDifficulty breathingLow blood pressureVomitingDiarrheaHivesItchy rash, Abnormal accumulation of interstitial fluid beneath skin and in body cavities. Also see Kidney insufficiency, and appropriate Lymph programs., Abnormal accumulation of interstitial fluid beneath skin and in body cavities. Also see Kidney insufficiency, and appropriate Lymph programs.Heart, Abnormal growth of tissue from mucous membrane., Acute intoxication symptoms include lightheadedness, dizziness, headache and nausea, and regular cumulative exposure to these toxic solvents over a number of years puts the individual at high risk for developing toxic encephalopathy., Also requires post-recovery saunas with electrolyte replacement. Other use: lymph drain., Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs., Also see Blood Purify programs., Also see Constipation, Auto Intoxication, and Autointoxication., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Kidney Insufficiency, and Lymph Stasis programs., Also see Salpingitis, and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease., Also see Stroke programs.Nerve, Anesthesia is the administration of medication to allow medical procedures to be done without pain, and in some cases, without the patient being aware during the procedure. There are a variety of types of anesthesia, as well as several different medical professions that are able to give anesthesia., Back spasms can be the result of injuries to the muscles, tendons, and ligaments in the back, or they can be related to more serious medical conditions. Heavy lifting is a common cause of back spasms.In addition to heavy lifting, any activity that puts excessive strain on the muscles and ligaments in the lower back can cause an injury. Sports such as football and golf can lead to back spasms because they demand that the back turn suddenly and repeatedly.Your back muscles may be more vulnerable if you have weak abdominal muscles, which help support the back. Weak or stiff muscles in the back itself can be injured more easily than muscles that are stronger and more limber.Back spasms may occur if you have arthritis or a ruptured disc in your spine. Arthritis in the lower back can put pressure on the spinal cord, which may cause pain in the back and the legs. A ruptured or bulging disc in the vertebrae may also pressure a nerve and result in back pain., Based on RTIs Herpes program; most freqs contract spread. Use for Measles, Chicken Pox, Smallpox, Mononucleosis, Shingles, Rubella, cold sores, Epstein Barr, Variola, Stomatitis, and Pyorrhea., Basically, detoxification means cleansing the blood. This is done by removing impurities from the blood in the liver, where toxins are processed for elimination. The body also eliminates toxins through the kidneys, intestines, lungs, lymphatic system, and skin., Bowels This is a major route of elimination of toxins from the body., Build-up of toxins in the intestines/colon. See Auto Intoxication, Constipation, Intestines to Release, Intestinal Obstruction, and Detox Autointoxication., Build-up of toxins in the intestines/colon. See Autointoxication, Constipation, Intestinal Obstruction, Intestines to Release, and Detox Autointoxication., Chronic cases will always recur until metal dentalwork is replaced with uranium-free porcelain. See Herpes Simplex i, and use Stomatitis programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs.Lung, Chronic widespread pain and heightened response to pressure with pronounced fatigue, sleep disturbance, stiff joints, and other symptoms. Also see Tendomyopathy. Other use: joint pains., Commonly caused by Gastroenteritis, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, urinary tract problems, and stomach inflammation., Dental care is the maintenance of healthy teeth and may refer to:Oral hygiene, the practice of keeping the mouth and teeth clean in order to prevent dental disordersDentistry, the professional care of teeth, including professional oral hygiene and dental surgeryOral Surgery, any of a number of medical procedures that involve artificially modifying dentition; in other words, surgery of the teeth and jaw bones, Detox extracellular mesenchymal matrix., detoxification means cleansing the blood. This is done by removing impurities from the blood in the liver, where toxins are processed for elimination. The body also eliminates toxins through the kidneys, intestines, lungs, lymphatic system, and skin., Drink lots of pure water., Drink lots of water and take an electrolyte solution. Use Electrolyte Levels program., Edema. Also see Kidney Insufficiency, and Lymph Stasis programs., General aid, especially if toxins are the cause. Use a good mineral supplement.Mind, Genetic form of Muscular Dystrophy., Group of movement disorders in early childhood with poor coordination, stiff/weak muscles, tremors, and possibly sensory problems., Group of movement, balance, and postural disorders that appears in early childhood., headache caused by systemic poisoning or associated with illness., Headache From Computer. Headaches from computers are often caused by computer vision syndrome (CVS). If you spend extended periods of time on your computer you might get a headache due to glare on the screen, poor lighting in your workspace, improper computer brightness and color, or a combination of these factors., Heavy metal toxicity has proven to be a major threat and there are several health risks associated with it. The toxic effects of these metals, even though they do not have any biological role, remain present in some or the other form harmful for the human body and its proper functioning. They sometimes act as a pseudo element of the body while at certain times they may even interfere with metabolic processes. Few metals, such as aluminium, can be removed through elimination activities, while some metals get accumulated in the body and food chain, exhibiting a chronic nature. Various public health measures have been undertaken to control, prevent and treat metal toxicity occurring at various levels, such as occupational exposure, accidents and environmental factors. Metal toxicity depends upon the absorbed dose, the route of exposure and duration of exposure, i.e. acute or chronic. This can lead to various disorders and can also result in excessive damage due to oxidative stress induced by free radical formation., Hives, often due to toxins. See Hives., Homeopathic nosode for Tuberculosis. See Tubercusosis, and Tuberculosis General., If micro-perforation has occurred, infection must be eliminated before drinking any water. A few drops may be fatal., Infection of periodontium causing inflammation of gums and bone loss. Although it may be controlled or eliminated with treatment, infection always returns whenever subject experiences stress or poor diet until dental mercury is removed. Also see Gingivitis.Teeth, Infection of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and inside of pelvis, usually by Neisseria Gonorrheae, or Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Fallopian Tube Infection, Salpingitis, Gonorrhea, and General Antiseptic programs., Infections contracted in a hospital/medical facility, or caused by a medical professional., Inflammation of gums caused by plaque leading to periodontitis. See Dental Infection, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis., Inflammation of pharynx. Can cause chronic sore throat, halitosis, and pharygeal ulcers. See Sore Throat, and Halitosis programs., Inflammation of prostate., Inherited muscle disorders that weaken the body and hinder normal movement. Also see Muscular Dystrophy programs., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Should be run once a month as maintenance. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., Itchy bumps on skin. See Urticaria programs., Localized fluid retention and tissue swelling in lymphatic system. Frequently caused by conventional cancer treatments or parasite infections., Lymph (from Latin, ancient Roman deity of fresh water, Lympha) is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to the central circulation. Interstitial fluid the fluid which is between the cells in all body tissues enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis., Mental illness, also called mental health disorders, refers to a wide range of mental health conditions N disorders that affect your mood, thinking and behavior. Examples of mental illness include depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, eating disorders and addictive behaviors., Middle ear swelling and/or infection and fever. See Ear Cholesteatoma and Ears programs. Always use Streptococcus Pneumonia with this. If uncomfortable, lower Amplitude.Ear, Most Lyme disease symptoms are actually excess inflammatory cytokine symptoms. Therefore, a die-off reaction consists of a worsening of many Lyme disease symptoms including: fatigue, brain fog, muscle and nerve pain, chills and sweats, and/or memory and thinking., Now called Candida Glabrata. Common biofilm-forming yeast causing disease for those in weakened condition or with suppressed immune function., Overacute smell and taste., Overacute smell and taste.Nose, Positive emotions feel good.Existing evidence suggests that positive emotions reliably alter peoples thinking and actions. Together with this past work, the experiments described in this article suggest that one reason positive emotions are worth pursuing is that they can help regulate negative emotions.Mind, Runny nose. See Sinusitis, and Cold programs., See Candida, and Candidiasis programs. Use Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris programs if no lasting relief achieved., See Gingivitis, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis programs.Gums, See High Blood Sugar program., See Hyperglycemia programs., See Kidney and Liver support programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, See Lymphangitis program., See Mal de Debarquement, Nausea and Cramping, Parasites Enterobiasis, Roundworm, Round Worms, and Parasites Roundworm General programs., See Nanobacter and Human T Lymphocyte Virus1. Can be caused by Enteroviruses such as Coxsackie B virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus B19, HIV, and by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis., See Parasites Tapeworm, Tapeworm, Parasites Taenia, and Taenia. Do not use until you are familiar with the tapeworm protocol., See Pneumonia Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, Bronchial, Pneumocytis Carinii, and Bronchial Pneumonia programs. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program.Lung, See Pullularia Pullulans and Sorghum Smut programs., See Vertigo, and Giddiness., Seek immediate medical attention for this., Stroke paralysis. See Stroke Follow Up., Sudden onset of pain., Swelling of the ovaries or fallopian tubes.Ovary, swollen lymph nodes will be close to where the problem is. When you have strep throat, lymph nodes in your neck may swell., Tapeworm in dogs, wolves, cats, and rodents that can infect man., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus and anterior pituitary gland., The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length., The lymph is moved through the body in its own vessels making a one-way journey from the interstitial spaces to the subclavian veins at the base of the neck. Since the lymphatic system does not have a heart to pump it, its upward movement depends on the motions of the muscle and joint pumps., The lymphatic system is, essentially, a huge drainage network for the body. It keeps fluid levels in balance, removes foreign bodies from the bloodstream and protects against infections.Lymph Detox is designed to support healthy lymphatic drainage, detoxification and function.Lymph, The most common symptoms of cervical cancer are:bleeding between periods.bleeding after sexual intercourse.bleeding in post-menopausal women.discomfort during sexual intercourse.vaginal discharge with a strong odor.vaginal discharge tinged with blood.pelvic pain., The source of many health issues arise when these toxins build up in the body over years.The liver is one of the bodys most essential organs that helps get rid of unwanted substances and toxins. The liver filters blood and metabolizes nutrients in order to keep us healthy., Theimmune systemis a host defense system comprising many biological structures andprocesseswithin anorganismthat protects againstdisease. To function properly, an immune system must detect a wide variety of agents, known aspathogens, fromvirusestoparasitic worms, anddistinguishthem from the organisms own healthytissue., Toxic headache headache due to systemic poisoning or associated with illness., Use General Antiseptic, Staphylococci, and Streptococcus Infection programs., Use Liver support programs., Yeast causing respiratory infection that can turn into meningitis.Lung |
| 540 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Lymphogranuloma Lymphoma 2, Causticum, Central Core Disease, Coxsackie B4, Detox Liver Kidneys Lymph Intestine, Herpes General 5, Herpes Type 2 Comp, Herpes Type 2A Secondary, Staphylococcus Pyogenes Aureus 2 | Abnormal lymphatic growths due to Chlamydia Trachomatis, and use Blood Cleanser., Congenital muscle disorder. Anesthesia may be contraindicated., Homeopathic remedy., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis., Now called Staphylococcus Aureus., Organ detox, Primarily genital., Primarily genital. Also use General Antiseptic program. |
| 543.6 | Spooky2 XTRA | Mycoplasma | Very small cell wall-deficient bacteria causing respiratory, pelvic inflammatory, and other diseases. |
| 558 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Hepatitis A 1, Hepatitis A 2, Hepatitis General 1 Virus, Influenza Virus British | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Infectious inflammation of liver (from feces-contaminated food or water). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver (from feces-contaminated food or water). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary.Liver, Infectious inflammation of liver. Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary. |
| 576 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Atherosclerosis, General Cleanser, Goiter 1, Goiter Struma Parenchyma, Herpes Zoster Virus, Hiatal Hernia 1, Lyme Disease W1, Staphylococci and Streptococcus V, Streptococcus and Staphylococci V, Trichophyton Nagel Secondary | Also called Esophageal Hernia. Protrusion of stomach into thorax through diaphragm defect. See Hernia Esophageal, and Hernia Hiatal., Also known as Borreliosis., Artery wall thickening due to white blood cells. Can be caused by Cytomegalovirus, and the bacteria Helicobacter Pylori and Chlamydia Pneumoniae., Detox program, Fungus that mostly infects nails. See Onchomycosis, Fungus General, Trichophyton General, and other Trichophyton programs., StaphylococcusandStreptococcusare both Gram positive organisms and cocci in shape. They areNon-motile,Non-Sporing andFacultative anaerobes., StaphylococcusandStreptococcusare both Gram positive organisms and cocci in shape. They areNon-motile,Non-Sporing andFacultative anaerobes.Staphylococci spherical Gram-positive parasitic bacteria that tend to form irregular colonies;, Swelling of neck or larynx due to enlargement of dysfunctional thyroid gland, usually because of iodine deficiency. Also see Struma programs. Use if swelling involves kidneys., Swelling of neck or larynx due to enlargement of dysfunctional thyroid gland, usually because of iodine deficiency. Also see Struma programs.Neck, Use for Chicken Pox and Shingles - see programs for both, and for Varicella. |
| 586.8 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ehrlichia Phagocytophila | See Rickettsia Rickettsii. |
| 594 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Cimicifuga, Coeliacia, Cryptococcus Neoformans, Iatrogenic Infections, Kidney Infection 1, Mold and Fungus General V, Pyelitis Proteus, Pyelitis Proteus 2, Pyrogenium 62 | Also called Caeliacia, Celiac or Coeliac Disease - see these programs., Also see specific types. See Mold, and Fungus programs., Bacteria commonly found in hospitals. Other use: Cimifuga (healing herb), mold., Bacteria commonly found in hospitals.Kidney, Drink lots of pure water., General homeopathic remedy for pus., Infections contracted in a hospital/medical facility, or caused by a medical professional., Plant family including Black Snakeroot and Black Cohosh., Yeast causing respiratory infection that can turn into meningitis.Lung |
| 608.4 | Spooky2 CAFL | Mycobacterium Avium | Genus of Actinobacteria causing lymphatic or GI tract lesions, mainly in the immunocompromised.Lung |
| 612 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 2, Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme, Coxsackie B3, Coxsackie General, Echo Virus, Endometritis Tuberculosa, Enterovirus, Fat Energy Metabolism, Fungus Black Nail, Influenza Vesica General, Leptospirosis, Leptospirosis 1, Leucosis, Leukocytosis, Lyme Dougs, Lyme General, Mucor Mucedo, Pleural Effusion | Also known as Borreliosis., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Excess fluid accumulating in the pleural cavity., Fat Metabolism. Almost all fat in your diet comes in the form of triglycerides.Upon reaching their destination, these compounds are either broken down and stored as free fatty acids in your liver or as body fat, or are fully metabolized and used as a source of energy by your muscle fibers., Fungus that causes rot in fruit and baked goods, sometimes found on feet and skin., Fungus that causes rot in fruit and baked goods, sometimes found on feet and skin. Other use: Leptospirosis., Generic term meaning small virus. Includes Echo, Coxsackie, and Polio., Homeopathic nosode for influenza/flu., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis. Also see Mumps., Inflammation of womb lining. See Echo Virus, Dysmenorrhea, and Menstrual Problems programs., Proliferation of tissues that form white blood cells. Considered to be foundational stage of leukemia. See Cancer Leukemia programs., Spirochete disease spread through animal urine that can cause meningitis, jaundice, anemia, miscarriage, and death. See Leptospira Interrogans Spirochete., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., Toenail and fingernail fungus. Also try Onychomycosis., Virus causing meningitis, particularly in children, and Endometritis Tuberculosa., White blood cell count above normal range, normally a sign of inflammation following infection, parasite infestation, or bone tumor. Also see Eosinophilia programs. |
| 630 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Bladder Infection, Borrelia Lyme 1, Borrelia Lyme 2, Cystitis, Inflammation Urethra, Lyme 1, Rhinoscleroma | Also known as Borreliosis., An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder, or urethra., Chronic granulomatous bacterial disease of nose that can sometimes infect the upper respiratory tract, usually due to subspecies of Klebsiella Pneumoniae., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., Urinary tract infection (UTI)., What is urethritis? Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body, becomes inflamed and irritated. Semen also passes through the male urethra. Urethritis typically causes pain while urinating and an increased urge to urinate |
| 648 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Cold Sores 3, Herpes Simplex i 3, Herpes Type 1 Anec Comp, Motion Sickness, Pancreas, Pancreas 2, Pancreas Balance 2, Sars 2 | Also use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program., Cold sores also called fever blisters are a common viral infection. They are tiny, fluid-filled blisters on and around your lips. These blisters are often grouped together in patches. After the blisters break, a crust forms over the resulting sore. Cold sores usually heal in two to four weeks without leaving a scar.Cold sores spread from person to person by close contact, such as kissing. Theyre caused by a herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) closely related to the one that causes genital herpes (HSV-2). Both of these viruses can affect your mouth or genitals and can be spread by oral sex. Cold sores are contagious even if you dont see the sores.Theres no cure for HSV infection, and the blisters may return. Antiviral medications can help cold sores heal more quickly and may reduce how often they return., Combines most anecdotal frequencies for Herpes Simplex i., Primarily orofacial. Use General Antiseptic program., See Mal de Debarquement, Nausea and Cramping, Parasites Enterobiasis, Roundworm, Round Worms, and Parasites Roundworm General programs., The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach. |
| 666 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Acute Pain, Adenovirus, Adenovirus 1, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 3, Astrocytoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Brain Tumor 2, Breast Fibroid Cysts, Breast Fibroid Cysts 2, Breast Fibromatosis 1, Cancer 4 W1, Cancer Astrocytoma, Cancer Basic 1, Cancer Basic 2, Cancer Basic 3, Cancer Basic 4, Cancer Basic 6, Cancer Basic program, Cancer Breast 1, Cancer BX Carcinoma Virus 3, Cancer General 1, Cancer General program 1, Cancer Leukemia, Cancer Leukemia 2, Cancer Melanoma 1, Cancer Melanoma 2, Cancer Non Hodgkins 1, Cancer Pain, Cancer Prostate, Cancer Prostate 1, Cancer Prostate 3, Cancer Skin, Carcinoma 3, Carpal Tunnel Secondary, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 1, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 3, Cataract, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 3, Cold 2, Croup, Dental Foci, Dental Foci 1, Dental Foci 2, Dental Infection, Dental Infection 1, Dental Infection and Earache, Dental Infection and Earache 1, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, Detox 1 Toxins in the Intestines, Detox 3 Toxins in the Kidneys and Liver, Detox 4 Toxins Throughout the Body, Fat Burn 1, Fat Obesity 2, Fibroids General, Fibroma, Fibroma 3, General Antiseptic, General Comprehensive, General Program Blaster 5, Gonads Inflammation 1, Impotence, Incontinence 1, Infections General Secondary, Infertility, Influenza 1999/2000 2, Influenza Grippe 1986 Tri, Leprosy Secondary Infection, Leukemia, Leukoplakia, Lymphoma Non Hodgkins, Mouth Eruptions White Patches, Orchitis, Osteomyelitis, Ovarian Disorders General, Pain Acute, Pain General, Pain Relief, Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatic Insufficiency 2, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Polyp General, Prostate Complaints, Prostate Enlarged, Prostate Problems General, Prostate Tumor, Prostatitis, Rotavirus, Scarlet Fever, Sciatica Ischias, Sexual Dysfunction Men, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Toothache, Tuberculosis General, Tumor Brain, Tumor Brain 3, Warts General, Wide-Spectrum ABX | A cold begins when a virus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat. Your immune system -- the bodys defense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., Abnormal growth of tissue from mucous membrane., Addresses multiple dental issues. Use if infection recovery is slow., Addresses multiple dental issues. Use if infection recovery is slow.Teeth, Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs., Also see Blood Purify programs., Also see Cancer Carcinoma., Also see Cancer programs., Also see Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Bowens Disease, and Cancer Lung Non-Small Cell programs., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see General Antiseptic programs., Also see Hansens Disease., Also see Infections General programs., Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser., Benign smooth muscle tumors of uterus. See Parasites General Flukes and Fascia programs.Uterus, Benign tumor clusters with aggressive growth., Benign tumor composed of fibrous or connective tissue., Benign tumor composed of fibrous or connective tissue. Other use: Leiomyoma., Brain cancer. Also see Cancer programs.Brain, Can cause upper respiratory and ear infections, tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, or croup., Can cause upper respiratory and ear infections, tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, or croup.Lungs Stomach Intestines, Cancer involving the blood-forming tissues in bone marrow. See Cancer Leukemia programs., Causes rash, strawberry tongue, sore throat, swollen glands, headache, and fever. Use Streptococcus Pyogenes., Clouding of lens of eye. Also see Eye and Eyes programs., Common skin cancer, mostly found on head or neck. Rarely fatal or metastatic., Common tumor of brain and central nervous system. Use Blood Cleanser. See Astrocytoma and Cancer Brain Tumor.Brain, From Dr. Richard Loyd. Rotavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses in the family Reoviridae. Rotaviruses are the most common cause of diarrhoeal disease among infants and young children. Nearly every child in the world is infected with a rotavirus at least once by the age of five., Gum disease: Also known as gingivitis, this condition occurs when bacteria build up under the gums and cause inflammation and bleeding.Some people with sinusitis also experience gum pain and toothache. Tooth abscess: A bacterial infection in the root of a tooth can cause an abscess or pus-filled sac., Hits Staphylococcus Aureus, E Coli, Pseudomonas, and others., Inability to produce or fertilise a human egg. Also see Impotence (men), and Frigidity (women)., inclusive, extensive, exhaustive, broad, wide, compendious, synoptic, sweeping, widespread, far-reaching, comprising, containing, all-embracing, all-inclusive, complete, thorough, discursive, encyclopedic, full, general, expansive, overall, blanket, umbrella; see also absolute 1, general 1, large 1, 2, whole 1., Infection and inflammation of bone and marrow. Usually caused by Staphylococcus Aureus, certain Streptococcus spp, Enterobacter spp, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Salmonella spp in Sickle Cell Anemia cases. See appropriate programs. Also see Infection Bone., Infection of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and inside of pelvis, usually by Neisseria Gonorrheae, or Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Fallopian Tube Infection, Salpingitis, Gonorrhea, and General Antiseptic programs., Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum.Lung, Inflammation of ovaries or testes - also see Hydrocele, Orchitis, Gonads, Testicular Diseases, Testicle Fluid, or appropriate organ programs.Testicle, Inflammation of prostate., Inflammation of testes due to TB, Mumps, Gonorrhea, Cancer, bacteria, etc. See causative condition if known. See Gonads inflammation, Testicle Fluid, Testicular Diseases, and Hydrocele programs., Lack of moderation or self-control, Look under name of condition causing pain., Malignant. See Cancer Prostate programs., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis.Nerve, Medley of useful frequencies., Most importantly, these cancers have readily identifiable targets for diagnosis, prevention and therapy. Vaccination programmes against two human tumour viruses, hepatitis B virus (HBV) and human papillomavirus (HPV), have already begun to alter age-old cancer patterns on an international scale3-5., Mostly affects skin, but can appear in mouth, intestines, or eyes. Use Blood Cleanser., Mostly affects skin, but can appear in mouth, intestines, or eyes. Use Blood Cleanser.Skin, Neglecting this can prevent recovery from any illness. Should also be treated professionally, preferably a holistic dentist. Also see Dental, Gingivitis, and Pyorrhea programs., Non-cancerous lump in breast., Non-cancerous lump in breast.Breast, Not sterility but failure to achieve or maintain erection. See Erectile Dysfunction, Nitric Oxide Generate, Sacral, Zinc Etc., and use Circulatory Stasis., Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to an extent that it may have a negative effect on health., Ovarian disorders may refer to diseases primarily affecting, or centered on, the ovaries.Ovary, Production of insulin has slowed. Run for Diabetes, but monitor blood sugar levels. If no improvement, test for insulin resistance.Pancreas, Respiratory condition due to viral infection of upper airway., Roots and gums., Sciatica is a medical condition characterized by pain going down the leg from the lower back. ... Weakness or numbness may occur in various parts of the affected leg and foot. About 90% of sciatica is due to a spinal disc herniation pressing on one of the lumbar or sacral nerve roots., See Acute Pain program. Also look under name of condition causing pain., See B-Cell Lymphoma, and Cancer Lymphoma Non-Hodgkins., See Cancer Astrocytoma, Gliomas, Glioblastoma, and Astrocytoma programs., See Cancer Astrocytoma, Gliomas, Glioblastoma, and Astrocytoma programs.Brain, See Cancer Basal Cell Skin Carcinoma, Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Cancer Melanoma. Use Blood Cleanser., See Cancer programs., See Erectile Dysfunction, Impotence, Nitric Oxide Generate, and Sacral, Zinc Etc. Also see Circulation, and Circulatory programs, and Orchitis., See Leucosis. Use Blood Cleanser.Blood, See Leukoplakia, Mucous Membrane General Inflammation, EBV, BX Virus, Papilloma, Cancer BX Virus, and Carcinoma programs.Mouth, See Prostatitis and other prostate programs. Use Streptococcus General, and Propionibacterium Acnes, and practise metals avoidance., See Streptococcus, and Propionibacterium Acnes programs, and practise metals avoidance., Signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess include:Severe, persistent, throbbing toothache that can radiate to the jawbone, neck or ear.Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.Sensitivity to the pressure of chewing or biting.Fever.Swelling in your face or cheek.Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck., Sudden onset of pain., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, Tooth abscesses, cavities, and impacted molars also can cause ear pain. Your doctor will be able to tell if your teeth are to blame by tapping on a tooth or your gums to see if they feel sore. SOURCES: Fairview Health Services Health Library: Earache, No Infection (Adult)., Use Blood Cleanser., Use Cancer Melanoma, and Blood Cleanser. Also helps with blood cell production problems in Morgellons.Lymph, Use Chronic Fatigue V, EBV, Fatigue General, Parasites General, Roundworm, and Flukes programs. If no response, try Cancer Leukemia Hairy Cell., Use Fungus Foot and General 1, and General Antiseptic programs. Also see Parasites General Flukes, and Roundworm programs.Skin, White patches on mucous membranes. See EBV, Mouth Eruptions White Patches, Papilloma, and Cancer Carcinoma programs., You might suffer from an earache and fever, or experience dizziness and nausea. However, theres one symptom you might not be aware is connected to the infection: tooth pain. Thats right tooth pain can develop as a result of an untreated ear infection. |
| 680.4 | Spooky2 CAFL | Mycobacterium Avium | Genus of Actinobacteria causing lymphatic or GI tract lesions, mainly in the immunocompromised.Lung |
| 684 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL | Pullularia Pullulans, Rhesus gravidarum, Rhesus Gravidatum | Homeopathic allergy remedy.Lung, Rhesus disease is a condition where antibodies in a pregnant womans blood destroy her babys blood cells. Its also known as haemolytic disease of the foetus and newborn (HDFN). Rhesus disease doesnt harm the mother, but it can cause the baby to become anaemic and develop jaundice. |
| 702 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Canker Sore 3, Human T Lymphotropic Virus6, Influenza 1994 Secondary, Lupus Erythematosus 1, Lupus General, Lupus Systemic Erythematosis SLE, Stomatitis | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Stomatitis Aphthous. Painful recurrent benign mouth ulcers., Autoimmune disease involving joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. Lupus Vulgaris is a common form that manifests disfigurement and destruction of skin and cartilage of face. Use Nanobacter and Parasites Flukes programs., Autoimmune disease involving joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. Use Nanobacter and Parasites Flukes programs., Causes leukemia/lymphoma and nerve demyelination. Use for HIV., inflammation of mouth and lips. See Candida, Herpes Simplex i, Stomatitis Aphthous, Pyorrhea, and Gingivitis programs. |
| 709.2 | Spooky2 XTRA | Bronchial Pneumonia 3, Emphysema 2, Klebsiella Pneumoniae 1 | Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also see Pneumonia Bronchial., Gram-negative bacteria normally present in mouth, skin, and intestines that causes serious lung conditions when inhaled - see Pneumonia programs. |
| 718.2 | Spooky2 CAFL | Salmonella, Salmonella Comp | All strains., Bacteria causing food poisoning |
| 720 | Chakra Frequencies, Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 CAFL UPDATED APR 2020, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Brain Tumor 1, Cancer Glioblastoma, Cerumen Ear Wax, Cold 1, CoronaCOV19_1, Coughing, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation, Dizziness 1, Ehrlichia 4, Felon 2, Felon 3, General Program Emem, Influenza Berlin, Influenza Berlin 55, Influenza Virus 1993/1994 Secondary, Medulloblastoma, Meningitis, Meningococcus Virus, Mesothelioma, Otitis Medinum, Personality Disorder Borderline, Prosthodontics, Pulmonary Cancer, Q Fever, Rhodococcus, Rickets 1, Rickettsia 1, Rickettsia 2, Rickettsia Rickettsii 2, Streptococcus Pyogenes 4, Third Eye Chakra, Tuberculosis Aviare, Tuberculosis General, Tumor Brain, Tumor Brain 2 | , A cough, also known as tussis, is a voluntary or involuntary act that clears the throat and breathing passage of foreign particles, microbes, irritants, fluids, and mucus; it is a rapid expulsion of air from the lungs., Acute inflammation of meningeal membranes, due to viral, bacterial (including Lyme spirochetes), or other organisms. Bacterial: use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Influenza Haemophilus Type B, and see Listeriose, and Leptospirosis. Viral: use Echo, Coxsackie, and Meningococcus programs., Also called a whitlow. Purulent infection of fingertips., Also called Group A beta-haemolytic Strep (GAS). Causes Sore Throat, skin inflammation, Scarlet Fever, Pharyngitis, Impetigo, Erysipelas, Frozen Shoulder, Cellulitis, Septicemia, Toxic Shock Syndrome, and acute Glomerulonephritis, and Beta Streptococcus. Use General Antiseptic., Also see Cancer programs., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Bacteria which can infect the immunocompromised. Also see Mycobacterium Infections programs, and try Diphtheria programs., Defective mineralization of bones due to vitamin D, phosphorus, or calcium deficiency., Dental prostheses., Formation of blood clots throughout the body, usually in critical illnesses., Homeopathic nosode for influenza/flu., Infectious disease caused by contact with animals with Rickettsia and Coxiella Burnetii. Symptoms may include headache, fever, chills, and sweats. See Rickettsia, and Typhoid Fever programs., Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum.Lung, Lung cancer/carcinoma. See appropriate Cancer programs., Medley of useful frequencies taken from Emem Rife machine., Middle ear swelling and/or infection and fever. See Ear Cholesteatoma and Ears programs. Always use Streptococcus Pneumonia with this. If uncomfortable, lower Amplitude.Ear, Most common malignant primary brain tumor in children, commonly metastasizing via spinal canal. Also see appropriate Cancer programs., OverviewThe common cold is a viral infection of your nose and throat (upper respiratory tract). Its usually harmless, although it might not feel that way. Many types of viruses can cause a common cold.Children younger than 6 are at greatest risk of colds, but healthy adults can also expect to have two or three colds annually.Most people recover from a common cold in a week or 10 days. Symptoms might last longer in people who smoke. If symptoms dont improve, see your doctor.SymptomsSymptoms of a common cold usually appear one to three days after exposure to a cold-causing virus. Signs and symptoms, which can vary from person to person, might include:Runny or stuffy noseSore throatCoughCongestionSlight body aches or a mild headacheSneezingLow-grade feverGenerally feeling unwell (malaise)The discharge from your nose may become thicker and yellow or green in color as a common cold runs its course. This isnt an indication of a bacterial infection., Pattern of abnormal behavior with impulsivity, unstable emotions, inconsistent relationships, and poor self-image., Pleomorphic bacteria transmitted by many arthropods, including chiggers, ticks, fleas, mites, and lice, as well as leeches and protists, causing Typhus, and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Also see Febris Wolhynia., Rare cancer of lining of organs, most commonly lungs, usually due to asbestos exposure. Also see Cancer Malignant Mesothelioma, and Simian Virus 40., Rickettsial tick-borne bacteria, common in Lyme Disease. See Rickettsia Rickettsii., See Cancer Astrocytoma, Gliomas, Glioblastoma, and Astrocytoma programs., See Cancer Astrocytoma, Gliomas, Glioblastoma, and Astrocytoma programs.Brain, See Ear Wax.Ear, See Vertigo, and Giddiness., Tick-transmitted causative agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever., Tyoe of brain/brain stem tumor. Use Blood Cleanser.Brain, Virus infecting the membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord, causing Meningitis. |
| 720.36 | Spooky2 CAFL | Sars 2 | Also use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program. |
| 738 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Atherosclerosis, Cancer Nasopharyngeal, Cancer Nasopharyngeal 2, Carbuncles, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 1, Deer Tick, Deer Tick 2, Dematium Nigrum, EBV 1, Epstein Barr Virus 1, Felon 1, Felon 3, Herpes Zoster Virus, Hiatal Hernia 1, Infectious Mononucleosis 1, Parasites Strongyloides Secondary, Shingles, Staphylococcus Aureus, Staphylococcus Aureus 1, Staphylococcus Pyogenes Albus 1, Trichophyton Nagel Secondary, Tumor Staphylococcus Aureus, Varicella | Also called a whitlow. Purulent infection of fingertips., Also called Epstein Barr Virus, or Human Herpesvirus 4. Causes mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and HIV. Also see Infectious Mononucleosis and Mononucleosis., Also called Esophageal Hernia. Protrusion of stomach into thorax through diaphragm defect. See Hernia Esophageal, and Hernia Hiatal., Also called glandular fever. Symptoms vary with age. Also see Mononucleosis, Epstein Barr Virus, and EBV., Also see Staphylococcus aureus programs., Artery wall thickening due to white blood cells. Can be caused by Cytomegalovirus, and the bacteria Helicobacter Pylori and Chlamydia Pneumoniae., Can cause boils, carbuncles, abscesses, tooth infection, heart disease, and infect tumors., Cancer of upper throat, nasal and auditory passages. See Epstein Barr Virus. Use Blood Cleanser. Other uses: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/CFS/ME, Mononucleosis.Throat, Cluster of boils. See Boils, Furunculosis, and Staphylococcus Aureus., Fungus that mostly infects nails. See Onchomycosis, Fungus General, Trichophyton General, and other Trichophyton programs., Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs., Herpes virus that causes Chicken Pox during childhood and Shingles (Herpes Zoster) in adulthood., Now called Staphylococcus Epidermidis., Roundworm which can infect human skin, lungs, and GI tract. Common in Morgellons. See Strongyloides, Parasites Strongyloides, Parasites Threadworm, and Strongyloidiasis., See Epstein Barr Virus. Use Blood Cleanser., Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area.Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide stripe either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area., Soil fungus found in human lesions., Tick bites., Use Chronic Fatigue V, EBV, Fatigue General, Parasites General, Roundworm, and Flukes programs. If no response, try Cancer Leukemia Hairy Cell., Use for Chicken Pox and Shingles - see programs for both, and for Varicella. |
| 756 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Asthma V, Bronchial Asthma 6, Goiter 1, Goiter Struma Cystica, Influenza Virus 1993/1994 Secondary, Mucocutan Perniciosis, Urea Plasma | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Damage to the mucocutaneous junction, or mucocutaneous part of the body where mucosa transitions to skin., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, Swelling of neck or larynx due to enlargement of dysfunctional thyroid gland, usually because of iodine deficiency. Also see Struma programs. Use if swelling involves cysts., Swelling of neck or larynx due to enlargement of dysfunctional thyroid gland, usually because of iodine deficiency. Also see Struma programs.Neck, Ureaplasma is a non-STI bacterium causing Vaginosis, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, and (non-gonoccal) Urethritis. |
| 774 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 CAFL UPDATED APR 2020, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Cataract Complicated, Cataract General 1, Cirrhosis of the Liver, Cold 6, Coraforce, CoronaCOV19_1, CoronaCOV19_3, Coxsackie B5, Dental Infection 2, Glanders, Glanders 3, Hemorrhoids, Hemorrhoids 2, Hemorrhoids 4, Hot Tub Folliculitis 4, Hot Tub Folliculitis 5, Listeriosis, Liver Necrosis 1, Mange, Mold and Fungus General V, Mold Mix B, Parasites Follicular Mange, Pneumonia General, Pseudomonas Mallei | , A cold begins when avirus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat.Your immune system -- the bodysdefense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., Also called Farcy. Weaponized zoonotic equine disease with respiratory system and oral lesions caused by Pseudomonas Mallei., Also called Piles. Also run circulation and circulatory programs alternatively on consecutive days for 10 days. Place electrodes on thighs., Also see specific types. See Mold, and Fungus programs., Causes Glanders, a blue pus infection of the respiratory system and mouth. Occasionally transmitted to humans by equines. See Glanders, Farcy, Mellei, and Melioidosis programs., Clouding of lens of eye. Also see Eye and Eyes programs., Clouding of lens of eye. Secondary type caused by disease, degeneration, or surgery. Also see Eye and Eyes programs., Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange., Due to Demodex mites. See Follicular Mange.Hair Skin, Failure of liver function due to long-term damage., Follicular infection by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, a bacterium common in hot tubs and water slides. Also see Folliculitis Hot Tub., Follicular infection by Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, a bacterium common in hot tubs and water slides. Also see Folliculitis Hot Tub.Hair, Homeopathic. Also used for Convoforce., Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis., Liver cell death caused by external factors rather than by apoptosis., See Pneumonia Klebsiella, Mycoplasma, Bronchial, Pneumocytis Carinii, and Bronchial Pneumonia programs. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program.Lung, Signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess include:Severe, persistent, throbbing toothache that can radiate to the jawbone, neck or ear.Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.Sensitivity to the pressure of chewing or biting.Fever.Swelling in your face or cheek.Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck., Somefrequenciesrepeatandtheordermaybeimportant, Toxic molds fall into five categories. Those categories are Penicilium, Fusarium, Stachybotrys, Aspergillus and Cladosporium. Each category includes many species of mold, and they have a wide variety of harmful qualities., Usually caused by eating food contaminated with Listeria Monocytogenes. Causes sepsis and meningitis. Also see Listeriosis, Streptococcus General, and Infections programs. |
| 792 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Basic 1, Cryptococcus Neoformans | Use Blood Cleanser., Yeast causing respiratory infection that can turn into meningitis.Lung |
| 810 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Adenoids, Borreliosis 2, Bronchial Asthma, Bronchial Asthma 3, Clostridium Enterocolitis, Crohns Disease 1, Endocrine Diseases, Pain Back, Parasites Entamoeba gingivalis trophozoite | Also called Clostridium Difficile. Can cause diarrhea following treatment with antibiotics., Also called Lyme Disease., Also called Naso/Pharyngeal Tonsil.Nose, Amebiasis is a disease caused by infection with a parasitic amoeba that, when symptomatic, can cause dysentery and invasive extraintestinal problems. The cause of amebiasis is mainly the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs.Lung, Inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of GI tract. See Colitis, Colon, and Parasites programs., Life cycle stage of protozoan found in dental spaces., Physical discomfort occurring anywhere on the spine or back, ranging from mild to disabling., Pineal, pituitary, thyroid, thymus, adrenal, pancreas, and ovary/testis gland conditions. |
| 824.4 | Spooky2 CAFL | Staphylococcus Aureus | Can cause boils, carbuncles, abscesses, tooth infection, heart disease, and infect tumors. |
| 828 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Lyme A, Fungus EW Range, Mycobacterium Avium | Antifungal, Genus of Actinobacteria causing lymphatic or GI tract lesions, mainly in the immunocompromised.Lung, Spirochete involved in Lyme disease. |
| 832.86 | Spooky2 XTRA | Haemophilus Influenzae 1, Haemophilus Influenzae 2 | Gram-negative bacterium causing Bacteremia, Pneumonia, Epiglottitis, Meningitis, Cellulitis, Osteomyelitis, and Arthritis. |
| 840.6 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Spp. Cysts | Experimental. Encysted bacterial agent of Lyme disease. |
| 846 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Bartonella Henselae, Cancer Lymphogranuloma Lymphoma 2, Cat Scratch Fever, Dengue Fever 1, Ehrlichia 5, Endometriosis 1, Fasciolopsis Buski Adult, Fasciolopsis Buski Eggs, Herpes General 5, Herpes Type 2A Secondary, Lyme and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever V, Parasites General Flukes, Pneumococcus, Rickettsia Rickettsii 3, Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever and Lyme V, Stomatitis Aphthous V, Streptococcus pneumoniae | Abnormal lymphatic growths due to Chlamydia Trachomatis, and use Blood Cleanser., Alpha-haemolytic species. Can cause Pneumonia, Emphysema, middle ear infection, Endocarditis, Peritonitis, Arthritis, Bacteremia, and Meningitis. See Diplococcus Pneumoniae, Alpha Streptococcus, and Parasites Streptococcus Pneumoniae., Also called breakbone fever. Mosquito-borne viral disease with fever, headache, muscle and joint pain., Also called Canker Sores. Repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers in otherwise healthy people. Also see Cancrum Oris programs.Mouth, Bacterium which causes Cat Scratch Fever. Common in Lyme and Morgellons.Lymph, Growth of uterine tissue outside the uterus that may cause pain, infertility, and abnormal bleeding. Use Parasites General. See Dysmenorrhea and Menstrual Problems.Uterus, Large common human intestinal fluke, also found in pigs. See Fluke Intestinal, Parasites Flukes Intestinal, and Parasites Intestinal Flukes., Life cycle stage of large common human intestinal fluke, also found in pigs. See Fluke Intestinal, Parasites Flukes Intestinal, and Parasites Intestinal Flukes., Pancreatic, liver, and intestinal flukes.Pancreas Liver Intestines, Potentially lethal tick-borne rickettsial illness with sudden onset of fever, headache, and muscle pain, followed by rash. Also see Lyme programs., Primarily genital., Primarily genital. Also use General Antiseptic program., Regional lymphadenopathy caused by Bartonella spp. after cat bite or scratch. Also use Bartonella., Rickettsial tick-borne bacteria, common in Lyme Disease. See Rickettsia Rickettsii., See Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever program., See Streptococcus Pneumoniae programs., Tick-transmitted causative agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. |
| 864 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 1, Alzheimers 4, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme, Borrelia Lyme 1, Borrelia Lyme 2, Borrelia Lyme Tertiary, Borreliosis 2, Cancer Cervical 2, Herpes Simplex RTI, Lyme 1, Lyme Disease 6, Lyme Tertiary, Mycoplasma Fermentans, Mycoplasma Fermentans Incognitus, Mycoplasma Lyme Disease, Yeast General V | ALS, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs., ALS,possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs., Also called Lyme Disease., Also known as Borreliosis., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Based on RTIs Herpes program; most freqs contract spread. Use for Measles, Chicken Pox, Smallpox, Mononucleosis, Shingles, Rubella, cold sores, Epstein Barr, Variola, Stomatitis, and Pyorrhea., Experimental. May be a factor in ALS, Chronic Fatigue, Alzheimers, Parkinsons, MS, and Lyme., See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimer. Chronic neurodegenerative illness., See Candida, and Candidiasis programs. Use Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris programs if no lasting relief achieved., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., The most common symptoms of cervical cancer are:bleeding between periods.bleeding after sexual intercourse.bleeding in post-menopausal women.discomfort during sexual intercourse.vaginal discharge with a strong odor.vaginal discharge tinged with blood.pelvic pain., Very small cell wall-deficient bacteria causing respiratory, pelvic inflammatory, and other diseases., Very small cell wall-deficient bacteria causing respiratory, pelvic inflammatory, and other diseases. This strain is implicated in AIDS/HIV. |
| 865.08 | Spooky2 XTRA | Lactobacillus Acidophilus 3 | Naturally occurring GI tract bacteria, with some strains having beneficial probiotic effects. Overgrowth can produce diarrhoea, bloating, liver infection, stomach inflammation, vaginal discomfort, oesophageal diseases, arthritis, skin problems, and lung artery blockages. |
| 878.4 | Spooky2 XTRA | Bartonella Species Self-Test, Bartonella Tamiae | All species 60 secs each. Run in Contact or Plasma Modes. Note running frequency when hits are felt, then use Reverse Lookup., First found in human blood in Thailand. |
| 880.2 | Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Lung Abscess 3, Mycoplasma Fermentans Incognitus | See Chemtrail detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., Very small cell wall-deficient bacteria causing respiratory, pelvic inflammatory, and other diseases. This strain is implicated in AIDS/HIV. |
| 882 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Fungus Flora 1, General Cleanser, Hiatal Hernia 1, Hiatal Hernia 2, Lyme Disease W1, Streptococcus Infection General | A fungus (plural: fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, fungi, which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals., Also called Esophageal Hernia. Protrusion of stomach into thorax through diaphragm defect. See Hernia Esophageal, and Hernia Hiatal., Also known as Borreliosis., Detox program, Streptococcus family. See General antiseptic, and other Streptococcus programs. |
| 900 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Addisons Disease, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Adrenomyeloneuropathy, Anthrax, Aortic Valve Stenosis, Arachnoid Cysts, Arachnoid Diverticula, Arm Injuries, Arrhythmia Cardiac, Arthritis, Arthritis Rheumatism and Osteoporosis, Asthma, Astigmatism, Babesiosis, Bacillus Anthracis 2, Bladder Exstrophy, Cancer Otorhinolaryngologic, Cancer Otorhinolaryngologic Neoplasms, Dental Infection and Earache, Dental Infection and Earache 1, Ear Diseases, Erectile Dysfunction, Ergot Poisoning, Ergotism, Erythema, Erythema Infectiosum, Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone, Gastrointestinal Disease, Geniculate Herpes Zoster, Healing Acceleration, Herpes Zoster, Histiocytoma Benign Fibrous, Holoprosencephaly, Hydrocephalus Normal Pressure, Hyperprolactinemia, Keratitis Ulcerative, Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber Syndrome, Larsen Syndrome, Luesinum and Syphilinum 2, Maxillofacial Procedures, Melioidosis, Microphthalmos, Monosomy, Morgellons Chronic Lesions and Fibres, Morgellons Internal Parasites, Muscle Spasticity, Myocardial Infarction, Nephritis Hereditary, Nephrosis, Onchomycosis, Ostomy, Otosclerosis, Pallister-Killian Syndrome, Paraganglioma, Parapsoriasis, Parasites Anaplasma marginale, Parasites Anaplasma Marginale 2nd, Parasites Anaplasma marginale: (2nd range), Parasites Ancylostoma braziliense (adult), Parasites Ancylostoma Braziliense Adult, Parasites Ancylostoma caninum, Parasites Ascaris megalocephala (male), Parasites Balantidium coli cysts, Parasites Besnoitia Lung Sect., Parasites Capillaria Hepatica Liver Sect., Parasites Clonorchis Sinensis 2, Parasites Common Roundworm Cats and Dogs, Parasites Cryptocotyle Lingua Adult, Parasites Dientamoeba Fragilis, Parasites Enterobius vermicularis, Parasites Eurytrema pancreaticum, Parasites Fasciola hepatica, Parasites Fasciola hepatica cercariae, Parasites Fasciola hepatica eggs, Parasites Fasciola hepatica miracidia, Parasites Fasciola hepatica rediae, Parasites Fasciolopsis buskii adult, Parasites Fasciolopsis buskii eggs, Parasites Fasciolopsis cercariae, Parasites Fasciolopsis miracidia, Parasites Fasciolopsis rediae, Parasites Flukes General, Parasites Gastrothylax elongatus, Parasites General Comprehensive, Parasites Giardia, Parasites Giardia Lamblia, Parasites giardia lamblia (trophozoites), Parasites Giardia Lamblia Type 2, Parasites Gyrodactylus, Parasites Haemonchus contortus, Parasites Hasstile sig. tricolor (adult), Parasites Helminthosporium, Parasites Hypodereum conoideum, Parasites Iodamoeba butschlii, Parasites Leishmania braziliensis, Parasites Leishmania donovani, Parasites Leishmania mexicana, Parasites Leishmania tropica, Parasites Leucocytozoon, Parasites Loa loa, Parasites Macracanthorhynchus, Parasites Metagonimus Yokogawai, Parasites Myxosoma, Parasites Naegleria fowleri, Parasites Onchocerca volvulus (tumor), Parasites Paragonimus Westermanii adult, Parasites Passalurus ambiguus, Parasites Plasmodium cynomolgi, Parasites Plasmodium falciparum, Parasites Plasmodium vivax, Parasites Pneumocystis carnii (lung), Parasites Prosthogonimus macrorchis(eggs), Parasites Sarcocystis, Parasites Schistosoma haematobium, Parasites Schistosoma mansoni, Parasites Stephanurus dentatus (ova), Parasites Stigeoclonium, Parasites Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Parasites Streptococcus pyogenes (tooth), Parasites Streptococcus sp. group G (tooth), Parasites Sub terminal spores, Parasites Threadworm, Parasites Tobacco mosaic virus, Parasites Toxoplasma (human strain), Parasites Treponema pallidum causes syphilis, Parasites Trichinella spiralis (muscle), Parasites Trichomonas vaginalis, Parasites Trichuris sp. (male), Parasites Troglodytella abrassari, Parasites Trypanosoma brucei, Parasites Trypanosoma cruzi (brain tissue), Parasites Trypanosoma equiperdum, Parasites Trypanosoma gambiense, Parasites Trypanosoma lewisi, Parasites Trypanosoma rhodesiense, Parasites Urocleidus, Parasites Veillonella dispar, Parkinsonian Disorders, Relapsing Fever, Scheuermanns Disease, Severs Disease/Calcaneal Apophysitis, Sialorrhea, Stomatognathic Diseases, Sweat Gland Diseases, Teratoma, Testicular Diseases, Tuberculosis Spinal, Typhoid Fever 3, Urination Disorders, Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome | A parasitic relationship is one in which one organism, the parasite, lives off of another organism, the host, harming it and possibly causing death. The parasite lives on or in the body of the host. A few examples of parasites are tapeworms, fleas, and barnacles., Abnormal growth of bone near middle ear which can lead to hearing loss., Abnormally high levels of prolactin in blood., Also called Adrenoleukodystrophy. Fatty acid oxidation disorder., Also called Adrenomyeloneuropathy. Fatty acid oxidation disorder., Also called Corneal Ulcer. Inflammatory or infective condition., Also called Dermatofibroma. Hard, solitary, slow-growing, benign skin papules., Also called Ergot Poisoning. Rye and cereal mold/mycotoxin which causes convulsive and gangrenous symptoms when ingested long-term., Also called Ergotism. Rye and cereal mold/mycotoxin which causes convulsive and gangrenous symptoms when ingested long-term., Also called Fifth Disease, or Slapped Cheek Syndrome. Common childhood condition., Also see Impotence and Circulatory Stasis programs., Also see Muscle Cramp(s), Muscles Stiff, Muscles to Relax, and other Muscle programs., Anaplasma marginale and Anaplasma phagocytophilum are the most important tick-borne bacteria of veterinary and public health significance, Ancylostoma caninum is a species of nematode known as a hookworm, which principally infects the small intestine of dogs., Any natural or surgically-created opening in the body or organs, such as a colostomy, or tracheostomy., Apply=.02% Feathering., Arachnoid cysts, or diverticula, of the spinal canal are uncommon lesions which can lie in the spinal extra or intradural spaces., Ascaris is a genus of parasitic nematode worms known as the small intestinal roundworms, which is a type of parasitic worm., Balantidium coli is an intestinal protozoan parasite that causes the infection called balantidiasis. While this type of infection is uncommon in the United States, humans and other mammals can become infected with Balantidium coli by ingesting infective cysts from food and water that is contaminated by feces., Blood flukes. Associated with bladder problems. Also see Schistosoma Haematobium, and Blood Fluke programs., Blurred vision due to corneal or lens defect., Borrelia infection caused by bites of body lice or ticks., Brain malfunction caused by decreased absorption of cerebrospinal fluid., BromhidrosisHidradenitis suppurativa also affects the apocrine glands,HyperhidrosisHypohidrosisMiliaria, Chagas disease (also termed American trypanosomiasis) is an infection caused by a protozoan parasite (Trypanosoma cruzi) that can result in acute inflammatory skin changes (chagomas) and eventually may cause infection and inflammation of many other body tissues, especially those of the heart and intestinal tract., Childhood skeletal disorder with uneven vertebral development, causing abnormal spinal curvature (kyphosis)., Chromosomal abnormality with presence of just one chromosome from a pair., Chronic adrenal insufficiency. See Adrenal programs., Commonly known as a heart attack. Exercise caution., Congenital disorder with dislocation of large joints and facial abnormalities., Cysts in brain meninges or spinal cord., Degenerative disease of renal tubules.Kidney, Developmental disorder where one or both eyes are abnormally small with anatomical malformations., Disorders of the mouth and jaws., Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children. Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes.Ear, Ear, nose, and throat cancers., Eurytrema pancreaticum is one of the most common flukes, which mainly infects ruminants globally and infects human beings accidentally; causing eurytremiasis that has high veterinary and economic importance., Excessive production of saliva. Can be caused by radiation, antipsychotics and other drugs, toxic metals, and pesticides., Failure of embryonic forebrain to full develop into two hemispheres, causing brain and facial defects., Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans., Fasciolopsis is a genus of trematodes. Only one species is recognised: Fasciolopsis buski. It is a notable parasite of medical importance in humans and veterinary importance in pigs. It is prevalent in Southern and Eastern Asia., Fluke found in fish which can infect man., Fluke found in fish. Also see Urocleidus., Gastrin-secreting tumor of pancreas (or other abdominal locations) that stimulates acid-secreting cells of stomach with consequent GI ulceration., Gastrointestinal disorders is the term used to refer to any condition or disease that occurs within the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract (also called the GI tract) is a series of hollow organs that form a long continuous passage from our mouth to our anus., Gastrothylax crumenifer (Platyhelminthes: Gastrothylacidae), is a highly pathogenic trematode parasite of goat., Genetic disorder with glomerulonephritis, End-Stage Renal Disease, Hearing Loss, Hematuria, and ProteinuriaKidney, Giardia lamblia, also known as Giardia intestinalis, is a flagellated parasitic microorganism, that colonizes and reproduces in the small intestine, causing giardiasis. The parasite attaches to the epithelium by a ventral adhesive disc or sucker, and reproduces via binary fission., Group C and G streptococcal infections are largely spread through secretions of the nose and throat of infected people, or person-to-person spread through direct contamination of wounds. Other types of Streptococcus bacteria can be spread from animals to humans and from humans to animals., Group of skin disorders characterized primarily by their resemblance to psoriasis., Homeopathic. See Syphilis. Use for chancres., Hookworm in cats and dogs which can infect humans., Hookworm in cats and dogs which can infect humans. Also see Larva Migrans, and Creeping Eruption programs., Hypoderaeum conoideum is a species of digenetic trematodes in the family Echinostomatidae. The known first intermediate hosts of Hypoderaeum conoideum include the freshwater snails Planorbarius corneus, Indoplanorbis exustus, Lymnaea stagnalis, Lymnaea limosa, Radix ovata and Radix rubiginosa., Includes Incontinence, Urinary Retention, UTIs, Oliguria, and prostate disorders. See programs for these, and Urologic Diseases., Infection of nail by mold, usually Trichophyton Rubrum, Trichophyton Nagel, Trichophyton Mentagrophytes, Trichophyton Tonsurans, Epidermophyton Floccosum, Candida Parapsilosis, and Ringworm (Microsporum Gypseum). Also see Dermatomycoses., Infectious disease due to Burkholderia pseudomallei (formerly Pseudomonas pseudomallei) causing pain in chest, bones, or joints; cough; skin infections, lung nodules and pneumonia. Closely related to Pseudomonas Mallei - see Glanders, Farcy, Pseudomonas Mallei, and Mallei., Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum., Iodamoeba bztschlii is a species of amoeba. It gets its name from its appearance when stained with iodine. Named for Otto Bztschli by Prowazek in 1912, Iodamoeba bztschlii is a nonpathogenic parasitic ameba, commonly found in the large intestines of people, pigs and other mammals., Irregular heartbeat, including tachycardia and bradycardia., Jaws and face., Leucocytozoon parasites infect many species of avian hosts, including domestic chicken., Liver fluke., Loa loa is the filarial nematode species that causes Loa loa filariasis. Loa loa actually means worm worm, but is commonly known as the eye worm, as it localizes to the conjunctiva of the eye. Loa loa is commonly found in Africa. It mainly inhabits rain forests in West Africa and has native origins in Ethiopia., Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus is an acanthocephalan parasite which lives in the intestines of pigs and other suids, and very occasionally in humans or dogs. It causes enteritis, gastritis or peritonitis. Its life cycle includes beetles of the genus Melolontha as intermediate hosts., Malaria-like illness caused by Babesia., May be due to bacteria like Chlamydia Pneumoniae., micropredation.Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Minor arm injuries are common. Symptoms often develop from everyday wear and tear, overuse, or an injury. Arm injuries are often caused by:Sports or hobbies.Work-related tasks.Work or projects around the home.Your child may injure his or her arm during sports or play or from accidental falls. The chance of having an injury is higher in contact sports (such as wrestling, football, or soccer) and in high-speed sports (such as biking, in-line skating, skiing, snowboarding, and skateboarding). Forearms, wrists, hands, and fingers are injured most often. An injury to the end of a long bone near a joint may harm the growth plate and needs to be checked by a doctor.Older adults have a greater chance for injuries and broken bones because they lose muscle mass and bone strength (osteoporosis) as they age. Older adults also have more problems with vision and balance, which increases their chances of having an accidental injury.Most minor injuries will heal on their own, and home treatment is usually all that is needed to relieve symptoms and promote healing., Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin., Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations., Naegleria fowleri infects people when water containing the ameba enters the body through the nose. This typically occurs when people go swimming or diving in warm freshwater places, like lakes and rivers. The Naegleria fowleri ameba then travels up the nose to the brain where it destroys the brain tissue., Narrowing of aortic valve of the heart.Heart, Nematode commonly found in undercooked pork causing Trichinosis., Nematode inhabiting the liver., Non-cancerous abnormal bone growth where normal bone is replaced with fibrous bone tissue., Onchocerciasis, or River Blindness, is a neglected tropical disease (NTD) caused by the parasitic worm Onchocerca volvulus., Only two species of Sarcocystis are known to utilize humans as a definitive host: S. hominis and S. suihominis. Humans become dead-end hosts when they ingest the oocysts of Sarcocystis species whose definitive hosts are mammalian species other than humans., Painful inflammation of growth plate in heel of growing children, typically adolescents., Paragonimus westermani is the major species of lung fluke that infects humans, causing paragonimiasis., Parasitic amoeba found in GI tract. See Dientamoeba Fragilis, and Dientamoebiasis programs., Parasitic worm., Passalurus ambiguus, the common rabbit pinworm, is host-specific. 3. It inhabits the small intestine, cecum, and colon, passing eggs into the feces without causing clinical signs., Pathogen causing Pneumonia, Bronchitis, Rhinitis, acute Sinusitis, Otitis Media, Conjunctivitis, Meningitis, Bacteremia, Sepsis, Osteomyelitis, septic Arthritis, Endocarditis, Peritonitis, Pericarditis, Cellulitis, and Brain Abscess. Also see Streptococcus Pneumoniae., Pathogenic plant fungi, some of which can infect man., Plasmodium cynomolgi is an apicomplexan parasite that infects mosquitoes and Asian Old World monkeys., Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that cause malaria in humans. It is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito. It is responsible for roughly 50% of all malaria cases., Plasmodium vivax is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most frequent and widely distributed cause of recurring malaria., Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) is a life-threatening lung infection that can affect people with weakened immune systems, such as those infected with HIV, the virus that causes AIDS., Prosthogonimus macrorchis is an avian parasite found in regions of the United States and Canada near the Great Lakes., Protozoan causing equine diseases. Also see Trypanosoma Equiperdum programs, and Trypanosomiasis., Protozoan causing pedunculated (stalked) lesions in skin, nose, and larynx., Protozoan causing Sleeping Sickness. Also see Trypanosoma Brucei, and Trypanosomiasis., Protozoan found in rats and carried by their fleas which can cause disease in humans., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing milder form of Leishmaniasis. This can be more serious in those with defective T-cell immunity. See Leishmania Mexicana, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin problems. See Leishmania Tropica, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin, mouth, and nasal conditions. See Leishmania Braziliensis, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing spleen and liver enlargement, and infection of bone marrow. See Leishmaniasis, Leishmania Donovani, and Leishman Donovan Bodies programs., Protozoan that colonizes GI tract. See Giardia, Giardia Lamblia, Lamblia, and Giardia Intestinalis programs., Protrusion of bladder through abdominal wall., Rare congenital condition where blood and/or lymph vessels fail to properly form., Rare neuroendocrine neoplasm found at various body sites. See Neuroendocrine Tumors and other appropriate Cancer programs., Reactivation of Herpes Zoster virus in ganglion of facial nerve, causing paralysis, pain, and taste loss. Also see Herpes Zoster Oticus., Redness of skin or mucous membranes from injury, infection, or inflammation., Roundworm, Roundworm which can infect human skin, lungs, and GI tract. Common in Morgellons. See Strongyloides, Parasites Strongyloides, Parasites Threadworm, and Strongyloidiasis., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., Serious disease of lungs, intestines, and skin. Weaponised., Skin parasite found in fish., Slowly progressive, degenerative, neurologic disorder. See Morbus Parkinson and Parkinsons Disease programs. Also Use Chlamydia Pneumoniae, and see Nocardia Asteroides., Stephanurus dentatus are stout-bodied worms (2Ð4.5 cm long) found encysted in pairs along the ureters in the perirenal fat and in the kidney., Stigeoclonium is a genus of green algae in the family Chaetophoraceae., Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacterium in the genus Streptococcus. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci. It is clinically important for humans. It is an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota., Testicular disease can take a variety of forms: Testicular cancer. Like any cancer, testicular cancer happens when cells in the testicle develop mutations that cause them to misbehave., The pinworm (species Enterobius vermicularis), also known as threadworm (in the United Kingdom and Australia) or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans., The trematode Fasciolopsis buski, the largest intestinal fluke of humans., This process of wound healing has four distinct phases that overlap with each other; haemostasis, inflammation, proliferation and remodelling., Tick- and fly-borne Rickettsia-like bacteria which live in blood cells. Found in some Lyme Disease cases., Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) is a positive-sense single stranded RNA virus in genus Tobamovirus that infects a wide range of plants, especially tobacco and other members of the family Solanaceae. The infection causes characteristic patterns, such as mosaic-like mottling and discoloration on the leaves., Tooth abscesses, cavities, and impacted molars also can cause ear pain. Your doctor will be able to tell if your teeth are to blame by tapping on a tooth or your gums to see if they feel sore. SOURCES: Fairview Health Services Health Library: Earache, No Infection (Adult)., Toxoplasmosis (tok-so-plaz-MOE-sis) is a disease that results from infection with the Toxoplasma gondii parasite, one of the worlds most common parasites. Infection usually occurs by eating undercooked contaminated meat, exposure from infected cat feces, or mother-to-child transmission during pregnancy., Trematoda is a clade within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It includes two groups of parasitic flatworms, known as flukes., Treponema pallidum is a spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws and is transmitted only amongst humans., Trichomoniasis (or NtrichÓ) is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected., Trypanosoma brucei is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus Trypanosoma. The parasite is the cause of a vector-borne disease of vertebrate animals, including humans, carried by genera of tsetse fly in sub-Saharan Africa. In humans T. brucei causes African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness., Type of fluke found in fish., Use for Chicken Pox and Shingles - see programs for both, and for Varicella., Use Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Typhi, and Rickettsia programs. See Q Fever program., Use Streptococcus Pneumonia, and Mycoplasma General if needed. See Bursitis., Usually benign tumor that may contain hair, teeth, bone, of other disparate tissues originating from different germ cell layers., Variety of Trypanosoma Brucei causing slow onset of Trypanosomiasis. See Trypanosoma Gambiense programs, and Trypanosomiasis., Veillonella are anaerobic, gram-negative cocci, part of the normal flora of the mouth, gastrointestinal tract, and vaginal tract. Veillonella dispar, V. atypica, and V. parvula have been cultured from human specimens. They are infrequently isolated in human infections., Very rare genetic disorder with developmental disability, epilepsy, hypotonia, both hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation, and other symptoms., Virus program, Weaponised bacteria that causes Anthrax., When spores are exposed to favorable conditions, they can germinate into a vegetative cell within 90 minutes. Endospores can form within different areas of the vegetative cell. They can be central, subterminal, or terminal. ... Subterminal endospores are located between the middle and the end of the cell., You might suffer from an earache and fever, or experience dizziness and nausea. However, theres one symptom you might not be aware is connected to the infection: tooth pain. Thats right tooth pain can develop as a result of an untreated ear infection. |
| 918 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Leukemia, Cancer Leukemia Feline, Ehrlichia Chaffeensis, Feline Cat Leukemia 1, Warts Plantar | Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser. Other use: Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV)., Cat. Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser.Blood, Feline leukemiavirus (FeLV) is a retrovirus that infectscats. FeLV can be transmitted from infectedcatswhen the transfer of saliva or nasal secretions is involved. If not defeated by the animals immune system, the virus can cause diseases which can be lethal., Rickettsial tick-borne bacteria, common in Lyme Disease. See Rickettsia Rickettsii., Use Fungus Foot and General 1, and General Antiseptic programs.Skin |
| 929.52 | Spooky2 XTRA | Adenovirus 2nd, Alpha Streptococcus 2, Bacillus Subtilis Niger 3, Bacillus Subtilis Niger 4, EBV 2, Epstein Barr Virus A | Also called Epstein Barr Virus, or Human Herpesvirus 4. Causes mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and HIV. Also see Infectious Mononucleosis and Mononucleosis. Other uses: Alpha Streptococcus, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome., Can cause upper respiratory and ear infections, tonsillitis, conjunctivitis, or croup., Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs., Metabolically-changed form of B Subtilis due to presence of Aspergillus Niger mold., Streptococcus species causing oxidation of iron in hemoglobin. |
| 944.64 | Spooky2 XTRA | Entamoeba Histolytica Trophozoite | Life cycle stage of GI tract parasitic amoeba causing tissue destruction, particularly liver damage, and amoebic dysentery - use Liver Support programs. |
| 951.84 | Spooky2 XTRA | Clostridium Acetobutylicum 1, Clostridium Acetobutylicum 2 | Used in genetic engineering. |
| 954 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza With Fever Virus | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 955.98 | Spooky2 XTRA | Lithium 7li | Element. |
| 957.78 | Spooky2 XTRA | Anaplasma Marginale 1 | Species of Rickettsia bacteria. Tick-borne. Involved in Lyme Disease. |
| 966.6 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hepatitis General 3 | Infectious inflammation of liver. Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary. |
| 972 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Crohns and Other Bowel Problems, Food Poisoning 1, Salmonella Comp, Salmonella Paratyphi B | All strains., Can cause paratyphoid fever (similar to typhoid). See Typhoid Fever., Food poisoning is a major cause of gastroenteritis, resulting in a well-known set of unpleasant symptoms., Inflammatory bowel disease that can affect any part of GI tract. Also see Ileocolitis Colon Inflammation.Intestines |
| 991.62 | Spooky2 XTRA | Leishmania Braziliensis | Type of intracellular protozoan human parasite found worldwide and transmitted by sandflies. See Parasites Leishmania Braziliensis, Leishmaniasis, and other Leishmania programs. |
| 1026 | Spooky2 XTRA | Healing 1 | General healing. |
| 1044 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 2, Candida 2, Enterovirus, Meningitis, Meningitis 1, Meningitis 5 | Acute inflammation of meningeal membranes, due to viral, bacterial (including Lyme spirochetes), or other organisms. Bacterial: use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Influenza Haemophilus Type B, and see Listeriose, and Leptospirosis. Viral: use Echo, Coxsackie, and Meningococcus programs., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Generic term meaning small virus. Includes Echo, Coxsackie, and Polio., Yeast. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 1044.54 | Spooky2 XTRA | Giardia Lamblia | Also called Giardia Intestinalis, or Lamblia. Parasitic protozoan that colonizes the GI tract. Also see Parasites Giardia. |
| 1055.52 | Spooky2 XTRA | Detox Plastics 2 | Bisphenol A, and Phthalates (DEHP, DINP, and DIDP). |
| 1062 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Chemical Spray-Related Illness, Detox Chemtrail 1, Ehrlichia 4, Fat Burn 3, Mycoplasma General, Q Fever, Rickets 1, Rickettsia, Rickettsia 1, Rickettsia 2, Rickettsia 3, Rickettsia Rickettsii 2 | Addresses aerially-sprayed toxic metals and biological agents. Also useful for lung and sinus problems. See Chemtrail Detox., Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs., Also use Chemtrail programs., Can be useful for lung, sinus, and other problems which do not respond to other programs., Defective mineralization of bones due to vitamin D, phosphorus, or calcium deficiency., Infectious disease caused by contact with animals with Rickettsia and Coxiella Burnetii. Symptoms may include headache, fever, chills, and sweats. See Rickettsia, and Typhoid Fever programs., Pleomorphic bacteria transmitted by many arthropods, including chiggers, ticks, fleas, mites, and lice, as well as leeches and protists, causing Typhus, and Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Also see Febris Wolhynia., Rickettsial tick-borne bacteria, common in Lyme Disease. See Rickettsia Rickettsii., Tick-transmitted causative agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. |
| 1070.82 | Spooky2 XTRA | Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 1 | Mycobacterium which causes tuberculosis (TB). Also see Tuberculosis programs, and Tuberculinum. |
| 1087.2 | Spooky2 XTRA | Mycoplasma | Very small cell wall-deficient bacteria causing respiratory, pelvic inflammatory, and other diseases. |
| 1134 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Albicans 2, Candida and Organ Support 2, Candida Secondary, Fungus General, Kidney Stimulation, Yeast General V | Combination treatment and support., Forty adult patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis were prospectively studied and randomized into two groups (control n = 20 and treatment n = 20). The treatment group underwent bilateral femoral quadriceps muscles electrical stimulation for 30 minutes during hemodialysis, three times per week, for two months. The patients were evaluated by pulmonary function test, maximum respiratory pressures, maximum one-repetition test, and six-minute walk test (6MWT), before and after the treatment protocol., See Candida and Yeast programs as well as other specific types., See Candida, and Candidiasis programs. Use Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris programs if no lasting relief achieved., Yeast species. See Parasites General, Roundworm, and Ascaris if these do not work long-term. |
| 1170 | Spooky2 CAFL | Mumps Secondary | Viral disease with fever, muscle pain,and headache, leading to painful swelling of parotid gland(s). Also see Mumps, Mumps Antigen, and Coxsackie programs.Mouth |
| 1242 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | E Coli Mutant Strain, Escherichia Coli Comp, Escherichia Coli Mutant Strain, Influenza Triple Nosode | Also called E Coli. Can infect wounds and urinary tract. Recommended in cancers. May need Adenovirus follow-up., Also called Escherichia Coli. Can infect wounds and urinary tract. Recommended in cancers. May need Adenovirus follow-up., Homeopathic remedy. |
| 1350 | Spooky2 ETDF | Craniopharyngioma | Rare brain tumor derived from embryonic pituitary tissue. |
| 1378.98 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Bladder 2 | Also see Bladder TBC, Cancer Bladder TBC, Cancer Urethral, Parasites, and Schistosoma. Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 1386 | Spooky2 CAFL | Cholesterinum | CHOLESTERINUM (Cholesterine) 30CH GR. Indications. Helps to support general liver and gallbladder health. |
| 1422 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | ALS 2, Enterovirus, Influenza Triple Nosode, Meningitis, Meningitis 1, Meningitis 5, Parkinsons V | Acute inflammation of meningeal membranes, due to viral, bacterial (including Lyme spirochetes), or other organisms. Bacterial: use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, Influenza Haemophilus Type B, and see Listeriose, and Leptospirosis. Viral: use Echo, Coxsackie, and Meningococcus programs., Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Generic term meaning small virus. Includes Echo, Coxsackie, and Polio., Homeopathic remedy., Slowly progressive, degenerative, neurologic disorder. See Morbus Parkinson and Parkinsonian Disorders programs. Also Use Chlamydia Pneumoniae, and see Nocardia Asteroides. |
| 1440 | Spooky2 XTRA | Lymphoma Non Hodgkins | See B-Cell Lymphoma, and Cancer Lymphoma Non-Hodgkins. |
| 1584 | Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Babesia, Babesia Lyme, Babesiosis, Rickettsia Rickettsii 1 | Malaria-like illness caused by Babesia., Protozoan causing malaria-like symptoms. Mostly tick-borne, but has been found in blood products., Protozoan causing malaria-like symptoms. Mostly tick-borne, but has been found in blood products.Blood, Tick-transmitted causative agent of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. |
| 1620 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dermatitis Exfoliative | Also called Erythroderma. Causes reddening and scaling of skin over almost the entire body. |
| 1638 | Spooky2 XTRA | Healing Infinite | The Infinity Healing Practice, created by Gabrielli LaChiara, is a body of teachings, tools, and activations that allow people to experience profound shifts in consciousness, creating greater ease and lightness in the body, mind and spirit. |
| 1656 | Spooky2 BIO | Tonsillar NOS | Homeopathic nosode for tonsils. |
| 1692 | Spooky2 XTRA | Dengue Fever 1 | Also called breakbone fever. Mosquito-borne viral disease with fever, headache, muscle and joint pain. |
| 1710 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptosporidiosis | GI tract infection caused by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium. |
| 1752.48 | Spooky2 XTRA | Dermatophagoides, Dermatophytoses | Also called Dermatophytosis, or Ringworm. Fungal infection of skin. See., Mite living in human homes which lives on dead skin flakes and whose droppings are allergenic. |
| 1799.64 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Species Self-Test, Borrelia VS2 | All species 60 secs each. Run in Contact or Plasma Modes. Note running frequency when hits are felt, then use Reverse Lookup., Type/strain: US-VS 2. |
| 1800 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Abdominal Inflammation, Acne 1, Actinomyces Israelii 1, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 2, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 3, Angina Pectoris, Apoplexy, Arteriosclerosis, Asthma, Asthma 1, Asthma 5, Ataxia General, Bladder Infection, Bone Disease and Periodontal, Bone Disease Periodontal Disease, Borrelia Lyme A, Bronchial Asthma, Bronchial Asthma 1, Bronchial Asthma 3, Cancer Ovarian, Chronic Fatigue Syndrome 2, Coordination Difficulties, Dental Foci, Dental Foci 1, Dental Foci 2, Dental Infection 1, Diabetes Secondary, Duodenal Ulcer 2, Epstein Barr Virus 2, Epstein Barr Virus 8, General Program Blaster 5, Gingivitis 1, Gum Disease, Heartburn Chronic, Herpes Mouth Sores, Herpes Simplex i 2, Herpes Type 1 Anec Comp, Herpes Zoster Secondary, High Blood Sugar, Hives, Hives 1, Hives 2, Hyperglycemia, Hypoglycemia, Iatrogenic Infections, Infection Bone, Infections General Tertiary, Infectious Mononucleosis 4, Inflammation Urethra, Influenza 2003/2004 1, Leiomyoma, Low Blood Sugar, Lung General Conditions, Nerve Disorders 1, Nerve Disorders and Neuropathy, Numbness, Oral Lesions, Orchitis, Osteomyelitis, Ovarian Disorders General, Pancreas Balance 2, Pancreatic Insufficiency, Pancreatic Insufficiency 2, Paralysis from Stroke, Pelvic Inflammatory Disease, Periodontal Disease, Polyp General, Prognathism, Pyorrhea, Salmonella Typhi 1, Shingles, Sore Throat, Spleen Enlarged 1, Stiff Muscles, Stroke Follow Up, Surgery Pre-op Post-op Prevent Infections, Thrombosis Infective Herpes Type, Toothache, Trigeminal Neuralgia, Typhoid Fever, Typhoid Fever 3, Typhoid General, Ulcers 1, Ulcers 2, Ulcers 4, Ulcers General, Urethritis, Urticaria, Warts General | A variety of different types of autoimmune diseases can produce symptoms of nerve pain and nerve damage. These include: multiple sclerosis, Guillain-Barr syndrome (a rare condition in which the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves), myasthenia gravis, lupus, and inflammatory bowel disease., Abnormal growth of tissue from mucous membrane., Addresses multiple dental issues. Use if infection recovery is slow., Addresses multiple dental issues. Use if infection recovery is slow.Teeth, Also called glandular fever. Symptoms vary with age. Also see Mononucleosis, Epstein Barr Virus, and EBV., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Gastroenteritis programs.Stomach, Also see General Antiseptic programs., Also see Osteomyelitis programs., Also see Stroke programs.Nerve, Also use Circulatory Stasis., An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder, or urethra., An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes the organ of which that membrane is a part from continuing its normal functions. According to Robins pathology, ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing out of inflamed necrotic tissue., An ulcer is a discontinuity or break in a bodily membrane that impedes the organ of which that membrane is a part from continuing its normal functions. According to Robins pathology, ulcer is the breach of the continuity of skin, epithelium or mucous membrane caused by sloughing out of inflamed necrotic tissue.Stomach, Bacterium normally found in colon, throat, or vagina causing deep, pus-filled holes in tissue. Also see Streptothrix, Actinomycosis, and Mycetoma., Can cause typhoid fever. See Typhoid Fever., Chest pain indicative of cardiac problems.Heart, Chronic cases will always recur until metal dentalwork is replaced with uranium-free porcelain. See Herpes Simplex i, and use Stomatitis programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs.Lung, Combines most anecdotal frequencies for Herpes Simplex i., Formation of blood clot affecting blood flow, associated with Herpesviridae infections. Not to be used with Arrhythmia., Hardening of arteries. Regeneration takes time. Try CMV programs.Veins, Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs., Hives, often due to toxins. See Hives., Incoordination of muscles. Slow results in some cases.Nerve, Infection and inflammation of bone and marrow. Usually caused by Staphylococcus Aureus, certain Streptococcus spp, Enterobacter spp, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Salmonella spp in Sickle Cell Anemia cases. See appropriate programs. Also see Infection Bone., Infection of periodontium causing inflammation of gums and bone loss. Although it may be controlled or eliminated with treatment, infection always returns whenever subject experiences stress or poor diet until dental mercury is removed. Also see Gingivitis.Teeth, Infection of uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and inside of pelvis, usually by Neisseria Gonorrheae, or Chlamydia Trachomatis. See Fallopian Tube Infection, Salpingitis, Gonorrhea, and General Antiseptic programs., Infections contracted in a hospital/medical facility, or caused by a medical professional., Inflammation of gums caused by plaque leading to periodontitis. See Dental Infection, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis., Inflammation of testes due to TB, Mumps, Gonorrhea, Cancer, bacteria, etc. See causative condition if known. See Gonads inflammation, Testicle Fluid, Testicular Diseases, and Hydrocele programs., Inflammation of urethra. See Vaginosis, and Chlamydia Trachomatis programs., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Should be run once a month as maintenance. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., Intensely painful neuropathic chronic disorder affecting the faces trigeminal nerve. Also see Neuralgia Trigeminal program., Itchy bumps on skin. See Urticaria programs., Locomotor dysfunction., Medley of useful frequencies., Neglecting this can prevent recovery from any illness. Should also be treated professionally, preferably a holistic dentist. Also see Dental, Gingivitis, and Pyorrhea programs., Ovarian disorders may refer to diseases primarily affecting, or centered on, the ovaries.Ovary, Peptic ulcer in first part of small intestine., Peripheral nerves disorder - see Peripheral Nervous System Diseases., Peripheral nerves disorder - see Peripheral Nervous System Diseases.Nerve, Pimples, white/blackheads, greasy skin, possible scars. Also see Propionibacterium Acnes.Skin, Primarily orofacial. Use General Antiseptic program., Production of insulin has slowed. Run for Diabetes, but monitor blood sugar levels. If no improvement, test for insulin resistance.Pancreas, Protruding lower jaw, considered a disorder only if it affects chewing, speech, or social function., See Bone Regeneration, Paradontosis, and Dental programs., See Bone Regeneration, Paradontosis, and Dental programs.Oral Cavity, See Chemtrail detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Gingivitis, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis programs.Gums, See High Blood Sugar program., See Hyperglycemia programs., See Hypoglycemia, and Hyperinsulism., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, See Low Blood Sugar program., See Muscles to Relax. Relax in a hot bath, liberally laced with epsom salt., See Paradontosis, Bone Regeneration, and Dental programs., See Paradontosis, Bone Regeneration, and Dental programs.Oral Cavity, See Pharyngitis, Streptococcus General, Streptococcus Pyogenes, and Actinomyces Israelii programs., Shingles, also known as zoster or herpes zoster, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area.Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide stripe either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be tingling or local pain in the area., Signs and symptoms of a tooth abscess include:Severe, persistent, throbbing toothache that can radiate to the jawbone, neck or ear.Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.Sensitivity to the pressure of chewing or biting.Fever.Swelling in your face or cheek.Tender, swollen lymph nodes under your jaw or in your neck., Smooth muscle benign tumor most commonly found in uterus, esophagus, and small bowel., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease., Splenomegaly is a condition that occurs when your spleen becomes enlarged. It is also commonly referred to as enlarged spleen orspleen enlargement., Starts in an ovary, producing abnormal invasive cells which spread., Stroke paralysis. See Stroke Follow Up., Take a good calcium/magnesium supplement and use the Water Cure. See Acidosis, Hernia, Hyperacidity, Staphylococcus, and Streptococcus General, and Heliobacter programs., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach., Typhus infection-related symptoms causing high fever, headache, and rash. Use Salmonella Typhi, and Rickettsia programs. See Q Fever program., Use Chronic Fatigue V, EBV, Fatigue General, Parasites General, Roundworm, and Flukes programs. If no response, try Cancer Leukemia Hairy Cell., Use for Chicken Pox and Shingles - see programs for both, and for Varicella., Use Fungus Foot and General 1, and General Antiseptic programs. Also see Parasites General Flukes, and Roundworm programs.Skin, Use General Antiseptic program., Use General Antiseptic, Staphylococci, and Streptococcus Infection programs., Use Salmonella Typhimurium, Salmonella Typhi, and Rickettsia programs. See Q Fever program., Warning: can cause large drop in blood sugar level. Other use: spleen secondary., What is urethritis? Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body, becomes inflamed and irritated. Semen also passes through the male urethra. Urethritis typically causes pain while urinating and an increased urge to urinate |
| 1818 | Spooky2 CAFL | Vision Acuity | See Eye Disorders, Eyesight to Improve, and Macular Degeneration and Visual Acuity programs. |
| 1836 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Ehrlichia Chaffeensis, Macular Degeneration and Visual Acuity, Macular Degeneration Visual Acuity | Age-related diminution or blurring of center of visual field. Use with Cataract programs., Rickettsial tick-borne bacteria, common in Lyme Disease. See Rickettsia Rickettsii. |
| 1854 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Macracanthorhynchus 2, Macular Degeneration and Visual Acuity, Macular Degeneration Visual Acuity | Acanthocephalan parasite living in the intestines of pigs and other suids, and occasionally in humans or dogs, causing enteritis, gastritis, or peritonitis., Age-related diminution or blurring of center of visual field. Use with Cataract programs. |
| 1890 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hemoglobinopathies | Genetic defects causing abnormal hemoglobin molecule structure. |
| 1933.2 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hepatitis General 3 | Infectious inflammation of liver. Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary. |
| 1998 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Borna Disease Virus BDV, Cancer Prostate, Cancer Prostate 2, Cancer Prostate 3, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 1, Dental Infection, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, General Comprehensive, General Program Blaster 5, Parasites General 2 | Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Gum disease: Also known as gingivitis, this condition occurs when bacteria build up under the gums and cause inflammation and bleeding.Some people with sinusitis also experience gum pain and toothache. Tooth abscess: A bacterial infection in the root of a tooth can cause an abscess or pus-filled sac., inclusive, extensive, exhaustive, broad, wide, compendious, synoptic, sweeping, widespread, far-reaching, comprising, containing, all-embracing, all-inclusive, complete, thorough, discursive, encyclopedic, full, general, expansive, overall, blanket, umbrella; see also absolute 1, general 1, large 1, 2, whole 1., Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis., Medley of useful frequencies., Roots and gums., Zoonotic virus that can infect nerve cells, causing Borna Disease. |
| 2016 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme, Borrelia Lyme 2, Borrelia Lyme 4, Borrelia Lyme A, Borrelia Lyme Tertiary, Borreliosis 1, Cancer Rhabdomyosarcoma, Cancer Rhabdomyosarcoma Embryonal, Lyme 2, Lyme 5, Lyme Disease, Lyme Disease 5, Lyme Disease A, Lyme Disease W3, Lyme General, Lyme Main Co-infections, Lyme Tertiary, Lymphoma Non Hodgkins, Morgellons Disease 1, Morgellons Disease 2 | Also called Borreliosis. Relapsing fever in humans and animals caused by parasitic spirochetes from ticks. Use Borreliosis, Babesia, and Parasites blood flukes programs., Also called Lyme Disease., Also called RMS. Connective tissue cancer. May arise from progenitor cells. Use Blood Cleanser., Also known as Borreliosis., Main frequencies for Lyme co-infections., Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin., Rare connective tissue cancer with cells resembling embryonic skeletal muscle. Use Blood Cleanser., See B-Cell Lymphoma, and Cancer Lymphoma Non-Hodgkins., Spirochete involved in Lyme disease. |
| 2052 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borna Disease Virus BDV | Zoonotic virus that can infect nerve cells, causing Borna Disease. |
| 2160 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Adenocarcinoma Esophageal, Cancer Breast 2, Cancer Breast 4, Cancer Breast 5, Cancer Carcinoma 3, Cancer Carcinoma General, Cancer Carcinoma Scan, Cancer Carcinoma Scan 2, Cancer Pancreatic 1, Carcinoma 2 | Also see Cancer Carcinoma., Also see Cancer Islet Cells Carcinoma and Cancer Pancreatic Exocrine and Islet Cell., Epithelial cell cancer - begins in tissue lining inner or outer surfaces of the body., Main low sub-harmonics of carcinoma. Use Blood Cleanser. See BX Virus, and Cancer BX Virus programs., Main low sub-harmonics of carcinoma. Use Blood Cleanser. See BX Virus, and Cancer BX Virus programs.Mouth, Malignant growths of glandular origins or with glandular traits (such as secretion). Use Blood Cleanser., Malignant growths of glandular origins or with glandular traits (such as secretion). Use Blood Cleanser.Throat, Use Blood Cleanser., Use Blood Cleanser. See BX Virus, and Cancer BX Virus programs. |
| 2173.86 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ornithonyssus Bird Mite 1 | Ornithonyssus is a mite genus of the family Macronyssidae. |
| 2232 | Spooky2 CAFL | Felis | Felis is a genus of small and medium-sized cat species native to most of Africa and south of 60? latitude in Europe and Asia to Indochina.Cats |
| 2250 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Adrenal Gland Balance, Adrenal Gland Stimulant 1, Alkalosis, Amnesia, Anencephaly, Anus Diseases, Arthrogryposis, Bladder Exstrophy, Bladder Infection, Cafe-au-Lait Spots, Cancer Prostate, Cancer Prostate 2, Cancer Prostate 2a, Cancer Prostate 2b, Cancer Prostate 3, Chondrosarcoma, Cranial Nerve II Diseases, Cystitis Interstitial, Depression Bipolar, Diaphragmatic Hernia, Diverticulitis, Enuresis 2, Epididymitis, Erysipelas, Facial Neuralgia, Factor XII Deficiency, Fatty Acid Oxidation Disorders, Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone, Fibrous Dysplasia Polyostotic, Freibergs Disease, Furunculosis, Gastroparesis, Genital Diseases Female, Genital Diseases Male, Giardiasis, Gingivitis, Glossitis Benign Migratory, Glossopharyngeal Nerve Diseases, Goldenhar Syndrome, Gynecomastia, Hantavirus Infections, Hearing Disorders, Hearing Loss Sudden, Hematologic Diseases, Hemiplegia, Hepatomegaly, Hernia Diaphragmatic, Hyperemesis Gravidarum, Hyponatremia, Incontinence 1, Inflammation Urethra, Larsen Syndrome, Lupus Erythematosus Cutaneous, Measles, Monosomy, Mutism, Myiasis, Nephrotic Syndrome, Neuromyelitis Optica, Neuronal Ceroid-Lipofuscinoses, Onchocerciasis 2, Optic Nerve Diseases, Otitis, Otosclerosis, Pallister-Killian Syndrome, Paraneoplastic Syndromes Nervous System, Parasites Schistosoma haematobium, Parasites Trypanosoma rhodesiense, Phlebitis, Prognathism, Prostate Enlarged, Prostatic Diseases, Prostatitis 1, Rectal Diseases, Sarcoma, Smith-Magenis Syndrome, Tachycardia, Trachoma, Tularemia, Ulnar Nerve Compression Syndrome, Urticaria | A female genital disease is a condition that affects the female reproductive system., A male genital disease is a condition that affects the male reproductive system. An example is orchitis., Abnormal growth of bone near middle ear which can lead to hearing loss., Also called Bipolar Disorder., Also called Bladder Pain Syndrome.Bladder, Also called Geographic Tongue. Inflammation of mucous membrane of tongue which moves over time., Also called Rubeola. Highly contagious condition with fever, cough, rhinitis, red eyes, followed by white oral spots and red skin rash., Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., An infection in any part of the urinary system, the kidneys, bladder, or urethra., Autoimmune disease involving joints, skin, kidneys, blood cells, heart, and lungs. Use Nanobacter and Parasites Flukes programs., Blood flukes. Associated with bladder problems. Also see Schistosoma Haematobium, and Blood Fluke programs., Causes can include Glaucoma, Optic Neuritis, tumors, trauma, and other eye problems., Chromosomal abnormality with presence of just one chromosome from a pair., Coagulation system deficiency of enzyme necessary for plasma clotting.Blood, Congenital disorder with dislocation of large joints and facial abnormalities., Congenital joint contractures in two or more body areas., Defect in diaphragm that allows abdominal organs to move into the chest., Delayed emptying of stomach into small intestine, usually due to vagus nerve damage., Developmental disorder - absence of major portions of brain, skull, and scalp., Developmental disorder affecting body and brain, including intellectual disability, broad face, difficulty sleeping, and various behavioral problems., Diaphragm defect that allows abdominal organs to move into chest cavity., Diseases of the ninth cranial (glossopharyngeal) nerve or its nuclei in the medulla. The nerve may be injured by diseases affecting the lower brain stem, floor of the posterior fossa, jugular foramen, or the nerves extracranial course. Clinical manifestations include loss of sensation from the pharynx, decreased salivation, and syncope. Glossopharyngeal neuralgia refers to a condition that features recurrent unilateral sharp pain in the tongue, angle of the jaw, external auditory meatus and throat that may be associated with SYNCOPE. Episodes may be triggered by cough, sneeze, swallowing, or pressure on the tragus of the ear., Disorders include Prostate Cancer, Prostatitis, and Prostate Hyperplasia., Disorders primarily affecting the blood., Ear infections., Endocrine system disorder with non-cancerous development of breasts in males. May also be caused by certain medications., Enlarged liver. Also see Liver Enlarged, and Liver Enlargement., Facial pain info, trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face.Face, Flat light-brown birthmarks., Genetic disorder of bones, skin pigmentation, and hormone problems with premature puberty., Group of genetic disorders caused by inability to produce or use one enzyme needed for fatty acid oxid oxidation., Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is a partial or total inability to hear. A deaf person has little to no hearing. Hearing loss may occur in one or both ears. In children, hearing problems can affect the ability to learn spoken language and in adults it can create difficulties with social interaction and at work. In some people, particularly older people, hearing loss can result in loneliness. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent.Hearing loss may be caused by a number of factors, including: genetics, ageing, exposure to noise, some infections, birth complications, trauma to the ear, and certain medications or toxins. A common condition that results in hearing loss is chronic ear infections. Certain infections during pregnancy, such as cytomegalovirus, syphilis and rubella, may also cause hearing loss in the child. Hearing loss is diagnosed when hearing testing finds that a person is unable to hear 25 decibels in at least one ear. Testing for poor hearing is recommended for all newborns. Hearing loss can be categorized as mild (25 to 40 dB), moderate (41 to 55 dB), moderate-severe (56 to 70 dB), severe (71 to 90 dB), or profound (greater than 90 dB). There are three main types of hearing loss: conductive hearing loss, sensorineural hearing loss, and mixed hearing loss.About half of hearing loss globally is preventable through public health measures. Such practices include immunization, proper care around pregnancy, avoiding loud noise, and avoiding certain medications. The World Health Organization recommends that young people limit the use of personal audio players to an hour a day in an effort to limit exposure to noise. Early identification and support are particularly important in children. For many hearing aids, sign language, cochlear implants and subtitles are useful. Lip reading is another useful skill some develop. Access to hearing aids, however, is limited in many areas of the world.As of 2013 hearing loss affects about 1.1 billion people to some degree. It causes disability in 5% (360 to 538 million) and moderate to severe disability in 124 million people. Of those with moderate to severe disability 108 million live in low and middle income countries. Of those with hearing loss, it began during childhood for 65 million. Those who use sign language and are members of Deaf culture see themselves as having a difference rather than an illness. Most members of Deaf culture oppose attempts to cure deafness and some within this community view cochlear implants with concern as they have the potential to eliminate their culture. The term hearing impairment is often viewed negatively as it emphasises what people cannot do., Hives, often due to toxins. See Hives., Impaired functioning of optic nerve.Eyes, Inability to speak often caused by speech disorder, hearing loss, or surgery., Infection by Giardia Lamblia. Also see Giardia Intestinalis, Parasites Giardia, and Lamblia., Infection by Onchocerca Volvulus., Infection normally with red facial, arm, or leg rash. Usually due to Streptococcus Pyogenes or other family members (see Streptococcal Infections)., Infestation of fly larvae (maggots). Also called Fly Strike. Often seen in Morgellons., Inflammation of diverticula in bowel wall caused by Diverticulosis. See Intestines Inflammation., Inflammation of gums caused by plaque leading to periodontitis. See Dental Infection, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis., Inflammation of prostate., Inflammation of testicle area, ducts. Also see Orchitis program., Intractable nausea, vomiting, and dehydration in pregnant women which can last till the birth., Kidney disorder with large Proteinuria leading to low protein blood levels, and Edema (use Ascites programs)., Lack of moderation or self-control, Low levels of sodium in blood., May be respiratory, metabolic, or combined., Memory loss.Brain, Metatarsal bone destruction caused by loss of blood supply., Multiple neurodegenerative disorders that result from excessive accumulation of lipopigments (lipofuscin) in tissues. Also see Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Non-cancerous abnormal bone growth where normal bone is replaced with fibrous bone tissue., Painful and potentially blinding infectious eye disease caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis., Paralysis of one side of the body., program of signs or symptoms due to cancer but not caused by local cancer cells., Protruding lower jaw, considered a disorder only if it affects chewing, speech, or social function., Protrusion of bladder through abdominal wall., Rapid heartbeat. Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable. See Heart Tonic, and Relaxation to Produce programs., Rare congenital defect with incomplete development of ear, nose, soft palate, lip, and mandible, and organ problems., Rectal problems include heamorrhoids, fissures, abscesses and incontinence. Cancer can affect the rectum. Pain or bleeding are signs that need medical attention., Rodent viruses which can infect humans and cause life-threatening illnesses., See Bed Wetting programs. Use Parasites General, Pinworms, and Ascaris programs., See Boils, and Furunculosis programs. Also use Staphylococcus Aureus., See Cancer Sarcoma, and BY Virus programs., See Prostatitis and other prostate programs. Use Streptococcus General, and Propionibacterium Acnes, and practise metals avoidance., Serious tick and arthropod borne infection with lesions and fever, spreading to lungs, lymphatic system, liver, and spleen. Use Francisella Tularensis., Simultaneous inflammation and demyelination of optic nerve (Optic Neuritis) and spinal cord (Myelitis)., Skeletal system cancer. See Cancer BY Virus, and Cancer Sarcoma programs., Sudden sensorineural (inner ear) hearing loss (SSHL), commonly known as sudden deafness, is an unexplained, rapid loss of hearing either all at once or over a few days., The adrenal glands (also known as suprarenal glands) are endocrine glands that produce a variety of hormones including adrenaline and the steroids aldosterone and cortisol. They are found above the kidneys. Each gland has an outer cortex which produces steroid hormones and an inner medulla. The adrenal cortex itself is divided into three zones: the zona glomerulosa, the zona fasciculata and the zona reticularis.The adrenal cortex produces three main types of steroid hormones: mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, and androgens. Mineralocorticoids (such as aldosterone) produced in the zona glomerulosa help in the regulation of blood pressure and electrolyte balance. The glucocorticoids cortisol and cortisone are synthesized in the zona fasciculata; their functions include the regulation of metabolism and immune system suppression. The innermost layer of the cortex, the zona reticularis, produces androgens that are converted to fully functional sex hormones in the gonads and other target organs. The production of steroid hormones is called steroidogenesis, and involves a number of reactions and processes that take place in cortical cells. The medulla produces the catecholamines adrenaline and noradrenaline, which function to produce a rapid response throughout the body in stress situations.A number of endocrine diseases involve dysfunctions of the adrenal gland. Overproduction of cortisol leads to Cushings syndrome, whereas insufficient production is associated with Addisons disease. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic disease produced by dysregulation of endocrine control mechanisms.A variety of tumors can arise from adrenal tissue and are commonly found in medical imaging when searching for other diseases.Adrenals, The anus is that part of the intestinal tract that passes through the muscular canal of the pelvis and anal sphincters. It is the final orifice through which stool passes out of the body. In adults, the anus is 4 to 5 centimeters long. The lower half of the anal canal has sensitive nerve endings. There are blood vessels under the lining, and in its mid portion there are numerous tiny, anal glands. This article describes four disorders that cause anal pain and irritation,Anal fissure - An anal fissure, also called an anorectal fissure, is a linear split or tear in the lining (anoderm) of the lower anal canal. Most anal fissures happen when a large, hard stool overstretches the anal opening and tears the delicate anoderm. Less often, anal fissures develop because of prolonged diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease or sexually transmitted diseases involving the anorectal area. Acute (short-term) anal fissures are usually superficial and shallow, but chronic (long-term) anal fissures may extend deeper through the anoderm to expose the surface of underlying muscle.Anal abscess - An anal abscess is a swollen, painful collection of pus near the anus. Most anal abscesses are not related to other health problems and arise spontaneously, for reasons that are unclear. They originate in a tiny anal gland, which enlarges to create a site of infection under the skin. In the United States, more than half of all anal abscesses occur in young adults between the ages of 20 and 40, and men are affected more often than women. Most anal abscesses are located near the opening of the anus but rarely can occur deeper or higher in the anal canal, closer to the lower colon or pelvic organs.Anal fistula - An anal fistula is an abnormal narrow tunnel-like passageway, which is the remnant of an old anal abscess after it has drained. It connects the mid portion of the anal canal (at the anal gland) to the surface of the skin. After an anal abscess has drained (either spontaneously or when lanced by a physician), an anal fistula will develop at least half of the time. Sometimes the opening of the fistula at the skin surface constantly discharges pus or bloody fluid. In other cases, the opening of the fistula closes temporarily, causing the old anal abscess to flare up again as a painful pocket of pus.Hemorrhoids - Hemorrhoids do not ordinarily cause pain. Nevertheless, sometime the blood vessels in a small hemorrhoid at the edge of the anal orifice can clot off (thrombosis). This may be triggered by a period of constipation of diarrhea. When thrombosis occurs, the external hemorrhoid becomes swollen, hard, and painful, sometimes with bloody discharge.Anus, Trapped ulnar nerve, which runs through the elbow., Trypanosoma brucei is a species of parasitic kinetoplastid belonging to the genus Trypanosoma. The parasite is the cause of a vector-borne disease of vertebrate animals, including humans, carried by genera of tsetse fly in sub-Saharan Africa. In humans T. brucei causes African trypanosomiasis, or sleeping sickness., Vein inflammation., Very rare genetic disorder with developmental disability, epilepsy, hypotonia, both hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation, and other symptoms., What is urethritis? Urethritis is a condition in which the urethra, or the tube that carries urine from the bladder to outside the body, becomes inflamed and irritated. Semen also passes through the male urethra. Urethritis typically causes pain while urinating and an increased urge to urinate |
| 2286 | Spooky2 CAFL | Sars 1 | Also use Streptococcus Pneumoniae program.Respiratory |
| 2322 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Dirofilaria Immitis 2, Dirofilaria Immitis 3, Heartworms, Parasites Heartworms | Also called Dog Heartworm, or Heartworm. Parasitic mosquito-borne filaria that can infect other animals, and humans. See Heartworms, and Parasites Heartworms., Also called Dog Heartworm. Parasitic mosquito-borne filaria that can infect other animals, and humans. See Dirofilaria Immitis and Parasites Heartworms., Mosquito-borne filaria. See Dirofilaria Immitis, Heartworms, Parasites Dirofilaria Immitis Dog Heartworm, and Parasites Heartworms.Lung |
| 2358 | Spooky2 CAFL | Multiple Sclerosis 3, Multiple Sclerosis 6 | Demyelinating disease. Aspartame, mercury, benzene, lead, and toluene can cause same symptoms. Use Chlamydia General, Herpes Type 6, and see ALS, Herpes General, Blastocystis Hominis, Parasites Flukes, Shigella, Nocardia, and Herpes Zoster programs.Nerve |
| 2502 | Spooky2 XTRA | Streptococcus Pyogenes 4 | Also called Group A beta-haemolytic Strep (GAS). Causes Sore Throat, skin inflammation, Scarlet Fever, Pharyngitis, Impetigo, Erysipelas, Frozen Shoulder, Cellulitis, Septicemia, Toxic Shock Syndrome, and acute Glomerulonephritis, and Beta Streptococcus. Use General Antiseptic. |
| 2520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hirsutism, Parasites Flukes Sheep Liver | Excessive hair growth in women in areas where terminal hair is normally absent or minimal., See Parasites Fasciola Hepatica programs, Parasites Sheep Liver Flukes, and Liver Flukes. |
| 2610 | Spooky2 ETDF | Metabolic Diseases | Large class of genetic diseases involving congenital disorders of metabolism. |
| 2664 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | HIV 3, Human T Lymphotropic Virus3, T Lymph Virus | Causes leukemia/lymphoma and nerve demyelination. Use for AIDS., Human T-Lymphotropic Virus. Family of viruses causing T Cell Leukemia, and the demyelinating disease HTLV-I associated myelopathy/tropical spastic paraparesis (HAM/TSP)., Retrovirus causing HIV Infection and AIDS. Also see Human T Lymphotropic Virus. |
| 2700 | Spooky2 CAFL | ALS 3 | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve |
| 2720.34 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia CA2-87, Borrelia Species Self-Test | All species 60 secs each. Run in Contact or Plasma Modes. Note running frequency when hits are felt, then use Reverse Lookup., Type/strain: US-CA 2-87. |
| 2790 | Spooky2 XTRA | BX Virus 1, Cancer Basic 6, Cancer BY Sarcoma Virus 1 | Cancer virus causing Carcinoma., Use Blood Cleanser., Virus causing sarcomas. Also use Blood Cleanser. |
| 2880 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pityriasis | Flaking or scaling of skin. |
| 2970 | Spooky2 ETDF | Eye Abnormalities | Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the physical disturbance of the center of the retina called the macula. Bulging Eyes. Cataracts. Cataracts in Babies. CMV Retinitis. Color Blindness. Crossed Eyes (Strabismus) Diabetic Macular Edema. |
| 3042 | Spooky2 CAFL | Cancer Leukemia T Cell | Attacks the immune systems T Cells. Use Blood Cleanser.Blood |
| 3222 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA | Smallpox, Variola, Variolinum | Also called Variola. Extremely contagious viral disease marked by fever, prostration, and a rash of small blisters. Also see Herpes Simplex RTI program., Also known as Smallpox. Also see Variolinum, and Herpes Simplex RTI., Homeopathic smallpox nosode. See Smallpox, Variolinum, and Herpes Simplex RTI. |
| 3636 | Spooky2 CAFL | ALS 2, Enterovirus | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, possibly due to Mycoplasma Fermentans. Use Multiple Sclerosis, and see Echo Virus, Coxsackie, Herpes 6, Bartonella, and Lyme programs.Nerve, Generic term meaning small virus. Includes Echo, Coxsackie, and Polio. |
| 3672 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Asthma, Asthma 2, Asthma 4, Basal Cell Carcinoma, Breast Tumors Benign, Breathe Easier, Breathing Deep, Bronchial Asthma 1, Bronchial Asthma 5, Bronchitis, Bronchitis 2, Cancer, Cancer Additional Frequencies 1, Cancer Basic 2, Cancer Basic 7, Cancer Bone, Cancer Experimental Additional, Cancer Experimental Additional Frequencies, Cancer Lung, Cancer Non Hodgkins 2, Cancer Prostate 1, Cancer Prostate 2, Cancer Skin, Cold 6, Croup, Emphysema, Emphysema 2, Flu 2, Influenza, Influenza 2003/2004 1, Lung General, Lung General 2, Lymphoma Non Hodgkins, Mammary Tumor Benign, Squamous Cell Carcinoma | A benign breast condition refers to a lump, cyst, or nipple discharge (fluid) of the female or male breast that is not cancerous. There are numerous benign breast conditions. For women, the most common ones are:Fibrocystic breast changes. Fibrosis feels like scar tissue and can be rubbery and firm. Cysts are sacs filled with fluid. They may enlarge and feel tender right before your period.Fibroadenomas. These are the most common breast lumps in younger women and are usually very small.Mastitis. Your breast can become enlarged because of infection. This can happen to anyone but usually happens when breastfeeding.Fat necrosis. These lumps form when areas of fatty breast tissue are damaged.Calcification. Small spots of calcium salts can show up anywhere in breast tissue. Usually, you cant feel them and they are not painful.Nipple discharge. Your nipples may leak fluid for a variety of reasons., A cold begins when avirus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat.Your immune system -- the bodysdefense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., A cold or the flu runs its course in a couple weeks, if youre lucky. After that, youre back to normal. But sometimes you may get bronchitis, too.Thats when your bronchial tubes, which carry air to your lungs, get infected and swollen. You end up with a nagging cough and a lot more mucus.You can get bronchitis in other ways, too, and there are actually two types of it:Acute bronchitis: This is the more common one. Symptoms last for a few weeks, but it doesnt usually cause any problems past that.Chronic bronchitis: This one is more serious, in that it keeps coming back or doesnt go away at all. Its one of the conditions that makes up whats called chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, A mammary tumor is a neoplasm originating in the mammary gland. It is a common finding in older female dogs and cats that are not spayed, but they are found in other animals as well.Breast, Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also see Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Bowens Disease, and Cancer Lung Non-Small Cell programs., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Influenza, and Grippe., Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi), the air passages between the mouth and nose and the lungs.More specifically, bronchitis describes a condition where the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes inflamed.Individuals with bronchitis have a reduced ability to breathe air and oxygen into their lungs; also, they cannot clear heavy mucus or phlegm from their airways.This article will cover the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention of bronchitis. Symptoms of bronchitisMan coughingBronchitis is characterized by persistent coughing.Signs and symptoms of both acute and chronic bronchitis include:Persistent cough, which may produce mucusWheezingLow fever and chillsChest tighteningSore throatBody achesBreathlessnessHeadachesBlocked nose and sinusesOne of the main symptoms of acute bronchitis is a cough that lasts for several weeks. It can sometimes last for several months if the bronchial tubes take a long time to heal fully.It is common for the symptoms of chronic bronchitis to get worse two or more times every year, and they are often worse during the winter months.However, a cough that refuses to go away could also be a sign of another illness such as asthma or pneumonia., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Common skin cancer, mostly found on head or neck. Rarely fatal or metastatic., Even though you cant see it, the air you breathe can affect your health. Polluted air can cause difficulty breathing, flare-ups of allergy or asthma, and other lung problems. Long-term exposure to air pollution can raise the risk of other diseases, including heart disease and cancer.Some people think of air pollution as something thats found mainly outside. They may picture cars idling or power plants with smoke stacks. But air pollution can also occur insidein homes, offices, or even schools., Experimental additional frequencies. Use Blood Cleanser., Lung cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the lungs. Your lungs are two spongy organs in your chest that take in oxygen when you inhale and release carbon dioxide when you exhale.Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths in the United States, among both men and women. Lung cancer claims more lives each year than do colon, prostate, ovarian and breast cancers combined.People who smoke have the greatest risk of lung cancer, though lung cancer can also occur in people who have never smoked. The risk of lung cancer increases with the length of time and number of cigarettes youve smoked. If you quit smoking, even after smoking for many years, you can significantly reduce your chances of developing lung cancer., Mutates to new strains constantly but these may be helpful. Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Neoplasms. Can be benign or malignant., Pay attention to how you feel when you inhale and exhale normally and when you breathe deeply. Shallow breathing often feels tense and constricted, while deep breathing produces relaxation. Now practice diaphragmatic breathing for several minutes. Put one hand on your abdomen, just below your belly button., Respiratory condition due to viral infection of upper airway., See B-Cell Lymphoma, and Cancer Lymphoma Non-Hodgkins., See Cancer Basal Cell Skin Carcinoma, Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Cancer Melanoma. Use Blood Cleanser., See Cancer programs. Use Blood Cleanser., See Chemtrail Detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs., See Chemtrail Detox, Nocardia Asteroides, and Alternaria Tenuis programs.Lung, See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, Use Blood Cleanser., Use Cancer Melanoma, and Blood Cleanser. Also helps with blood cell production problems in Morgellons. |
| 3780 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Candidiasis Vulvovaginal, Meckel Diverticulum | Also called Vaginal Thrush., Congenital bulge in small intestine causing severe pain, abdominal bloating, and rectal bleeding. |
| 3798 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Fibromyalgia 2, Fibromyalgia 5 | Chronic widespread pain and heightened response to pressure with pronounced fatigue, sleep disturbance, stiff joints, and other symptoms. Also see Tendomyopathy. |
| 3870 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fasciitis, Fasciitis Necrotizing, Polyarteritis Nodosa, Purpura Schoenlein-Henoch | Commonly called Flesh-eating Disease. Also use Streptococcus Pyogenes, Staphylococcus Aureus, Clostridium Perfringens, and Bacteroides Fragilis. Also see Fournier Gangrene, and Gangrene., Disease of skin and other organs most common in children. In skin, it causes palpable purpura (small hemorrhages); often with kidney problems, joint and abdominal pain., Inflammation of connective tissue surrounding muscle and internal organs. See Fascia programs., Systemic vasculitis of small- or medium-sized muscular arteries, usually involving renal and visceral vessels but not pulmonary circulation. |
| 4014 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Immune System Stimulation 1, Immune System Stimulation 3, Immune System Stimulation 4, Interleukin, Lymphocytes Stimulate, Morgellons Disease 1, Morgellons Disease 2, White Blood Cell Stimulation | Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin., Normalize. Also see Leukocytogenesis Stimulate., Normalize. Also see Leukocytogenesis Stimulate. NB: minimum of 5 treatments.Immune system, See Immune System Stimulation, Leukocytogenesis Stimulate, and Leukopenia programs., Type of white blood cell including T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells. Use in immune stimulation., Vital to immune system. Use to stimulate lymphocyte production. |
| 4050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Retardation Mental | Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability and mental retardation (MR), is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by significantly impaired intellectual and adaptive functioning. |
| 4122 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 VEGA, Spooky2 XTRA | Cryptosporidium, Cryptosporidium Parvum, Parasites General Alternative V | micropredation.Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Parasitic protozoa causing diarrhea. See Cryptosporidiosis. |
| 4140 | Spooky2 ETDF | Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I | Severe pain, swelling, and skin changes in parts or all of the body. Also called Causalgia, and Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy. |
| 4230 | Spooky2 XTRA | Meridians - Large Intestine | Abbreviated as LI or CO (colon), described in Chinese as The Large Intestine channel of Hand Yangming. |
| 4320 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Lyme Disease W3, Lyme Dougs, Parasites Entamoeba coli trophozoites, Parasites Entamoeba gingivalis trophozoite, Parasites Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite | A parasitic infection of the colon with the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica., Also known as Borreliosis., Amebiasis is a disease caused by infection with a parasitic amoeba that, when symptomatic, can cause dysentery and invasive extraintestinal problems. The cause of amebiasis is mainly the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica., ETDFLAlso for Parasites Endolimax nana trophozoites and cysts, Life cycle stage of protozoan found in dental spaces. |
| 4392 | Spooky2 CAFL | Cancer Neuroblastoma, Sinusitis 2 | Experimental. Mainly a childhood neuroendocrine cancer. Use Blood Cleanser.Nerve, Inflammation of mucous membrane that lines paranasal sinuses. Also see Lung Sinus Bacteria, and Sinus Bacteria. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and appropriate Sinusitis and Rhinitis programs. |
| 4500 | Spooky2 CAFL | Paramecium Caudatum, Rotifer | Eukaryotic unicellular organism., Phylum of microscopic aquatic animals. |
| 4628.34 | Spooky2 XTRA | Nanobacter 2, Nanobacter 3 | Nanobacterium sanguineum, found in calcium deposits in arteries, kidneys, gallbladder, muscles, and joints and in autoimmune diseases like lupus, psoriasis, scleroderma, etc. Immunomodulator present in cancer and Morgellons/Lyme. |
| 4698 | Spooky2 XTRA | Nogier E | From Dr. Pankaj Mishra. Nerves, pain relief, neuralgia, Herpes zoster, spine/brain, reflex arc, medullary disorders. |
| 5004 | Spooky2 XTRA | Streptococcus Pyogenes 4 | Also called Group A beta-haemolytic Strep (GAS). Causes Sore Throat, skin inflammation, Scarlet Fever, Pharyngitis, Impetigo, Erysipelas, Frozen Shoulder, Cellulitis, Septicemia, Toxic Shock Syndrome, and acute Glomerulonephritis, and Beta Streptococcus. Use General Antiseptic. |
| 5058 | Spooky2 CAFL | Cholesteatoma | Benign tumor usually found in middle ear and mastoid region. |
| 5148 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Alzheimers 1, Alzheimers 2, Alzheimers 3, Alzheimers 4 | See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimer. Chronic neurodegenerative illness., See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimer. Chronic neurodegenerative illness.Brain |
| 5310 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Cervical 2, Herpes Progenitalis, Herpes Progenitalis 1, Herpes Simplex RTI, Pseudo-Gaucher Disease | Based on RTIs Herpes program; most freqs contract spread. Use for Measles, Chicken Pox, Smallpox, Mononucleosis, Shingles, Rubella, cold sores, Epstein Barr, Variola, Stomatitis, and Pyorrhea., Genetic disorder in which glucocerebroside accumulates in cells and certain organs, with bruising, fatigue, anemia, low blood platelet count, and enlargement of liver and spleen., Primarily genital., The most common symptoms of cervical cancer are:bleeding between periods.bleeding after sexual intercourse.bleeding in post-menopausal women.discomfort during sexual intercourse.vaginal discharge with a strong odor.vaginal discharge tinged with blood.pelvic pain. |
| 5346 | Spooky2 CAFL | Oospora | Spores of fertilized oospheres in some algae, fungi, and oomycetes. May be implicated in Morgellons Disease. |
| 5364 | Spooky2 XTRA | Artery Plaque | Usually atheroma - swelling in arteries full of pus. |
| 5490 | Spooky2 ETDF | Granulomatosis Wegeners | Also called Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA). Serious systemic vasculitis that involves granulomatosis and polyangiitis. |
| 5562 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza 2003/2004 2 | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 5580 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | AIDS, Bulla, Hernia, Herpes Labialis, Herpes Simplex, Herpesviridae Infections, HIV AIDS, HIV Infections, HIV Related Infections, Hydronephrosis, Hypersomnia Periodic, Hypertrophy Right Ventricular, Hypogonadism, Hypophosphatasia, Intestinal Polyps, Kleine-Levin Syndrome, Laryngostenosis, Mucopolysaccharidoses, Muscle Spasticity | Acquired immune deficiency., Also see Muscle Cramp(s), Muscles Stiff, Muscles to Relax, and other Muscle programs., Diminished function of ovaries/testes with consequent lower levels of sex hormones., Distension and dilation of the renal pelvis and calyces, usually caused by obstruction of the free flow of urine., Excessive daytime sleep or sleepiness, or abnormally prolonged nighttime sleep. See Kleine-Levin Syndrome., Fluid-filled blister., Herpes viral infections. Use General Antiseptic program., In anatomy, a polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, ear, sinus(es), urinary bladder, and uterus., Metabolic disorders affecting ability to build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin, and connective tissue., Narrowing or stricture of the larynx., Primarily orofacial., Primarily orofacial. Use General Antiseptic program., Protrusion of organ through wall of its containing cavity., Rare genetic metabolic bone disease., Rare sleep disorder with hypersomnia and cognitive/mood changes. See Hypersomnia Periodic., Retrovirus causing HIV Infection and AIDS. Also see Human T Lymphotropic Virus., Thickening and enlargement of walls of hearts right ventricle. |
| 5630.4 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Species Self-Test, Borrelia Veery | All species 60 secs each. Run in Contact or Plasma Modes. Note running frequency when hits are felt, then use Reverse Lookup., Type/strain: Veery. First found in Veery thrush. |
| 5670 | Spooky2 ETDF | Royer Syndrome | Also called Prader-Willi Syndrome. Rare genetic disorder with low muscle tone, short stature, incomplete sexual development, cognitive disabilities, behavior problems, and chronic insatiable hunger. |
| 5742 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Mange, Mange Follicular, Mange Follicular 1, Parasites Scabies | Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange., Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange.Hair Skin, Sarcoptic mange is a contagious dermatitis found in many animals caused by scabies mites. Also see Scabies, and Sarcoptes Scabiei Itch programs.Skin |
| 5850 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dupuytrens Contracture, Echinococcosis, Phenylketonurias, Pleural Diseases, Puerperal Disorders, Puerperal Infection, Quadriplegia | 4th and 5th finger curling into palm, unable to straighten., Bacterial infection of female reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage, commonly by Streptococcus Pyogenes and anaerobic Streptococcus spp, Staphylococcus spp, E Coli, and Clostridium spp., Disorders affecting the thin fluid-filled space between the two pulmonary pleurae (visceral and parietal) of each lung, including Pneumothorax, Pleural Effusion, and pleural tumors., Disorders arising during the postnatal period (about six weeks)., Inborn metabolic error with impaired metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Sufferers must never ingest aspartame., Infestation of Echinococcus tapeworms. Also called Hydatid disease., Paralysis from illness or injury with partial or total loss of use of all four limbs and torso. |
| 5859.36 | Spooky2 XTRA | Fat Burn 4 | Also run Hypophyseal Disturbances, Lymph Stasis Secondary, and appropriate Detox programs. |
| 5868 | Spooky2 CAFL | Hookworm, Parasites Hookworm | Blood-feeding roundworm. See Parasites Hookworm, Creeping Eruption, and Larva Migrans., See Hookworm, Ancylostoma, Larva Migrans, and Creeping Eruption programs.Intestines |
| 6210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cooleys Anemia, Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome | Also called Thalassemia. Genetic disorder with abnormal formation of hemoglobin. Also see Chromosome 16 Abnormalities., Rare neurological disorder with recurring facial paralysis, swelling of face and lips, and folds and furrows in tongue. |
| 6516 | Spooky2 BIO, Spooky2 CAFL | Tuberculosis Klebsiella | Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see Klebsiella, TB, and Tuberculinum., Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see Klebsiella, TB, and Tuberculinum.Lung |
| 6534 | Spooky2 XTRA | Virus General 4 | A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus at an extraordinary rate. |
| 6750 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Ependymoma, Pilonidal Cyst, Polyomavirus Infections | Central nervous system tumor, usually intracranial in children and spinal in adults. See Cancer programs., Family of viruses including Simian Virus 40, JC virus, BK virus, and Merkel Cell virus., Painful cyst or abscess near or on the natal cleft of the buttocks that often contains hair and skin debris. |
| 6984 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza General 1 | Winter 1998/1999. Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 7002 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza General 1 | Winter 1998/1999. Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 7290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Angiomyxoma | Frequently recurring benign tumor of vulva or pelvis. |
| 7344 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | Allergies 2, Asthma, Asthma 4, Bordetella Pertussis 4, Breast Tumors Benign, Breathe Easier, Breathing Deep, Bronchial Asthma 1, Bronchitis, Chemical Spray-Related Illness, Cold 6, Cold In Head Or Chest 2, Croup, Dengue Fever 2, Detox Chemtrail 1, Emphysema, Emphysema 2, Flu 2, Guillain-Barre Syndrome, Immune System Stabilization, Influenza, Influenza 2000/2002, Influenza 2003/2004 1, Mammary Tumor Benign, Morgellons Disease 1, Morgellons Disease 2, Mycoplasma General, Pertussis Secondary | A benign breast condition refers to a lump, cyst, or nipple discharge (fluid) of the female or male breast that is not cancerous. There are numerous benign breast conditions. For women, the most common ones are:Fibrocystic breast changes. Fibrosis feels like scar tissue and can be rubbery and firm. Cysts are sacs filled with fluid. They may enlarge and feel tender right before your period.Fibroadenomas. These are the most common breast lumps in younger women and are usually very small.Mastitis. Your breast can become enlarged because of infection. This can happen to anyone but usually happens when breastfeeding.Fat necrosis. These lumps form when areas of fatty breast tissue are damaged.Calcification. Small spots of calcium salts can show up anywhere in breast tissue. Usually, you cant feel them and they are not painful.Nipple discharge. Your nipples may leak fluid for a variety of reasons., A cold begins when avirus attaches to the lining of your nose or throat.Your immune system -- the bodysdefense against germs -- sends out white blood cells to attack this invader., A head cold occurs when a viral infection causes symptoms primarily in the head, such as a stuffy nose or a headache. It differs from a chest cold because of the location of the symptoms. Chest colds cause symptoms including chest congestion and coughing., A mammary tumor is a neoplasm originating in the mammary gland. It is a common finding in older female dogs and cats that are not spayed, but they are found in other animals as well.Breast, Addresses aerially-sprayed toxic metals and biological agents. Also useful for lung and sinus problems. See Chemtrail Detox., Also called breakbone fever. Mosquito-borne viral disease with fever, headache, muscle and joint pain., Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Influenza, and Grippe., Also use Chemtrail programs., Bacteria causing Pertussis (whooping cough)., Bronchitis is an inflammation or swelling of the bronchial tubes (bronchi), the air passages between the mouth and nose and the lungs.More specifically, bronchitis describes a condition where the lining of the bronchial tubes becomes inflamed.Individuals with bronchitis have a reduced ability to breathe air and oxygen into their lungs; also, they cannot clear heavy mucus or phlegm from their airways.This article will cover the causes, symptoms, treatments, and prevention of bronchitis. Symptoms of bronchitisMan coughingBronchitis is characterized by persistent coughing.Signs and symptoms of both acute and chronic bronchitis include:Persistent cough, which may produce mucusWheezingLow fever and chillsChest tighteningSore throatBody achesBreathlessnessHeadachesBlocked nose and sinusesOne of the main symptoms of acute bronchitis is a cough that lasts for several weeks. It can sometimes last for several months if the bronchial tubes take a long time to heal fully.It is common for the symptoms of chronic bronchitis to get worse two or more times every year, and they are often worse during the winter months.However, a cough that refuses to go away could also be a sign of another illness such as asthma or pneumonia., Can be useful for lung, sinus, and other problems which do not respond to other programs., Chronic inflammatory disease of airways - see Asthma programs., Even though you cant see it, the air you breathe can affect your health. Polluted air can cause difficulty breathing, flare-ups of allergy or asthma, and other lung problems. Long-term exposure to air pollution can raise the risk of other diseases, including heart disease and cancer.Some people think of air pollution as something thats found mainly outside. They may picture cars idling or power plants with smoke stacks. But air pollution can also occur insidein homes, offices, or even schools., Morgellons disease (MD) is a skin condition characterized by the presence of multicolored filaments that lie under, are embedded in, or project from skin., Mutates to new strains constantly but these may be helpful. Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Normalize. Also see Leukocytogenesis Stimulate., Pay attention to how you feel when you inhale and exhale normally and when you breathe deeply. Shallow breathing often feels tense and constricted, while deep breathing produces relaxation. Now practice diaphragmatic breathing for several minutes. Put one hand on your abdomen, just below your belly button., Respiratory condition due to viral infection of upper airway., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs., See Liver Support, and Parasites Roundworm and Ascaris programs. Also see Bronchial Asthma programs.Lung, See Pullularia Pullulans, and Sorghum Smut programs., Serious autoimmune disorder with rapid-onset muscle weakness, pain, and sensation changes like numbness and/or tingling. Can be caused by the bacterium Campylobacter jejuni, and with the viruses Cytomegalovirus and Enterovirus., Whooping Cough. |
| 7632 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza 2003/2004 2 | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 7884 | Spooky2 XTRA | Virus General 4 | A virus is a biological agent that reproduces inside the cells of living hosts. When infected by a virus, a host cell is forced to produce thousands of identical copies of the original virus at an extraordinary rate. |
| 7938 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hip Joint Pain | See Arthritis programs. |
| 8082 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza 2003/2004 2 | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 8280 | Spooky2 CAFL | Jade Machine Color Code Light Blue | Healing color system similar to SpectroChrome. Wavelength transposed to frequency. |
| 8368.2 | Spooky2 XTRA | BX Virus 2, Cancer BY Sarcoma Virus 2, Cancer Hodgkins Disease 2, Lymphogranuloma 1 | Also called Hodgkins lymphoma. Cancer of the lymphatic system that is both chronic and progressive., Also see Cancer Hodgkins Disease, and Hodgkins Disease., Cancer virus causing Carcinoma., Virus causing sarcomas. Also use Blood Cleanser. |
| 8478 | Spooky2 CAFL | Streptococcus Viridans | Alpha-haemolytic species causing dental caries and Endocarditis - see appropriate programs, and Alpha Streptococcus. |
| 8820 | Spooky2 ETDF | Chakra Balance (Fabian Maman Set) | Balance the Chakras and You Balance Your Life. Experience the self-healing, self-balancing power of prana. |
| 8856 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 XTRA | CMV 1, Cytomegalovirus CMV 1, Cytomegalovirus CMV 2, Herpes Type 5, Legionella, Legionella Pneumophila | Causes Infectious Mononucleosis, and retinitis. Also see Cytomegalovirus, CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, and HHV5 programs., Cytomegalovirus, also known as Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5., Gram-negative bacteria causing Legionnaires Disease and other problems., Gram-negative bacteria causing Legionnaires Disease. Associated with condensed or treated water that migrate to lung tissue and produce severe respiratory problems, fever, headache, abdominal pain, and may affect kidneys and liver.Lung, Herpes Type 5. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs., Herpes Type 5. Duty Cycle=72. Dr. H Clarks frequencies included. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs. |
| 8910 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza 1993 Secondary | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 9000 | Spooky2 CAFL, Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Arthritis, Arthritis Rheumatism and Osteoporosis, Astrocytoma, Cancer Breast 4, Cholecystitis, Exostoses, Fibrocystic Breast Disease, Fibromyalgia 1, Fibromyalgia 4, Fusobacterium Infections, Graft vs Host Disease, Hamartoma Syndrome Multiple, Horner Syndrome, Hyperbilirubinemia Hereditary, Jaw Diseases, Ludwigs Angina, Peroxisomal Disorders, Raynauds Disease, Schizophrenia, Sialorrhea, Vesico-Ureteral Reflux, Werner Syndrome | Also called Adult Progeria. Rare genetic disorder with premature aging. Also see Progeria program., Backflow of urine from bladder to kidneys, leading to UTIs (see UTI programs) and Pyelonephritis. Also see Cysto Pyelo Nephritis., Bacteria causing periodontal disease, Lemierres Syndrome, and skin ulcers - see appropriate programs. Implicated in colon cancers., Brain cancer. Also see Cancer programs., Chronic widespread pain and heightened response to pressure with pronounced fatigue, sleep disturbance, stiff joints, and other symptoms. Also see Tendomyopathy., Common disorder after tissue graft/transplant where white blood cells in the graft tissue attack the host body., Condition where bilirubin levels are elevated, for reasons that can be attributed to a metabolic disorder., Conditions caused by defects in peroxisome functions which may be due to defects in single enzymes., Excessive production of saliva. Can be caused by radiation, antipsychotics and other drugs, toxic metals, and pesticides., Formation of new bone on surface of existing bone due to excess calcium. Also see Calcium programs., Inflammation of the gallbladder. See Gallbladder programs., Markedly reduced blood flow due to cold or emotional stress, causing discoloration of fingers, toes, and sometimes other areas., May be due to bacteria like Chlamydia Pneumoniae., Multiple non-malignant tumors composed of normal tissue growing in a disorganized mass., Non-cancerous breast lumps often related to menstrual cycle. Try Mastitis, and see Fascia programs., Potentially life-threatening cellulitis of floor of mouth, almost always caused by untreated dental infection., Symptoms appearing when the sympathetic trunk nerve group is damaged, mostly ocular., Use Blood Cleanser., Use Streptococcus Pneumonia, and Mycoplasma General if needed. See Bursitis., Use Tuberculosis programs., Usually this is the result of clenching your jaw or grinding your teeth over a long time, usually at night. Direct damage to the joint can also be caused from certain injuries or arthritis. |
| 9090 | Spooky2 CAFL | Influenza Virus 1993/1994 Secondary | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 9720 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pagets Disease of Bone | Also called Osteitis Deformans, or Osteitis. Condition with deranged bone remodelling, leading to enlarged and/or misshapen bones. |
| 9918 | Spooky2 CAFL UPDATED APR 2020, Spooky2 XTRA | Corona Virus Sars, CoronaCOV19_2, CoronaCOV19_3 | , Somefrequenciesrepeatandtheordermaybeimportant, Upper respiratory and GI tract infections. |
| 10026 | Spooky2 XTRA | BX Virus 2, Cancer Basic 2, Cancer BX Carcinoma Virus 1, Cancer BX Carcinoma Virus 4, Cancer BY Sarcoma Virus 2, Cancer Hodgkins Disease 2, Carcinoma 2, Lymphogranuloma 1 | Also called Hodgkins lymphoma. Cancer of the lymphatic system that is both chronic and progressive., Also see Cancer Carcinoma., Also see Cancer Hodgkins Disease, and Hodgkins Disease., Cancer virus causing Carcinoma., Use Blood Cleanser., Virus causing carcinomas. Also use Blood Cleanser., Virus causing sarcomas. Also use Blood Cleanser. |
| 10530 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Analgesia, Anti-Glomerular Basement Membrane Disease, Asperger Syndrome, Biliary Atresia, Caroli Disease, Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia, Cushing Syndrome, Cystinuria, Diplopia, Endophthalmitis, Exanthema Subitum, Fibromatosis Juvenile Hyaline, Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Disease, Grippe, Hearing Loss Sudden, Hemosiderosis, Hyperostosis, Influenza B, Influenza Bird H5N1, Influenza Human, Parasites Trichomonas vaginalis, Parasites Trypanosoma lewisi, Pseudomyxoma Peritonei, Taeniasis, Toxocariasis, Usher Syndrome, Whipworm Infections | Also called Gelatinous Ascites. Caused by cancerous cells (mucinous adenocarcinoma) that produce abundant mucin., Also called Goodpastures Syndrome. Autoimmune disease of lungs and kidneys.Lung Kidney, Also called Roseola, or Sixth Disease. Febrile condition in very young children with red skin rash and three-day fever., Also see Flu and Grippe programs., Also see Flu and Influenza programs., Autism spectrum disorder., Caused by infection of tapeworm - pork, beef, or Taenia Asiatica. See Parasites Taenia, Taenia, Parasites Tapeworm, Tapeworm, Cysticercosis, and Neurocysticercosis programs., Caused by prolonged exposure to cortisol, either from medications or due to a tumor., Childhood liver disease with blocked, narrow, or missing bile ducts., Dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts., Excessive growth of bone., Eye muscle problem that causes double vision., Form of Iron overload disorder resulting in accumulation of hemosiderin. Also see Hemochromatosis., Genetic disorder causing cystine stones in kidneys, bladder, and ureters., Infection in humans of dog, cat, or fox roundworm., Inflammation of internal coats of eye, usually due to bacteria or fungi., Influenza B virus is the only species in the genus Betainfluenzavirus in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. Influenza B virus is only known to infect humans and seals with influenza., Now called Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia. Non-infectious, with many possible causes., Pain relief., Protozoan found in rats and carried by their fleas which can cause disease in humans. See Trypanosoma Lewisi, and Trypanosomiasis., Rare genetic disorder with gene mutation causing hearing loss and visual impairment., Sexually transmitted infection of protozoan causing vaginitis in women and urethritis in men. See Trichomonas programs., Strains of the influenza virus that primarily infect birds, but can also infect humans., Sudden sensorineural (inner ear) hearing loss (SSHL), commonly known as sudden deafness, is an unexplained, rapid loss of hearing either all at once or over a few days., Type of Roundworm. Also see Parasites Trichuris, Parasites Whipworm, and Trichuris Species Male programs., Very rare disease with pearly or tan nodules or papules on face, scalp, and back. Often mistaken for Neurofibromatosis., Very rare inherited prion disease, usually familial. |
| 10800 | Spooky2 XTRA | Morgellons Chronic Lesions and Fibres, Morgellons Internal | Apply=.02% Feathering. |
| 10890 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Adiadochokinesis, Ascariasis, Broncho Pulmonary Dysplasia, Cancer Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, Cancer Gestational Tumor, Cancer Oropharyngeal, Cerebellar Ataxia, Chorioretinitis, Costello Syndrome, Cryptorchidism, Diaphragmatic Hernia, Encopresis, Esophageal Atresia, Gait Disorders Neurological, Hamartoma Syndrome Multiple, Hernia Diaphragmatic, Paraphilias, Parasites Macracanthorhynchus, Scabies, Synovitis, Urogenital Surgical Procedures, Vestibular Neuronitis | Abnormal cell changes, usually pre-cancerous., Absence of one or both testicles from scrotum - usually undescended., Also called FCS Syndrome. Rare genetic disorder that affects many part of the body., Also see Parasites Scabies, and Sarcoptes Scabiei Itch. Also use Psorinum., Birth defect where the esophagus fails to properly connect to the stomach., Caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris Lumbricoides., Defect in diaphragm that allows abdominal organs to move into the chest., Deviations from normal walking patterns caused by neurological disorders., Diaphragm defect that allows abdominal organs to move into chest cavity., Diseases of the inner ear. See Labyrinthitis, and Labyrinth Diseases., Inability to make certain movements in quick succession., Inflammation of eyes vascular coat. Often due to Toxoplasmosis and Cytomegalovirus (CMV) - see these programs., Inflammation of synovial membrane lining joints which possess cavities., Intense sexual arousal by atypical objects, situations, or individuals., Lack of coordination originating in the cerebellum., Middle throat - base of tongue, tonsils, soft palate, and pharynx. May be due to Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)., Multiple non-malignant tumors composed of normal tissue growing in a disorganized mass., Parasitic worm found in GI tract of pigs and boars., Pregnancy-related tumor., Pregnancy-related tumor. Other use: Diffuse Cerebral Sclerosis of Schilder., Urogenital Surgical Procedures. Definition: Surgery performed on the urinary tract or its organs and on the male or female genitalia., Voluntary or involuntary fecal soiling, usually in children. |
| 11250 | Spooky2 XTRA | Bacterial Capsules 1, Cancer Basic 5, Diplococcus Pneumoniae 2, Streptococcus Pyogenes 1, Streptococcus Pyogenes 3, Streptococcus Pyogenes 7 | Also called Group A beta-haemolytic Strep (GAS). Causes Sore Throat, skin inflammation, Scarlet Fever, Pharyngitis, Impetigo, Erysipelas, Frozen Shoulder, Cellulitis, Septicemia, Toxic Shock Syndrome, and acute Glomerulonephritis, and Beta Streptococcus. Use General Antiseptic., Also called Streptococcus Pneumoniae., Outer envelope of bacterial cell wall., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 11430 | Spooky2 XTRA | BY Virus 3, Cancer Basic 6 | Cancer virus causing Sarcoma., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 11484 | Spooky2 XTRA | Mange | Contagious dermatitis found in many mammals caused by Demodex mites living in the hair follicles. See Follicular Mange. |
| 11656.62 | Spooky2 XTRA | Salmonella Paratyphi 2 | Can cause paratyphoid fever (similar to typhoid). See Typhoid Fever. |
| 11700 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dystonia | Movement disorder with muscle contractions causing twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. |
| 12223.44 | Spooky2 XTRA | Clostridium Acetobutylicum 1 | Used in genetic engineering. |
| 12232.8 | Spooky2 XTRA | Bacillus Anthracis Spores | Weaponised bacteria that causes Anthrax. |
| 12330 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia, Arteriovenous Malformations, Astigmatism, Bannayan-Zonana Syndrome, Burkholderia Infections, Cancer Lymphoma Non-Hodgkins, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, Chalazion, Cyclosporiasis, Cystinosis, Encephalitis Herpes Simplex, Eosinophilia, Fatigue Syndrome Chronic, Helminthiasis, Hemorrhoids, Horner Syndrome, Hyperlipidemia Familial Combined, Hypertension Pulmonary, Lactose Intolerance, Liver Diseases, Metabolic Syndrome X, Osteoporosis, Papillomavirus Infections, Parasites Flatworms, Parasites Gyrodactylus, Parasites Pancreatic Flukes, Periodontal Diseases, Photophobia, Pneumothorax, Pseudo-Gaucher Disease, Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White Syndrome | 90% of all Lymphomas are non-Hodgkins., Abnormal accumulation of air or gas in pleural spaces. Also see Pleural Diseases., Abnormal artery-vein connections, bypassing capillaries, normally in the CNS., Also called Piles. Also run circulation and circulatory programs alternatively on consecutive days for 10 days. Place electrodes on thighs., Also see Parasites Flukes Pancreatic, Pancreas Fluke, and Eurytrema Pancreaticum., Associated with obesity, raised BP, high fasting plasma glucose, high serum triglycerides, and low HDL, with risk of cardiovascular disease or diabetes. Can be caused by the bacteria Chlamydia pneumoniae and Helicobacter pylori, as well as the viruses Cytomegalovirus and Herpes simplex virus 1., Bacteria found mostly in equine animals that can cause serious diseases in humans. Likely weaponised., Blurred vision due to corneal or lens defect., CFS. Also see Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, and Chronic Fatigue programs., Chronic liver disease in the clinical context is a disease process of the liver that involves a process of progressive destruction and regeneration of the liver parenchyma leading to fibrosis and cirrhosis., Condition where count of eosinophil white blood cells is abnormally high, usually indicating parasites or allergic reaction., Cyst in eyelid due to blocked meibomian gland., Discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure., Disorder of hearts electrical system, causing episodes of Tachycardia, with palpitations, dizziness, shortness of breath, or faints. See Heart Fast Palpitations, Dizziness, Giddiness, Dyspnea, and Fainting programs., Domed papules/nodules on head or neck.Skin, Flukes., Genetic disease with overgrowth of lipomas, hemangiomas, and head enlargement., Genetic disorder in which glucocerebroside accumulates in cells and certain organs, with bruising, fatigue, anemia, low blood platelet count, and enlargement of liver and spleen., Genetic disorder with abnormally high levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood., Genetic disorder with distinct craniofacial features, heart defects, intellectual impairment, seizures, and growth restriction., Genetic lysosomal storage disorder with abnormal amounts of cystine., GI tract infection due to parasitic protist Cyclospora., High blood pressure in lung vasculature, causing dizziness, shortness of breath, faints, and swollen leg., Infection of worms like tapeworm, flukes, or roundworm. See appropriate program if parasite has been identified., Inflammation of the tissue of brain and spinal cord due to Herpes Simplex., Invented disease. Actually caused by the body stealing calcium from bones to neutralise and balance an excessively acidic system., Lactose intolerance is a condition in which people have symptoms due to the decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis., See Paradontosis, Bone Regeneration, and Dental programs., Skin parasite found in fish., Symptoms appearing when the sympathetic trunk nerve group is damaged, mostly ocular., Virus causing warts, or lesions leading to cancers of reproductive system, genitals, anus, and oropharynx. See appropriate Cancer, and Human Papilloma Virus HPV programs. |
| 12340.62 | Spooky2 XTRA | Branhamella Neisseria Catarrhalis 1 | Also called Moraxella and Neisseria Catarrhalis. Causes respiratory, ear, eye, CNS, and joint infections. |
| 12453.12 | Spooky2 XTRA | B Coli Rod | Bacillus Coli, now called Escherichia Coli, or E Coli. |
| 12534.12 | Spooky2 XTRA | BX Virus 1, Cancer BX Carcinoma Virus 4, Cancer BY Sarcoma Virus 1 | Cancer virus causing Carcinoma., Virus causing carcinomas. Also use Blood Cleanser., Virus causing sarcomas. Also use Blood Cleanser. |
| 12565.62 | Spooky2 XTRA | Leishmania Tropica | Type of intracellular protozoan human parasite found worldwide and transmitted by sandflies. See Parasites Leishmania Tropica, Leishmaniasis, and other Leishmania programs. |
| 12690 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Argentaffinoma, Cancer Carcinoid Tumor Gastrointestinal, Cancer Esophageal, Cancer Metastasis (Organ) Comprehensive, Diphtheria, Eye Hemorrhage, Fibrosis, Gastroschisis, Histiocytosis, Lordosis, Meckel Diverticulum, Scrub Typhus, Vasospasm Intracranial | A subconjunctival hemorrhage occurs when a tiny blood vessel breaks just underneath the clear surface of your eye . The conjunctiva cant absorb blood very quickly, so the blood gets trapped., Also called Carcinoid Syndrome - refers to symptoms secondary to carcinoid tumors., Bacteria causing sore throat, fever, rapid heartbeat, nausea, chills, and headache. Toxins may damage heart and nerves. See Corynebacterium Diphtheriae., Congenital bulge in small intestine causing severe pain, abdominal bloating, and rectal bleeding., Congenital defect with opening in abdominal wall through which organs may protrude., Disorder with excessive numbers of histiocytes (tissue macrophages - immune system components)., ETDFL Breast, lung, prostate, bowel/colon/rectal, Liver, Endometrial, Excessive inward curvature of lower back - the opposite to kyphosis., Form of typhus, usually caused by chigger bite., Formation of excess fibrous connective tissue in organ or other tissue., Slow-growing and potentially malignant., Stenosis of artery in brain which may cause tissue damage. May indicate subarachnoid hemorrhage - see Cerebral Hemorrhage, and other Hemorrhage programs., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 12785.94 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ascaris Larvae | Parasitic roundworm Ascaris Lumbricoides. |
| 13353.12 | Spooky2 XTRA | Chilomastix Cysts (Rat), Fasciola Hepatica 1, Fasciola Hepatica 2, Fasciolopsis Rediae | Also see Liver Flukes, Parasites Flukes Liver, Parasites Flukes Sheep Liver, Parasites Liver Flukes, and Parasites Sheep Liver Flukes., Life cycle stage of large common human intestinal fluke, also found in pigs. See Fluke Intestinal, Parasites Flukes Intestinal, and Parasites Intestinal Flukes., Protozoan which lives in the GI tract. |
| 13500 | Spooky2 XTRA | Endolimax Nana Trophozoites Cysts 2, Fasciolopsis Rediae, Mycobacterium Tuberculosis 1 | Genus of amoeba causing diarrhea, whose presence indicates ingestion of fecal matter., Life cycle stage of large common human intestinal fluke, also found in pigs. See Fluke Intestinal, Parasites Flukes Intestinal, and Parasites Intestinal Flukes., Mycobacterium which causes tuberculosis (TB). Also see Tuberculosis programs, and Tuberculinum. |
| 14514.12 | Spooky2 XTRA | Allergy Pollen | Pollen is one of the most common triggers of seasonal allergies. Many people know pollen allergy as hay fever. Experts usually refer to pollen allergy as seasonal allergic rhinitis.Each spring, summer and fall, plants release tiny pollen grains to fertilize other plants of the same species. Most of the pollens that cause allergic reactions come from trees, weeds and grasses. These plants make small, light and dry pollen grains that travel by the wind.Grasses are the most common cause of allergy. Ragweed is a main cause of weed allergies. Other common sources of weed pollen include sagebrush, pigweed, lambs quarters and tumbleweed. Certain species of trees, including birch, cedar and oak, also produce highly allergenic pollen.Plants fertilized by insects, like roses and some flowering trees, like cherry and pear trees, usually do not cause allergic rhinitis. |
| 15030 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Stomach, Pituitary Diseases, Temporomandibular Joint Dysfunction Syndrome | Disorders of pituitary gland including Hypothyroidism, Hyperpituitarism, Diabetes Insipidus, tumors, and adenomas., Pain and dysfunction of jaw muscles and joint, with restricted movement and noises., See Heliobacter Pylori. Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 15035.94 | Spooky2 XTRA | Hymenolepis Diminuta | Rat tapeworm which can be passed to man by accidental ingestion of insects. |
| 15750 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Lip and Oral Cavity, Cancer Lung Non-Small Cell, Cancer Lung Small Cell, Cancer Mouth, Cancer Oral, Mold Lycogala, Reptile Diseases, Tetrahydrobiopterin Deficiency, Tietzes Syndrome, Trichomonas Infections | Cancer that develops in any part of the mouth., Here are some of the most commondiseasesamong reptiles and amphibians. Herpesvirus. Poxvirus. Adenovirus. Ranavirus. Reovirus. Flavivirus. With Reptiles and Amphibians, Hygiene Is a Must., Includes Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Large Cell Carcinoma, and Adenocarcinoma., More metastatically aggressive than other lung cancers. Also called Oat Cell Carcinoma., Painful inflammation and swelling of costal (rib) cartilages. Also see Intercostal Neuralgia, and Neuralgia Intercostal programs., Parasitic protozoan, usually sexually transmitted, causing vaginal irritation with discharge and itching., Rare metabolic disorder that increases blood levels of phenylalanine, causing problems ranging from low muscle tone to intellectual disability., Slime mold. Implicated in Morgellons., Use Blood Cleanser., Use Blood Cleanser. Also use for cancers of paranasal sinus, nasal cavity, salivary gland, and lip. |
| 15930 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Emphysema Pulmonary, Pulmonary Emphysema | Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also see Emphysema, Chronic Airflow Obstruction, COAD, COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Chemtrails, and Parasites programs. |
| 16020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Respiratory Distress Syndrome Newborn | Syndrome in premature newborns due to structural immaturity in lungs, or to neonatal infection. Can also be genetic. |
| 16200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Behcet Syndrome | Rare immune-related systemic vasculitis with mucous membrane ulcers and eye problems. |
| 17395.02 | Spooky2 XTRA | Tin 117sn | Metal element. |
| 18000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Fournier Gangrene, Kartagener Syndrome, Mold Griseofulvin | Mycotoxin derived from Penicillium mold. Used as antifungal drug which can cause nasty side effects., Rare genetic disorder where respiratory cilia action is defective, causing poor mucus clearance and consequent lung infections., Type of necrotizing fasciitis, usually perineal. See Fasciitis Necrotizing, and Gangrene. Also use Streptococcus Pyogenes, Staphylococcus Aureus, Clostridium Perfringens, and Bacteroides Fragilis. |
| 18810 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypocupremia Congenital | Copper deficiency as a result of heredity. |
| 19168.02 | Spooky2 XTRA | Bacillus Subtilis Niger 4, Beta Streptococcus 2, Entamoeba Histolytica 3, Food Poisoning 1, Food Poisoning 2, Salmonella Typhimurium 2 | Can cause fever, GI tract/lung problems, liver and spleen enlargement., Destroys red blood cells., Food poisoning is a major cause of gastroenteritis, resulting in a well-known set of unpleasant symptoms., Food poisoning, also called foodborne illness, is illness caused by eating contaminated food. Infectious organisms including bacteria, viruses and parasites or their toxins are the most common causes of food poisoning.Infectious organisms or their toxins can contaminate food at any point of processing or production. Contamination can also occur at home if food is incorrectly handled or cooked.Food poisoning symptoms, which can start within hours of eating contaminated food, often include nausea, vomiting or diarrhea. Most often, food poisoning is mild and resolves without treatment. But some people need to go to the hospital.SymptomsFood poisoning symptoms vary with the source of contamination. Most types of food poisoning cause one or more of the following signs and symptoms:NauseaVomitingWatery or bloody diarrheaAbdominal pain and crampsFeverSigns and symptoms may start within hours after eating the contaminated food, or they may begin days or even weeks later. Sickness caused by food poisoning generally lasts from a few hours to several days., GI tract parasitic amoeba causing tissue destruction, particularly liver damage, and amoebic dysentery - use Liver Support programs., Metabolically-changed form of B Subtilis due to presence of Aspergillus Niger mold. |
| 19800 | Spooky2 XTRA | Corynebacterium Xerosis 1 | Can cause Endocarditis, skin infections, and other illnesses. |
| 19890 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Pulmonary Edema | Fluid accumulation in air spaces and parenchyma of lungs. |
| 20250 | Spooky2 XTRA | Proteus Mirabilis 1 | Bacteria which can produce high levels of urease, hydrolyzing urea to ammonia (common in Lyme), thus making urine more alkaline, which can cause Kidney Stones - see programs for this and Kidney Calculi. Also see Ammonia Remove, and Urea Cycle Disorders. |
| 21060 | Spooky2 XTRA | Pseudomyxoma Peritonei 1 | SRH4. Also called Gelatinous Ascites. |
| 21259.08 | Spooky2 XTRA | Parasites Clonorchis Sinensis 1 | Liver fluke. Also for Fasciola Hepatica Cercariae. |
| 21409.38 | Spooky2 XTRA | Gardnerella 2, Gardnerella Vaginalis 2 | Also called Gardnerella Vaginalis. Bacteria that can infect and inflame the vaginal mucosa., Also called Gardnerella. Bacteria that can infect and inflame the vaginal mucosa. |
| 21888 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Spirochete Inhabited Microbes, Lyme Spirochete Inhabited Microbes | Also known as Borreliosis., Targets Borrelia-infected organisms. |
| 22500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Adenoma, Adenoma Basal Cell, Adenoma Microcystic, Adenoma Monomorphic, Agammaglobulinemia, Alagille Syndrome, Antiphospholipid Syndrome, Awakening Epilepsy, Blepharoptosis, Burkholderia Infections, Cancer Leukemia, Cancer Nasopharyngeal, Cancer Ovarian, Cerebrohepatorenal Syndrome, Chondromalacia Patellae, Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, Demyelinating Diseases, Ebola 1, Endodontics, Epilepsy, Evans Syndrome, Factor V Deficiency, Fatigue Syndrome Chronic, Fusobacterium Infections, Gallbladder Diseases, Gingivitis, Halitosis, Headache, Hemorrhagic Fevers Viral, Hepatolenticular Degeneration, Herpes Simplex, Hodgkin Disease, Hyperventilation, Irritable Bowel Syndrome, Lacrimal Apparatus Diseases, Lymphogranuloma Inguinale, Lymphogranuloma Malignant, Mandibulofacial Dysostosis, Mediastinal Cyst, Monkeypox, Mucopolysaccharidoses, Mumps, Nail Disease, Osteitis Deformans, Paralysis, Paraphilias, Parasites General, Parasites Pancreatic Flukes, Pinworms, Tardive Dyskinesia, Thrombasthenia, Tinea, Torticollis, Trigeminal Neuralgia, Virus Comprehensive, Vitamin B12 Deficiency, Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome, Zellweger Syndrome, Zenker Diverticulum | Abnormality of blood platelets, causing coagulation problems., Also called Hemorrhagic Fever. Use with 3.1MHz carrier (not needed in Remote Mode)., Also called Hodgkins disease and Hodgkins lymphoma., Also called Pagets Disease of Bone. Condition with deranged bone remodelling, leading to enlarged and/or misshapen bones., Also called Pancreatic Serous Cystadenoma - benign pancreatic tumor., Also called Ulnar Nerve Entrapment., Also called Warthins Tumor - benign cystic tumor of salivary glands., Also called Wilsons Disease. Genetic disorder with accumulation of copper in tissues., Also see Cholecystitis programs., Also see Parasites Flukes Pancreatic, Pancreas Fluke, and Eurytrema Pancreaticum., Autoimmune disease where antibodies attack red blood cells and platelets., Bacteria causing periodontal disease, Lemierres Syndrome, and skin ulcers - see appropriate programs. Implicated in colon cancers., Bacteria found mostly in equine animals that can cause serious diseases in humans. Likely weaponised., Bad breath. See Streptococcus Pneumonia, Streptococcus Aureus, Pharyngitis, Dental, Parasites General, and General Antiseptic programs., Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser. Also use for plasma cell neoplasms., Benign epithelial tumor with glandular associations., CAFL Anecdotal. Use also for Vitamin B Deficiency., Cancer of upper throat, nasal and auditory passages. See Epstein Barr Virus. Use Blood Cleanser. Other use: Gilbert Disease., CFS. Also see Chronic Fatigue Syndrome, and Chronic Fatigue programs., Coagulation system protein deficiency leading to predisposition for hemorrhage., Common GI parasitic worm, with Anal Itching. Also see Enterobius Vermicularis, Enterobiasis, Parasites Enterobiasis, and Threadworm programs., Conditions of eye structures for producing and draining tears - see appropriate Eye programs., Congenital disorder with multiple organ and system problems. Also called Zellweger Syndrome.Kidney, Congenital malformations of skull, jaw, face, and neck., Destruction of nerve neurons myelin sheath. Causes may be genetic, infectious, autoimmune, pesticides, insecticides, or herbicides., Disorder with involuntary repetitive movements. Caused by antipsychotic drug use for longer than three months in adults, and GI drugs in children and infants., Diverticulum (or pouch) in pharynx just above esophageal sphincter, causing swallowing difficulties, cough, and halitosis., Dystonic neck muscle condition with abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position., Epilepsy is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.Anyone can develop epilepsy. Epilepsy affects both males and females of all races, ethnic backgrounds and ages.Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people with epilepsy simply stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure, while others repeatedly twitch their arms or legs. Having a single seizure doesnt mean you have epilepsy. At least two unprovoked seizures are generally required for an epilepsy diagnosis.Treatment with medications or sometimes surgery can control seizures for the majority of people with epilepsy. Some people require lifelong treatment to control seizures, but for others, the seizures eventually go away. Some children with epilepsy may outgrow the condition with age., Epilepsy with grand mal seizures on awakening., ETDFL Includes H1N1, H5N1, Ebola, Rhinoviruses, Rotaviruses, Influenza A-B, Excessive and inappropriate removal of carbon dioxide from the body via the lungs., Eyelid droop. Also called Ptosis., Genetic disorder affecting major organs., Genetic disorder with distinct craniofacial features, heart defects, intellectual impairment, seizures, and growth restriction., Headache is the symptom of pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It occurs in migraines (sharp, or throbbing pains), tension-type headaches, and cluster headaches. Frequent headaches can affect relationships and employment.There is also an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions whether serious or not. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society. Causes of headaches may include dehydration, fatigue, sleep deprivation, stress, the effects of medications, the effects of recreational drugs, viral infections, loud noises, common colds, head injury, rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage, and dental or sinus issues.Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication. A headache is one of the most commonly experienced of all physical discomforts.About half of adults have a headache in a given year.Tension headaches are the most common, affecting about 1.6 billion people (21.8% of the population) followed by migraine headaches which affect about 848 million (11.7%)., Inflammation of gums caused by plaque leading to periodontitis. See Dental Infection, Dental Infection Roots and Gums, Pyorrhea, and Stomatitis., Inflammation of the back of the kneecap and softening of cartilage., Intense sexual arousal by atypical objects, situations, or individuals., Intensely painful neuropathic chronic disorder affecting the faces trigeminal nerve. Also see Neuralgia Trigeminal program., Loss of function in one or more muscles which may be accompanied by sensory loss., Low-grade malignant salivary gland neoplasm. See Cancer programs.Cancer, Lymphatic system disease caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis., Metabolic disorders affecting ability to build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin, and connective tissue., micropredation.Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Now called Hodgkin Disease, and see Cancer Hodgkin Disease., Primarily orofacial. Use General Antiseptic program., Primary immune deficiency disease. Synonymous with Hypogammaglobulinemia., Promotes thrombosis and pregnancy-related complications., Rare congenital disorder with reduction or absence of functional peroxisomes in cells. Also see Peroxisomal Disorders, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Leukodystrophy, Refsum Disease, and Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Ringworm. Also see Epidermophyton Floccosum, Microsporum Audouini, Nagel Trichophyton, and Fungus General programs., See Colitis and Parasites General programs., Starts in an ovary, producing abnormal invasive cells which spread., Thisconditionmay follow certaindiseasessuch as syphilis, or can result from fever, trauma, systemic upsets or adverse reaction to drugs. Onychorrhexis also known as brittlenails, is brittleness with breakage offingernailsor toenails., Treatment of dental pulp, especially by root canals., Tumors found in the cavity containing heart, trachea, and esophagus - include neurogenic, thymoma, lymphoma, pheochromocytoma, and germ cell tumors including teratoma, thyroid tissue, and parathyroid lesions., Viral disease with fever, muscle pain,and headache, leading to painful swelling of parotid gland(s). Also see Mumps, Mumps Antigen, and Coxsackie programs., Viruses causing this include Ebola, Marburg, Lassa, Rift Valley Fever, and Hantavirus, among others., Zoonotic viral disease transmitted via animal bite or blood contact. Symptoms similar to Smallpox, to which it is related. |
| 22680 | Spooky2 ETDF | Neutropenia | Abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (type of white blood cell). |
| 23958 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 24354 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 24750 | Spooky2 XTRA | Myiasis | Infestation of fly larvae (maggots). Also called Fly Strike. Common in Morgellons. |
| 25290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptorchidism | Absence of one or both testicles from scrotum - usually undescended. |
| 26010 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mongolism | Also see Down Syndrome programs. |
| 27000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Ostomy, Proctocolitis, Russell Silver Syndrome, Vertigo | Any natural or surgically-created opening in the body or organs, such as a colostomy, or tracheostomy., Inflammation of rectum and colon. Causes include Chlamydia Trachomatis, Lymphogranuloma Venereum, Neisseria Gonorrhoeae, HSV, and Campylobacter spp., Type of dwarfism., Use Otitis Medinum, and Streptococcus Pneumoniae programs. See General Antiseptic program. |
| 29783.0754 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer Cell Repair Scalar | Experimental. Use sine. Scalar sub-harmonics of 380nm light per Dr. Fritz-Albert Popps biophoton research. |
| 30420 | Spooky2 ETDF | Airsickness | Airsickness is a type of motion sickness, caused by conflicting signals your senses tell your brain. Your eyes adjust to the lack of movement around you and send a message to your brain that you are sitting still. Your inner ear, however, senses the actual movement. |
| 30780 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mite Infestations | Mite Infestation, also known as mite infestations, is related to scabies and demodicidosis. An important gene associated with Mite Infestation is CFTR (CF Transmembrane Conductance Regulator). |
| 31230 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Wilms Tumor, Knee Injury | Also called nephroblastoma. Kidney cancer occurring mostly in children. Also see Wilms Tumor, and Rhabdoid Tumor., With a sudden meniscus tear, a pop may be heard or felt in the knee. After the initial injury, pain, swelling, and tightness may increase over the next few days. The most common knee injury is the torn meniscus. Although a torn meniscus can happen to anyone, this injury occurs most often to athletes. |
| 31320 | Spooky2 CAFL | Blepharisma | Ciliate water-dwelling protist. |
| 31500 | Spooky2 XTRA | Myiasis | Infestation of fly larvae (maggots). Also called Fly Strike. Common in Morgellons. |
| 32130 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lactose Intolerance | Lactose intolerance is a condition in which people have symptoms due to the decreased ability to digest lactose, a sugar found in dairy products. |
| 32580 | Spooky2 ETDF | Langer-Giedion Syndrome | Rare genetic disorder caused by deletion of chromosomal material, associated with mild/moderate learning difficulties. |
| 32670 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 32850 | Spooky2 ETDF | Corticobasal CBGD | Rare progressive neurodegenerative condition with marked movement disorders and cognitive dysfunction |
| 33390 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypertension | See Blood Pressure High. |
| 35190 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Carotid Artery Narrowing, Carotid Stenosis, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency, Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome | Also see Carotid Artery Narrowing., Also see Carotid Stenosis., Genetic disorder with disturbed development of functional T cells and B cells, caused by numerous genetic mutations., Inborn error of cholesterol synthesis causing multiple physical malformations. |
| 35370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Funnel Chest | Also called Pectus Excavatum. Congenital deformity of wall of chest, causing caved-in appearance. |
| 35712 | Spooky2 XTRA | Mycoplasma Salivarium 1 | Implicated in eye/ear disorders, oral infections, septic arthritis, and periodontal disease. Run each frequency for 18 min after building up. |
| 35910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Freibergs Disease, Parasites Follicular Mange | Due to Demodex mites. See Follicular Mange., Metatarsal bone destruction caused by loss of blood supply. |
| 36000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Vitamin C Deficiency | CAFL Anecdotal. |
| 36900 | Spooky2 XTRA | Morgellons Chronic Lesions and Fibres | Apply=.02% Feathering. |
| 37530 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Pulmonary Edema | Fluid accumulation in air spaces and parenchyma of lungs. |
| 37998 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ebola 2 | Also called Hemorrhagic Shock. Use with 3.1MHz carrier (not needed in Remote Mode). |
| 38304 | Spooky2 XTRA | Borrelia Burgdorferi Lyme | Spirochete involved in Lyme disease. |
| 39150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Sexual Libido Boost | Sexual desire is complex, with both psychological and physical components. Even when a person has a physical condition that affects libido, such as diabetes, improving the emotional and psychological response to sex can improve libido and sexual functioning. |
| 41580 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hemoptysis | Coughing up blood. |
| 42570 | Spooky2 ETDF | Anankastic Personality Disorder | Also called Obsessive Compulsive Personality Disorder (OCPD). |
| 42750 | Spooky2 ETDF | Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections | Many species of bacteria with outer membranes which can cause toxic shock, and defeat antibiotics. |
| 43200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Typhoid Fever | Typhus infection-related symptoms causing high fever, headache, and rash. Use Salmonella Typhi, and Rickettsia programs. See Q Fever program. |
| 43380 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ascites 2 | SRH4. Fluid in peritoneal cavity. Converted from F165 format - may need Duty Cycle of 55%. |
| 45000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Angiolymphoid Hyperplasia with Eosinophilia, Arthritis Rheumatoid, Astrocytoma, Barth Syndrome, Cooleys Anemia, Factor XI Deficiency, Factor XII Deficiency, Fasciculation, Ludwigs Angina, Myoclonus, Nail-Patella Syndrome, Parasites Giardia, Parasites Urocleidus, Romberg Disease, Stiff-Person Syndrome, Tietzes Syndrome, Trachoma, Typhus Epidemic Louse-Borne, Urethral Stricture, Uveitis, Vitamin B12 Deficiency, White Dot Syndrome | Also called Facial Hemiatrophy. Neurocutaneous disorder with tissue degeneration beneath skin, usually on one side of the face., Also called Haemophilia C. Relatively common but mild form of Haemophilia.Blood, Also called Iritis. Inflammation of eyes uvea, lying between retina and sclera/cornea., Also called Thalassemia. Genetic disorder with abnormal formation of hemoglobin. Also see Chromosome 16 Abnormalities., Being deficient in vitamin B-12 causes physical and psychological symptoms, including nerve problems, fatigue, and difficulty thinking., Brain cancer. Also see Cancer programs., Brief, involuntary twitching of muscle or group of muscles., Coagulation system deficiency of enzyme necessary for plasma clotting.Blood, Domed papules/nodules on head or neck.Skin, Fluke found in fish. Also see Urocleidus., Genetic disorder affecting multiple body systems, found only in males., Genetic disorder with poorly developed nails and kneecaps. Can also affect other areas of body, such as elbows, chest, and hips., Inflammatory eye disorders with white dots on the interior surface of eye causing blurred vision and visual field loss., Involuntary muscle twitches., Muscles and tendons. May be due to bacteria like Chlamydia Pneumoniae. Use General Antiseptic and Parasites General if no response. See Bursitis., Narrowing of urethra due to injury, medical procedures, infection, and some non-infectious types of Urethritis., Painful and potentially blinding infectious eye disease caused by Chlamydia Trachomatis., Painful inflammation and swelling of costal (rib) cartilages. Also see Intercostal Neuralgia, and Neuralgia Intercostal programs., Parry-Romberg syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by slowly progressive deterioration (atrophy) of the skin and soft tissues of half of the face (hemifacial atrophy), usually the left side. It is more common in females than in males., Potentially life-threatening cellulitis of floor of mouth, almost always caused by untreated dental infection., Protozoan that colonizes GI tract. See Giardia, Giardia Lamblia, Lamblia, and Giardia Intestinalis programs., Rare neurologic disorder with progressive rigidity and stiffness, primarily affecting truncal muscles and superimposed by spasms, resulting in postural deformities. Chronic pain, impaired mobility, and lumbar hyperlordosis are common., Use Rickettsia, and Lice Infestations programs. |
| 45738 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 46980 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida LoPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida HiPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 47250 | Spooky2 ETDF | Muscular Dystrophies | Inherited muscle disorders that weaken the body and hinder normal movement. Also see Muscular Dystrophy programs. |
| 47430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Flukes General | Trematoda is a clade within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It includes two groups of parasitic flatworms, known as flukes. |
| 48150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Corneal Dystrophy Hereditary | Abnormal accumulation of extraneous material in corneas.Eyes |
| 49500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Thromboangiitis Obliterans | Recurring progressive inflammation and clot formation in small and medium blood vessels of hands and feet, usually in smokers. |
| 51156 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida HiPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida LoPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 51300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Endodontics | Treatment of dental pulp, especially by root canals. |
| 52200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Puerperal Infection | Bacterial infection of female reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage, commonly by Streptococcus Pyogenes and anaerobic Streptococcus spp, Staphylococcus spp, E Coli, and Clostridium spp. |
| 55170 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Caroli Disease | Dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts. |
| 55440 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Schistosoma haematobium | Blood flukes. Associated with bladder problems. Also see Schistosoma Haematobium, and Blood Fluke programs. |
| 55710 | Spooky2 ETDF | Proteus Syndrome | Rare congenital disorder causing skin overgrowth and atypical bone development, often accompanied by tumors over half the body. |
| 56376 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 56520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cooleys Anemia | Also called Thalassemia. Genetic disorder with abnormal formation of hemoglobin. Also see Chromosome 16 Abnormalities. |
| 57420 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida HiPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida LoPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 58806 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 58914 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida HiPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida LoPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 63000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Platelet Storage Pool Deficiency | Blood coagulation disorder. |
| 65160 | Spooky2 ETDF | Xeroderma Pigmentosum | Rare genetic disorder of DNA repair in which ability to repair damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light is deficient. |
| 65430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Pancreatic Flukes | Also see Parasites Flukes Pancreatic, Pancreas Fluke, and Eurytrema Pancreaticum. |
| 67500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Adhesions Pelvic, Agnosia, Alzheimer Disease, Amblyopia, Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, Aneurysm, Anisakiasis, Ankyloglossia, Arthrogryposis, Beriberi, Bipolar Disorder, Burning Mouth Syndrome, Cancer Trophoblastic, Cancer Trophoblastic Neoplasms, Croup, Cryptogenic Infantile Spasms, Dysentery, Emphysema Pulmonary, Gonadal Disorders, Heart Disease & COPD Comprehensive, Heart Diseases, Hydrocephalus, Hydrocephalus Normal Pressure, Hypogonadism, Lysosomal Storage Diseases, Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney, Myocarditis, Osteopetrosis, Parasites Haemonchus contortus, Parasites Leishmania braziliensis, Parasites Leishmania donovani, Parasites Leishmania mexicana, Parasites Leishmania tropica, Parasites Trichuris, Parasites Trypanosoma brucei, Parasites Turbatrix, Prosopagnosia, Pulmonary Emphysema, Rhinoscleroma, Sciatica, Seizures, Smith-Magenis Syndrome, Spasm, Tarlov Cysts, Tetanus, Tularemia, Urologic Diseases, Von Willebrand Disease, Werner Syndrome | Abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the brain, causing increased intracranial pressure., Acute diarrhea with blood and mucus. Also see Entamoeba Histolytica, Shigella, and appropriate Salmonella and Campylobacter programs., Also called Adult Progeria. Rare genetic disorder with premature aging. Also see Progeria program., Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also called Tongue-Tie. Congenital, due to a short frenulum., Also called vinegar eels. Non-parasitic nematodes feeding on mother of vinegar, filtered by suppliers., Also see Cancer Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, and Cancer Trophoblastic Neoplasms., Also see Cancer Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, and Cancer Trophoblastic., Also see Emphysema, Chronic Airflow Obstruction, COAD, COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Chemtrails, and Parasites programs., Blood coagulation disorder, usually hereditary., Brain malfunction caused by decreased absorption of cerebrospinal fluid., Bulge in weak blood vessel wall., Child epilepsy syndrome with unknown cause., Chronic granulomatous bacterial disease of nose that can sometimes infect the upper respiratory tract, usually due to subspecies of Klebsiella Pneumoniae., Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and heart failure are different conditions. ... With activity, blood flow must increase, and your heart must pump harder and faster. If your heart cant keep up, blood Nbacks upÓ into your lungs. This fluid congestion causes shortness of breath., Congenital joint contractures in two or more body areas., Congenital or acquired dysfunction of the urinary system. Also see Urination Disorders., Developmental disorder affecting body and brain, including intellectual disability, broad face, difficulty sleeping, and various behavioral problems., Diminished function of ovaries/testes with consequent lower levels of sex hormones., Diseases of ovaries or testes - also see Hydrocele, Orchitis, Gonads, Testicular Diseases, Testicle Fluid, or appropriate organ programs., Disorder with pronounced transitions between depression and elevation., Due to eating raw/undercooked fish infected with parasitic nematode., Genetic condition caused by malformed kidneys consisting of variously-sized cysts., Impairment of ability to recognize faces, including ones own., Impairs male sexual development., Inability to process information from one sensory system, usually after brain injury or illness., Infection and inflammation of heart muscle, usually due to viruses such as Parvovirus B19, or to bacteria like Borrelial Burgdorferi, or parasites like Trypanosoma Cruzi., Infectious disease of central nervous system caused by Clostridium Tetani., Internal cell enzyme disorders disrupting metabolism. Also see Leukodystrophy Metachromatic., Internal scar tissue following injury or surgery., Lazy eye., Meningeal cysts in spinal canal containing nerve fibres., Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable., Oral burning sensation with no medically identifiable cause., Pain radiating down leg from lower back, usually due to spinal disc herniation. Also see Disc Herniated, Disc Slipped, Disc Swelling, Hernia Disc, Herniated Disc Reduce Swelling, Intervertebral Disc Displacement, Slipped Discs, Lumbar Compression,and Polyradiculopathy., Parasitic worm., Primarily due to thiamine deficiency (vitamin B1) with CNS, neuro, cardiac, motor, and psych problems., Protozoan causing Sleeping Sickness. Also see Trypanosoma Brucei, and Trypanosomiasis., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing milder form of Leishmaniasis. This can be more serious in those with defective T-cell immunity. See Leishmania Mexicana, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin problems. See Leishmania Tropica, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin, mouth, and nasal conditions. See Leishmania Braziliensis, and Leishmaniasis programs., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing spleen and liver enlargement, and infection of bone marrow. See Leishmaniasis, Leishmania Donovani, and Leishman Donovan Bodies programs., Respiratory condition due to viral infection of upper airway., See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimers. Chronic neurodegenerative illness., Serious tick and arthropod borne infection with lesions and fever, spreading to lungs, lymphatic system, liver, and spleen. Use Francisella Tularensis., Sudden attack of Convulsions and/or loss of consciousness, typical of Epilepsy and other conditions like Hyperglycemia., Sudden involuntary contraction of muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ such as the heart., Type of Roundworm called Whipworm. Also see Parasites Whipworm, Whipworm Infections, Trichuris Species Male, and Roundworm programs., Very rare inherited disorder where bone becomes denser than normal. |
| 67553.64 | Spooky2 XTRA | Detox Plastics 2 | Bisphenol A, and Phthalates (DEHP, DINP, and DIDP). |
| 67860 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida LoPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida HiPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 67950 | Spooky2 ETDF | Beals Syndrome | Rare congenital disorder with multiple joint contractures. |
| 70542 | Spooky2 CAFL | Scleroderma V | Chronic systemic autoimmune disease with hardening of skin. A more severe form also affects internal organs. Also use Nanobacter programs. |
| 71100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Tumor Breast Non Malignant | Benign (non-cancerous) breast conditions are very common, and most women have them. ... Unlike breast cancers, benign breast conditions are not life-threatening. But some are linked with a higher risk of getting breast cancer later on. Some breast changes may not cause symptoms and may be found during a mammogram. |
| 71874 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 73890 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibrocystic Breast Disease | Non-cancerous breast lumps often related to menstrual cycle. Try Mastitis, and see Fascia programs. |
| 73980 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pemphigoid Bullous | Acute or chronic autoimmune skin disease, involving the formation of blisters. |
| 77665.5666 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cytomegalovirus CMV 1 | Herpes Type 5. Dowsed by Newport. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs. |
| 78300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Embolism Cholesterol | Usually caused by atherosclerotic plaque break-up. |
| 81000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Slime Molds 1 | From Dr. Hulda Clark. Targets Arcyria, Lycogala, and Stemonitis. Common in Morgellons. |
| 81270 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome | Rare autoimmune disorder with weakness of limb muscles, often accompanying cancer, typically small cell lung cancer. |
| 82530 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mesothelioma | Rare cancer of lining of organs, most commonly lungs, usually due to asbestos exposure. Also see Cancer Malignant Mesothelioma, and Simian Virus 40. |
| 84942 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 85230 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Hyperthyroidism, Hypothyroidism | Excess production of thyroid hormone, leading to Thyrotoxicosis., Underproduction of thyroid hormone, mainly caused by lack of iodine in the diet, or by Hashimotos. See Goiter, and Struma programs. |
| 85500 | Spooky2 ETDF | HSAN Type I | Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy. Type I has nerve abnormalities in hands and feet. Also see Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathies program. |
| 85680 | Spooky2 ETDF | Iritis, Machado-Joseph Disease | Also called Uveitis. Inflammation of eyes uvea, lying between retina and sclera/cornea., Rare inherited neurodegenerative disease that causes progressive cerebellar ataxia, leading to lack of muscle control. |
| 87300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Anaphylaxis, Cancer Extracranial Tumor | Germ cell. Class of tumors originating from gonadal germ cells. Sites: cranium, mouth, neck, mediastinum, pelvis, ovary, testis., Serious rapid allergic reaction. Other use: Extracranial Germ Cell Tumor. |
| 88740 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida HiPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida LoPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 89100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypocupremia Congenital | Copper deficiency as a result of heredity. |
| 89298 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida Organ Support | Run with Candida HiPower and Candida LoPower programs. From Pulsed Technologies. |
| 90000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Adhesions Pelvic, Agammaglobulinemia, Alphavirus Infections, Angioedema, Ascariasis, Bacteremia, Berylliosis, Biotinidase Deficiency, Blepharospasm, Brain Concussion, Brain Diseases, Brain Ischemia, Cancer Eye Cancer, Cancer Eye Cancer Intraocular Melanoma, Carcinoma, Cardiovascular Diseases, Eye Infections, Factor V Deficiency, Freibergs Disease, Hepatomegaly, Hordeolum, Hyperoxaluria, Kernicterus, Parasites Flukes General, Parasites Passalurus ambiguus, Parasites Trypanosoma equiperdum, Parasites Trypanosoma gambiense, Parasites Trypanosoma lewisi, Pemphigus, Ranula, Retinoblastoma, Scoliosis, Stomatognathic Diseases, Strabismus, Tracheoesophageal Fistula, Trigeminal Neuralgia, Urethritis, Urogenital Surgical Procedures, Ventricular Fibrillation, Vocal Cord Paralysis, Wolman Disease, Wounds and Injuries, Yaws | Abnormal connection between trachea and esophagus., Abnormal lateral curvatures of spine, Also see Alignment of Individual, Distortion, and Lumbar Vertebrae Deformed., Also called Uveal Melanoma. Arises from eye colour pigments., Autoimmune skin disorder characterized by blisters in the outer layer of skin and mucous membranes., Bilirubin-induced brain dysfunction. Also see Bilirubinemia and Hyperbilirubinemia Hereditary., Cardiovascular disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those that affect your hearts muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease., Caused by the parasitic roundworm Ascaris Lumbricoides., Causes And Types Of Eye Infections. Examples of viral, fungal and bacterial eye infections include: Pink eye, or conjunctivitis. Conjunctivitis, also called pink eye, is a common, highly contagious eye infection that often is spread among children in day care centers, classrooms and similar environments., Chronic lung disease due to beryllium exposure., Coagulation system protein deficiency leading to predisposition for hemorrhage., Disorders of the mouth and jaws., Enlarged liver. Also see Liver Enlarged, and Liver Enlargement., Enzyme deficiency caused by failure to process biotin (vitamin B7) in food., Excessive urinary excretion of oxalate - may indicate presence of calcium oxalate Kidney Stones., Eye squint, commonly called crossed eyes. Also see Esotropia and Eye programs., Head injury with temporary loss of brain function., Heart disease describes a range of conditions that affect your heart. Diseases under the heart disease umbrella include blood vessel diseases, such as coronary artery disease; heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias); and heart defects youre born with (congenital heart defects), among others.The term heart disease is often used interchangeably with the term cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those that affect your hearts muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease.Many forms of heart disease can be prevented or treated with healthy lifestyle choices.SymptomsHeart disease symptoms depend on what type of heart disease you have.Symptoms of heart disease in your blood vessels (atherosclerotic disease)Cardiovascular disease symptoms may be different for men and women. For instance, men are more likely to have chest pain; women are more likely to have other symptoms along with chest discomfort, such as shortness of breath, nausea and extreme fatigue.Symptoms can include:Chest pain, chest tightness, chest pressure and chest discomfort (angina)Shortness of breathPain, numbness, weakness or coldness in your legs or arms if the blood vessels in those parts of your body are narrowedPain in the neck, jaw, throat, upper abdomen or backYou might not be diagnosed with cardiovascular disease until you have a heart attack, angina, stroke or heart failure. Its important to watch for cardiovascular symptoms and discuss concerns with your doctor. Cardiovascular disease can sometimes be found early with regular evaluations., Inflammation of urethra. See Vaginosis, and Chlamydia Trachomatis programs., Injury to laryngeal nerves, causing hoarseness, lack of vocal power, and severe shortness of breath., Insufficient blood flow to brain causing vision, movement, and speech problems., Intensely painful neuropathic chronic disorder affecting the faces trigeminal nerve. Also see Neuralgia Trigeminal program., Internal scar tissue following injury or surgery., Metatarsal bone destruction caused by loss of blood supply., Pinworms found in rabbits and hares. See Passalurus Ambiguus programs., Presence of bacteria in the blood., Primary immune deficiency disease. Synonymous with Hypogammaglobulinemia., Protozoan causing equine diseases. Also see Trypanosoma Equiperdum programs, and Trypanosomiasis., Protozoan found in rats and carried by their fleas which can cause disease in humans. See Trypanosoma Lewisi, and Trypanosomiasis., Rapid swelling of oral, throat, and facial tissues., Rare form of cancer rapidly developing from immature cells of retina, most commonly in young children. Also see appropriate Cancer programs., See Stye program. Use Staphylococcus Infection program., Swelling of connective tissue on floor of mouth composed of mucin (mucocele) from ruptured salivary gland., Trematoda is a clade within the phylum Platyhelminthes. It includes two groups of parasitic flatworms, known as flukes., Tropical infection of skin, bones, and joints caused by Treponema Pallidum spirochete., Uncontrolled eyelid twitch., Uncoordinated contraction of the ventricular heart muscles, usually leading to cardiac arrest - see Myocardial Infarction, and use caution., Under-production of active lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) enzyme, with serious digestive problems, usually in infants. See Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Urogenital Surgical Procedures. Definition: Surgery performed on the urinary tract or its organs and on the male or female genitalia., Use Blood Cleanser., Use General Antiseptic. See all Healing programs, and Jade Machine programs., Uveal or Intraocular Melanoma. Arises from eye colour pigments., Variety of Trypanosoma Brucei causing slow onset of Trypanosomiasis. See Trypanosoma Gambiense programs, and Trypanosomiasis., Viral group causing infectious arthritis, encephalitis, fever, and rashes., Your brain is your bodys control center. Its part of the nervous system, which also includes the spinal cord and a large network of nerves and neurons. Together, the nervous system controls everything from your senses to the muscles throughout your body.When your brain is damaged, it can affect many different things, including your memory, your sensation, and even your personality. Brain disorders include any conditions or disabilities that affect your brain. This includes conditions that are caused by:illnessgeneticstraumatic injuryThis is a broad category of disorders, which vary greatly in symptoms and severity. Keep reading to learn about some of the largest categories of brain disorders. |
| 93150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Sexual Libido Boost | Sexual desire is complex, with both psychological and physical components. Even when a person has a physical condition that affects libido, such as diabetes, improving the emotional and psychological response to sex can improve libido and sexual functioning. |
| 95220 | Spooky2 ETDF | Chronic Hepatitis, Hepatitis A, Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Hepatitis Viral Human | Infectious inflammation of liver (from blood or body fluids). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver (from blood-to-blood contact). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver (from feces-contaminated food or water). Also run Hepatitis General, Blood Purify, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni programs if necessary., Infectious inflammation of liver., Inflammation of liver. |
| 95310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Germ Cell, Cancer Germ Cell Tumor Extragonadal, Cystinosis | Class of tumors originating from gonadal germ cells. Sites: cranium, mouth, neck, mediastinum, pelvis, ovary, testis., Class of tumors originating from gonadal germ cells. Sites: cranium, mouth, neck, mediastinum, pelvis, ovary, testis. Other use: dentigerous cyst., Genetic lysosomal storage disorder with abnormal amounts of cystine. |
| 95670 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Kernicterus, Kidney Calculi, Lyme Borreliosis, Lyme Disease | Also called Borreliosis., Also called Kidney Stones. Also see Gravel in Urine, and Gravel Deposits., Bilirubin-induced brain dysfunction. Also see Bilirubinemia and Hyperbilirubinemia Hereditary., Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by a bacterium named Borrelia spread by ticks. The most common sign of infection is an expanding area of redness on the skin, known as erythema migrans, that appears at the site of the tick bite about a week after it occurred. |
| 99180 | Spooky2 XTRA | Candida HiPower | From Pulsed Technologies. Alternate daily with Candida LoPower, and run with Candida Organ Support program. |
| 103500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adiadochokinesis | Inability to make certain movements in quick succession. |
| 105210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Congenital Fiber Type Disproportion | Muscular condition that may accompany some neurological disorders. |
| 105750 | Spooky2 ETDF | Glioma | Brain or spinal tumor that arises from glial cells. See Cancer Gliomas, and Tumor Brain programs. |
| 107100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Helicobacter Pylori | Also called Heliobacter Pylori. See Ulcer programs. Usually present in Morgellons. |
| 110250 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adiposis Dolorosa, Alkalosis, Amaurosis Fugax, Anemia Hemolytic, Gassers Syndrome, Wernicke Encephalopathy, Whooping Cough | Abnormal breakdown of red blood cells.Blood, Also called Hemolytic-uremic Syndrome. Disease with hemolytic anemia, acute kidney failure, and low platelet count, usually in children. Also use E Coli and Shigella programs., Also known as Dercums Disease - multiple painful lipomas. See Lipomatosis and Lipoma programs., Constellation of neurological symptoms caused by CNS lesions due to exhaustion of B-vitamin reserves, in particular thiamine (vitamin B1)., May be respiratory, metabolic, or combined., See Pertussis, and Pertussis Secondary programs., Transient loss of sight in one eye. |
| 110970 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Diabetes Insipidus | Characterized by excessive thirst and urination. |
| 112050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mastocytosis | Rare mast cell disease in adults and children caused by cell and precursor proliferation, causing itching, hives, and anaphylactic shock. |
| 112500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptosporidiosis, Gynecomastia, Meconium Aspiration Syndrome, Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Rhinitis, Schizencephaly, Scrub Typhus | Congenital disorder with brittle bones prone to fracture, due to defective or no connective tissue production., Endocrine system disorder with non-cancerous development of breasts in males. May also be caused by certain medications., Form of typhus, usually caused by chigger bite., GI tract infection caused by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium., Lung problems caused by inhalation during birth of fetal stool material in amniotic fluid., Rare birth defect with abnormal brain clefts causing symptoms including epilepsy, motor deficits, and psychomotor retardation., Runny nose. See Sinusitis, and Cold programs. |
| 112950 | Spooky2 ETDF | Retroperitoneal Fibrosis | Proliferation of fibrous tissue in retroperitoneum, containing kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and other structures. May cause lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, and deep vein thrombosis. |
| 115290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Neurofibromatoses | Collection of genetically inherited conditions which are clinically and genetically different and present a high chance of tumor formation. |
| 115830 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Pheochromocytoma | Neuroendocrine tumor of medulla of adrenal glands. |
| 117000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Coloboma | A hole in one of the eyes structures. |
| 119340 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | African Lymphoma, Anthrax, Auricular Cancer, Brachial Plexus Neuritis, Burkitt Lymphoma, Cancer Brain Tumor, Cancer Ear, Chancroid, Encopresis, Holoprosencephaly, Lesch-Nyhan Syndrome, Stomatitis Aphthous, Sweat Gland Diseases, Testicular Diseases, Vitiligo | Also called Burkitts Lymphoma., Also called Canker Sores. Repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers in otherwise healthy people. Also see Cancrum Oris programs., Also called juvenile gout. Rare inherited disorder with build-up of uric acid in body fluids. See Gout programs., BromhidrosisHidradenitis suppurativa also affects the apocrine glands,HyperhidrosisHypohidrosisMiliaria, Cancer of lymphatic system. Also called African Lymphoma., Cancer of the ear, head, and neck., Failure of embryonic forebrain to full develop into two hemispheres, causing brain and facial defects., Loss of pigmentation in areas of skin. Use with B Complex with extra PABA internally and PABA Cream topically. See E Coli, Parasites General, and Fungus programs if required., See Astrocytoma and Cancer Astrocytoma. Use Blood Cleanser., Serious disease of lungs, intestines, and skin. Weaponised., Shoulder, arm, or neck pain due to brachial plexus damage., Signs and Symptoms of Nasopharyngeal CancerHearing loss, ringing in the ear, pain, or feeling of fullness in the ear (especially on one side only)Ear infections that keep coming back.Nasal blockage or stuffiness.Nosebleeds.Headaches.Facial pain or numbness.Trouble opening the mouth.Blurred or double vision., STD with painful genital sores., Testicular disease can take a variety of forms: Testicular cancer. Like any cancer, testicular cancer happens when cells in the testicle develop mutations that cause them to misbehave., Voluntary or involuntary fecal soiling, usually in children. |
| 121500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Complex Regional Pain Syndrome Type I | Severe pain, swelling, and skin changes in parts or all of the body. Also called Causalgia, and Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy. |
| 121590 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibromatosis Aggressive | Rare condition with desmoid tumors which arise from fibroblasts, usually abdominal. |
| 122310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Royer Syndrome | Also called Prader-Willi Syndrome. Rare genetic disorder with low muscle tone, short stature, incomplete sexual development, cognitive disabilities, behavior problems, and chronic insatiable hunger. |
| 122850 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypertension Portal | High blood pressure in portal venous system (liver). |
| 125190 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cartilage Diseases, Chlamydiaceae Infections, Choledochal Cyst, Chondromalacia Patellae | All species., Also called bile duct cysts., Cartilage is the tough but flexible tissue that covers the ends of your bones at a joint. It also gives shape and support to other parts of your body, such as your ears, nose and windpipe. Healthy cartilage helps you move by allowing your bones to glide over each other. It also protects bones by preventing them from rubbing against each other.Injured, inflamed, or damaged cartilage can cause symptoms such as pain and limited movement. It can also lead to joint damage and deformity. Causes of cartilage problems includeTears and injuries, such as sports injuriesGenetic factorsOther disorders, such as some types of arthritisOsteoarthritis results from breakdown of cartilage., Inflammation of the back of the kneecap and softening of cartilage., There are several inflammatory rheumatic diseases that lead to arthritis and can severely damage cartilage tissue. These include rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, and seronegative spondyloarthropathies. |
| 125280 | Spooky2 ETDF | Salpingitis | Also see Fallopian Tube Infection, and Pelvic Inflammatory Disease. |
| 125370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Gait Disorders Neurological, Gaucher Disease, Osteomalacia | Deviations from normal walking patterns caused by neurological disorders., Genetic disorder with bruising, fatigue, anemia, low platelet count, and enlarged liver and spleen., Softening of bones usually due to low phosphate or calcium levels. Called Rickets in children. |
| 125910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors, Onchocerciasis, Osteopetrosis | GI tract connective tissue tumors. Also see Sarcoma, and Cancer Sarcoma programs., Infection by Onchocerca Volvulus., Very rare inherited disorder where bone becomes denser than normal. |
| 126000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 HC, Spooky2 XTRA | Lycogala, Molds General, Slime Molds 1, Sterigmatocystin_3, Tumor General Non Malignant | Also see specific types. See Mold and Fungus, and Fungus programs., From Dr. Hulda Clark. Targets Arcyria, Lycogala, and Stemonitis. Common in Morgellons., Mycotoxin. Other use: Lycogala., Slime mold., This is a general term that can refer to benign (generally harmless) or malignant (cancerous) growths. Benign tumors are non-malignant/non-cancerous tumor. A benign tumor is usually localized, and does not spread to other parts of the body. Most benign tumors respond well to treatment. |
| 128159.7732 | Spooky2 XTRA | Ascaris Megalocephala All Stages | First freq wakes hibernating parasites, last two kill Candida tropicalis (needed by this). Colloidal silver in large doses kills non-hiberators. Multiple treatments over many days may be needed. |
| 132300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Proteinuria | Excess serum proteins in urine, causing it to foam on micturition. |
| 132750 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hyperacusis | Increased sensitivity to everyday environmental sounds. |
| 135000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mitral Stenosis, Phenylketonurias | Inborn metabolic error with impaired metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Sufferers must never ingest aspartame., Narrowing of the hearts mitral valve. Use with caution. |
| 137250 | Spooky2 ETDF | Schistosomiasis | Blood fluke infection. Also see Blood Flukes, Bilharzia, Schistosoma Haematobium, Parasites Schistosoma Haematobium, Schistosoma Mansoni, and Parasites Schistosoma Mansoni. |
| 142020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mumps | Viral disease with fever, muscle pain,and headache, leading to painful swelling of parotid gland(s). Also see Mumps, Mumps Antigen, and Coxsackie programs. |
| 144900 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone, Fibrous Dysplasia Polyostotic | Genetic disorder of bones, skin pigmentation, and hormone problems with premature puberty., Non-cancerous abnormal bone growth where normal bone is replaced with fibrous bone tissue. |
| 145440 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibromatosis Juvenile Hyaline | Very rare disease with pearly or tan nodules or papules on face, scalp, and back. Often mistaken for Neurofibromatosis. |
| 151200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Gyrate Atrophy | Also called Ornithine aminotransferase deficiency. Inherited disorder with poor night vision, leading to blindness. |
| 152010 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypersensitivity Immediate | Also called Type I hypersensitivity. Type of allergic response. |
| 153000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Flukes Intestinal | Only one species is recognised: Fasciolopsis buski. It is a notable parasite of medical importance in humans and veterinary importance in pigs. It is prevalent in Southern and Eastern Asia. The term for infestation with Fasciolopsis is fasciolopsiasis. |
| 155610 | Spooky2 ETDF | Monosomy | Chromosomal abnormality with presence of just one chromosome from a pair. |
| 157500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cysts, Escherichia Coli Infections, Eye Abnormalities, Facial Hemiatrophy, Fatigue, Nephritis Hereditary, Otosclerosis, Polyendocrinopathies Autoimmune | Abnormal growth of bone near middle ear which can lead to hearing loss., Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the physical disturbance of the center of the retina called the macula. Bulging Eyes. Cataracts. Cataracts in Babies. CMV Retinitis. Color Blindness. Crossed Eyes (Strabismus) Diabetic Macular Edema., Also called E Coli. Can infect wounds and urinary tract. Recommended in cancers. May need Adenovirus follow-up., Also called Romberg Disease. Neurocutaneous disorder with tissue degeneration beneath skin, usually on one side of the face.Face, Closed sac with abnormal walls containing air, fluids, or semi-solids., Fatigue is a term used to describe an overall feeling of tiredness or lack of energy. It isnt the same as simply feeling drowsy or sleepy. When youre fatigued, you have no motivation and no energy. Being sleepy may be a symptom of fatigue, but its not the same thing.Fatigue is a common symptom of many medical conditions that range in severity from mild to serious. Its also a natural result of some lifestyle choices, such as lack of exercise or poor diet.If your fatigue doesnt resolve with proper rest and nutrition, or you suspect its caused by an underlying physical or mental health condition, see your doctor. They can help diagnose the cause of your fatigue and work with you to treat it., Genetic disorder with glomerulonephritis, End-Stage Renal Disease, Hearing Loss, Hematuria, and ProteinuriaKidney, Heterogeneous group of rare diseases with autoimmune activity against more than one endocrine organ, although other organs can be affected. |
| 159300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Campylobacter Infections | Bacteria causing food poisoning, usually found in poultry. |
| 162810 | Spooky2 ETDF | Chondroectodermal Dysplasia | Also called Ellis-van Creveld Syndrome. Genetic skeletal and cardiac disorder. |
| 162900 | Spooky2 ETDF | Immune System Diseases | Genetic and acquired. Autoimmunities include chronic Lyme, scleroderma, lupus, vasculitis, Graves disease, and some anemias and myopathies. |
| 168300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Ludwigs Angina | Potentially life-threatening cellulitis of floor of mouth, almost always caused by untreated dental infection. |
| 175050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Alphavirus Infections, Xeroderma Pigmentosum | Rare genetic disorder of DNA repair in which ability to repair damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light is deficient., Viral group causing infectious arthritis, encephalitis, fever, and rashes. |
| 175410 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Turbatrix | Also called vinegar eels. Non-parasitic nematodes feeding on mother of vinegar, filtered by suppliers. |
| 180000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cervix Incompetence, Uterine Cervical Incompetence | Condition where cervix begins to dilate and thin before pregnancy has reached term., Premature dilatation and thinning of cervix causing possible miscarriage or preterm birth. |
| 185580 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypertension | See Blood Pressure High. |
| 190890 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cystic Fibrosis | Also called Mucoviscidosis. Use Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Breathing Deep, and General Antiseptic programs. See Parasites General, and Roundworm programs if no progress. |
| 193500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hemorrhagic Fevers Viral | Viruses causing this include Ebola, Marburg, Lassa, Rift Valley Fever, and Hantavirus, among others. |
| 201330 | Spooky2 ETDF | Polychondritis Relapsing | Multi-systemic condition with inflammation and deterioration of cartilage. Can cause joint deformity and be life-threatening if respiratory tract, heart valves, or blood vessels are involved. |
| 201510 | Spooky2 ETDF | Postcommissurotomy Syndrome | program of distressing symptoms arising after mitral valve surgeries. |
| 202500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Diabetes Insipidus, Eczema, Peters Anomaly | Also called Dermatitis. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches.Skin, Characterized by excessive thirst and urination., Failure in normal development of part of the eye. |
| 202590 | Spooky2 ETDF | Typhus Epidemic Louse-Borne | Use Rickettsia, and Lice Infestations programs. |
| 202770 | Spooky2 ETDF | Emesis | Vomiting. |
| 205110 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pain Back | Physical discomfort occurring anywhere on the spine or back, ranging from mild to disabling. |
| 205830 | Spooky2 ETDF | Splenic Rupture | Rupture of spleen. |
| 207000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Osteomyelitis | Infection and inflammation of bone and marrow. Usually caused by Staphylococcus Aureus, certain Streptococcus spp, Enterobacter spp, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Salmonella spp in Sickle Cell Anemia cases. See appropriate programs. Also see Infection Bone. |
| 212850 | Spooky2 ETDF | Communication Disorders, Ecthyma Contagious | Affects ability to communicate., Also called Orf Disease. Viral skin disease mainly found in sheep and goats, but which can infect man. |
| 213930 | Spooky2 ETDF | Paronychia | Painful fungal (usually Candida Albicans) or bacterial (usually Streptococcus Pyogenes) infection of finger where nail and skin meet. |
| 219510 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pruritus | Pruritus is defined as an unpleasant sensation that provokes the desire to scratch. Certain systemic diseases have long been known to cause pruritus that ranges in intensity from a mild annoyance to an intractable, disabling condition. |
| 220050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypocupremia Congenital | Copper deficiency as a result of heredity. |
| 220500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Congenital Fiber Type Disproportion | Muscular condition that may accompany some neurological disorders. |
| 224370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adenoma, Anemia Megaloblastic, Hematoma Epidural Cranial, Pseudomyxoma Peritonei, Vascular Diseases, Wolf-Hirschhorn Syndrome | Also called Gelatinous Ascites. Caused by cancerous cells (mucinous adenocarcinoma) that produce abundant mucin., Benign epithelial tumor with glandular associations., Due to inhibition of DNA synthesis in red blood cell production.Blood, Genetic disorder with distinct craniofacial features, heart defects, intellectual impairment, seizures, and growth restriction., Includes Peripheral Vascular Diseases, Raynauds Disease, and coagulation disorders - see appropriate programs., Traumatic brain injury with build-up of blood between brain and skull. |
| 225000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Angina Pectoris, Anisakiasis, Anxiety Disorders, Arteriovenous Malformations, Arthritis Rheumatoid, Bells Palsy, Bruxism, Burkholderia Infections, Burns, Cerebral Palsy, Cholelithiasis, Chordoma, Emetophobia, Histiocytosis Langerhans Cell, Neuroses Anxiety, Parasites Fasciolopsis rediae, Smallpox, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, Stroke, Tangier Disease, Ulnar Nerve Compression Syndrome, Xerostomia | A mental health disorder characterized by feelings of worry, anxiety, or fear that are strong enough to interfere with ones daily activities, A neurotic person experiences emotional distress and unconscious conflict, which are manifested in various physical or mental illnesses. ... Neurotic tendencies are common and may manifest themselves as acute or chronic anxiety, depression, an obsessiveÐcompulsive disorder, a phobia, or a personality disorder., Abnormal artery-vein connections, bypassing capillaries, normally in the CNS., Also called Variola. Extremely contagious viral disease marked by fever, prostration, and a rash of small blisters. Also see Herpes Simplex RTI program., Anxiety disorders are a group of mental disorders characterized by significant feelings of anxiety and fear. Anxiety is a worry about future events, and fear is a reaction to current events. These feelings may cause physical symptoms, such as a fast heart rate and shakiness. There are several anxiety disorders, including generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobia, social anxiety disorder, separation anxiety disorder, agoraphobia, panic disorder, and selective mutism. The disorder differs by what results in the symptoms. People often have more than one anxiety disorder.The cause of anxiety disorders is a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Risk factors include a history of child abuse, family history of mental disorders, and poverty. Anxiety disorders often occur with other mental disorders, particularly major depressive disorder, personality disorder, and substance use disorder. To be diagnosed symptoms typically need to be present for at least 6 months, be more than what would be expected for the situation, and decrease functioning. Other problems that may result in similar symptoms include hyperthyroidism; heart disease; caffeine, alcohol, or cannabis use; and withdrawal from certain drugs, among others.Without treatment, anxiety disorders tend to remain. Treatment may include lifestyle changes, counselling, and medications. Counselling is typically with a type of cognitive behavioral therapy. Medications, such as antidepressants, benzodiazepines, or beta blockers, may improve symptoms.About 12% of people are affected by an anxiety disorder in a given year, and between 5% and 30% are affected over a lifetime. They occur in females about twice as often as in males, and generally begin before age 25 years. The most common are specific phobias, which affect nearly 12%, and social anxiety disorder, which affects 10%. Phobias mainly affect people between the ages of 15 and 35, and become less common after age 55. Rates appear to be higher in the United States and Europe.Mind, Bacteria found mostly in equine animals that can cause serious diseases in humans. Likely weaponised., Chest pain indicative of cardiac problems.Heart, Commonly called Gallstones., Dry mouth which may be due to changes in saliva composition or production. Commonly caused by drugs., Due to eating raw/undercooked fish infected with parasitic nematode., Emetophobia is a phobia that causes overwhelming, intense anxiety pertaining to vomiting. This specific phobia can also include subcategories of what causes the anxiety, including a fear of vomiting in public, a fear of seeing vomit, a fear of watching the action of vomiting or fear of being nauseated., Free-living liver fluke larvae with sucker., Grinding of teeth., Group of movement, balance, and postural disorders that appears in early childhood., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., Life-threatening skin condition where cell death causes epidermis to separate from dermis. Commonly caused by drugs such as epilepsy medication Lamotrigine, infections, or (rarely) cancers., Muscles and tendons. May be due to bacteria like Chlamydia Pneumoniae. Use General Antiseptic and Parasites General if no response. See Bursitis., One-sided facial paralysis due to nerve dysfunction., Rare disorder involving clonal proliferation of Langerhans cells, abnormal cells derived from bone marrow migrating from skin to lymph nodes., Rare inherited disorder with severe reduction in HDL (good cholesterol) in blood., Skull and spinal tumors., Trapped ulnar nerve, which runs through the elbow., Use in Contact Mode immediately to halt tissue damage and pain. |
| 225360 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dental Comprehensive, Periodontal Diseases | ETDFL Oral Health, includes Periodontal Disease, See Paradontosis, Bone Regeneration, and Dental programs. |
| 225540 | Spooky2 ETDF | Esophageal Atresia, Esophageal Diseases, Esophagitis, Klippel-Feil Syndrome | Birth defect where the esophagus fails to properly connect to the stomach., Congenital spinal deformity involving fusion of two or more cervical vertebrae., Esophageal disease. Esophageal diseases can derive from congenital conditions, or they can be acquired later in life. Many people experience a burning sensation in their chest occasionally, caused by stomach acids refluxing into the esophagus, normally called heartburn., Inflammation of the esophagus, making swallowing food difficult. |
| 229320 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Adrenoleukodystrophy, Adrenomyeloneuropathy, Barretts Esophagus, Bladder Diseases, Cancer Genital Male, Cancer Genital Neoplasms Male, Cancer Thymoma, Cancer Thymoma Malignant, Catheterization, Cherubism, Chorea, Shoulder Injuries, Telangiectasias, Thalamic Diseases, Urinary Bladder Diseases, Wernicke Encephalopathy, Wounds Penetrating and Non-penetrating | Abnormal cell change of lower esophagus caused by chronic acid exposure., Abnormal growths or tumors. Use Blood Cleanser., Abnormal involuntary movement disorder., Abnormal small dilated blood vessels on skin or mucous membranes, most common near nose, cheeks, and chin, and also on legs., Also called Adrenoleukodystrophy. Fatty acid oxidation disorder., Also called Adrenomyeloneuropathy. Fatty acid oxidation disorder., Cardiac catheterization (cardiac cath or heart cath) is a procedure to examine how well your heart is working. A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a large blood vessel that leads to your heart., Constellation of neurological symptoms caused by CNS lesions due to exhaustion of B-vitamin reserves, in particular thiamine (vitamin B1)., Genetic disorder causing prominence of lower part of face., Includes Cystitis, bladder rupture, and obstruction (tamponade)., Includes post-stroke thalamic syndrome, thalamic infarction, akinetic mutism, thalamocortical dysrhythmia, Korsakoffs syndrome, and Fatal Familial Insomnia., shoulder problem, including shoulder and upper arm sprains and strains., Symptoms of a UTI in the bladder may include:Cloudy, bloody, or foul-smelling urine.Pain or burning during urination.Strong and frequent need to urinate, even right after emptying the bladder.A mild fever below 101?F in some people.Bladder, Uncommon tumor of thymus, associated with Myasthenia Gravis., Use Blood Cleanser., Use General Antiseptic. See all Healing programs, and Jade Machine programs. |
| 233910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Papilledema, Seasonal Affective Disorder | Mental state and sometimes behavioral changes in response to seasonal patterns., Swelling in the eyeball due to increased intracranial pressure. |
| 234000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 RIFE, Spooky2 XTRA | Blackwater Fever, Tetanus | Complication of malaria that can lead to kidney failure., Crane=120, Rife (1936)=1200, 700000, 15779. Infectious disease of central nervous system caused by Clostridium Tetani., RifeVideos (1936). Sourced from http://www.rifevideos.com/dr_rifes_true_original_frequencies. |
| 242100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mesothelioma | Rare cancer of lining of organs, most commonly lungs, usually due to asbestos exposure. Also see Cancer Malignant Mesothelioma, and Simian Virus 40. |
| 247500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Common cold, Eclampsia, Ectropion, Empty Sella Syndrome, Hypokalemia, Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome, Ovarian Cysts | Eversion of the lower eyelid., Fluid-filled sac in ovary, sometime causing pain or bloating., Hypertensive disorder of pregnancy. Also see Hypertension., Low levels of potassium in the blood. See Minerals - Potassium, and Potassium k programs., OverviewThe common cold is a viral infection of your nose and throat (upper respiratory tract). Its usually harmless, although it might not feel that way. Many types of viruses can cause a common cold.Children younger than 6 are at greatest risk of colds, but healthy adults can also expect to have two or three colds annually.Most people recover from a common cold in a week or 10 days. Symptoms might last longer in people who smoke. If symptoms dont improve, see your doctor.SymptomsSymptoms of a common cold usually appear one to three days after exposure to a cold-causing virus. Signs and symptoms, which can vary from person to person, might include:Runny or stuffy noseSore throatCoughCongestionSlight body aches or a mild headacheSneezingLow-grade feverGenerally feeling unwell (malaise)The discharge from your nose may become thicker and yellow or green in color as a common cold runs its course. This isnt an indication of a bacterial infection., Rare neurological disorder with recurring facial paralysis, swelling of face and lips, and folds and furrows in tongue., Shrinkage or deformation of pituitary gland. |
| 247590 | Spooky2 ETDF | Medulloblastoma | Most common malignant primary brain tumor in children, commonly metastasizing via spinal canal. Also see appropriate Cancer programs. |
| 255870 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hyperaldosteronism | Excess aldosterone produced by the adrenal glands - can lead to low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia). |
| 270000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypocalcemia | Low calcium levels in blood. |
| 275670 | Spooky2 ETDF | Intestinal Polyps | In anatomy, a polyp is an abnormal growth of tissue projecting from a mucous membrane. If it is attached to the surface by a narrow elongated stalk, it is said to be pedunculated; if it is attached without a stalk, it is said to be sessile. Polyps are commonly found in the colon, stomach, nose, ear, sinus(es), urinary bladder, and uterus. |
| 283500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Purpura Thrombocytopenic | Purpura associated with reduction in circulating blood platelets from a variety of causes. |
| 288000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 HC | Molds General, Mucor Mucedo | Also see specific types. See Mold and Fungus, and Fungus programs., Fungus that causes rot in fruit and baked goods, sometimes found on feet and skin. Other use: Griseofulvin. |
| 291240 | Spooky2 ETDF | Sexual (Male) erectile dysfunction, Sexual Disorders General program, Sexual Libido Boost | Erectile dysfunction (impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having erection trouble from time to time isnt necessarily a cause for concern., Sexual desire is complex, with both psychological and physical components. Even when a person has a physical condition that affects libido, such as diabetes, improving the emotional and psychological response to sex can improve libido and sexual functioning., Sexual dysfunction generally is classified into four categories: Desire disorders Nlack of sexual desire or interest in sex. Arousal disorders Ninability to become physically aroused or excited during sexual activity. Orgasm disorders Ndelay or absence of orgasm. |
| 292500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Corneal Edema, Craniofacial Dysostosis, Gallbladder Diseases, Gastrointestinal Disease, Hypercholesterolemia | Also see Cholecystitis programs., Gastrointestinal disorders is the term used to refer to any condition or disease that occurs within the gastrointestinal tract. The gastrointestinal tract (also called the GI tract) is a series of hollow organs that form a long continuous passage from our mouth to our anus., High levels of cholesterol in the blood., Now called Crouzon Syndrome. Malformation of skull and facial bones., Swelling of cornea. May be indicated by seeing rainbows around lights, especially at night.Eyes |
| 295290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cyanosis | Bluish coloration of tissue due to low oxygen saturation. See Hypoxia, and Circulatory Stasis. |
| 301230 | Spooky2 ETDF | Renal Dialysis | Also see End Stage Renal Disease and appropriate kidney programs.Kidney |
| 302580 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibrocystic Breast Disease | Non-cancerous breast lumps often related to menstrual cycle. Try Mastitis, and see Fascia programs. |
| 309600 | Spooky2 ETDF | Knee Injury | With a sudden meniscus tear, a pop may be heard or felt in the knee. After the initial injury, pain, swelling, and tightness may increase over the next few days. The most common knee injury is the torn meniscus. Although a torn meniscus can happen to anyone, this injury occurs most often to athletes. |
| 310500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pyoderma Gangrenosum | Rare skin disorder of unknown cause. Small pustules develop into large ulcers at various body sites. Use Parasites General, and General Antiseptic programs. |
| 314370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Carotid Artery Narrowing | Also see Carotid Stenosis. |
| 315000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Hypertension Portal, Influenza B | Also see Flu and Grippe programs., High blood pressure in portal venous system (liver)., Influenza B virus is the only species in the genus Betainfluenzavirus in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. Influenza B virus is only known to infect humans and seals with influenza. |
| 315270 | Spooky2 KHZ | Stuttering | Also see Stammering program. |
| 317250 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer, Cancer Rhabdomyosarcoma, Rhabdomyolysis | Also called RMS. Connective tissue cancer. May arise from progenitor cells. Use Blood Cleanser., Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread., Condition where damaged skeletal striated muscle breaks down rapidly, which can lead to kidney failure. Caused by trauma, strenuous exercise, and statin or fibrate drugs. |
| 323010 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Hypersomnia Periodic, Kleine-Levin Syndrome | Excessive daytime sleep or sleepiness, or abnormally prolonged nighttime sleep. See Kleine-Levin Syndrome., Rare sleep disorder with hypersomnia and cognitive/mood changes. See Hypersomnia Periodic. |
| 325170 | Spooky2 ETDF | Shy-Drager Syndrome, Skin Ulcer | Degeneration of nerve cells in specific areas of brain, causing problems with movement, balance, and autonomic functions., Skin lesion exhibiting complete loss of epidermis and often portions of dermis and even subcutaneous fat. |
| 325350 | Spooky2 KHZ | Epstein Barr Virus Infections | Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs. |
| 325440 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pemphigus | Autoimmune skin disorder characterized by blisters in the outer layer of skin and mucous membranes. |
| 325620 | Spooky2 ETDF | Keratitis, Keratoconus | Degenerative eye disorder with structural corneal changes., Inflammation of the cornea of the eye, usually painful and gritty. |
| 325710 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Anencephaly, Astigmatism, Cancer Prostate 2a, Cancer Prostate 2b, Chediak-Higashi Syndrome, Stickler Syndrome | Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Blurred vision due to corneal or lens defect., Developmental disorder - absence of major portions of brain, skull, and scalp., Genetic disorder with increased infection susceptibility, partial albinism, and peripheral neuropathy., Genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen, with distinctive facial abnormalities, eye problems, hearing loss, and joint problems. |
| 326070 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cystinuria, Erectile Dysfunction, Glaucoma, Parasites Gyrodactylus | Also see Impotence and Circulatory Stasis programs., Genetic disorder causing cystine stones in kidneys, bladder, and ureters., Group of eye diseases that can cause optic nerve damage and vision loss. Also see Eye Glaucoma, and Eyes Glaucoma., Skin parasite found in fish. |
| 326160 | Spooky2 ETDF | Heart Defects Congenital, Hepatomegaly, Mucolipidoses, Nervous System Diseases | Diseases which damage or impair nerves in the central or peripheral nervous systems., Enlarged liver. Also see Liver Enlarged, and Liver Enlargement., Genetic disorder affecting normal turnover of various materials within cells., Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable. |
| 330210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dystonia | Movement disorder with muscle contractions causing twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal postures. |
| 331885.62 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 336420 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cestode Infections | Tapeworm infections. |
| 337500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Liver Cancer, Essential Tremor, Incontinentia Pigmenti, Schizophrenia | Genetic disorder affecting skin (various types of lesions), hair, teeth, nails, and CNS., Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach.Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung or breast and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer. This type of cancer is named after the organ in which it began such as metastatic colon cancer to describe cancer that begins in the colon and spreads to the liver., Most common movement disorder affecting finger, hands, arms, and sometimes other parts of the body., Use Tuberculosis programs. |
| 345690 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Emphysema Pulmonary, Pulmonary Emphysema | Also called COPD or Chronic Airflow Obstruction. Also see Chemtrails and Parasites.Lung, Also see Emphysema, Chronic Airflow Obstruction, COAD, COPD Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Chemtrails, and Parasites programs. |
| 346050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lactobacillus Acidophilus | Naturally occurring GI tract bacteria, with some strains having beneficial probiotic effects. Overgrowth can produce diarrhoea, bloating, liver infection, stomach inflammation, vaginal discomfort, oesophageal diseases, arthritis, skin problems, and lung artery blockages. |
| 347400 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Treponema pallidum causes syphilis | Treponema pallidum is a spirochaete bacterium with subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel, and yaws and is transmitted only amongst humans. |
| 351000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 HC | Jobs Syndrome, Parasites Flukes Lymph, Serratia Marcescens Sweep | Group of genetic immune disorders with recurrent staphylococcal and severe lung infections as well as facial, dental, and skeletal abnormalities., Hospital-acquired bacteria causing bacteremia, urinary tract, eye, and wound infections. Weaponised, and common in Morgellons., Some protozoa and parasitic flukes are also capable of causing infections of the human circulatory system. Although these infections are rare in the US, they continue to cause widespread suffering in the developing world today. Fungal infections of the circulatory system are very rare. |
| 352800 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Besnoitia Lung Sect. | Protozoan causing pedunculated (stalked) lesions in skin, nose, and larynx. |
| 355230 | Spooky2 ETDF | Leiomyosarcoma | Smooth muscle malignant tumor most commonly found in uterus, intestines, blood vessels and skin. |
| 355680 | Spooky2 ETDF | MELAS Syndrome, Respiratory Chain Deficiencies Mitochondrial | Deficiencies in electron transport chain in mitochondria that converts oxygen to enable ATP generation. Also see Electron Transport Chain Def., Mitochondrial Encephalomyopathy, Lactic acidosis, and Stroke-like episodes. Genetic disorder affecting brain/CNS and muscles. |
| 357300 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Adhesive Capsulitis, Adrenal Gland Diseases, Aniridia, Aspergillosis, Autonomic Nervous System Diseases, Blastocystis Hominis Infections, Brachial Plexus Neuritis, Bronchiectasis, Bursitis, Cancer Tonsil, Choroideremia, Pruritus Vulvae, Reinkes Edema, Sick Building Syndrome, Stomatitis Aphthous, Trichomonas Infections, Vocal Cord Paralysis | Absence of irises, usually in both eyes - can be congenital or due to injury.Eye, Also called Canker Sores. Repeated formation of benign and non-contagious mouth ulcers in otherwise healthy people. Also see Cancrum Oris programs., Chronic dilatation of the bronchi., Condition where occupants experience acute health and comfort effects that appear linked to time spent in a building, but no illness or cause can be identified., Genetic disorder leading to blindness., Genital itch (vulval)., Infection by Aspergillus fungi, mainly pulmonary. Also see Aspergillus and Aflatoxin., Inflammation of synovial fluid sacs. May be caused by many organisms. Experiment with Arthritis programs as well., Injury to laryngeal nerves, causing hoarseness, lack of vocal power, and severe shortness of breath., Parasitic protozoan, usually sexually transmitted, causing vaginal irritation with discharge and itching., Protozoan causing GI tract problems. Often misdiagnosed as Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)., See Frozen Shoulder and Stiff Shoulder. Use Streptococcus Pneumoniae, and also try S. Pyogenes and S. Mitis.Shoulder, Shoulder, arm, or neck pain due to brachial plexus damage., Swelling of vocal cords due to fluid between vocal ligament and mucosa, causing voice timbre changes and hoarseness., The adrenal glands are small glands located on top of each kidney. They produce hormones that you cant live without, including sex hormones and cortisol. Cortisol helps you respond to stress and has many other important functions.With adrenal gland disorders, your glands make too much or not enough hormones. In Cushings syndrome, theres too much cortisol, while with Addisons disease, there is too little. Some people are born unable to make enough cortisol.Causes of adrenal gland disorders includeGenetic mutationsTumors including pheochromocytomasInfectionsA problem in another gland, such as the pituitary, which helps to regulate the adrenal glandCertain medicinesTreatment depends on which problem you have. Surgery or medicines can treat many adrenal gland disorders.Adrenals, The ANS controls involuntary body functions., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 360000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fournier Gangrene, Herpes Simplex 2, Leaky Gut Syndrome | Also see Candida programs., Primarily genital. Use General Antiseptic program., Type of necrotizing fasciitis, usually perineal. See Fasciitis Necrotizing, and Gangrene. Also use Streptococcus Pyogenes, Staphylococcus Aureus, Clostridium Perfringens, and Bacteroides Fragilis. |
| 361780.74 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 362520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hyperbilirubinemia Hereditary | Condition where bilirubin levels are elevated, for reasons that can be attributed to a metabolic disorder. |
| 367020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pemphigoid Bullous | Acute or chronic autoimmune skin disease, involving the formation of blisters. |
| 369000 | Spooky2 RIFE | Tuberculosis Rod Form | Crane=803, Rife (1936)=8300, 583000, 541142. Infectious disease usually due to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis, affecting lungs and other parts of body. Also see TB, and Tuberculinum. |
| 375030 | Spooky2 ETDF | African Lymphoma, Burkitt Lymphoma, Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis | Also called Burkitts Lymphoma., Cancer of lymphatic system. Also called African Lymphoma., Rare chronic form of progressive brain inflammation caused by persistent infection with Measles virus. |
| 375300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Streptococcus pyogenes (tooth) | Streptococcus pyogenes is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacterium in the genus Streptococcus. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci. It is clinically important for humans. It is an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota. |
| 375750 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome, Cancer Skin, Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Overgrowth disorder with increased risk of childhood cancer., See Cancer Basal Cell Skin Carcinoma, Cancer Squamous Cell Carcinoma, and Cancer Melanoma. Use Blood Cleanser., Type of skin cancer which can manifest in many other parts of the body. |
| 375930 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Pulmonary Edema | Fluid accumulation in air spaces and parenchyma of lungs. |
| 376290 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Adrenal Hyperplasia, Alkaptonuria, Amoebiasis, Amphibian Diseases, Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, Anemia Megaloblastic, Appendicitis, Ataxia Telangiectasia, Attention Deficit Disorder, Attention Deficit Disorder with Hyperactivity, Back Pain, Behcet Syndrome, Broncho Pulmonary Dysplasia, Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic, Fever, Gastroesophageal Reflux, Intestinal Neuronal Dysplasia, Leukodystrophy Metachromatic, Nocardia Infections, Parasites Roundworms, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Sialorrhea, Thrombosis, Tietzes Syndrome, Trichothiodystrophy Syndromes, Urinary Tract Infections, Varicose Veins, Whiplash Injuries, Xanthomatosis | A fever is a body temperature that is higher than normal. A normal temperature can vary from person to person, but it is usually around 98.6 F. A fever is not a disease. It is usually a sign that your body is trying to fight an illness or infection. Infections cause most fevers., Abnormal cell changes, usually pre-cancerous., Also called ADD. May be important to avoid preservatives, aspartame, dyes, and other toxins., Also called ADHD. May be important to avoid preservatives, aspartame, dyes, and other toxins., Also called Black Urine Disease. Asymptomatic in children, in adults it causes disabling joint pain., Also called GERD. Esophageal damage caused by stomach acid., Also called nematodes. Also see Parasites Nematode, Round Worms, and Roundworm programs., Also called SARS, or Sars. Also see Sars, and use Streptococcus Pneumoniae programs., Also spelled Amebiasis., Back pain is one of the most common reasons people go to the doctor or miss work, and it is a leading cause of disability worldwide. Most people have back pain at least once., Congenital. May cause vomiting and sexual development problems.Adrenals, Due to inhibition of DNA synthesis in red blood cell production.Blood, Enlarged and twisted veins, usually on leg, due to valve defects., Excessive production of saliva. Can be caused by radiation, antipsychotics and other drugs, toxic metals, and pesticides., Formation of blood clot affecting blood flow., If micro-perforation has occurred, infection must be eliminated before drinking any water. A few drops may be fatal., Impairs male sexual development., Impairs movement/coordination, weakens immune system, and prevents DNA repair., Inherited disorder inhibiting intestinal peristalsis, and thus digestion., Inherited disorders with brittle hair/nails, short stature, and intellectual impairment. Photosensitivity is also present in many cases., Lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in large foam cells in skin lesions, with chronic biliary tract obstruction, and primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Also see Biliary Atresia, Biliary Tract Diseases, and Hyperlipidemia Familial Combined., Lysosomal storage disease affecting the growth and development of myelin nerve sheath. See Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Micro-organism causing nocardosis, an infectious pulmonary disease with abscesses in lungs. Found in Parkins Disease. See Streptothrix program., Painful inflammation and swelling of costal (rib) cartilages. Also see Intercostal Neuralgia, and Neuralgia Intercostal programs., Range of neck injuries caused by or related to sudden distortion, as in a traffic accident., Rare immune-related systemic vasculitis with mucous membrane ulcers and eye problems., Some of the more common amphibian diseases with bacterial etiologies include bacterial dermatosepticemia or Nred leg syndrome,Ó flavobacteriosis, mycobacteriosis, and chlamydiosis. The most common viral diseases of amphibians are caused by the ranaviruses, which have an impact on many species of anurans and caudates., Thickening of myocardium which can cause sudden death., UTI. See Bacterium Coli, E Coli, and Chlamydia Trachomatis programs. |
| 377910 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Alzheimer Disease, Anaplasmosis, Antithrombin III Deficiency, Atrial Fibrillation, Barth Syndrome, Blepharoptosis, Cancer Stomach, Cardiomyopathy Congestive, Cardiomyopathy Dilated, Chromosome 17 Abnormalities, Fusobacterium Infections, Glycogen Storage Disease, Leukopenia, Sleep Apnea Central, Urinary Retention, Wolman Disease | Abnormal heart rhythm., Bacteria causing periodontal disease, Lemierres Syndrome, and skin ulcers - see appropriate programs. Implicated in colon cancers., Condition caused by anaplasma (Rickettsia bacteria). Involved in Lyme Disease., Eyelid droop. Also called Ptosis., Genetic disorder affecting multiple body systems, found only in males., Genetic or acquired defects in processing of glycogen synthesis or breakdown in muscles, liver, and other cells., Hereditary disorder with recurring venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and fetal death., Inability to completely empty bladder, common in prostatic disorders (see appropriate programs)., Low white blood cell count. Also use Leukocytogenesis Stimulate, and other White Blood Cell programs., Now called Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM). Enlargement of heart affecting pump function., See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimers. Chronic neurodegenerative illness., See Congestive Cardiomyopathy., See Heliobacter Pylori. Use Blood Cleanser., Suspension of external breathing during sleep. Reported to help with Bartonella rash in Morgellons and Lyme., Too many to list here., Under-production of active lysosomal acid lipase (LAL) enzyme, with serious digestive problems, usually in infants. See Lysosomal Storage Diseases. |
| 378000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Trichomonas vaginalis, Staphylococcal Infections | See other Staphylococci/Staphylococcus programs., Trichomoniasis (or NtrichÓ) is a very common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by infection with a protozoan parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. Although symptoms of the disease vary, most people who have the parasite cannot tell they are infected. |
| 382500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Krukenberg Tumor | Metastasized malignancy in ovary, usually from GI tract primary cancer. See appropriate Cancer programs. |
| 385200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Troglodytella abrassari | Virus program |
| 385650 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mandibulofacial Dysostosis | Congenital malformations of skull, jaw, face, and neck. |
| 386550 | Spooky2 ETDF | Salmonella Infections | Bacteria causing food poisoning or blood infections in sub-Saharan Africa. |
| 387000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Acne, Parasites Anaplasma marginale, Parasites Entamoeba histolytica trophozoite, Parasites Schistosoma haematobium, Parasites Schistosoma mansoni | A parasitic infection of the colon with the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica., Blood flukes. Associated with bladder problems. Also see Schistosoma Haematobium, and Blood Fluke programs., Pimples, white/blackheads, greasy skin, possible scars. Also see Propionibacterium Acnes., Tick- and fly-borne Rickettsia-like bacteria which live in blood cells. Found in some Lyme Disease cases. |
| 391500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hartnup Disease | Genetic metabolic disorder affecting absorption of essential amino acids. |
| 392310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Photophobia | Discomfort or pain to the eyes due to light exposure. |
| 393750 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Chilomonas Whole Mount, Parasites Trypanosoma gambiense | GI tract protozoan not considered parasitic by medicine, but occurring with other parasite infections., Variety of Trypanosoma Brucei causing slow onset of Trypanosomiasis. See Trypanosoma Gambiense programs, and Trypanosomiasis. |
| 394200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Clostridium Infections | Clostridium difficile, which experts recently reclassified as Clostridioides difficile, is a bacterium that resides in the gut. When the levels of gut bacteria become imbalanced, this bacterium can multiply and cause severe health problems. Healthcare professionals call this infection C. difficile or C. diff. |
| 395910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Histidinemia | Originally believed to be linked to developmental disorders, but now classed as a benign inborn error of metabolism. |
| 396000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Clostridium Infections, Nausea, Parasites Entamoeba coli trophozoites, Parasites Trypanosoma gambiense | Clostridium difficile, which experts recently reclassified as Clostridioides difficile, is a bacterium that resides in the gut. When the levels of gut bacteria become imbalanced, this bacterium can multiply and cause severe health problems. Healthcare professionals call this infection C. difficile or C. diff., ETDFLAlso for Parasites Endolimax nana trophozoites and cysts, Other use: Bryozoa Cristatalla., Variety of Trypanosoma Brucei causing slow onset of Trypanosomiasis. See Trypanosoma Gambiense programs, and Trypanosomiasis. |
| 398700 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Trypanosoma gambiense | Variety of Trypanosoma Brucei causing slow onset of Trypanosomiasis. See Trypanosoma Gambiense programs, and Trypanosomiasis. |
| 400050 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Leishmania braziliensis | Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin, mouth, and nasal conditions. See Leishmania Braziliensis, and Leishmaniasis programs. |
| 401220 | Spooky2 ETDF | Genital Diseases Male | A male genital disease is a condition that affects the male reproductive system. An example is orchitis. |
| 404370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cardiac Hypertrophy, Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic | Thickening of myocardium which can cause sudden death., Thickening of ventricular walls of heart. |
| 405000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Ecthyma Contagious, Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome, Hyperaldosteronism, Parasites Leishmania tropica, Stigeoclonium 3 | Also called Orf Disease. Viral skin disease mainly found in sheep and goats, but which can infect man., Excess aldosterone produced by the adrenal glands - can lead to low blood potassium levels (hypokalemia)., Inherited connective tissue disorder with six different types., Protozoan spread by sandflies causing skin problems. See Leishmania Tropica, and Leishmaniasis programs., Toxic green algae. |
| 408150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Dirofilaria Immitis Dog Heartworm | Mosquito-borne filaria. See Dirofilaria Immitis, Heartworms, and Parasites Heartworms. |
| 409950 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Cryptocotyle Lingua Adult | Type of fluke found in fish. |
| 411120 | Spooky2 ETDF | Niemann-Pick Diseases | Group of severe genetic metabolic disorders that allow the fat sphingomyelin to accumulate in cells. Also see Lysosomal Storage Diseases. |
| 412020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Q Fever | Infectious disease caused by contact with animals with Rickettsia and Coxiella Burnetii. Symptoms may include headache, fever, chills, and sweats. See Rickettsia, and Typhoid Fever programs. |
| 412110 | Spooky2 KHZ | Munchausen Syndrome | Factitious disorder where sufferers feign disease, illness, or psychological trauma to fain attention, sympathy, or reassurance. |
| 413910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypoxia Brain | Low oxygen. Use Circulatory Stasis, and see Cyanosis. |
| 414000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Parasites Cryptocotyle Lingua Adult, Parasites Myxosoma, Romberg Disease | Also called Facial Hemiatrophy. Neurocutaneous disorder with tissue degeneration beneath skin, usually on one side of the face., Myxobolus cerebralis is a myxosporean parasite of salmonids that causes whirling disease in farmed salmon and trout and also in wild fish populations., Parry-Romberg syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by slowly progressive deterioration (atrophy) of the skin and soft tissues of half of the face (hemifacial atrophy), usually the left side. It is more common in females than in males., Type of fluke found in fish. |
| 419310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hookworm Infections | Infection by blood-feeding roundworms. See Hookworm, Creeping Eruption, and Larva Migrans. |
| 421020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Endometrial Cancer | Cancer arising from wombs lining, most commonly after menopause, and associated with obesity, hypertension, diabetes, and excess estrogen. |
| 421200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lissencephaly | Rare brain formation disorder with lack of lobe folding. |
| 423000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Enterobius vermicularis, Parasites Fasciola hepatica miracidia | Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans., The pinworm (species Enterobius vermicularis), also known as threadworm (in the United Kingdom and Australia) or seatworm, is a parasitic worm. It is a nematode (roundworm) and a common intestinal parasite or helminth, especially in humans. |
| 423900 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Echinoparyphium Recurvatum | Fluke usually found in European freshwater snails. See Echinoparyphium Recurvatum programs. |
| 425160 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Anophthalmos, Spinal Cord Diseases, Stroke, Tonsillitis, Whipworm Infections, Wounds Penetrating and Non-penetrating | Developmental problem resulting in absence of one or both eyes.Eye, Inflammation of tonsils, caused by viruses or bacteria., Insufficient blood flow to brain resulting in cell death. Also see Inosine Production Stimulate., These disorders include fluid-filled cavities (syrinxes), blockage of the blood supply, inflammation (as occurs in acute transverse myelitis), tumors, abscesses, bleeding (hemorrhage), vitamin B12 or copper deficiency, infection with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), multiple sclerosis, and syphilis., Type of Roundworm. Also see Parasites Trichuris, Parasites Whipworm, and Trichuris Species Male programs., Use General Antiseptic. See all Healing programs, and Jade Machine programs. |
| 425340 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pinworms, Poland Syndrome | Common GI parasitic worm, with Anal Itching. Also see Enterobius Vermicularis, Enterobiasis, Parasites Enterobiasis, and Threadworm programs., Rare birth defect with underdevelopment or absence of chest muscle on one side of body, and also usually webbed fingers. |
| 425430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fecal Incontinence, Friedreichs Ataxia, Parasites Fischoederius Elongatus, Parasites Trypanosoma lewisi | Fecal incontinence is the inability to control bowel movements, causing stool (feces) to leak unexpectedly from the rectum. Also called bowel incontinence, fecal incontinence ranges from an occasional leakage of stool while passing gas to a complete loss of bowel control., Fluke found in ruminants., Genetic disease causing progressive nervous system damage. Can lead to Scoliosis, heart disease, and diabetes., Protozoan found in rats and carried by their fleas which can cause disease in humans. See Trypanosoma Lewisi, and Trypanosomiasis. |
| 425520 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Giardiasis, Graft vs Host Disease, Hearing Loss Sudden, Hematuria, Neuroma Acoustic | Also called Vestibular schwannoma. Benign intracranial tumor which arises from Schwann cells which create myelin sheaths., Common disorder after tissue graft/transplant where white blood cells in the graft tissue attack the host body., Infection by Giardia Lamblia. Also see Giardia Intestinalis, Parasites Giardia, and Lamblia., Presence of blood in urine. May signal kidney stones or a tumor in the urinary tract. See Gravel Deposits, Kidney Stones, Kidney Calculi, Bladder TBC, and Cancer Bladder programs., Sudden sensorineural (inner ear) hearing loss (SSHL), commonly known as sudden deafness, is an unexplained, rapid loss of hearing either all at once or over a few days. |
| 425610 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypothermia | Core body temperature below 35C (95F) as a result of exposure to cold. |
| 425700 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Clonorchis Sinensis 2 | Liver fluke. |
| 425790 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hyperlipidemia Familial Combined, Hypertension | Genetic disorder with abnormally high levels of lipids and lipoproteins in the blood., See Blood Pressure High. |
| 425880 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mixed Connective Tissue | Autoimmune disease combining symptoms of scleroderma, myositis, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and possibly other conditions. |
| 426420 | Spooky2 ETDF | Kuru | Transmissible spongiform encephalopathy caused by a prion. See Creutzfeldt-Jakob and Prions programs. |
| 427500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cranial Nerve Diseases, Parasites Fasciola hepatica rediae, Retroperitoneal Fibrosis, Rubella | Fasciola hepatica, also known as the common liver fluke or sheep liver fluke, is a parasitic trematode of the class Trematoda, phylum Platyhelminthes. It infects the livers of various mammals, including humans., German or 3-Day Measles. Infectious disease with rash, sore throat, itching, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes. See Measles Rubella and German Measles programs., Impaired functioning of one of the 12 cranial nerves., Proliferation of fibrous tissue in retroperitoneum, containing kidneys, aorta, renal tract, and other structures. May cause lower back pain, kidney failure, hypertension, and deep vein thrombosis. |
| 430650 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Capillaria Hepatica Liver Sect. | Nematode inhabiting the liver. |
| 431190 | Spooky2 ETDF | Labyrinth Diseases | Diseases of the inner ear. See Labyrinthitis, and Vestibular Neuronitis. |
| 432000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Entamoeba coli trophozoites, Parasites Fasciolopsis rediae | ETDFLAlso for Parasites Endolimax nana trophozoites and cysts, Fasciolopsis is a genus of trematodes. Only one species is recognised: Fasciolopsis buski. It is a notable parasite of medical importance in humans and veterinary importance in pigs. It is prevalent in Southern and Eastern Asia. |
| 433800 | Spooky2 XTRA | Parasites Entamoeba gingivalis trophozoite | Life cycle stage of protozoan found in dental spaces. |
| 434160 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Prostate 2a, Cancer Thoracic, Cancer Thyroid, Cancer Trophoblastic | Also see Cancer Gestational Trophoblastic Tumor, and Cancer Trophoblastic Neoplasms., Also see Prostate Adenomium, and Prostate Hyperplasia. Use Blood Cleanser., Cancers located in the thorax. Use Blood Cleanser., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 434250 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adrenoleukodystrophy, Angiofibroma, Aspergillosis, Polycystic Kidney Diseases, Scotoma, Zellweger Syndrome | Also called Adrenomyeloneuropathy. Fatty acid oxidation disorder., Area of partially or completely diminished visual acuity surrounded by field of normal vision., Genetic disorder in which abnormal cysts develop and grow in the kidneys., Infection by Aspergillus fungi, mainly pulmonary. Also see Aspergillus and Aflatoxin., Rare congenital disorder with reduction or absence of functional peroxisomes in cells. Also see Peroxisomal Disorders, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Leukodystrophy, Refsum Disease, and Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Small papules over the side of the nose and on cheeks.Skin |
| 434340 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Myelodysplastic Syndrome | Bone marrow stem cell disorder causing blood production problems. |
| 434610 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Larynx | Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 434700 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Gestational Tumor | Pregnancy-related tumor. |
| 437850 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Iodamoeba butschlii | Iodamoeba bztschlii is a species of amoeba. It gets its name from its appearance when stained with iodine. Named for Otto Bztschli by Prowazek in 1912, Iodamoeba bztschlii is a nonpathogenic parasitic ameba, commonly found in the large intestines of people, pigs and other mammals. |
| 441000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 XTRA | Parasites Entamoeba gingivalis trophozoite, Parasites Passalurus ambiguus | Amebiasis is a disease caused by infection with a parasitic amoeba that, when symptomatic, can cause dysentery and invasive extraintestinal problems. The cause of amebiasis is mainly the protozoan parasite Entamoeba histolytica., Life cycle stage of protozoan found in dental spaces., Passalurus ambiguus, the common rabbit pinworm, is host-specific. 3. It inhabits the small intestine, cecum, and colon, passing eggs into the feces without causing clinical signs. |
| 442350 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Urocleidus | Fluke found in fish. Also see Urocleidus. |
| 442800 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Macracanthorhynchus | Macracanthorhynchus hirudinaceus is an acanthocephalan parasite which lives in the intestines of pigs and other suids, and very occasionally in humans or dogs. It causes enteritis, gastritis or peritonitis. Its life cycle includes beetles of the genus Melolontha as intermediate hosts. |
| 443160 | Spooky2 ETDF | Ludwigs Angina | Potentially life-threatening cellulitis of floor of mouth, almost always caused by untreated dental infection. |
| 444150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Passalurus ambiguus | Passalurus ambiguus, the common rabbit pinworm, is host-specific. 3. It inhabits the small intestine, cecum, and colon, passing eggs into the feces without causing clinical signs. |
| 450000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Amino Acid Metabolism, Anomia, Astrocytoma, Bird Diseases, Blounts Disease, Burns, Cancer Osteosarcoma, Carcinoma Small Cell, Central Cord Syndrome, Chediak-Higashi Syndrome, Choledochal Cyst, Chondroma, Eclampsia, Exostoses, Neuronal Ceroid-Lipofuscinoses, Parasites Roundworms, Parasites Urocleidus, Takayasu Arteritis, Thalamic Diseases | Aggressive malignant bone tumor in children and young adults. Other use: Osteochondritis., Also called bile duct cysts., Also called nematodes. Also see Parasites Nematode, Round Worms, and Roundworm programs., Also see Cancer Carcinoma., Benign tumor in cartilage., Blounts disease is a growth disorder of the tibia (shin bone) that causes the lower leg to angle inward, resembling a bowleg. It is also known as tibia vara., Brain cancer. Also see Cancer programs., Fluke found in fish. Also see Urocleidus., Formation of new bone on surface of existing bone due to excess calcium. Also see Calcium programs., Genetic disorder with increased infection susceptibility, partial albinism, and peripheral neuropathy., Hypertensive disorder of pregnancy. Also see Hypertension., Includes post-stroke thalamic syndrome, thalamic infarction, akinetic mutism, thalamocortical dysrhythmia, Korsakoffs syndrome, and Fatal Familial Insomnia., Language disorder - problems recalling words or names., Large vessel granulomatous Vasculitis with Fibrosis and Stenosis. Mainly affects aorta and its branches, and pulmonary arteries., Most common form of cervical spine injury., Multiple neurodegenerative disorders that result from excessive accumulation of lipopigments (lipofuscin) in tissues. Also see Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Normalisation.Cell, The four diseases that most frequently affect birds that use feeders are: salmonella, trichomoniasis, aspergillosis, and avian pox. All of these diseases are transmitted from one bird to another at feeding stations, especially when overcrowding occurs. Birds are also susceptible to mites and lice. There are many steps you can take to help keep feeder birds and people safe and healthy., Use in Contact Mode immediately to halt tissue damage and pain. |
| 451170 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Agammaglobulinemia, Aniridia, Arteriosclerosis, Balanitis, Bowens Disease, Canavan Disease, Cancer Genital Neoplasms Female, Cancer Urologic Neoplasms, Cardiomyopathy Dilated, Central Nervous System Diseases, Central Nervous System Infections, Cholera, Methemoglobinemia, Morgellons Int and Ext Parasites, Morgellons Internal Parasites, Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration, Parasites Fasciola hepatica miracidia, Parasites General Comprehensive, Parasites Trichomonas vaginalis, Parasites Turbatrix, XYY Karyotype | Abnormal growths or tumors. Use Blood Cleanser., Absence of irises, usually in both eyes - can be congenital or due to injury.Eye, Also called Squamous Cell carcinoma in Situ. Can manifest on skin and sex organs., Also called Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ. Can manifest on skin and sex organs., Also called vinegar eels. Non-parasitic nematodes feeding on mother of vinegar, filtered by suppliers., Apply=.02% Feathering., Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS).Every disease has different signs and symptoms. Some of them are persistent headache; pain in the face, back, arms, or legs; an inability to concentrate; loss of feeling; memory loss; loss of muscle strength; tremors; seizures; increased reflexes, spasticity, tics; paralysis; and slurred speech. One should seek medical attention if affected by these., Degenerative brain with iron accumulation disease leading to Parkinsons Disease, dementia, dystonia, and death., Degenerative genetic cerebral disease involving neuronic myelin damage., Due to methemoglobin, a form of hemoglobin with ferric rather than ferrous iron, leading to impaired oxygen delivery to tissues., Extremely contagious and serious bacterial infection of small intestines., Free-living sheep liver fluke larvae. See Parasites Flukes Sheep Liver, Parasites Sheep Liver Flukes, and Liver Flukes., Genetic condition where a male has one extra male chromosome, associated with increased early growth, slightly lower IQ, and learning difficulties., Hardening of arteries. Regeneration takes time. Try CMV programs., Includes all bladder cancers, renal cell cancer, and prostate cancer.Kidney, Infections of the nervous system are potential life-threatening and are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Prompt recognition and treatment of a central nervous system (CNS) infection is crucial for patient survival, as these infections have a high morbidity and mortality. CNS infections include meningitis, encephalitis, and brain abscesses., Inflammation of the glans penis, with many possible causes., micropredation.Like predation, parasitism is a type of consumer-resource interaction, but unlike predators, parasites, with the exception of parasitoids, are typically much smaller than their hosts, do not kill them, and often live in or on their hosts for an extended period. Parasites of animals are highly specialised, and reproduce at a faster rate than their hosts. Classic examples include interactions between vertebrate hosts and tapeworms, flukes, the malaria-causing Plasmodium species, and fleas., Primary immune deficiency disease. Synonymous with Hypogammaglobulinemia., See Congestive Cardiomyopathy., Sexually transmitted infection of protozoan causing vaginitis in women and urethritis in men. See Trichomonas programs. |
| 454500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Pancreatic Exocrine and Islet Cell, Carcinoma Basal Cell, Cerebral Palsy, Chicken Pox | Also see Cancer Carcinoma., Also see Cancer Islet Cells Carcinoma and Cancer Pancreatic., Group of movement, balance, and postural disorders that appears in early childhood., See Herpes Zoster. |
| 454950 | Spooky2 ETDF | Parasites Sarcocystis | Only two species of Sarcocystis are known to utilize humans as a definitive host: S. hominis and S. suihominis. Humans become dead-end hosts when they ingest the oocysts of Sarcocystis species whose definitive hosts are mammalian species other than humans. |
| 465300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Diabetes Gestational | Condition where women without diabetes exhibit high blood glucose levels during pregnancy. |
| 465532.56 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 465750 | Spooky2 ETDF | Rickets | Defective mineralization of bones due to vitamin D, phosphorus, or calcium deficiency. |
| 471870 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mumps | Viral disease with fever, muscle pain,and headache, leading to painful swelling of parotid gland(s). Also see Mumps, Mumps Antigen, and Coxsackie programs. |
| 472500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Amyotonia Congenita, Cold Common, Common cold, Cubital Tunnel Syndrome, Empty Sella Syndrome, Fibromatosis Aggressive, Hypoglycemia, Muscular Diseases, Neuromuscular Diseases, Pruritus, Pseudotumor Cerebri, Renal Artery Obstruction | Also called hypotonia, or floppy baby syndrome. Due to low muscle tone/strength. Also see Languorous Paralysis., Also called renal artery stenosis. Also see Circulation, and Circulatory programs.Kidney, Also called Ulnar Nerve Entrapment., Diseases which affect muscles and/or their nervous system control., Neurological disorder with increased intracranial pressure in the absence of a tumor or other disorders., Neuromuscular diseases are those that affect the muscles and/or their nervous control. In general, problems with nervous control can cause spasticity or paralysis, depending on the location and nature of the problem. A large proportion of neurological disorders, ranging from cerebrovascular accident (stroke) and Parkinsons disease to CreutzfeldtJakob disease, can lead to problems with movement or motor coordination., OverviewThe common cold is a viral infection of your nose and throat (upper respiratory tract). Its usually harmless, although it might not feel that way. Many types of viruses can cause a common cold.Children younger than 6 are at greatest risk of colds, but healthy adults can also expect to have two or three colds annually.Most people recover from a common cold in a week or 10 days. Symptoms might last longer in people who smoke. If symptoms dont improve, see your doctor.SymptomsSymptoms of a common cold usually appear one to three days after exposure to a cold-causing virus. Signs and symptoms, which can vary from person to person, might include:Runny or stuffy noseSore throatCoughCongestionSlight body aches or a mild headacheSneezingLow-grade feverGenerally feeling unwell (malaise)The discharge from your nose may become thicker and yellow or green in color as a common cold runs its course. This isnt an indication of a bacterial infection., Program for the common cold, Pruritus is defined as an unpleasant sensation that provokes the desire to scratch. Certain systemic diseases have long been known to cause pruritus that ranges in intensity from a mild annoyance to an intractable, disabling condition., Rare condition with desmoid tumors which arise from fibroblasts, usually abdominal., See Low Blood Sugar program., Shrinkage or deformation of pituitary gland. |
| 473582.1726 | Spooky2 XTRA | Colloidal Silver Scalar | Scalar sub-harmonics of sub-10nm spheroid colloidal nanoparticles. |
| 475110 | Spooky2 ETDF | Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, Thrombophlebitis, Torticollis, Trypanosomiasis, Tumor Virus Infections | Conditions caused by Trypanosoma protozoans, including Sleeping Sickness, and Chagas Disease. Also see Trypanosoma, Protozoan Infections, and Protozoa programs., Due to compression of neurovascular bundle passing between two scalene muscles at upper chest/upper limb area. Also try Brachial Neuralgia, Brachial Plexus Neuritis, Hypochondrium, and Nerve Compression Syndromes., Dystonic neck muscle condition with abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position., Inflammation of vein walls from clotting. Use on lab animals only? See Circulatory Stasis., Oncoviruses that can cause cancer. See appropriate Cancer programs. |
| 475290 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Coxsackie Virus Infections, Hemangioma Cavernous, Neuromyelitis Optica | Infects heart, pleura, pancreas, and liver, causing pleurodynia, myocarditis, pericarditis, and hepatitis. Found with Bacteroides fragilis., Malformation involving multiple blood vessels and resembling tumor., Simultaneous inflammation and demyelination of optic nerve (Optic Neuritis) and spinal cord (Myelitis). |
| 475470 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Gastroschisis, Human Papilloma Virus HPV, Panniculitis, Papilloma | Congenital defect with opening in abdominal wall through which organs may protrude., Group of diseases with inflammation of subcutaneous adipose tissue., Virus causing warts, or lesions leading to cancers of reproductive system, genitals, anus, and oropharynx. See appropriate Cancer, and Human Papilloma Virus HPV programs., Virus causing warts, or lesions leading to cancers of reproductive system, genitals, anus, and oropharynx. See appropriate Cancer, and Papilloma HPV programs. |
| 475560 | Spooky2 ETDF | Nervous System Diseases | Diseases which damage or impair nerves in the central or peripheral nervous systems. |
| 482130 | Spooky2 ETDF | Prostate Enlarged | See Prostatitis and other prostate programs. Use Streptococcus General, and Propionibacterium Acnes, and practise metals avoidance. |
| 485190 | Spooky2 ETDF | Scheuermanns Disease | Childhood skeletal disorder with uneven vertebral development, causing abnormal spinal curvature (kyphosis). |
| 486900 | Spooky2 ETDF | Leiomyosarcoma | Smooth muscle malignant tumor most commonly found in uterus, intestines, blood vessels and skin. |
| 491310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lassa Fever | Acute viral hemorrhagic fever similar to Ebola and with multiple symptoms. |
| 492570 | Spooky2 ETDF | Esotropia | Inward eye squint, or Strabismus. |
| 493020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pneumothorax | Abnormal accumulation of air or gas in pleural spaces. Also see Pleural Diseases. |
| 493200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Retinoschisis | Eye disease with abnormal splitting of retinas neurosensory layers, usually in the outer layer. |
| 495000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Amaurosis Fugax, Phlebotomus Fever, Rectal Prolapse | Also called Pappataci Fever. Viral febrile arboviral infection caused by sandfly bites., Movement of rectal walls such that they protrude from anus, or result in internal intussusception., Transient loss of sight in one eye. |
| 497610 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Brain Concussion, Brain Diseases, Hemosiderosis, Lymphedema, Parasites Nematode, Smith-Magenis Syndrome, White Dot Syndrome | Also see Parasites Roundworm programs, Round Worms, and Roundworm., Developmental disorder affecting body and brain, including intellectual disability, broad face, difficulty sleeping, and various behavioral problems., Form of Iron overload disorder resulting in accumulation of hemosiderin. Also see Hemochromatosis., Head injury with temporary loss of brain function., Inflammatory eye disorders with white dots on the interior surface of eye causing blurred vision and visual field loss., Localized fluid retention and tissue swelling in lymphatic system. Frequently caused by conventional cancer treatments or parasite infections., Your brain is your bodys control center. Its part of the nervous system, which also includes the spinal cord and a large network of nerves and neurons. Together, the nervous system controls everything from your senses to the muscles throughout your body.When your brain is damaged, it can affect many different things, including your memory, your sensation, and even your personality. Brain disorders include any conditions or disabilities that affect your brain. This includes conditions that are caused by:illnessgeneticstraumatic injuryThis is a broad category of disorders, which vary greatly in symptoms and severity. Keep reading to learn about some of the largest categories of brain disorders. |
| 512910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Plant Poisoning | Some plants can be poisonous if you eat them. Others can hurt you if you get them on your skin. For some plants, all parts of the plant are poisonous. |
| 514350 | Spooky2 ETDF | Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome, Slow Virus Diseases | Also called SARS, or Sars. Also see Sars, and use Streptococcus Pneumoniae programs., Diseases that, after long latency, follow a slow, progressive course over months or years, often of central nervous system. |
| 515160 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Aicardi Syndrome, Alopecia, Alzheimer Disease, Apraxias, Astrocytoma, Cancer Pancreatic Exocrine and Islet Cell, Cancer Thymoma, Cancer Thymoma Malignant, Cardiac Hypertrophy, Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic, Thalamic Diseases, XYY Karyotype | Also see Cancer Islet Cells Carcinoma and Cancer Pancreatic., Brain cancer. Also see Cancer programs., Genetic condition where a male has one extra male chromosome, associated with increased early growth, slightly lower IQ, and learning difficulties., Genetic syndrome with partial or complete absence of corpus callosum and eye abnormalities., Includes post-stroke thalamic syndrome, thalamic infarction, akinetic mutism, thalamocortical dysrhythmia, Korsakoffs syndrome, and Fatal Familial Insomnia., Loss of hair., Motor disorder due to brain damage.Brain, See ALS programs. Also called Alzheimers. Chronic neurodegenerative illness., Thickening of myocardium which can cause sudden death., Thickening of ventricular walls of heart., Uncommon tumor of thymus, associated with Myasthenia Gravis. |
| 515430 | Spooky2 KHZ | Parasites Fasciola hepatica eggs | Egg stage of sheep liver fluke. See Parasites Flukes Sheep Liver, Parasites Sheep Liver Flukes, and Liver Flukes. |
| 515700 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Malignant Mesothelioma, Chancroid, Factor XI Deficiency, Factor XII Deficiency, Glaucoma, Goldenhar Syndrome, Hallucinations, Hartnup Disease, Headache, Hordeolum, Klinefelter Syndrome, Larva Migrans, Leucine Metabolism Disorders, Leukodystrophy Metachromatic, Lipoma, Loiasis, Lymphangioma, Paraphilias, Pulmonary Embolism, Shy-Drager Syndrome | A hallucination is a perception in the absence of external stimulus that has qualities of real perception. Hallucinations are vivid, substantial, and are perceived to be located in external objective space. They are distinguishable from several related phenomena, such as dreaming, which does not involve wakefulness; pseudohallucination, which does not mimic real perception, and is accurately perceived as unreal; illusion, which involves distorted or misinterpreted real perception; and imagery, which does not mimic real perception and is under voluntary control. Hallucinations also differ from delusional perceptions, in which a correctly sensed and interpreted stimulus (i.e., a real perception) is given some additional (and typically absurd) significance.Hallucinations can occur in any sensory modalityvisual, auditory, olfactory, gustatory, tactile, proprioceptive, equilibrioceptive, nociceptive, thermoceptive and chronoceptive.A mild form of hallucination is known as a disturbance, and can occur in most of the senses above. These may be things like seeing movement in peripheral vision, or hearing faint noises or voices. Auditory hallucinations are very common in schizophrenia. They may be benevolent (telling the subject good things about themselves) or malicious, cursing the subject, etc. Auditory hallucinations of the malicious type are frequently heard, for example people talking about the subject behind their back. Like auditory hallucinations, the source of the visual counterpart can also be behind the subjects back. Their visual counterpart is the feeling of being looked or stared at, usually with malicious intent. Frequently, auditory hallucinations and their visual counterpart are experienced by the subject together.Hypnagogic hallucinations and hypnopompic hallucinations are considered normal phenomena. Hypnagogic hallucinations can occur as one is falling asleep and hypnopompic hallucinations occur when one is waking up. Hallucinations can be associated with drug use (particularly deliriants), sleep deprivation, psychosis, neurological disorders, and delirium tremens.The word hallucination itself was introduced into the English language by the 17th-century physician Sir Thomas Browne in 1646 from the derivation of the Latin word alucinari meaning to wander in the mind. For Browne, hallucination means a sort of vision that is depraved and receive[s] its objects erroneously., Affects lungs and organ linings. Asbestos-related. Other use: fatty liver., Also called Haemophilia C. Relatively common but mild form of Haemophilia.Blood, Benign, soft tumor of fatty tissue. Use Liver Support program., Blockage of artery in the lungs by something from elsewhere in the body., Coagulation system deficiency of enzyme necessary for plasma clotting.Blood, Degeneration of nerve cells in specific areas of brain, causing problems with movement, balance, and autonomic functions., Genetic metabolic disorder affecting absorption of essential amino acids., Genetic metabolic disorder affecting processing of leucine amino acid. Also see Branched-Chain Ketoaciduria, and Maple Syrup Urine Disease., Group of eye diseases that can cause optic nerve damage and vision loss. Also see Eye Glaucoma, and Eyes Glaucoma., Headache is the symptom of pain anywhere in the region of the head or neck. It occurs in migraines (sharp, or throbbing pains), tension-type headaches, and cluster headaches. Frequent headaches can affect relationships and employment.There is also an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions whether serious or not. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society. Causes of headaches may include dehydration, fatigue, sleep deprivation, stress, the effects of medications, the effects of recreational drugs, viral infections, loud noises, common colds, head injury, rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage, and dental or sinus issues.Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication. A headache is one of the most commonly experienced of all physical discomforts.About half of adults have a headache in a given year.Tension headaches are the most common, affecting about 1.6 billion people (21.8% of the population) followed by migraine headaches which affect about 848 million (11.7%)., Intense sexual arousal by atypical objects, situations, or individuals., Lysosomal storage disease affecting the growth and development of myelin nerve sheath. See Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Malformations of lymphatic system with large or microscopic cysts., Meandering bright red tracks in skin caused by Hookworm infection. Also see Ancylostoma programs, and Creeping Eruption., Rare congenital defect with incomplete development of ear, nose, soft palate, lip, and mandible, and organ problems., See Stye program. Use Staphylococcus Infection program., Skin and eye disease due to loa loa nematode worm transmitted by deer fly and mango fly., STD with painful genital sores., Symptoms arising from presence of two or more X chromosomes in males, primarily sterility. |
| 517500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Agammaglobulinemia, Amino Acid Metabolism, Anemia Hemolytic, Aniridia, Ascorbic Acid Deficiency, Autistic Disorder, Berylliosis, Borna Disease, Brucellosis, Canavan Disease, Cancer Testicular, Capgras Syndrome, Cartilage Diseases, Central Nervous System Diseases, Central Nervous System Infections, Chicken Pox, Chondroma, Cryptococcosis, Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia, Cyclothymic Disorder, Gassers Syndrome, Gastritis Hypertrophic, Gastroenteritis, Optic Atrophies Hereditary, Pagets Disease Mammary, Pagets Disease of Bone, Pantothenate Kinase-Associated Neurodegeneration, Parasites Fasciola hepatica rediae, Von Hippel-Lindau Disease | Abnormal breakdown of red blood cells.Blood, Absence of irises, usually in both eyes - can be congenital or due to injury.Eye, Also called Bangs Disease. Causes fever, GI tract and other serious problems., Also called Cyclothymia. Chronic mood disorder less severe than Bipolar Disorder., Also called Hemolytic-uremic Syndrome. Disease with hemolytic anemia, acute kidney failure, and low platelet count, usually in children. Also use E Coli and Shigella programs., Also called MŽnŽtriers Disease. Premalignant condition with inflammation of gastric mucosa., Also called Osteitis Deformans, or Osteitis. Condition with deranged bone remodelling, leading to enlarged and/or misshapen bones., Also called scurvy. Vitamin C deficiency. See Avitaminosis, Vitamin C Deficiency, and other deficiency programs., Belief that someone known has been replaced by an impostor. Thought to be due to neuroanatomical damage., Benign tumor in cartilage., Cartilage is the tough but flexible tissue that covers the ends of your bones at a joint. It also gives shape and support to other parts of your body, such as your ears, nose and windpipe. Healthy cartilage helps you move by allowing your bones to glide over each other. It also protects bones by preventing them from rubbing against each other.Injured, inflamed, or damaged cartilage can cause symptoms such as pain and limited movement. It can also lead to joint damage and deformity. Causes of cartilage problems includeTears and injuries, such as sports injuriesGenetic factorsOther disorders, such as some types of arthritisOsteoarthritis results from breakdown of cartilage., Central nervous system diseases, also known as central nervous system disorders, are a group of neurological disorders that affect the structure or function of the brain or spinal cord, which collectively form the central nervous system (CNS).Every disease has different signs and symptoms. Some of them are persistent headache; pain in the face, back, arms, or legs; an inability to concentrate; loss of feeling; memory loss; loss of muscle strength; tremors; seizures; increased reflexes, spasticity, tics; paralysis; and slurred speech. One should seek medical attention if affected by these., Chronic lung disease due to beryllium exposure., Degenerative brain with iron accumulation disease leading to Parkinsons Disease, dementia, dystonia, and death., Degenerative genetic cerebral disease involving neuronic myelin damage., Free-living sheep liver fluke larvae with sucker. See Parasites Flukes Sheep Liver, Parasites Sheep Liver Flukes, and Liver Flukes., Genetic disorder affecting vision, heart, and circulatory system, with possible brain and spine tumors., Infections of the nervous system are potential life-threatening and are caused by pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, and fungi. Prompt recognition and treatment of a central nervous system (CNS) infection is crucial for patient survival, as these infections have a high morbidity and mortality. CNS infections include meningitis, encephalitis, and brain abscesses., Infectious neuro syndrome causing abnormal behaviour and possible death, due to BDV., Inflammation of GI tract involving stomach and small intestine. Drink lots of fluids and replace salts., Normalisation.Cell, Now called Bronchiolitis Obliterans Organizing Pneumonia. Non-infectious, with many possible causes., Primary immune deficiency disease. Synonymous with Hypogammaglobulinemia., Progressive optic nerve damage with symmetric bilateral central visual loss., See Autism., See Herpes Zoster., There are several inflammatory rheumatic diseases that lead to arthritis and can severely damage cartilage tissue. These include rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, gout, systemic lupus erythematosus, and seronegative spondyloarthropathies., Type of malignant breast cancer with appearance of eczema, usually affecting nipple and areola. Also see appropriate Cancer programs., Use Blood Cleanser., Yeast infection that starts in lungs and can cause meningitis and other problems. Also see Torulopsis programs. |
| 525150 | Spooky2 ETDF | Retinitis Pigmentosa | Inherited degenerative eye disease with severe vision impairment due to degeneration of rod photoreceptor cells in retina. |
| 526500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Distal Trisomy | Genetic condition with slow postnatal growth and serious intellectual problems. |
| 527400 | Spooky2 KHZ | Stuttering | Also see Stammering program. |
| 535230 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Respiratory Tract Neoplasms, Cancer: Respiratory Tract | Cancer of the Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses Malignancies arising from the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses are relatively rare tumors of the head and neck. They account for only 3% of all upper respiratory tract cancers, with a yearly incidence of 1 per 100,000 people., Includes Laryngeal and Lung Cancers. |
| 535590 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Hyperthyroidism | Excess production of thyroid hormone, leading to Thyrotoxicosis. |
| 537300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mal de Debarquement | Also called Disembarkation Syndrome. Neurological condition with prolonged motion sickness and distress after travel. |
| 540000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Digestive System | Gastro-Intestinal (GI) cancer is a term for the group of cancers that affect the digestive system. This includes cancers of the oesophagus, gallbladder & biliary tract, liver, pancreas, stomach, small intestine, bowel (large intestine or colon and rectum), and anus. GI cancer is the most common form of cancer., The digestive or gastrointestinal (G.I.) system is made up of the esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. These organs work together to break down the food you eat into nutrients that are absorbed by the bloodstream and carried to all of the cells in your body. This is what gives your body the vital fuel it needs to function.Facts about Digestive CancersColorectal cancer is the #3 diagnosed cancer in the US and the #2 cause of cancer related death in men and women. Many digestive cancers are found in later stages, but colorectal cancer can be found and treated in earlier stages or even prevented due to screening exams.The American Cancer Society reports that even though colorectal cancer is found more often in people ages 50 and older, its on the rise in people under age 50. A study from 1974-2013 found a 1% increase per year in the colon cancer incidence of people 20-49; and an increase per year in the new cases of rectal cancer in adults 20-39 (3%) and 40-54 (2%).The Pancreatic Cancer Action Network reports that pancreatic cancer is expected to be the second cause of cancer-related death by 2020.According to the Esophageal Cancer Action Network, Esophageal cancer caused by long-time GERD (adenocarcinoma) is one of the fastest growing cancers in the US.The CDC reports that liver cancer is increasing approximately 2.3% per year and the death rate is growing rapidly at 3% per year. The cause of this increase is credited mostly to an increase in the cases of Hepatitis C especially in the baby boomer generation. |
| 545310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Digestive System Diseases, Digestive System Surgical Procedures | Stomach and intestines. |
| 553500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mutism, Otosclerosis | Abnormal growth of bone near middle ear which can lead to hearing loss., Inability to speak often caused by speech disorder, hearing loss, or surgery. |
| 555300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia | Cardiac arrhythmia caused by heart muscle genetic defects. |
| 557820 | Spooky2 ETDF | Macular Degeneration | Age-related diminution or blurring of center of visual field. Use with Cataract programs. |
| 561510 | Spooky2 ETDF | Peripheral Nervous System Diseases, Peripheral Vascular Diseases | Disorders affecting nerves which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function., Narrowing of arteries other than those that supply the heart or brain, |
| 562500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cleidocranial Dysplasia, Coronaviridae Infections, Empyema Pleural, Evans Syndrome, Factor X Deficiency, Legionellosis, Rat Bite Fever | Accumulation of pus in pleural cavity, usually in Pneumonia., Also called Cleidocranial Dysostosis. Congenital disorder with delayed ossification of skeletal midline., Also called Legionnaires Disease. See Legionella programs., Autoimmune disease where antibodies attack red blood cells and platelets., Coagulation system deficiency of enzyme necessary for blood clotting., Rare serious condition caused by contact with rodent bites, urine, or secretions. Also try Streptothrix programs., Upper respiratory and GI tract infections. |
| 567000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adie Syndrome | Neurological disorder causing dilation problems with eye pupils.Nerve Eye |
| 570510 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Liver Cancer, Essential Tremor | Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach.Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung or breast and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer. This type of cancer is named after the organ in which it began such as metastatic colon cancer to describe cancer that begins in the colon and spreads to the liver., Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen., Most common movement disorder affecting finger, hands, arms, and sometimes other parts of the body. |
| 571500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Robinow Syndrome | Very rare genetic disorder with short-limbed dwarfism, abnormalities in head, face, and external genitalia, and vertebral segmentation. |
| 575280 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Salmonella Enteriditis Gut, Salmonella Infections, Samters Syndrome | Bacteria causing food poisoning or blood infections in sub-Saharan Africa., Condition where asthma is induced by aspirin or other NSAIDs. Also see Asthma and related programs. |
| 575370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Blounts Disease, Cancer Osteosarcoma | Aggressive malignant bone tumor in children and young adults. Other use: Osteochondritis., Blounts disease is a growth disorder of the tibia (shin bone) that causes the lower leg to angle inward, resembling a bowleg. It is also known as tibia vara. |
| 596520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Miller Fisher Syndrome | Subtype of Guillain-Barre Syndrome, usually without limb weakness. |
| 607500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Eczema, Menstruation Disturbances, Nail Disease | Also called Dermatitis. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches.Skin, Also see Dysmenorrhea, and Endometriosis programs., Thisconditionmay follow certaindiseasessuch as syphilis, or can result from fever, trauma, systemic upsets or adverse reaction to drugs. Onychorrhexis also known as brittlenails, is brittleness with breakage offingernailsor toenails. |
| 607590 | Spooky2 ETDF | Phobic Disorders | Anxiety disorders characterised by fear of objects or situations. |
| 621810 | Spooky2 ETDF | Ear Diseases | Ear infections are the most common illness in infants and young children. Tinnitus, a roaring in your ears, can be the result of loud noises, medicines or a variety of other causes.Ear |
| 622530 | Spooky2 ETDF | Bedsores, Pneumothorax | Abnormal accumulation of air or gas in pleural spaces. Also see Pleural Diseases., Also called Pressure ulcers. |
| 625230 | Spooky2 ETDF | Menieres Disease | Auditory vertigo associated with deafness and tinnitus. See Deafness, Otitis, and Tinnitus programs. Use General Antiseptic. |
| 625680 | Spooky2 ETDF | Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome | Rare neurological disorder with recurring facial paralysis, swelling of face and lips, and folds and furrows in tongue. |
| 631170 | Spooky2 ETDF | Labyrinthitis | Inflammation of inner ear, leading to Vertigo, Hearing Loss, or Tinnitus. Also see Vestibular Neuronitis, and Labyrinth Diseases. |
| 635310 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Dejerine-Sottas Disease, Refsum Disease | Also called CharcotÐMarieÐTooth disease type 3., Genetic neurological condition caused by excessive phytanic acid in cells and tissues. |
| 638190 | Spooky2 ETDF | Frigidity, Sexual (Male) erectile dysfunction, Sexual Disorders General program | Erectile dysfunction (impotence) is the inability to get and keep an erection firm enough for sex. Having erection trouble from time to time isnt necessarily a cause for concern., Failure of a female to respond to sexual stimulus; aversion on the part of a woman to sexual intercourse; failure of a female to achieve an orgasm (anorgasmia) during sexual intercourse., Sexual dysfunction generally is classified into four categories: Desire disorders Nlack of sexual desire or interest in sex. Arousal disorders Ninability to become physically aroused or excited during sexual activity. Orgasm disorders Ndelay or absence of orgasm. |
| 642060 | Spooky2 ETDF | Alkalosis, Angelman Syndrome, Antithrombin III Deficiency, Blue Rubber Bleb Nevus Syndrome, Cushing Syndrome, Ventricular Fibrillation, Xanthomatosis | Caused by prolonged exposure to cortisol, either from medications or due to a tumor., Hereditary disorder with recurring venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and fetal death., Lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in large foam cells in skin lesions, with chronic biliary tract obstruction, and primary Biliary Cirrhosis. Also see Biliary Atresia, Biliary Tract Diseases, and Hyperlipidemia Familial Combined., May be respiratory, metabolic, or combined., Neuro-genetic disorder with intellectual and developmental disabilities., Uncoordinated contraction of the ventricular heart muscles, usually leading to cardiac arrest - see Myocardial Infarction, and use caution., Venous malformations in the GI tract and on skin. |
| 652500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Purpura Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic | Rare disorder of blood coagulation, causing many microscopic clots to form in small blood vessels. |
| 654030 | Spooky2 ETDF | Polyarteritis Nodosa | Systemic vasculitis of small- or medium-sized muscular arteries, usually involving renal and visceral vessels but not pulmonary circulation. |
| 655200 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Amblyopia, Amniotic Band Syndrome, Aortic Valve Stenosis, Arteriovenous Malformations, Barretts Esophagus, Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome, Bone Diseases, Broncho Pulmonary Dysplasia, Cancer Bladder, Cancer Lung Non-Small Cell, Cancer Lung Small Cell, Cancer Malignant Mesothelioma, Cataract, Chondromalacia Patellae, Dysentery, Epilepsy, Fabry Disease, Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Disease, Metabolic Stress, Septo-Optic Dysplasia, Shock Hemorrhagic, Skin Diseases, Skin Ulcer, Smith-Lemli-Opitz Syndrome, Stress Disorders Post-Traumatic, Tick Paralysis, Typhus Epidemic Louse-Borne, Urea Cycle Disorders | Abnormal artery-vein connections, bypassing capillaries, normally in the CNS., Abnormal cell change of lower esophagus caused by chronic acid exposure., Abnormal cell changes, usually pre-cancerous., Acute diarrhea with blood and mucus. Also see Entamoeba Histolytica, Shigella, and appropriate Salmonella and Campylobacter programs., Affects lungs and organ linings. Asbestos-related. Other use: fatty liver., Also see Bladder TBC, Cancer Bladder TBC, Cancer Urethral, Parasites, and Schistosoma. Use Blood Cleanser., Caused by toxin produced by tick salivary gland, injected after prolonged bite., Clouding of lens of eye. Also see Eye and Eyes programs., Conditions of human integumentary system., Congenital - due to trapping of fetal limbs by fibrous bands while in utero., Disorder due to metabolic reaction to stress produced by events, substances, activities, worries, or the like., Epilepsy is a central nervous system (neurological) disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness.Anyone can develop epilepsy. Epilepsy affects both males and females of all races, ethnic backgrounds and ages.Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people with epilepsy simply stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure, while others repeatedly twitch their arms or legs. Having a single seizure doesnt mean you have epilepsy. At least two unprovoked seizures are generally required for an epilepsy diagnosis.Treatment with medications or sometimes surgery can control seizures for the majority of people with epilepsy. Some people require lifelong treatment to control seizures, but for others, the seizures eventually go away. Some children with epilepsy may outgrow the condition with age., Genetic disorder with deficiency of enzyme to remove ammonia from blood. May be useful for Lyme., Genetic predisposition to Basal Cell Carcinoma development., Inborn error of cholesterol synthesis causing multiple physical malformations., Includes Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Large Cell Carcinoma, and Adenocarcinoma., Inflammation of the back of the kneecap and softening of cartilage., Lazy eye., Life-threatening condition with low blood distribution to tissues, causing cell injury and inadequate tissue function., More metastatically aggressive than other lung cancers. Also called Oat Cell Carcinoma., Narrowing of aortic valve of the heart.Heart, Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition thats triggered by a terrifying event N either experiencing it or witnessing it. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares and severe anxiety, as well as uncontrollable thoughts about the event., Rare congenital malformation syndrome with underdevelopment of optic nerve, pituitary gland dysfunction, and absence of septum pellucidum (part of brain). Also see Schizencephaly., Rare genetic lysosomal storage disorder with a wide range of systemic symptoms., Skin lesion exhibiting complete loss of epidermis and often portions of dermis and even subcutaneous fat., Use Rickettsia, and Lice Infestations programs., Very rare inherited prion disease, usually familial., Your bones help you move, give you shape and support your body. They are living tissues that rebuild constantly throughout your life. During childhood and your teens, your body adds new bone faster than it removes old bone. After about age 20, you can lose bone faster than you make bone. To have strong bones when you are young, and to prevent bone loss when you are older, you need to get enough calcium, vitamin D, and exercise. You should also avoid smoking and drinking too much alcohol.Bone diseases can make bones easy to break. Different kinds of bone problems includeLow bone density and osteoporosis, which make your bones weak and more likely to breakOsteogenesis imperfecta makes your bones brittlePagets disease of bone makes them weakBones can also develop cancer and infectionsOther bone diseases, which are caused by poor nutrition, genetics, or problems with the rate of bone growth or rebuilding |
| 671220 | Spooky2 ETDF | Multiple Sclerosis | Demyelinating disease. Aspartame, mercury, benzene, lead, and toluene can cause same symptoms. Use Chlamydia General, Herpes Type 6, and see ALS, Herpes General, Blastocystis Hominis, Parasites Flukes, Shigella, Nocardia, and Herpes Zoster programs. |
| 673110 | Spooky2 ETDF | Heart Catheterization | Note: cardiac conditions are inherently unstable. |
| 673290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Neurocysticercosis | Infection of brain by Taenia solium, a pork tapeworm. |
| 675000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dyslipidemias, Influenza Bird H5N1 | Abnormal amounts of lipids in the blood., Strains of the influenza virus that primarily infect birds, but can also infect humans. |
| 675360 | Spooky2 ETDF | Erysipelas | Infection normally with red facial, arm, or leg rash. Usually due to Streptococcus Pyogenes or other family members (see Streptococcal Infections). |
| 675540 | Spooky2 ETDF | Erdheim-Chester Disease | Abnormal multiplication of histiocyte white blood cells affecting bones and bone marrow. |
| 677787.7878 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cytomegalovirus CMV 1 | Herpes Type 5. Dowsed by Newport. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs. |
| 678510 | Spooky2 ETDF | Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome | Life-threatening nerological disorder most commonly caused by neuroleptic/antipsychotic drugs. |
| 682020 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Anemia Iron-Deficiency, Arthritis Rheumatoid, Brain Abscess, Cancer Lip and Oral Cavity, Cancer Mouth, Cancer Oral, Chancroid, Fistula, Goldenhar Syndrome, Hematologic Diseases, Hirsutism, Jacobsen Syndrome, Lyme Borreliosis, Lyme Disease, Pain, Pulmonary Edema, Spinal Stenosis, Syringomyelia, Thymoma, Tularemia | Abnormal connection between two hollow organs, intestines, or blood vessels., Abnormal narrowing of spinal canal causing neurological deficit., Also called Borreliosis., Cancer that develops in any part of the mouth., Decreased red blood cells and hemoglobin due to insufficient iron., Disorder where a cyst or cavity forms within spinal cord, resulting in pain, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness., Disorders primarily affecting the blood., Excessive hair growth in women in areas where terminal hair is normally absent or minimal., Fluid accumulation in air spaces and parenchyma of lungs., Look under name of condition causing pain., Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by a bacterium named Borrelia spread by ticks. The most common sign of infection is an expanding area of redness on the skin, known as erythema migrans, that appears at the site of the tick bite about a week after it occurred., May be due to Aspergillus, Zygomycota, or Fusarium molds., Muscles and tendons. May be due to bacteria like Chlamydia Pneumoniae. Use General Antiseptic and Parasites General if no response. See Bursitis., Rare congenital defect with incomplete development of ear, nose, soft palate, lip, and mandible, and organ problems., Rare congenital disorder with intellectual disabilities, facial/skeletal and heart defects, and a variety of other problems., Serious tick and arthropod borne infection with lesions and fever, spreading to lungs, lymphatic system, liver, and spleen. Use Francisella Tularensis., STD with painful genital sores., Uncommon tumor of thymus, most associated with Myasthenia Gravis. Also see Cancer Thymoma programs., Use Blood Cleanser., Use Blood Cleanser. Also use for cancers of paranasal sinus, nasal cavity, salivary gland, and lip. |
| 684810 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Afibrinogenemia, Alopecia, Anemia Hemolytic, Aphasia, Arteriosclerosis, Birt-Hogg-Dube Syndrome, Brown Sequard Syndrome, Cancer Genital Male, Cancer Genital Neoplasms Male, Capgras Syndrome, Cerebral Gigantism, Gassers Syndrome, Strabismus, Temporomandibular Joint Disorders, Tricuspid Atresia, Vitiligo, XYY Karyotype | Abnormal breakdown of red blood cells.Blood, Abnormal growths or tumors. Use Blood Cleanser., Also called Hemolytic-uremic Syndrome. Disease with hemolytic anemia, acute kidney failure, and low platelet count, usually in children. Also use E Coli and Shigella programs., Also called Sotos Syndrome. Excessive physical growth in early years., Belief that someone known has been replaced by an impostor. Thought to be due to neuroanatomical damage., Blood clotting disorder.Blood, Congenital heart disease with complete absence of tricuspid valve., Damage to one side of spinal cord, causing paralysis and loss of proprioception on that side, and loss of pain and temperature sensation on the other., Eye squint, commonly called crossed eyes. Also see Esotropia and Eye programs., Genetic condition where a male has one extra male chromosome, associated with increased early growth, slightly lower IQ, and learning difficulties., Genetic disorder causing predisposition to kidney cancer, cysts, and fibrofolliculomas., Hardening of arteries. Regeneration takes time. Try CMV programs., Language/speech disorders.Brain, Loss of hair., Loss of pigmentation in areas of skin. Use with B Complex with extra PABA internally and PABA Cream topically. See E Coli, Parasites General, and Fungus programs if required., Pain and dysfunction of jaw muscles and joint, with restricted movement and noises., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 691020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dermatitis Exfoliative, Popliteal Cyst | Also called Erythroderma. Causes reddening and scaling of skin over almost the entire body., Benign swelling of the semimembranosus or other synovial bursa behind the knee joint. Found in Lyme Disease. |
| 692010 | Spooky2 ETDF | Inflammation | Inflammation (from Latin: inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. |
| 692100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lichen Planus | Skin and/or mucous membrane disease that resembles lichen, with unknown cause. |
| 695610 | Spooky2 ETDF | Miller Fisher Syndrome | Subtype of Guillain-Barre Syndrome, usually without limb weakness. |
| 697500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Pheochromocytoma, Facial Nerve Diseases, Facial Neuralgia, Graves Disease, Rat Bite Fever, Retropharyngeal Abscess, Rosacea, Sandhoff Disease | Abscess in throat tissues behind posterior pharyngeal wall. Also see Abscesses programs., Autoimmune disorder affecting thyroid gland, often causing Hyperthyroidism and enlargement. Also see Hyperthyroid programs., Facial pain info, trigeminal neuralgia is an inflammation of the trigeminal nerve causing extreme pain and muscle spasms in the face.Face, Includes facial paralysis.Face, Long term skin condition with facial redness, small dilated blood vessels on face, papules, pustules, and swelling. May be associated with Demodex Folliculorum mites., Neuroendocrine tumor of medulla of adrenal glands., Rare lysosomal genetic lipid storage disorder with progressive nervous system destruction., Rare serious condition caused by contact with rodent bites, urine, or secretions. Also try Streptothrix programs. |
| 705870 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Kawasaki Disease, Mucocutaneous Lymph Node Syndrome, Multicystic Dysplastic Kidney | Also called Kawasaki Disease. Autoimmune disease, mainly in children, with inflammation and vasculitis in medium-sized blood vessels., Autoimmune disease with inflammation of medium-sized blood vessels. Most common in under-5s., Genetic condition caused by malformed kidneys consisting of variously-sized cysts. |
| 706500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Endoscopy | Medical procedure that uses a small camera on a tube to look inside the body. |
| 708570 | Spooky2 ETDF | Distal Trisomy, Embryopathies | Developmental disorders or diseases in embryos., Genetic condition with slow postnatal growth and serious intellectual problems. |
| 709830 | Spooky2 ETDF | Adenomatous Polyposis Coli (APC), Animal Diseases, Aspergillosis, Biliary Tract Diseases, Breast Cyst, Breast Diseases, Cherubism, Hypotension, POEMS Syndrome, Vitamin B12 Deficiency, Zellweger Syndrome | Being deficient in vitamin B-12 causes physical and psychological symptoms, including nerve problems, fatigue, and difficulty thinking., Diseases of animals, Fluid-filled sac in breast. Generally benign., Genetic disorder causing prominence of lower part of face., Infection by Aspergillus fungi, mainly pulmonary. Also see Aspergillus and Aflatoxin., Low blood pressure., Most women experience breast changes at some time. Your age, hormone levels, and medicines you take may cause lumps, bumps, and discharges (fluids that are not breast milk).If you have a breast lump, pain, discharge or skin irritation, see your health care provider. Minor and serious breast problems have similar symptoms. Although many women fear cancer, most breast problems are not cancer., One of the most common causes of extrahepatic biliary obstruction is choledocholithiasis, with one or more stones in the common bile duct or common hepatic duct causing biliary obstruction., Protein encoded by APC gene, a tumor suppressor.DNA, Rare congenital disorder with reduction or absence of functional peroxisomes in cells. Also see Peroxisomal Disorders, Adrenoleukodystrophy, Leukodystrophy, Refsum Disease, and Lysosomal Storage Diseases., Rare syndrome with plasma-cell proliferative disorder (usually myeloma), polyneuropathy, and effects on many other organ systems. See Myeloproliferative Disorders and Polyneuropathies. |
| 713340 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Eosinophilia | Condition where count of eosinophil white blood cells is abnormally high, usually indicating parasites or allergic reaction. |
| 715230 | Spooky2 ETDF | Incontinentia Pigmenti | Genetic disorder affecting skin (various types of lesions), hair, teeth, nails, and CNS. |
| 717210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Clostridium Enterocolitis | Also called Clostridium Difficile. Can cause diarrhea following treatment with antibiotics. |
| 719010 | Spooky2 ETDF | Jobs Syndrome | Group of genetic immune disorders with recurrent staphylococcal and severe lung infections as well as facial, dental, and skeletal abnormalities. |
| 720000 | Spooky2 RIFE | Streptococcus Pyogenes | Crane=880, Rife (1936)=8450. Also called Group A beta-haemolytic Strep (GAS). Causes Sore Throat, skin inflammation, Scarlet Fever, Pharyngitis, Impetigo, Erysipelas, Frozen Shoulder, Cellulitis, Septicemia, Toxic Shock Syndrome, and acute Glomerulonephritis, and Beta Streptococcus. Use General Antiseptic. |
| 721620 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dermoid Cyst | Tumor, usually benign, that contains tissue types inconsistent with its location. |
| 722520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Migraine Disorders | Also use Parasites Strongyloides, and Parasites General programs. |
| 722700 | Spooky2 ETDF | Coccidioidomycosis, Depressive Disorder, Retinoschisis, Rift Valley Fever | Also called Clinical Depression or Unipolar Disorder. Also see Depression programs., Eye disease with abnormal splitting of retinas neurosensory layers, usually in the outer layer., Fungal infection by Coccidiodes Immitis - see this program. Usually respiratory, and can involve fever, muscle/joint pain, rash/lesions, and headache., Viral disease that can cause mild to life-threatening symptoms, usually contracted from infected animals, or by infected mosquito bites. |
| 724500 | Spooky2 KHZ | Breast Neoplasms Male | Lump which may be malignant or benign. |
| 725310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Prosthesis Implantation, Protozoan Infections | An artificial device used to replace a missing body part, such as a limb, tooth, eye, or heart valve, or replacement of a missing body part with such a device., Disorders caused by unicellular eukaryotic organisms, including Malaria, Amoebiasis, Giardiasis, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptosporidiosis, Trichomoniasis, Chagas Disease, Leishmaniasis, and others. |
| 735300 | Spooky2 ETDF | Costello Syndrome | Also called FCS Syndrome. Rare genetic disorder that affects many part of the body. |
| 742500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Congenital Abnormalities, Congenital Fiber Type Disproportion | Congenital anomalies are also known as birth defects, congenital disorders or congenital malformations. Congenital anomalies can be defined as structural or functional anomalies (e.g. metabolic disorders) that occur during intrauterine life and can be identified prenatally, at birth or later in life., Congenital anomalies are important causes of infant and childhood deaths, chronic illness and disability. Through the resolution on birth defects of the Sitxty-third World Health Assembly (2010), Member States agreed to promote primary prevention and improve the health of children with congenital anomalies by:developing and strengthening registration and surveillance systemsdeveloping expertise and building capacitystrengthening research and studies on etiology, diagnosis and preventionpromoting international cooperation., Muscular condition that may accompany some neurological disorders. |
| 747000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mastoiditis | Inflammation of bony structure of the skull behind ears below eye level. |
| 751770 | Spooky2 ETDF | Microvascular Angina | Type of coronary heart disease that affects the arterioles and capillaries. Can be caused by Herpes Simplex virus 1 and the bacterium Chlamydia pneumoniae. |
| 753210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypercalcemia | Excess calcium in the blood. See appropriate Calcium programs, and Calcifications. |
| 756720 | Spooky2 ETDF | Nonverbal Learning Disorder | Neurological disorder characterized by verbal strengths and visual-spatial, motor, and social skills difficulties. |
| 761850 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome, Arthritis Juvenile Chronic, Arthritis Juvenile Rheumatoid, Sprengels Deformity, Syphilis Congenital, Taeniasis, Tourette Syndrome | Caused by infection of tapeworm - pork, beef, or Taenia Asiatica. See Parasites Taenia, Taenia, Parasites Tapeworm, Tapeworm, Cysticercosis, and Neurocysticercosis programs., Impairs male sexual development., Inherited disorder with multiple motor tics and at least one vocal tic., Juvenile idiopathic arthritis, formerly known as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, is the most common type of arthritis in children under the age of 16.Juvenile idiopathic arthritis can cause persistent joint pain, swelling and stiffness. Some children may experience symptoms for only a few months, while others have symptoms for the rest of their lives.Some types of juvenile idiopathic arthritis can cause serious complications, such as growth problems, joint damage and eye inflammation. Treatment focuses on controlling pain and inflammation, improving function, and preventing joint damage., Rare congenital skeletal abnormality where one shoulder blade sits higher on the back than the other., Use Streptococcus Pneumonia, and Mycoplasma General if needed. See Bursitis., Use Treponema Pallidum, and see Luesinum and Syphilinum programs. |
| 772200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Movement Disorder | Includes tremors, palsy, choreas, akathisia, tardive dyskinesia, dystonias, RLS, tics, spasms, and others - also see appropriate programs. |
| 772290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptococcosis | Yeast infection that starts in lungs and can cause meningitis and other problems. Also see Torulopsis programs. |
| 773910 | Spooky2 ETDF | Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation | Formation of blood clots throughout the body, usually in critical illnesses. |
| 775170 | Spooky2 ETDF | Choledochal Cyst | Also called bile duct cysts. |
| 775350 | Spooky2 ETDF | Erdheim-Chester Disease | Abnormal multiplication of histiocyte white blood cells affecting bones and bone marrow. |
| 778500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Erythema | Redness of skin or mucous membranes from injury, infection, or inflammation. |
| 791280 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | EBV Infections, Epstein Barr Virus Infections | Also called Epstein Barr Virus, or Human Herpesvirus 4. Causes mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and HIV. Also see Infectious Mononucleosis and Mononucleosis., Herpes virus causing Mononucleosis, also called Infectious Mononucleosis or Glandular Fever - see programs for these, and see EBV programs. |
| 792000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer, Cancer Cervical, Cervix Incompetence, Uterine Cervical Incompetence | Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread., Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix N the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer.Uterus, Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina.Various strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer.When exposed to HPV, a womans immune system typically prevents the virus from doing harm. In a small group of women, however, the virus survives for years, contributing to the process that causes some cells on the surface of the cervix to become cancer cells.You can reduce your risk of developing cervical cancer by having screening tests and receiving a vaccine that protects against HPV infection.Cervical cancer care at Mayo ClinicSymptomsFemale reproductive organsFemale reproductive systemEarly-stage cervical cancer generally produces no signs or symptoms.Signs and symptoms of more-advanced cervical cancer include:Vaginal bleeding after intercourse, between periods or after menopauseWatery, bloody vaginal discharge that may be heavy and have a foul odorPelvic pain or pain during intercourseUterus, Condition where cervix begins to dilate and thin before pregnancy has reached term., Premature dilatation and thinning of cervix causing possible miscarriage or preterm birth. |
| 792900 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Diabetes Insipidus | Characterized by excessive thirst and urination. |
| 795690 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cystic Fibrosis | Also called Mucoviscidosis. Use Pseudomonas Aeruginosa, Breathing Deep, and General Antiseptic programs. See Parasites General, and Roundworm programs if no progress. |
| 796500 | Spooky2 ETDF | Communication Disorders, Digestive System Diseases, Digestive System Surgical Procedures, Gangrene, Genital Diseases Female, Retinal Detachment, Robinow Syndrome, Schizencephaly | A female genital disease is a condition that affects the female reproductive system., Affects ability to communicate., Eye disorder due to fluid leaking behind the retina through physical damage, by traction, or by fluid exuding from the retina., Rare birth defect with abnormal brain clefts causing symptoms including epilepsy, motor deficits, and psychomotor retardation., Stomach and intestines., Tissue necrosis due to insufficient blood supply. Also see Clostridium, Circulatory Stasis, Infections General, and Bacterium Coli programs., Very rare genetic disorder with short-limbed dwarfism, abnormalities in head, face, and external genitalia, and vertebral segmentation. |
| 799877.88 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cytomegalovirus CMV 1 | Herpes Type 5. Dowsed by Newport. Also see CMV, Salivary Gland Virus, HHV5, and Herpes Type 5 programs. |
| 802440 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dermatomyositis | Connective tissue disease affecting skin, muscles, and possibly heart, lungs, esophagus, and joints. |
| 813960 | Spooky2 ETDF | Alagille Syndrome, Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome | Genetic disorder affecting major organs., Rare autoimmune disorder with weakness of limb muscles, often accompanying cancer, typically small cell lung cancer. |
| 814500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Factor X Deficiency | Coagulation system deficiency of enzyme necessary for blood clotting. |
| 815580 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Multiple Myeloma, Cancer Multiple Myeloma/Plasma Cell Neoplasms | Plasma cell blood cancer arising in bone marrow. Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 821430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dandy-Walker Syndrome | Congenital brain malformations. |
| 821520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Platelet Storage Pool Deficiency | Blood coagulation disorder. |
| 822060 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dermatitis, Dermatitis Exfoliative | Also called Eczema. Skin condition with itchy, weeping, crusting patches., Also called Erythroderma. Causes reddening and scaling of skin over almost the entire body. |
| 823410 | Spooky2 ETDF | Helicobacter Pylori, Keratitis Ulcerative | Also called Corneal Ulcer. Inflammatory or infective condition., Also called Heliobacter Pylori. See Ulcer programs. Usually present in Morgellons. |
| 824940 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypocalcemia | Low calcium levels in blood. |
| 825030 | Spooky2 ETDF | Renal Dialysis | Also see End Stage Renal Disease and appropriate kidney programs.Kidney |
| 825750 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cutis Laxa | Connective tissue disorder where the skin loses elasticity and hangs loose.Skin |
| 828000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Arthritis Post-infectious, Arthritis Reactive, Arthropathy Neurogenic | Rapidly destructive joint disease with impaired pain sensation., Use Streptococcus pneumonia, and Mycoplasma General if needed. See Bursitis., Use Streptococcus pPneumonia, and Mycoplasma general if needed. See Bursitis. |
| 831330 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Osteosarcoma, Sarcoma Osteogenic | Cancerous tumor of bone. See appropriate Cancer and Sarcoma programs., Malignant tumor in bone. Also see Osteosarcoma, Cancer Sarcoma, and BY Virus programs. |
| 832590 | Spooky2 ETDF | Myocarditis | Infection and inflammation of heart muscle, usually due to viruses such as Parvovirus B19, or to bacteria like Borrelial Burgdorferi, or parasites like Trypanosoma Cruzi. |
| 837000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Tenosynovitis, Tonsillitis | Inflammation of sheath surrounding tendon, most commonly bacterial in origin. Try Neisseria Gonorrheae program., Inflammation of tonsils, caused by viruses or bacteria. |
| 839340 | Spooky2 ETDF | Lassa Fever | Acute viral hemorrhagic fever similar to Ebola and with multiple symptoms. |
| 839430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Rheumatic Disease, Rheumatic Fever | Conditions causing chronic pain, often intermittent, affecting joints and/or connective tissue. See Rheumatism, Joint, Joints, and Connective Tissue programs, as well as specific body part programs., Rheumatic fever (RF) is an inflammatory disease that can involve the heart, joints, skin, and brain. The disease typically develops two to four weeks after a streptococcal throat infection. Signs and symptoms include fever, multiple painful joints, involuntary muscle movements, and occasionally a characteristic non-itchy rash known as erythema marginatum. |
| 840960 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Larynx | Laryngeal cancer occurs in the larynx, or voice box.The larynx is a short, triangular passageway just below the pharynx in the neck. It is about 2 inches wide.The larynx has three main parts:the glottis is the middle part of the larynx that contains the vocal cordsthe supraglottis is the tissue above the glottisthe subglottis is the tissue below the glottis that connects to the trachea, which takes air to the lungsCancer can develop in any part of the larynx but usually begins in the glottis. Most laryngeal cancers start in the flat, scale-like squamous cells that line the inner walls of the larynx., Use Blood Cleanser. |
| 845100 | Spooky2 ETDF | Sialorrhea | Excessive production of saliva. Can be caused by radiation, antipsychotics and other drugs, toxic metals, and pesticides. |
| 845280 | Spooky2 ETDF | Rhabdoid Tumor | Very aggressive form of tumor originally described as a variant of Wilms Tumor, mainly a kidney tumor occurring mostly in children. Also see Cancer Wilms Tumor, and Wilms Tumor. |
| 846000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Chromosome 18 Abnormalities | Too many to list here. |
| 850320 | Spooky2 ETDF | Otosclerosis | Abnormal growth of bone near middle ear which can lead to hearing loss. |
| 852930 | Spooky2 ETDF | Nocturia | Having to wake from sleep to urinate. Also see Prostate programs. |
| 853020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Protozoan Infections | Disorders caused by unicellular eukaryotic organisms, including Malaria, Amoebiasis, Giardiasis, Toxoplasmosis, Cryptosporidiosis, Trichomoniasis, Chagas Disease, Leishmaniasis, and others. |
| 855720 | Spooky2 ETDF | Quadriplegia | Paralysis from illness or injury with partial or total loss of use of all four limbs and torso. |
| 862020 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cranial Nerve Diseases | Impaired functioning of one of the 12 cranial nerves. |
| 864000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Bedsores | Also called Pressure ulcers. |
| 871020 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypercalcemia | Excess calcium in the blood. See appropriate Calcium programs, and Calcifications. |
| 871200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Ecthyma Contagious | Also called Orf Disease. Viral skin disease mainly found in sheep and goats, but which can infect man. |
| 875340 | Spooky2 ETDF | Ectropion, Pityriasis | Eversion of the lower eyelid., Flaking or scaling of skin. |
| 875430 | Spooky2 ETDF | Fibrocystic Breast Disease | Non-cancerous breast lumps often related to menstrual cycle. Try Mastitis, and see Fascia programs. |
| 875520 | Spooky2 ETDF | Bergers Disease, Osteomalacia | Also called IgA Nephropathy. Inflammation of glomeruli of kidney., Softening of bones usually due to low phosphate or calcium levels. Called Rickets in children. |
| 879210 | Spooky2 ETDF | Embryopathies | Developmental disorders or diseases in embryos. |
| 879930 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptorchidism, Paraproteinemias | Absence of one or both testicles from scrotum - usually undescended., Excessive amounts of paraprotein or single monoclonal gammaglobulin in blood, usually due to underlying immunoproliferative disorder. |
| 881190 | Spooky2 ETDF | Keloid | Type of scar resulting from overgrowth of collagen at the site of a healed skin injury. |
| 882450 | Spooky2 ETDF | Food Poisoning | Food poisoning, also called foodborne illness, is illness caused by eating contaminated food. Infectious organisms including bacteria, viruses and parasites or their toxins are the most common causes of food poisoning.Infectious organisms or their toxins can contaminate food at any point of processing or production. Contamination can also occur at home if food is incorrectly handled or cooked.Food poisoning symptoms, which can start within hours of eating contaminated food, often include nausea, vomiting or diarrhea. Most often, food poisoning is mild and resolves without treatment. But some people need to go to the hospital.SymptomsFood poisoning symptoms vary with the source of contamination. Most types of food poisoning cause one or more of the following signs and symptoms:NauseaVomitingWatery or bloody diarrheaAbdominal pain and crampsFeverSigns and symptoms may start within hours after eating the contaminated food, or they may begin days or even weeks later. Sickness caused by food poisoning generally lasts from a few hours to several days. |
| 888030 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hemoglobinuria Paroxysmal, Hot Flashes | Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood characterized by destruction of red blood cells by the complement system, a part of the bodys innate immune system., Type of flushing due to low levels of estradiol, common in menopause. |
| 889905.78 | Spooky2 SD | Geranium Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 891000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Oculomotor Nerve Diseases | Paralysis of nerve due to trauma, Demyelinating Diseases, high intracranial pressure, brain Cancer, Hemorrhage, or microvascular diseases such as Diabetes - see appropriate programs. |
| 891270 | Spooky2 ETDF | Dracunculiasis | Infection of human or dog by guinea worm. Causes slowly moving burning pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting. |
| 900000 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Carbohydrate-Deficient Glycoprotein Syndrome, Syringomyelia, Thyroiditis | Disorder where a cyst or cavity forms within spinal cord, resulting in pain, paralysis, weakness, and stiffness., Inflammation of thyroid gland. Can be caused by drugs or radiation. Includes Hashimotos. Also see Hypothyroid, and Hypothyroidism programs., Now called Congenital Disorder of Glycosylation. Can cause serious organ system failure in infants. |
| 901170 | Spooky2 ETDF | Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation | Formation of blood clots throughout the body, usually in critical illnesses. |
| 905310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cancer Comprehensive, Cancer Leukemia, Retinoschisis | Begins in bone marrow, causing white blood cell abnormalities. Use Blood Cleanser. Also use for plasma cell neoplasms., ETDFL Focus on Leukemia, Lymphoma, Brain, Sarcomas, Blood, Bone Cancer, Eye disease with abnormal splitting of retinas neurosensory layers, usually in the outer layer. |
| 907110 | Spooky2 ETDF | Mastoiditis | Inflammation of bony structure of the skull behind ears below eye level. |
| 912330 | Spooky2 ETDF | Spinal Dysraphism, Stress Disorders Post-Traumatic, Strongyloidiasis | Also called Spina Bifida., Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a mental health condition thats triggered by a terrifying event N either experiencing it or witnessing it. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares and severe anxiety, as well as uncontrollable thoughts about the event., Roundworm which can infect human skin, lungs, and GI tract. Common in Morgellons. See Strongyloides, Parasites Strongyloides, and Parasites Threadworm. |
| 913500 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Osteosarcoma, Sarcoma Osteogenic | Cancerous tumor of bone. See appropriate Cancer and Sarcoma programs., Malignant tumor in bone. Also see Osteosarcoma, Cancer Sarcoma, and BY Virus programs. |
| 915480 | Spooky2 ETDF | Exanthema Subitum | Also called Roseola, or Sixth Disease. Febrile condition in very young children with red skin rash and three-day fever. |
| 915930 | Spooky2 ETDF | Rabies | Also known as hydrophobia. See Lyssavirus, and Lyssinum programs. |
| 921060 | Spooky2 ETDF | Diphyllobothriasis | Infection caused by Diphyllobothrium tapeworm, commonly Diphyllobothrium Latum. |
| 923310 | Spooky2 ETDF | Pterygium | A Pinguecula (Penqueculum?) is called a Pterygium if it invades the cornea of the eye. |
| 925290 | Spooky2 ETDF | Cryptosporidiosis | GI tract infection caused by the protozoan parasite Cryptosporidium. |
| 927000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Autoimmune Diseases, Choledochal Cyst, Colic, Dysautonomia Familial, HSAN Type IV, Onchocerciasis, Pityriasis | Also called bile duct cysts., Disorder of autonomic nervous system affecting its development and that of sensory nervous system., Flaking or scaling of skin., Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathy. Type IV has insensitivity to pain, inability to sweat and intellectual disability. Also see Hereditary Sensory and Autonomic Neuropathies program., Infection by Onchocerca Volvulus., Pain which starts and stops abruptly, usually due to contractions of tubular structure. Use Cramping and Nausea, and General Antiseptic programs., See Nanobacter and Human T Lymphocyte Virus1. Can be caused by Enteroviruses such as Coxsackie B virus, Epstein-Barr virus, Cytomegalovirus, Parvovirus B19, HIV, and by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis. |
| 943200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hydrocephalus Normal Pressure | Brain malfunction caused by decreased absorption of cerebrospinal fluid. |
| 951300 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | All Diabetes Comprehensive - Type 1 & 2 + Onset, Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes Mellitus Type 1, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 | Diabetes is a disease in which your blood glucose, or blood sugar, levels are too high. Glucose comes from the foods you eat. Insulin is a hormone that helps the glucose get into your cells to give them energy. With type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin., Due to insulin resistance, where cells dont respond to it correctly., Failure of pancreas to produce sufficient insulin. |
| 952200 | Spooky2 ETDF | Porphyrias | Several rare disorders of the nervous system and skin. |
| 956160 | Spooky2 ETDF | Melkersson-Rosenthal Syndrome | Rare neurological disorder with recurring facial paralysis, swelling of face and lips, and folds and furrows in tongue. |
| 971550 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ | Cancer Liver Cancer, Essential Tremor | Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen, beneath your diaphragm and above your stomach.Several types of cancer can form in the liver. The most common type of liver cancer is hepatocellular carcinoma, which begins in the main type of liver cell (hepatocyte). Other types of liver cancer, such as intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma, are much less common.Cancer that spreads to the liver is more common than cancer that begins in the liver cells. Cancer that begins in another area of the body such as the colon, lung or breast and then spreads to the liver is called metastatic cancer rather than liver cancer. This type of cancer is named after the organ in which it began such as metastatic colon cancer to describe cancer that begins in the colon and spreads to the liver., Liver cancer is cancer that begins in the cells of your liver. Your liver is a football-sized organ that sits in the upper right portion of your abdomen., Most common movement disorder affecting finger, hands, arms, and sometimes other parts of the body. |
| 975870 | Spooky2 ETDF | Hypercalcemia | Excess calcium in the blood. See appropriate Calcium programs, and Calcifications. |
| 981000 | Spooky2 ETDF | Encephalomyelitis | Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord. |
| 986220 | Spooky2 ETDF, Spooky2 KHZ, Spooky2 XTRA | Alpha-Mannosidosis, Anus Diseases, Arnold-Chiari Malformation, Biotinidase Deficiency, Cancer Head and Neck, Carpal Tunnel Syndrome, CHARGE Syndrome, Cholelithiasis, Osteoarthritis, Sepsis, Somatoform Disorders, Spinal Osteophytosis, Stiff-Person Syndrome, Sweat Gland Diseases, Syphilis Congenital, Tendinopathy, Tendonitis and Tibialis Posterior, Tetanus, Tinea, Tracheoesophageal Fistula, Venous Insufficiency, Vitreous Disorders | Abnormal connection between trachea and esophagus., Also spelt Tendinitis. Inflammation or tears in posterior tibial tendon, leading to flatfoot. See Tendons Repair program., Brain condition with many symptoms, including tinnitus and numbness/tingling of extremities., BromhidrosisHidradenitis suppurativa also affects the apocrine glands,HyperhidrosisHypohidrosisMiliaria, Chronic tendon injury., Commonly called Gallstones., Condition where immune response to infection harms tissues or organs. Usually bacterial, but can be fungal, viral, or parasitical., Disorder where veins cant pump enough blood back to heart. Includes Varicose Veins., Disorders of vitreous body of eye. Also see Eye, Eyes, and Vision programs., Enzyme deficiency caused by failure to process biotin (vitamin B7) in food., Formation of Bone Spurs in spine., Genetic disorder with eye, ear, nose, heart, genito-urinary, and growth problems., Genetic enzymatic disease causing inability to process sugars., Head and neck cancer is a term used to define cancer that develops in the mouth, throat, nose, salivary glands, oral cancers or other areas of the head and neck. Most of these cancers are squamous cell carcinomas, or cancers that begin in the lining of the mouth, nose and throat., Infectious disease of central nervous system caused by Clostridium Tetani., Joint disease resulting from breakdown of cartilage and bone. Use Arthritis programs, and try Yersinia Pestis programs., Median nerve compression at wrist, causing pain, numbness, and tingling. Also use Arthritis., Rare neurologic disorder with progressive rigidity and stiffness, primarily affecting truncal muscles and superimposed by spasms, resulting in postural deformities. Chronic pain, impaired mobility, and lumbar hyperlordosis are common., Ringworm. Also see Epidermophyton Floccosum, Microsporum Audouini, Nagel Trichophyton, and Fungus General programs., Symptoms suggesting physical illness or injury that cannot be explained by a medical condition or the direct effect of a substance, and not attributable to another mental disorder., The anus is that part of the intestinal tract that passes through the muscular canal of the pelvis and anal sphincters. It is the final orifice through which stool passes out of the body. In adults, the anus is 4 to 5 centimeters long. The lower half of the anal canal has sensitive nerve endings. There are blood vessels under the lining, and in its mid portion there are numerous tiny, anal glands. This article describes four disorders that cause anal pain and irritation,Anal fissure - An anal fissure, also called an anorectal fissure, is a linear split or tear in the lining (anoderm) of the lower anal canal. Most anal fissures happen when a large, hard stool overstretches the anal opening and tears the delicate anoderm. Less often, anal fissures develop because of prolonged diarrhea, inflammatory bowel disease or sexually transmitted diseases involving the anorectal area. Acute (short-term) anal fissures are usually superficial and shallow, but chronic (long-term) anal fissures may extend deeper through the anoderm to expose the surface of underlying muscle.Anal abscess - An anal abscess is a swollen, painful collection of pus near the anus. Most anal abscesses are not related to other health problems and arise spontaneously, for reasons that are unclear. They originate in a tiny anal gland, which enlarges to create a site of infection under the skin. In the United States, more than half of all anal abscesses occur in young adults between the ages of 20 and 40, and men are affected more often than women. Most anal abscesses are located near the opening of the anus but rarely can occur deeper or higher in the anal canal, closer to the lower colon or pelvic organs.Anal fistula - An anal fistula is an abnormal narrow tunnel-like passageway, which is the remnant of an old anal abscess after it has drained. It connects the mid portion of the anal canal (at the anal gland) to the surface of the skin. After an anal abscess has drained (either spontaneously or when lanced by a physician), an anal fistula will develop at least half of the time. Sometimes the opening of the fistula at the skin surface constantly discharges pus or bloody fluid. In other cases, the opening of the fistula closes temporarily, causing the old anal abscess to flare up again as a painful pocket of pus.Hemorrhoids - Hemorrhoids do not ordinarily cause pain. Nevertheless, sometime the blood vessels in a small hemorrhoid at the edge of the anal orifice can clot off (thrombosis). This may be triggered by a period of constipation of diarrhea. When thrombosis occurs, the external hemorrhoid becomes swollen, hard, and painful, sometimes with bloody discharge.Anus, Use Treponema Pallidum, and see Luesinum and Syphilinum programs. |
| 1071710.28 | Spooky2 SD | Lavender Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 1206000 | Spooky2 RIFE | Contagious Conjunctivitis | See Chlamydia Trachomatis and Bacillus Subtilis. |
| 1274050.8 | Spooky2 SD | Lemon Citrus Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 1604250 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer BXBY 2 | From Paul Gruszka. |
| 1674000 | Spooky2 RIFE | Influenza | Also see Flu and Grippe programs. |
| 1800000 | Spooky2 RIFE | Catarrh | Inflammation of mucous membranes causing thick mucus exudate. |
| 1901021.58 | Spooky2 SD | Ginger Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2266727.04 | Spooky2 SD | Ginger Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2404123.74 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2435945.94 | Spooky2 SD | Frankincense (Olibanim) Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2481801.48 | Spooky2 SD | Lavender Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2759313.78 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 2762626.86 | Spooky2 SD | Ginger Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3014638.2 | Spooky2 SD | Ginger Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3066630.48 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3208500 | Spooky2 XTRA | Cancer BXBY 2 | From Paul Gruszka. |
| 3252675.6 | Spooky2 SD | Lavender Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3276000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Tetanus | Hoyland MOR. Infectious disease of central nervous system caused by Clostridium Tetani. |
| 3349553.94 | Spooky2 SD | Peppermint Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3357266.58 | Spooky2 SD | Frankincense (Olibanim) Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 3687042.96 | Spooky2 SD | Ginger Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 4649543.82 | Spooky2 SD | Lavender Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 4665378.78 | Spooky2 SD | Frankincense (Olibanim) Essential Oil (SD) | These frequencies were derived using Spooky Sample Digitizer.Spooky2 Sample Digitizer is a revolutionary way of determining resonant frequencies of both pathogens and substances.Samples within Sample Digitizer form a biological capacitor. By analysing the frequency spectrum response of this capacitor, the Spooky2 software identifies the resonant peaks. Each peak is a pathogen hit or substance molecular resonance point.Spooky brings this technology to end users at an affordable price. Because we care.Frequency range 100 kHz - 5 MHz.Frequency resolution 0.005%.Hit threshold 0.Max hits 60.Sample loops 14.Repeat 1.Max Current / RA |
| 7325370 | Spooky2 ETDF | Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage | Gastrointestinal bleeding (GI bleed), also known as gastrointestinal hemorrhage, is all forms of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract, from the mouth to the rectum. When there is significant blood loss over a short time, symptoms may include vomiting red blood, vomiting black blood, bloody stool, or black stool. |
| 13497912.882 | Spooky2 XTRA | Gingerol + Shogaol | Experimental. Active constituents of ginger. May be useful for Rheumatoid Arthritis, and cancers of blood, lung, bowel, breast, ovaries, and pancreas. Also see appropriate programs. Do NOT use together with NAC. |
| 18000000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Essential Oil - Dragon Time | 72MHz. Use damped wave, or for simple waves program X to 5. Blend: clary sage, fennel, lavender, marjoram, yarrow, jasmine. Supports emotions during female monthly cycle. Others: M-Grain, Three Wise Men. |
| 22500000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Essential Oil - Citrus Fresh | 90MHz. Use damped wave, or for simple waves program X to 5. Blend: orange, tangerine, mandarin, grapefruit, lemon, spearmint. Immune system. Promotes security, creativity, and joy. Others: Envision, Exodus II. |
| 24750000 | Spooky2 XTRA | Essential Oil - Gathering | 99MHz. Use damped wave, or for simple waves program X to 5. Blend: lavender, galbanum, frankincense, geranium, ylang ylang, spruce, cinnamon, rose, sandalwood. Unifies spiritually and emotionally. Other: Magnify Your Purpose. |
| 27735768 | Spooky2 XTRA | Lyme Disease VHF | Experimental. Requires H-Bomb square. |
| 43245000 | Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Staph | From Patent No., From Patent US 6,321,120 B1 |
| 43351830 | Spooky2 PROV, Spooky2 XTRA | Diseases General, Miscellaneous diseases | From Patent No.: US 6,321,120 B1, From Patent US 6,321,120 B1 |
All Frequencies
Go to top| Category | Indication | Frequencies |
|---|---|---|
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Root Chakra | 396 |
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Sacral Chakra | 417 |
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Solar Chakra | 528 |
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Heart Chakra | 639 |
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Throat Chakra | 741 |
| Ancient Solfeggio (Chakra) Frequencies | Third Eye Chakra | 852 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Root Chakra | 432 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Sacral Chakra | 480 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Solar Chakra | 528 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Heart Chakra | 600 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Throat Chakra | 672 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Third Eye Chakra | 720 |
| Chakra Frequencies | Crown Chakra | 768 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Conception Vessel | 104 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Governing Vessel | 104 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Large Intestine Meridian | 108 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Liver Meridian | 108 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Urinary Bladder Meridian | 112 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Small Intestine Meridian | 120 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Kidney Meridian | 120 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Gallbladder Meridian | 120 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Heart Meridian | 126 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Lung Meridian | 126 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Spleen Meridian | 132 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Stomach Meridian | 132 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Triple Heater Meridian | 152 |
| Dr Yoshio Manaka Frequencies | Pericardium Meridian | 176 |
| Dr. Horowitz Frequencies | Energetic Anesthesia | 174 |
| Dr. Horowitz Frequencies | Blockage in Aura and Misalignment of Chakra system | 285 |
| Dr. Horowitz Frequencies | Universal Wisdom | 963 |
| General | Relaxation | 128 |
| General | Cosmic Healing | 432 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Kidney Meridian | 2 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Gallbladder Meridian | 2, 50 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Lung Meridian | 5 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Large Intestine Meridian | 5 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Pericardium Meridian | 10 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Triple Burner Meridian | 10 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Heart Meridian | 20 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Small Intestine Meridian | 20 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Liver Meridian | 50 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Spleen Meridian | 100 |
| Naomoto Channel Frequencies | Stomach Meridian | 100 |
| Nogier Frequencies | U: Universal Frequency | 1.14 |
| Nogier Frequencies | A: Cellular Vitality/Regenerating - Stimulation | 2.28 |
| Nogier Frequencies | B: Nutritional Metabolism/Regenerating - Stimulation | 4.56 |
| Nogier Frequencies | C: Movement: Bones, Muscles, Joints [Muscle Relaxation] - Stimulation | 9.125 |
| Nogier Frequencies | D: Coordination/Muscle Relaxation - Stimulation | 18.25 |
| Nogier Frequencies | E: Nerves/Pain - Stimulation | 36.5 |
| Nogier Frequencies | F: Emotional Reactions/Regenerating | 73 |
| Nogier Frequencies | G: Intellectual Organization/Inflammation/Pain/Muscle Relaxation | 146 |
| Nogier Frequencies | A (Higher octave): Cellular Vitality/Regenerating - Sedation | 292 |
| Nogier Frequencies | B (Higher octave): Nutritional Metabolism/Regenerating - Sedation | 584 |
| Nogier Frequencies | C (Higher octave): Movement: Bones, Muscles, Joints [Muscle Relaxation] - Sedation | 1168 |
| Nogier Frequencies | D (Higher octave): Coordination/Muscle Relaxation - Sedation | 2336 |
| Nogier Frequencies | E (Higher octave): Nerves/Pain - Sedation | 4672 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Red | 40 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Orange | 50 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Yellow | 52 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Brown | 60 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Green | 68 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Violet | 80 |
| Olav Skille Frequencies | Blue | 86 |
| Schumann Frequency | Earth Frequency | 7.83 |
| Tesla Violet Ray | Tesla Healing | 500000 |
| Ultimate Zapper QE-4 | All bacteria, virus destroy | 2500 |
Magic Squares
Go to top
|
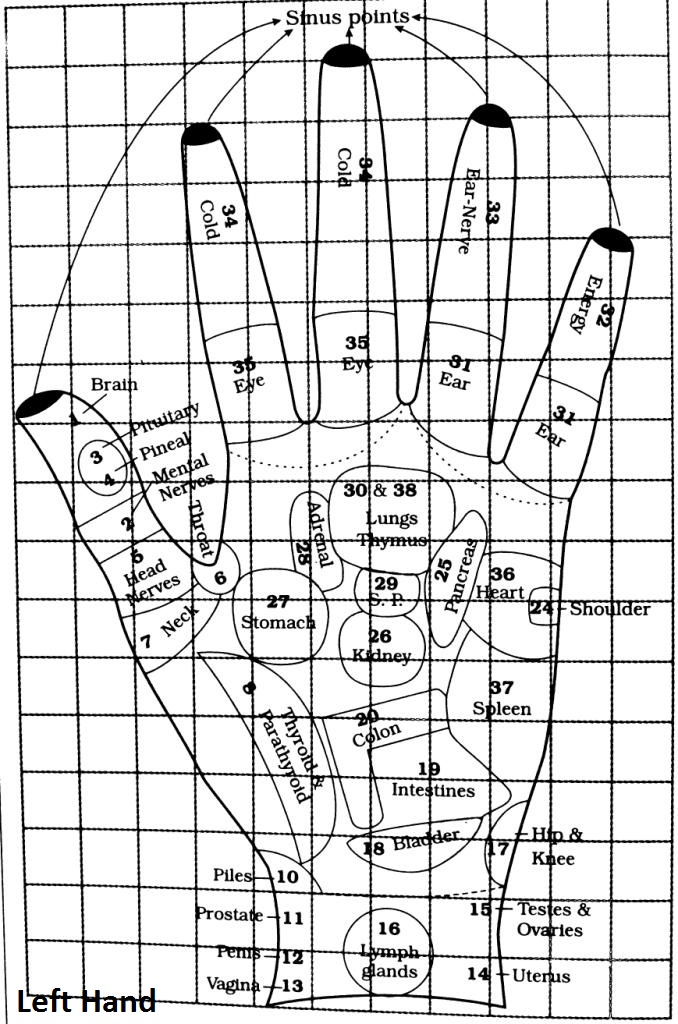
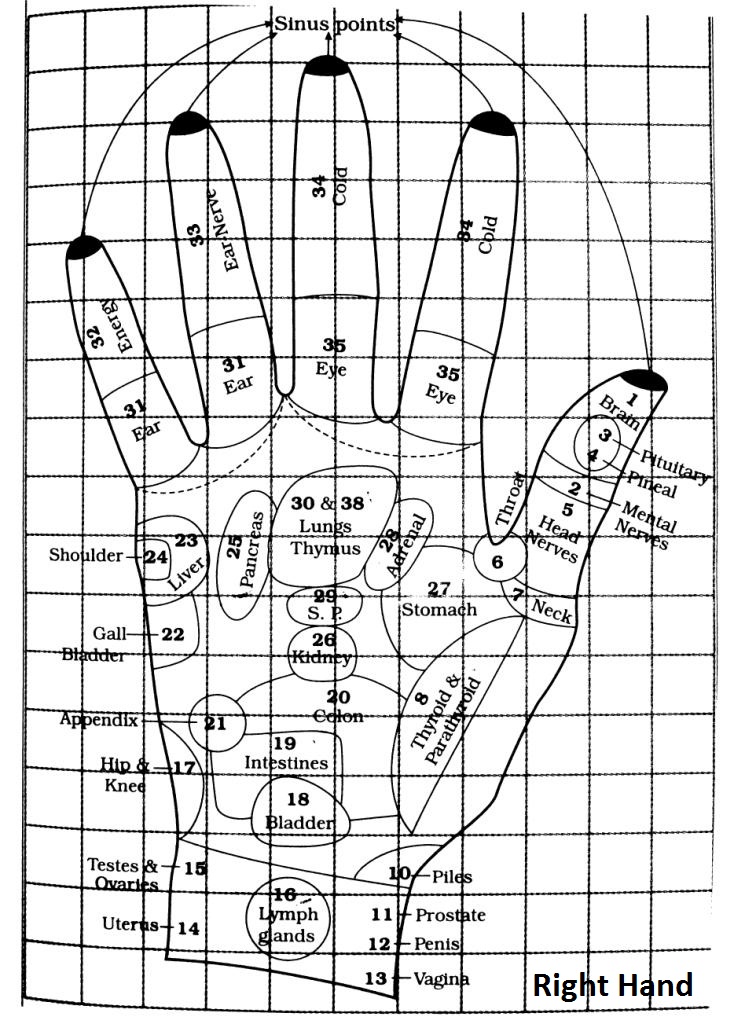

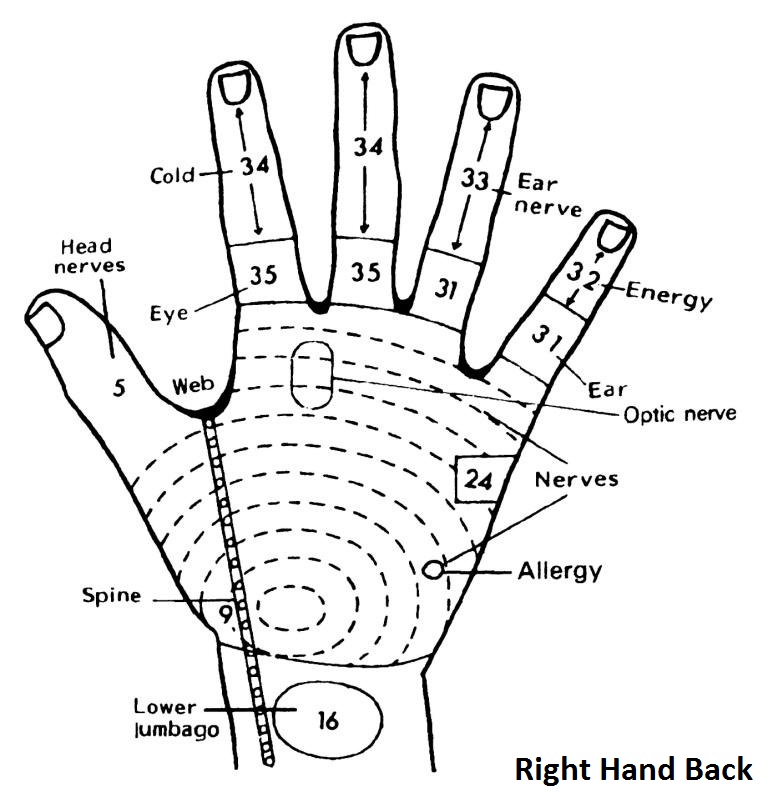
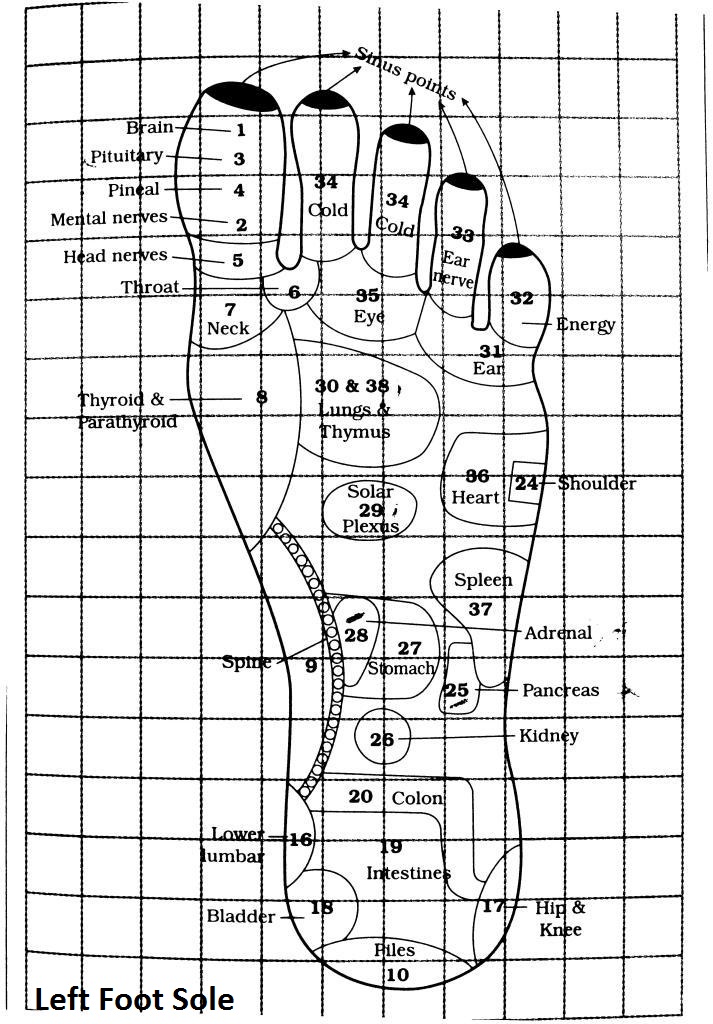

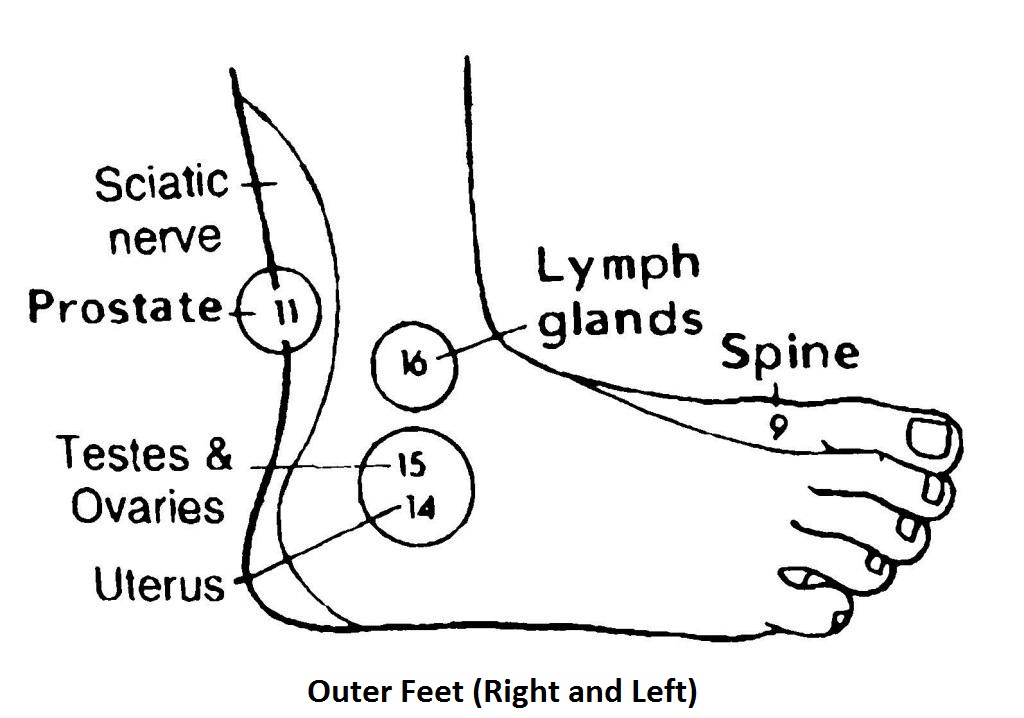
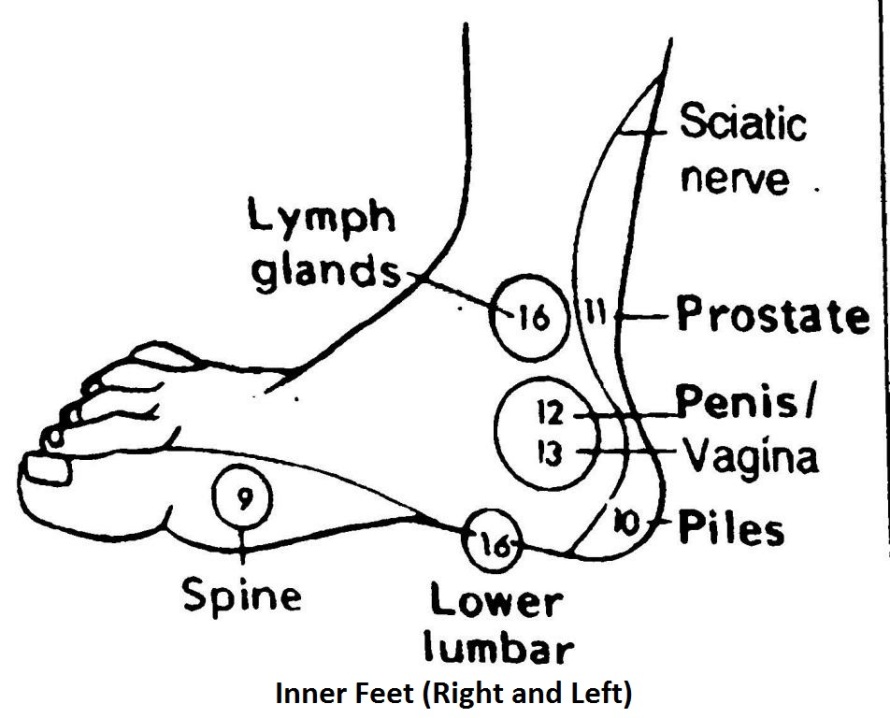

Important Information: